- Week 1 : Project Management
- Week 2 : Computer-aided
- Week 3 : Computer Controlled Cutting
- Week 4 : Embedded Programming
- Week 5 :3D Scanning and Printing
- Week 6 : Electronic Design
- Week 7 : Computer Controlled Machining
- Week 8 : Electronics Production
- Week 9 : Input Devices
- Week 10 : Output Devices
- Week 11 : Networking and Communication
- Week 12 : Mechanical Design and Machine Design
- Week 13 : Midterm Review
- Week 14 : Molding and Casting
- Week 15 : Interface and Application Programming
- Week 16 : System Integeration
- Week 17 : Wildcard Week
- Week 18 : Applications and Implications, Project Development
- Week 19 : Invention, Intellectual property and Income
- Week 20 : FInal Project Requirements
Week 7: Computer Controlled Machining
Objectives of the Week
Group Assignment
Individual Assignment
Group Assignment Contribution
In this Week, I have Contributed in doing the CAM toolpath for my CNC Machine for making different type of Joints to my Wood Fabricated things
Common Wood Joints
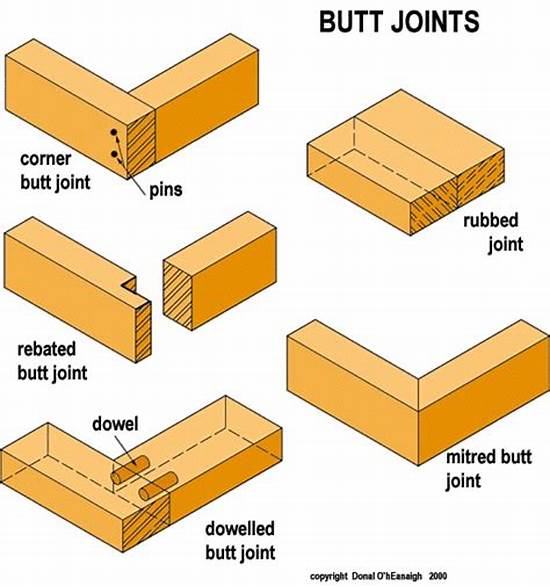
1. Butt Joint
The butt joint is the simplest type of wood joint where two pieces of wood are joined by simply butting them together. They are usually glued, nailed, or screwed, and are often reinforced for strength.
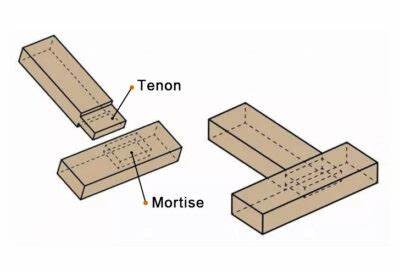
2. Mortise and Tenon Joint
This is a strong and traditional joint where a projecting tenon fits into a matching mortise (hole) cut into the other piece. It’s commonly used in furniture for its durability and precise fit.
3. Dovetail Joint (Main Focus)
The dovetail joint is known for its strength, resistance to pulling apart, and aesthetic appeal. It is often used in drawers, boxes, and fine woodworking.
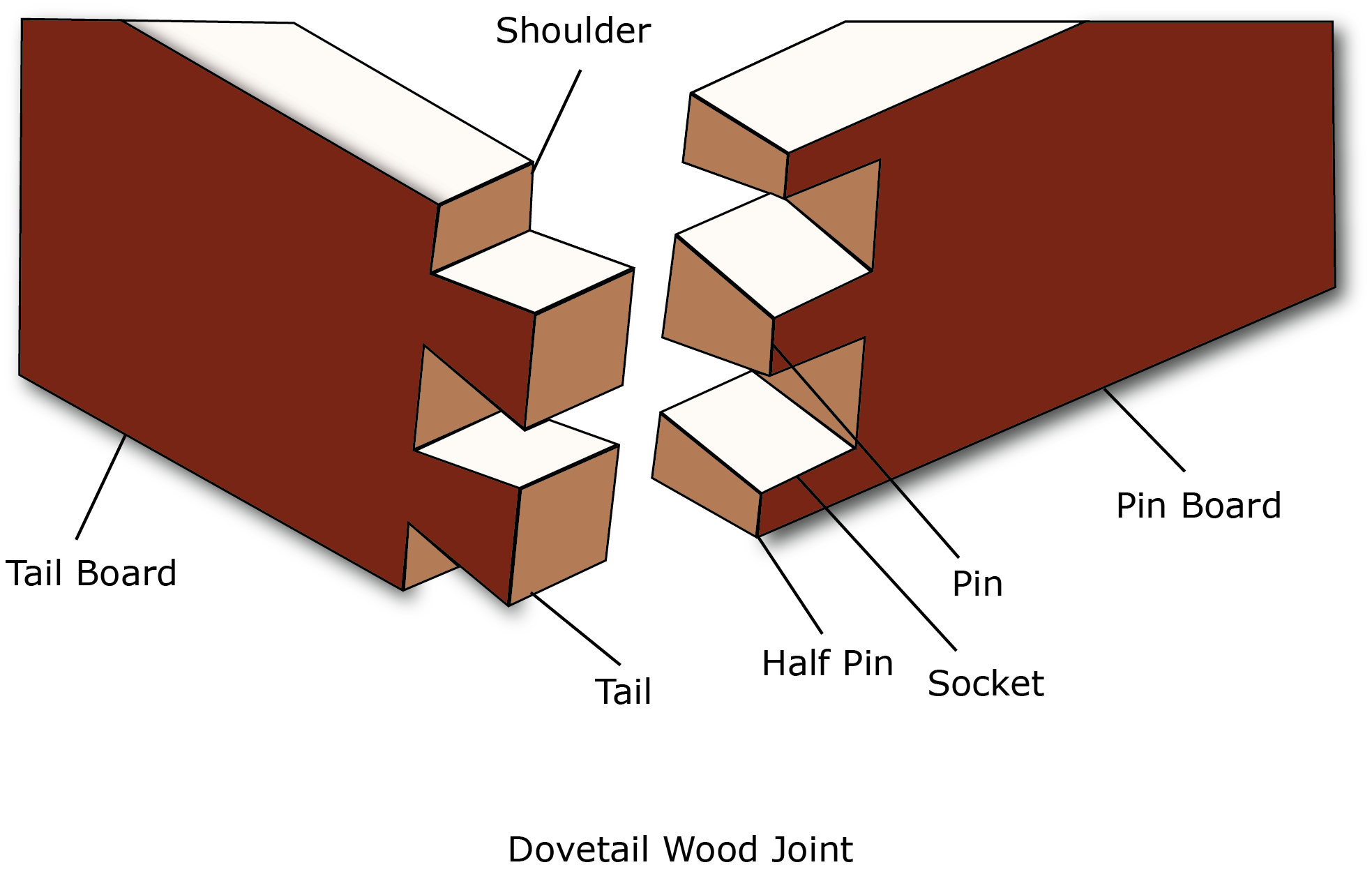
Key Features of Dovetail Joints:
- Consists of interlocking "tails" and "pins" cut at angles.
- Creates a mechanical lock without needing nails or screws.
- Excellent resistance to tension (pulling apart).
- Often used in visible joints because of its decorative look.
- Requires skill and precision to cut, traditionally done by hand or with a jig.
Types of Dovetail Joints:
- Through Dovetail: Both ends of the joint are visible.
- Half-Blind Dovetail: Only one side shows the joint, common in drawer fronts.
- Secret Mitered Dovetail: Hidden from all sides, used for elegant boxes.
Advantages of Dovetail Joints:
- Strong and durable without hardware.
- Resistant to wear and tear over time.
- Enhances the craftsmanship and value of woodwork.
In summary, while there are many ways to join wood, the dovetail joint stands out as a hallmark of traditional woodworking mastery due to its strength, longevity, and beautiful appearance.
To Know More About How I make this....Individual Assignment
Now Let's jump into the Individual Assignment
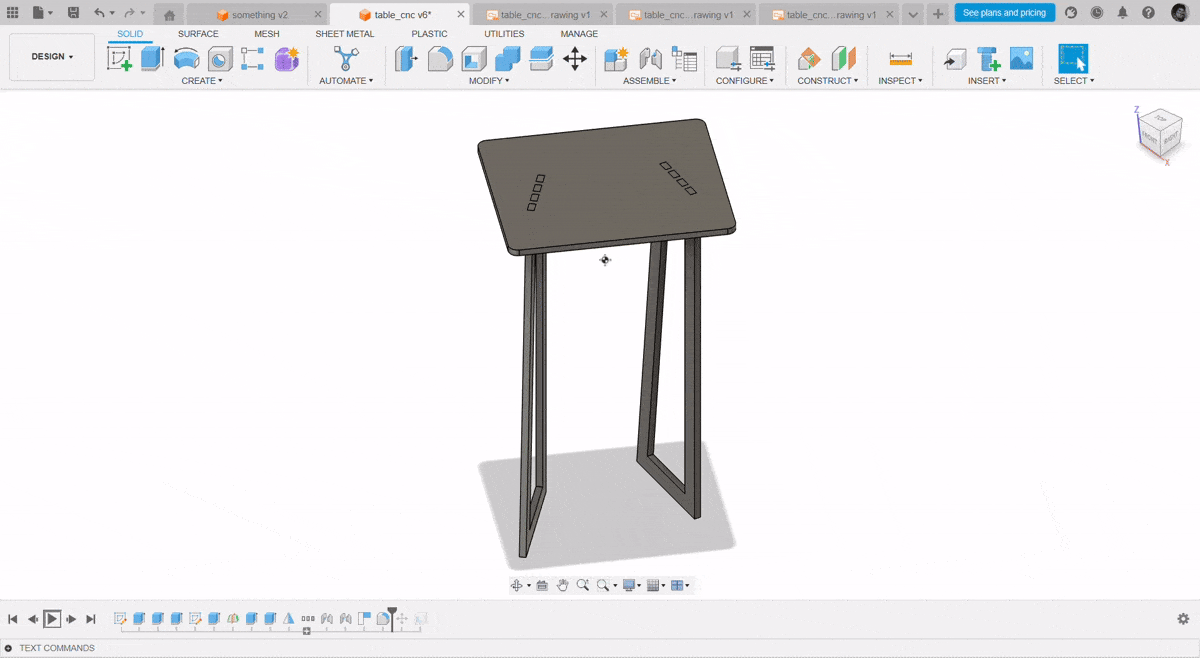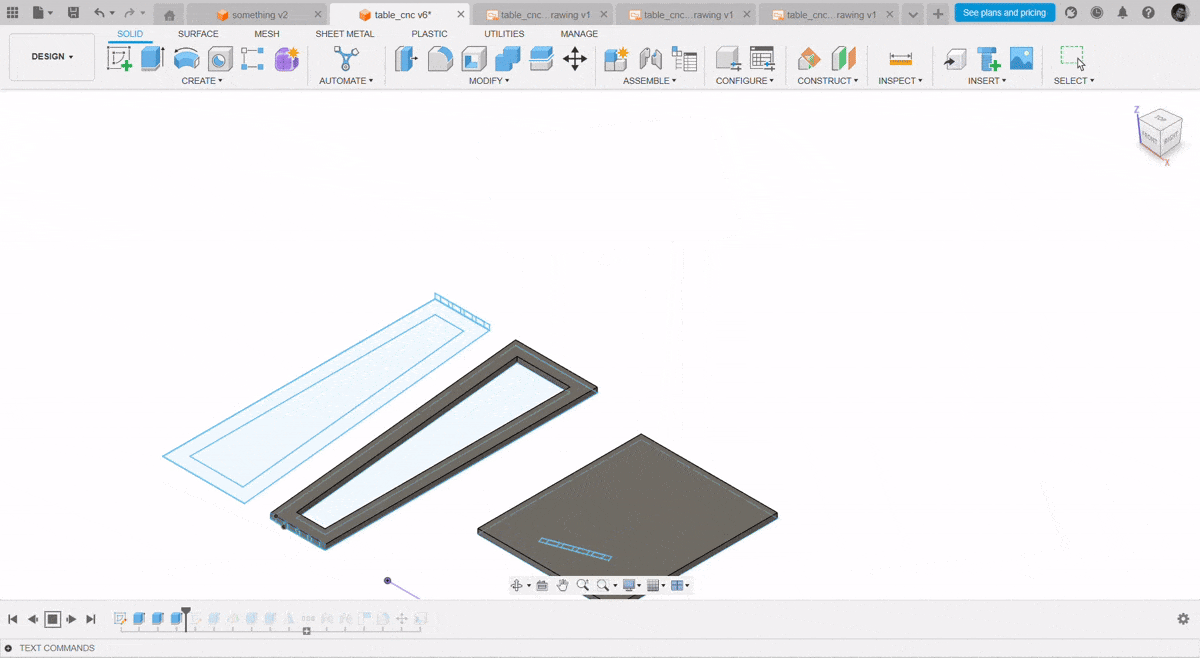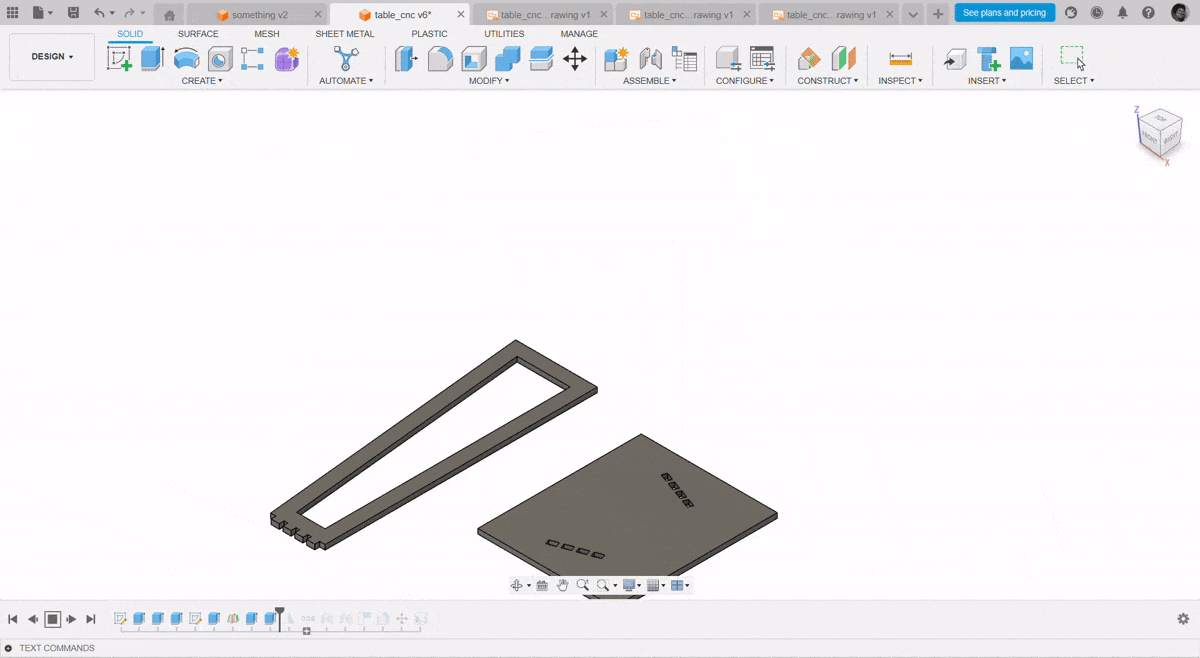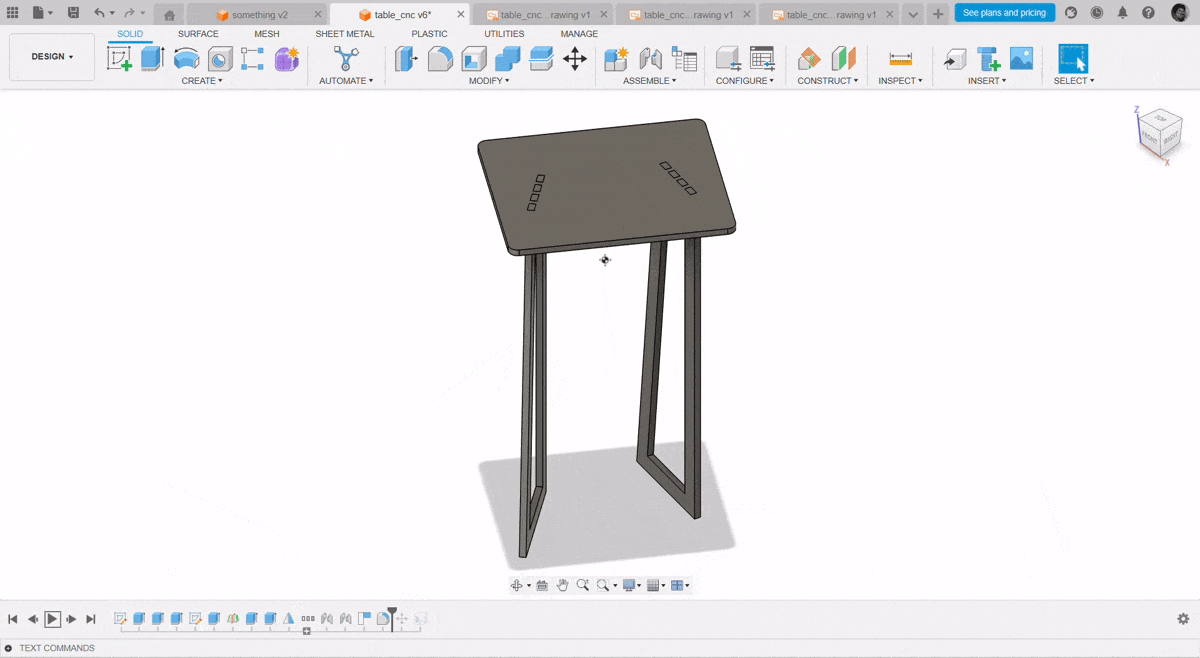
Design a BYTES Table
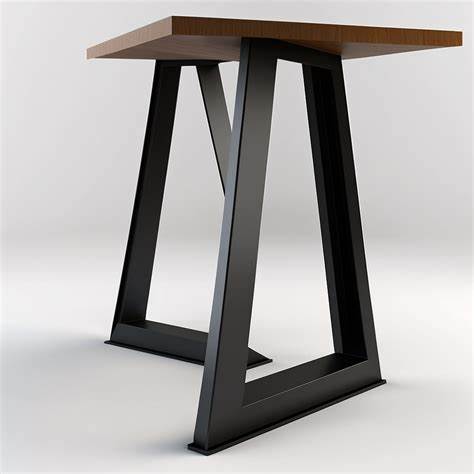

I just got much more thinking, How we will work while having a sip of coffee or have a nice dehyradation time. So I want myself to design something that can be used while working on laptops while having quick bytes
Concept to Design
I have used the Fusion 360 Software to design this thing
Artcam Software
ArtCAM is a software for designing and manufacturing 2D and 3D models. It is a powerful tool for creating complex designs and models with ease. It is used by designers, engineers, and manufacturers to create detailed designs and models quickly and easily.
ArtCAM can be used to create 2D and 3D models from scratch, as well as to modify existing designs. It has a wide range of tools and features that make it easy to create complex designs and models. It also has a powerful rendering engine that allows users to see their designs in high-quality 3D.
Download Artcam Software
To download the Artcam software, click here.
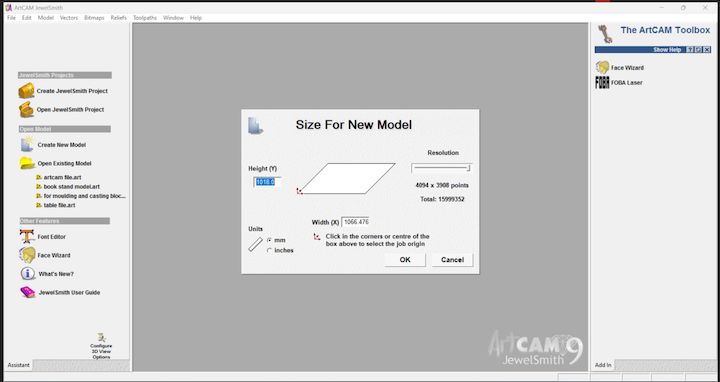
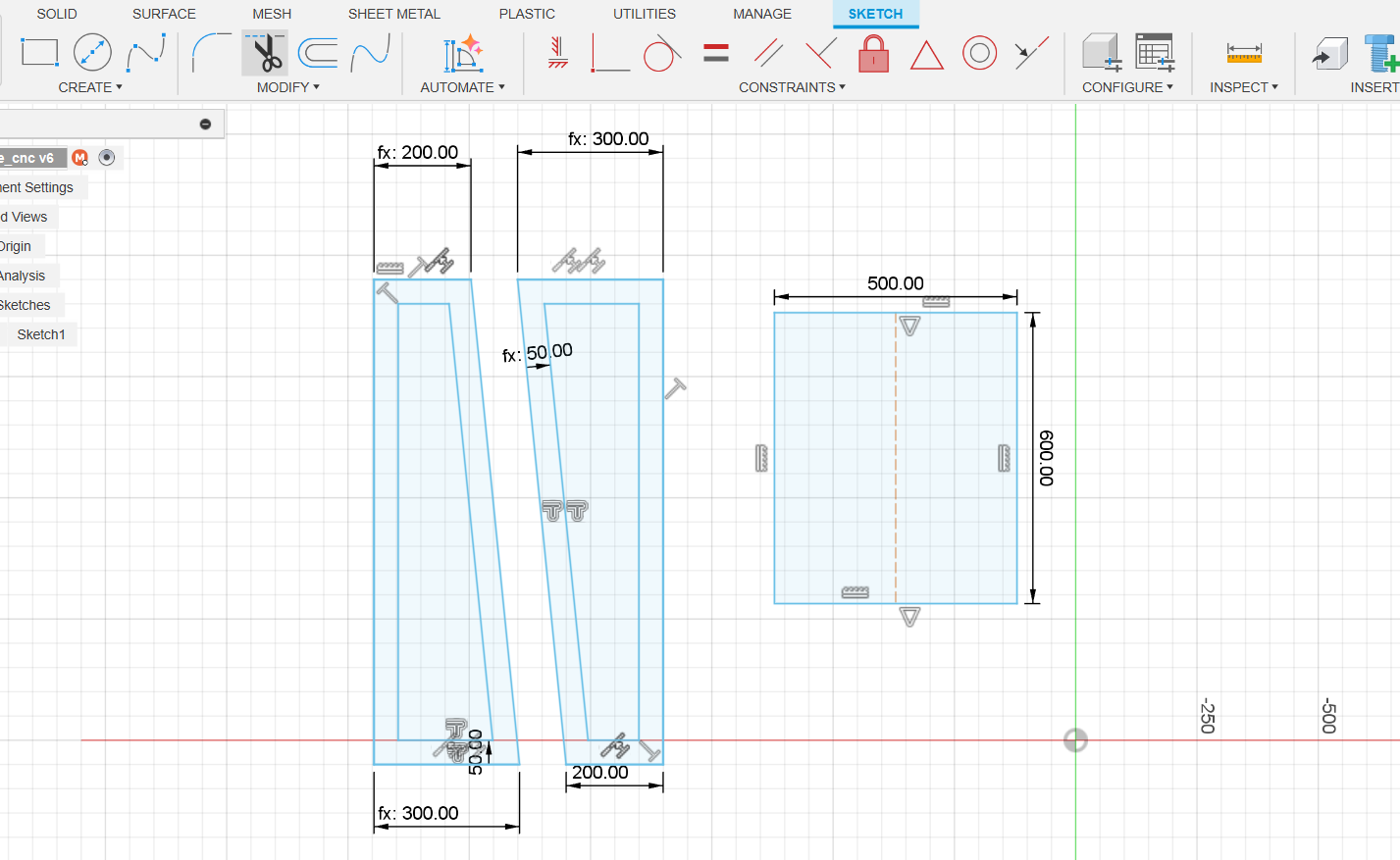
In this step, I set up the material size in millimeters (mm) for my model in ArtCAM Jewelsmith 9.1. I carefully defined the width, height, and thickness of the material to ensure the design fits accurately within the working area, enabling precise cutting and alignment during fabrication.
In the Vector option of ArtCAM Jewelsmith 9.1, I clicked on “Load Vector” to import my DXF file. This allowed me to bring in the design I created earlier and prepare it for toolpath creation and further operations like engraving or cutting.
Importing Files in Artcam
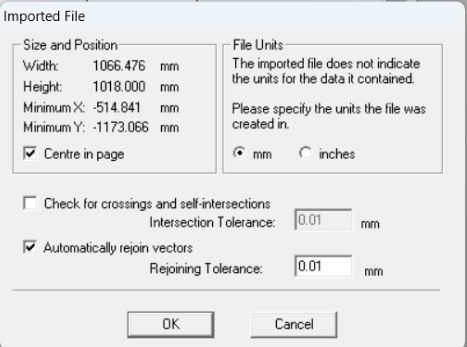
Imported File
Tool Path for Internal Cutting
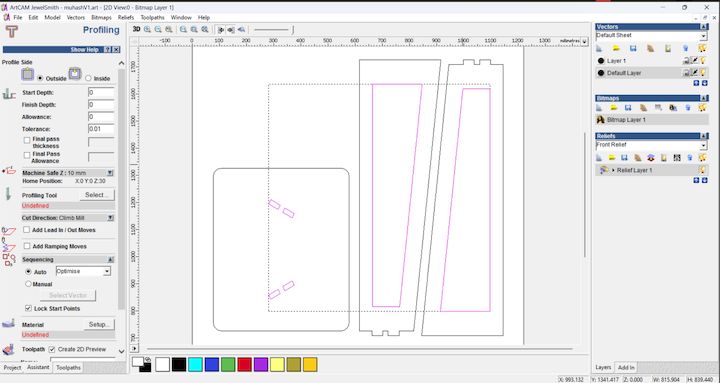
I aligned it properly within the material workspace to ensure accurate machining. Proper alignment ensures the design fits within the set material boundaries and is positioned correctly for toolpath generation and cutting operations.
Material Cut area selection
Tool bit Selection
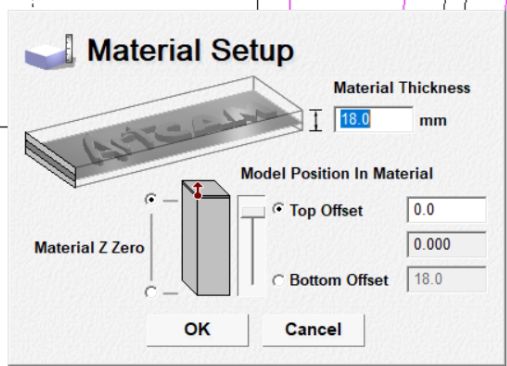
Based on the material thickness, I set the finish depth to 18 mm to ensure complete cutting through the stock. This depth setting aligns with the actual material size, allowing precise machining without leaving any excess material at the base.
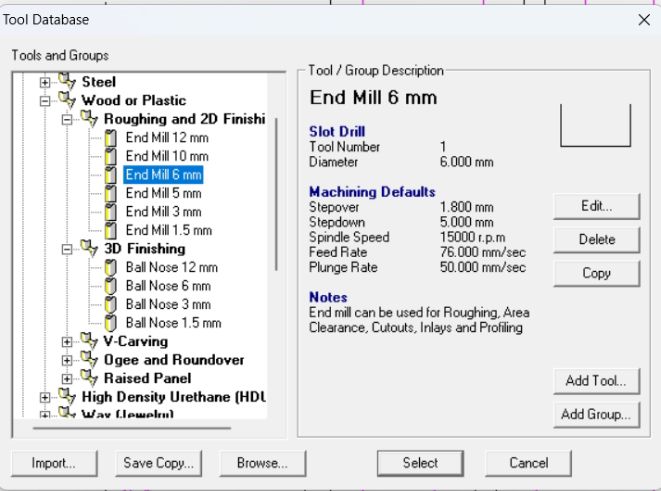
In this step, I selected the tool bit that I wanted to use for cutting and its come around 6mm ball mill cutting tool
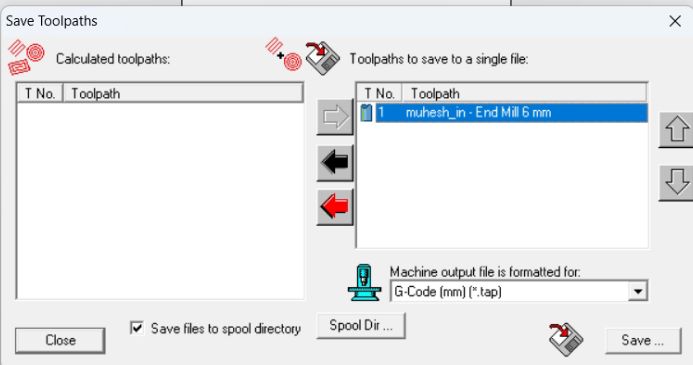
Saving the Tool Path
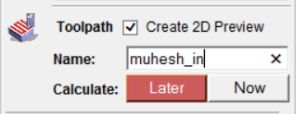
And I am Going to save the tool path that we have previously developed for working on and going to name it as "muhesh_in"
External Tool Path Cutting
Now we are gonna repeat the same process that we were using for the internal tool path and create the External tool path
Machining Process
Now Let's see How machining process were done for the Design developed
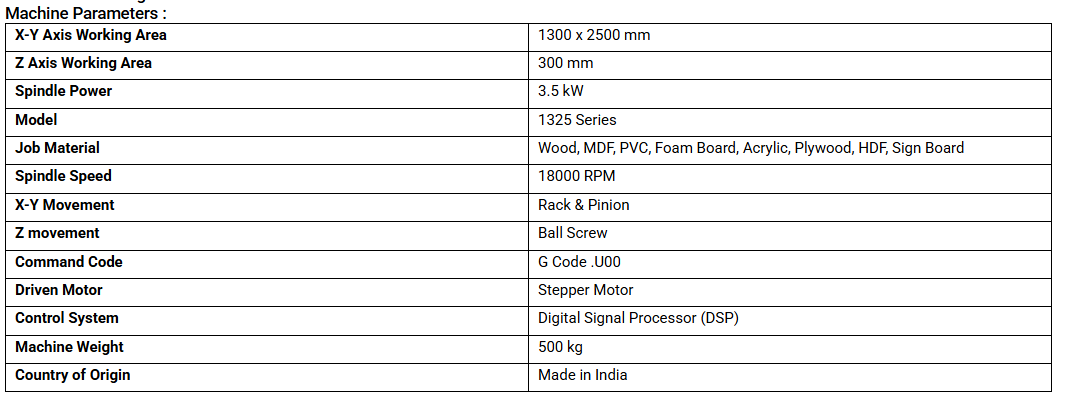
The below mentioned image is the Specifications of our Woood Routing CNC Machine
Initial Setup
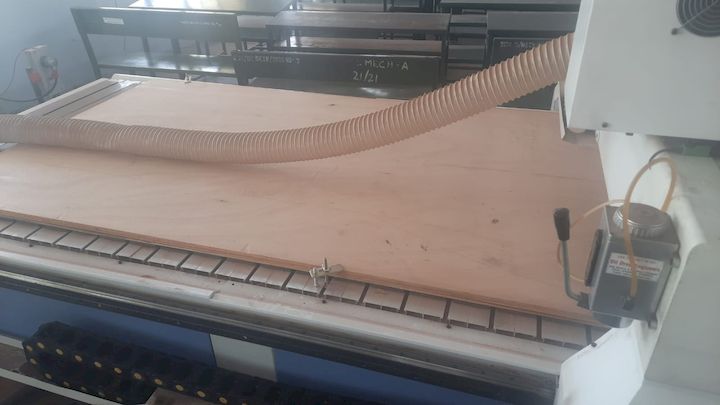

Before getting into the actual works, Initially we need to setup the machine like checking the tools and setting the spindle speed
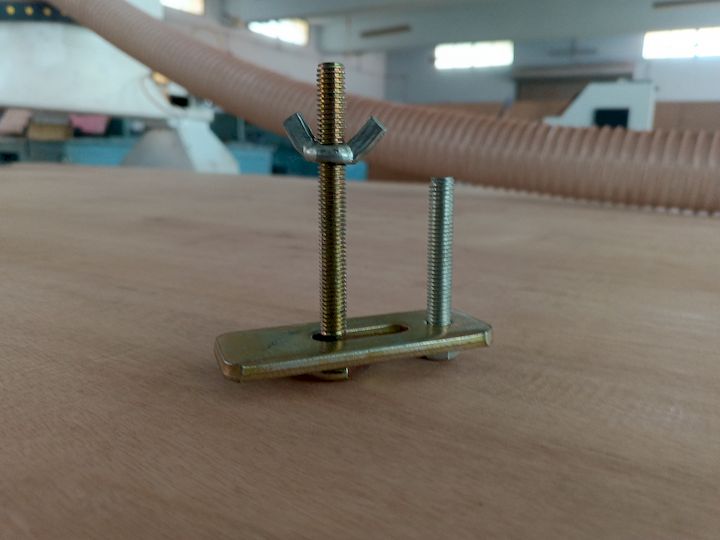

Now what are gonna do is clamp the material with the bed using the clamps and then having the material ready for the machining
I secured the 18mm plywood using appropriate fixtures to ensure it remained stable during the machining process. This helped prevent any movement or vibration, allowing for accurate and precise cuts. Proper fixturing is essential for maintaining alignment and achieving consistent results in fabrication.
Using the teach pendant, I controlled the CNC wood routing machine to accurately set the origin point. This step ensures that the machine starts cutting from the correct reference position, allowing for precise alignment of the toolpath with the material. Proper origin setting is critical for accurate machining.
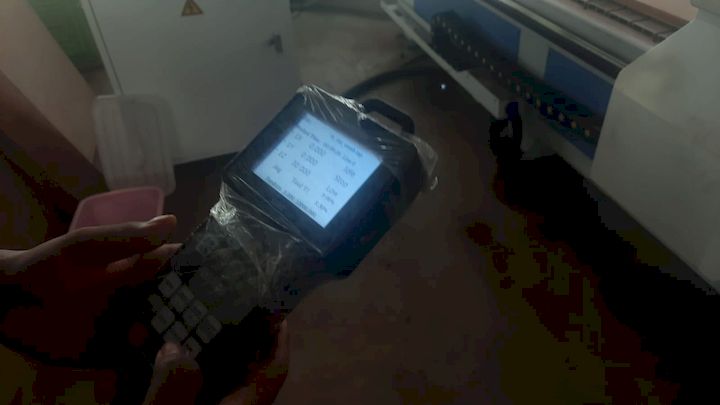

To set up the tool at the proper origin, I verified the alignment by checking the X, Y, and Z coordinates manually. I ensured the tool touched the surface accurately without damaging the material. This verification step is essential to maintain cutting precision and avoid any misalignment during machining.
After transferring the file to the CNC machine using a pen drive, I loaded the program and initiated the run. I closely monitored the initial steps to ensure proper execution, verifying that the toolpath aligned with the material setup to achieve accurate cutting results without any errors.
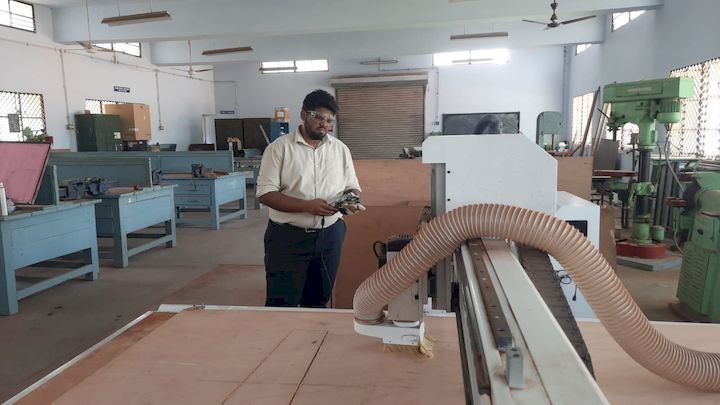

After that, I ran the code for the inside cut operation, ensuring the tool followed the correct path within the designated boundaries. I monitored the cut depth and alignment closely to maintain precision and avoid any deviation from the intended design.
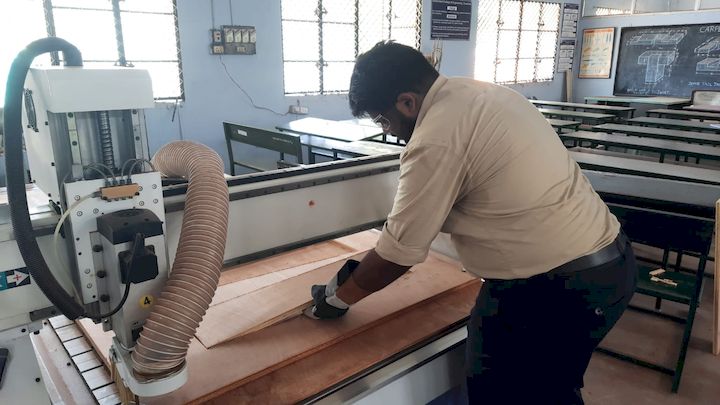

After completing the inside cut, I proceeded with the outside cut operation. This step involved cutting along the outer edges of the design to separate the final part from the material. I ensured the tool settings and origin remained accurate to achieve a clean and precise finish.
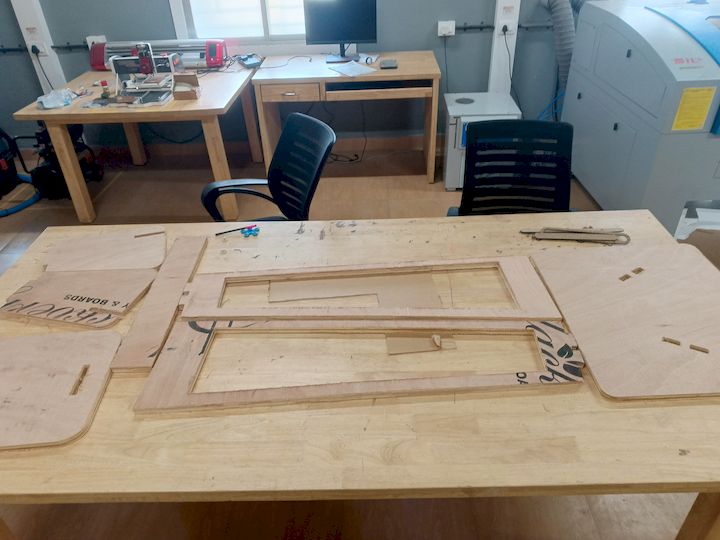

Post Processing
After cutting the components, I assembled them by carefully aligning and fixing each part together as per the design. I used appropriate tools and fixtures to ensure stability and accuracy during the assembly process, resulting in a structurally sound final model.
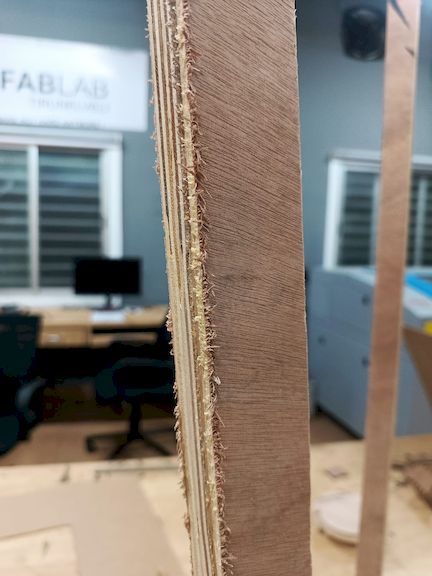
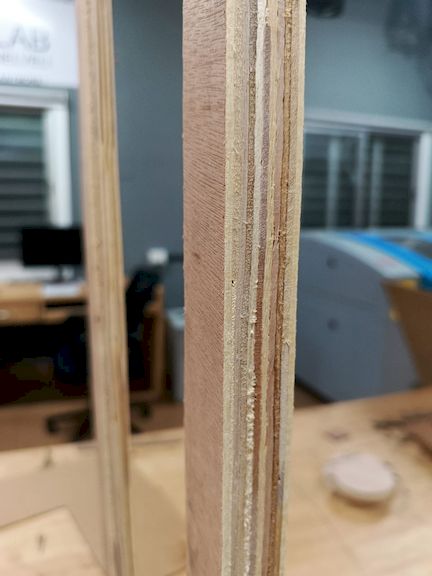


Assembly
Finally assembling all the parts after the Post Processsing
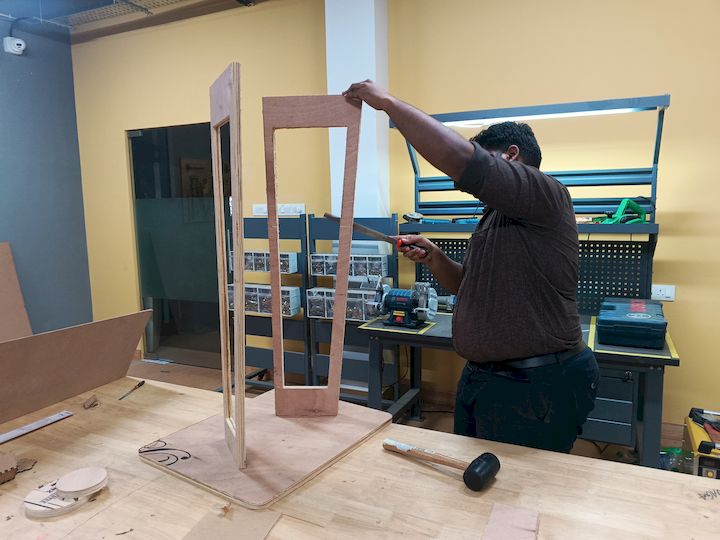
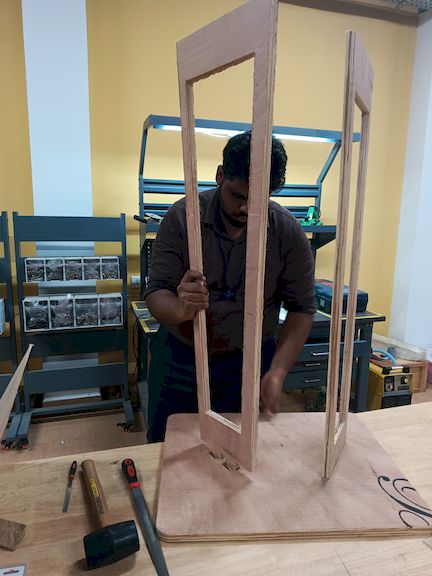


Hero Shot