'Kindness begets kindness: the dwellings of the kind-hearted do not collapse totally, those of the wicked do not collapse in half.'
African Proverbs
Input Devices
Wikipedia , Computer Hope , Techopedia , and other innumerable other websites agreed that an 'Input device' is a hardware or peripheral device used to send data to a computer. An input device allows users to communicate and feed instructions and data to computers for processing, display, storage and/or transmission. In the digital fabrication world, this definition still holds true. However, in terms of the components that are considered as input devices extends beyond those computer peripherals such as keyboards, mouse, microphone etc. The extension of input devices in the electronic or digital fabrication world includes sensors, such as those used to detect motion (PIR - Pyroelectric and Doppler radar), basic switch (pushbuttons), those used to detect distance (such as ultrasonic sensors), and temperature sensor just to name a few.
In a nutshell, a sensor is a device that detects and responds to some type of input from the physical environment. The specific input could be light, heat, motion, moisture, pressure, or any one of a great number of other environmental phenomena. A sensor is always used with other electronics ( Reference1, Reference2 )
QuestionWhat Sensor is in high demand during the Corona virus invasion?
AnswerTemperature sensor
Below you will find a brief description and pictures of some basic sensors that will be used during this phase of the study.
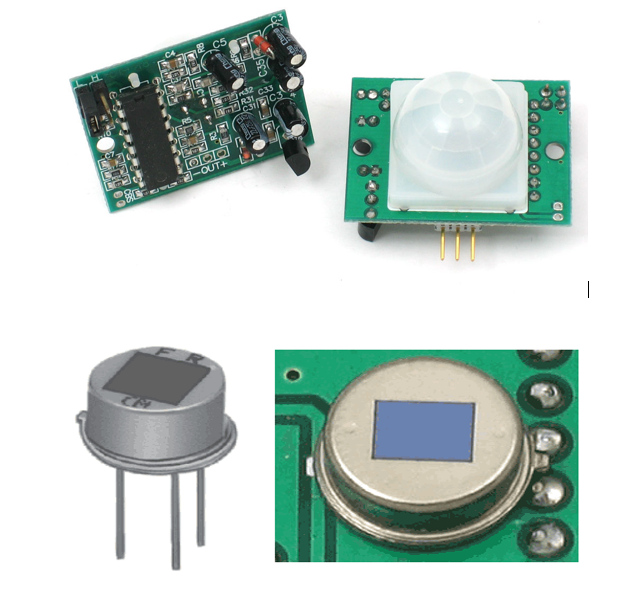
PIR Sensor
PIR sensor - often referred to as PIR, "Passive Infrared", "Pyroelectric", or "IR motion" sensors, are small, affordable, easy to use and low-power electronic component that senses any motion within the range of the device. It almost always used to detect whether a human has moved in or out of the sensors range ( Reference ). It works by detecting levels of infrared radiations. Since everything emits some level of radiations, either low level or higher. The hotter the component or material is, the more radiation it will emit. Hence the more easy the PIR sensor will be able to respond.
Ultrasonic Sensor
Ultrasonic sensor is a sensor that measures the distance by using ultrasonic waves. The sensor head emits an ultrasonic wave and receives the wave reflected back from the target. Ultrasonic Sensors measure the distance to the target by measuring the time between the emission and reception (Reference).Note This is how it works, 'An optical sensor has a transmitter and receiver, whereas an ultrasonic sensor uses a single ultrasonic element for both emission and reception. In a reflective model ultrasonic sensor, a single oscillator emits and receives ultrasonic waves alternately. This enables miniaturization of the sensor head.'
The distance is calculated with the formula below:
Distance (L) = 1/2 X T X C
where L is the distance, T is the time between the emission and reception, and C is the sonic speed. (The value is multiplied by 1/2 because T is the time for go-and-return distance.)

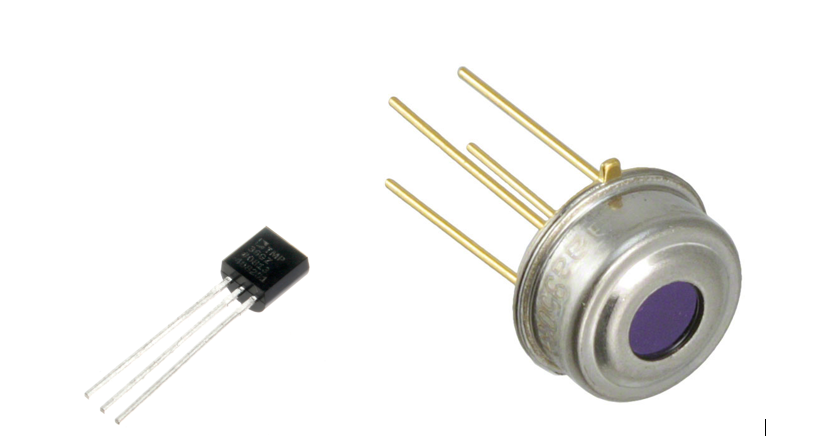
A temperature sensor is a device, usually an RTD (resistance temperature detector) or a thermocouple, that collects the data about temperature from a particular source and converts the data into understandable form for a device or an observer (Reference). Note Temperature Sensors measure the amount of heat energy or even coldness that is generated by an object or system, allowing us to “sense” or detect any physical change to that temperature producing either an analogue or digital output (Reference).
Light Sensor
A Light Sensor generates an output signal indicating the intensity of light by measuring the radiant energy that exists in a very narrow range of frequencies basically called “light”, and which ranges in frequency from “Infra-red” to “Visible” up to “Ultraviolet” light spectrum. The light sensor is a passive devices that convert this “light energy” whether visible or in the infra-red parts of the spectrum into an electrical signal output (Reference).

This ends the explanation section. To view the assignment, click Assignment or simply go to the assignments sections below.
