- Week 1 : Project Management
- Week 2 : Computer-aided
- Week 3 : Computer Controlled Cutting
- Week 4 : Embedded Programming
- Week 5 :3D Scanning and Printing
- Week 6 : Electronic Design
- Week 7 : Computer Controlled Machining
- Week 8 : Electronics Production
- Week 9 : Input Devices
- Week 10 : Output Devices
- Week 11 : Networking and Communication
- Week 12 : Mechanical Design and Machine Design
- Week 13 : Midterm Review
- Week 14 : Molding and Casting
- Week 15 : Interface and Application Programming
- Week 16 : System Integeration
- Week 17 : Wildcard Week
- Week 18 : Applications and Implications, Project Development
- Week 19 : Invention, Intellectual property and Income
- Week 20 : FInal Project Requirements
Week 3 : Computer Controlled Cutting
Objectives of the Week
Design, lasercut, and document a parametric construction kit, accounting for the lasercutter kerf, which can be assembled in multiple ways. Cut something on the vinyl cutter
Group Assignment
For more About Group AssignmentsKerf Measurement
Procedure
Using LaserCAD software for sending the design to the Laser machine
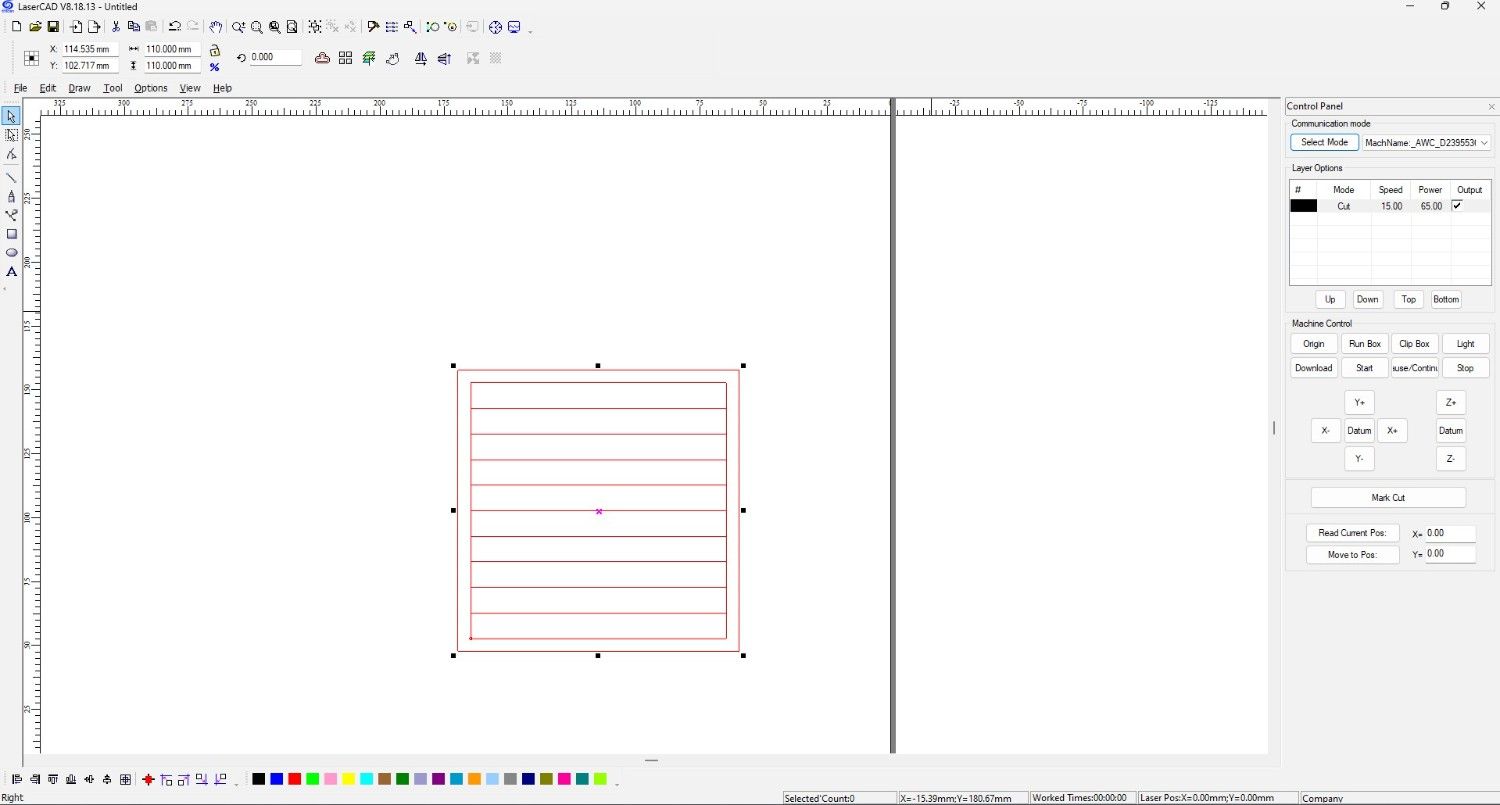
Cutting Designed files for measurement
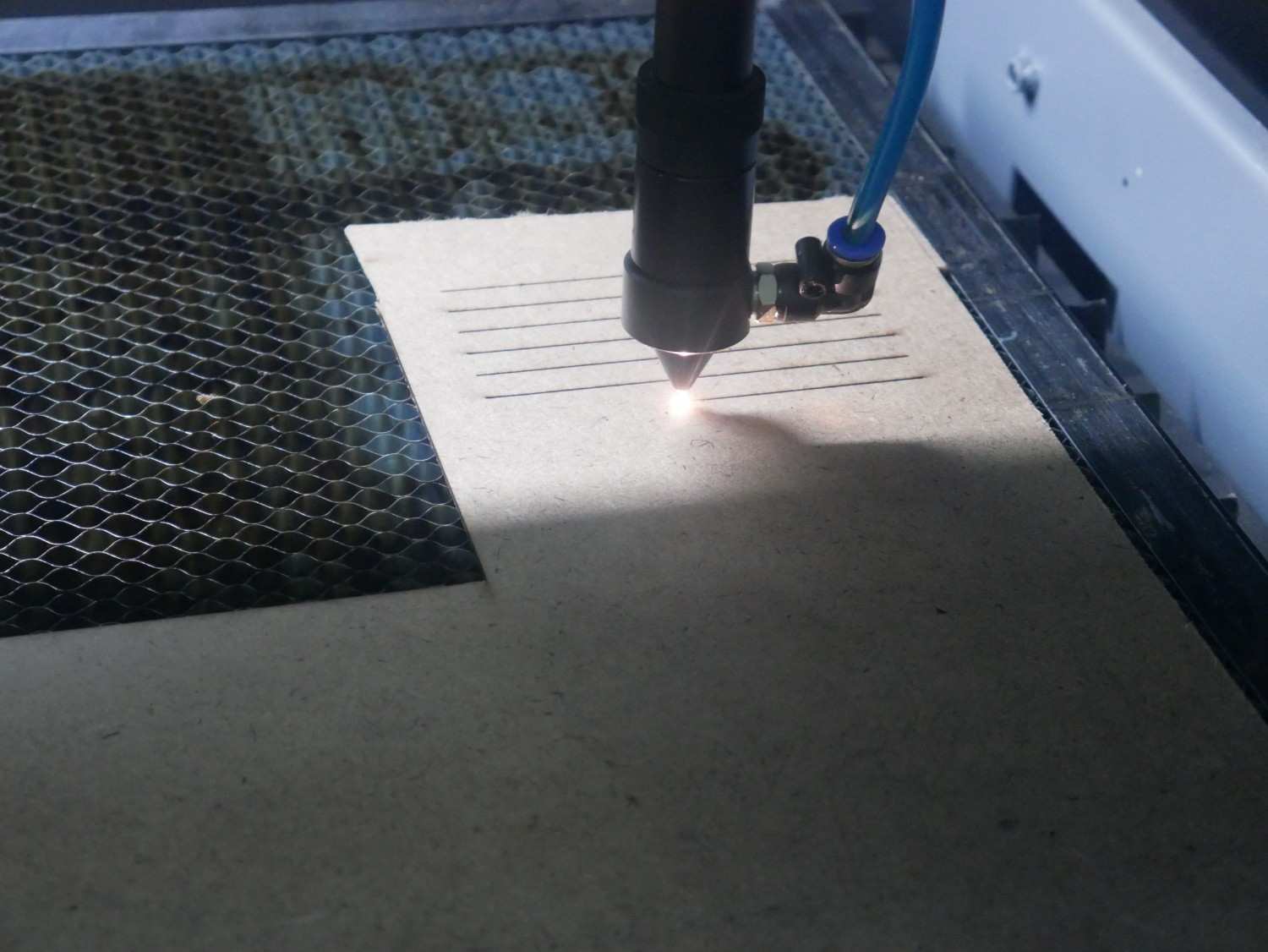
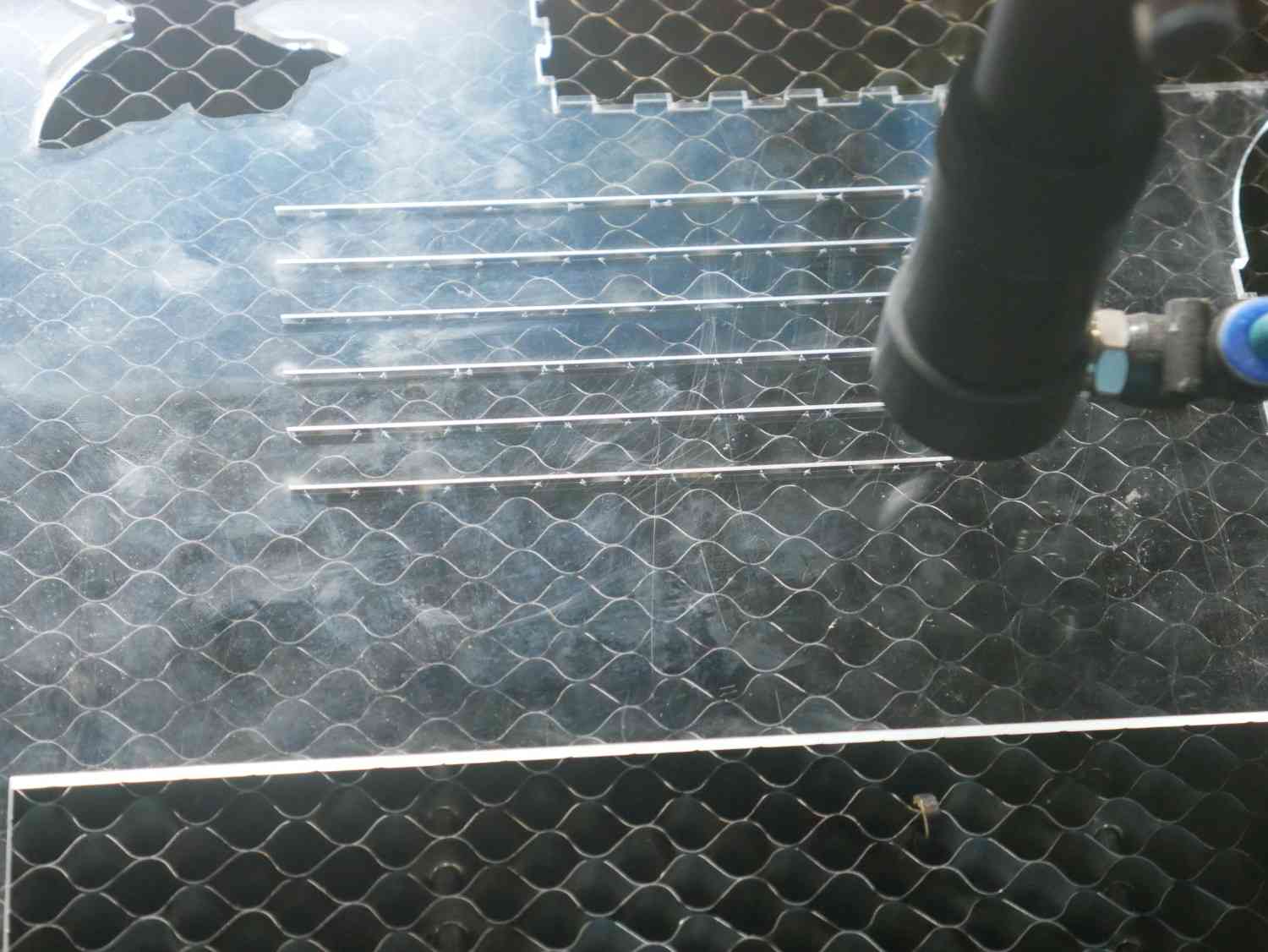


Measuring the Files for the Kerf Measurement in both MDF and Acrylic materials
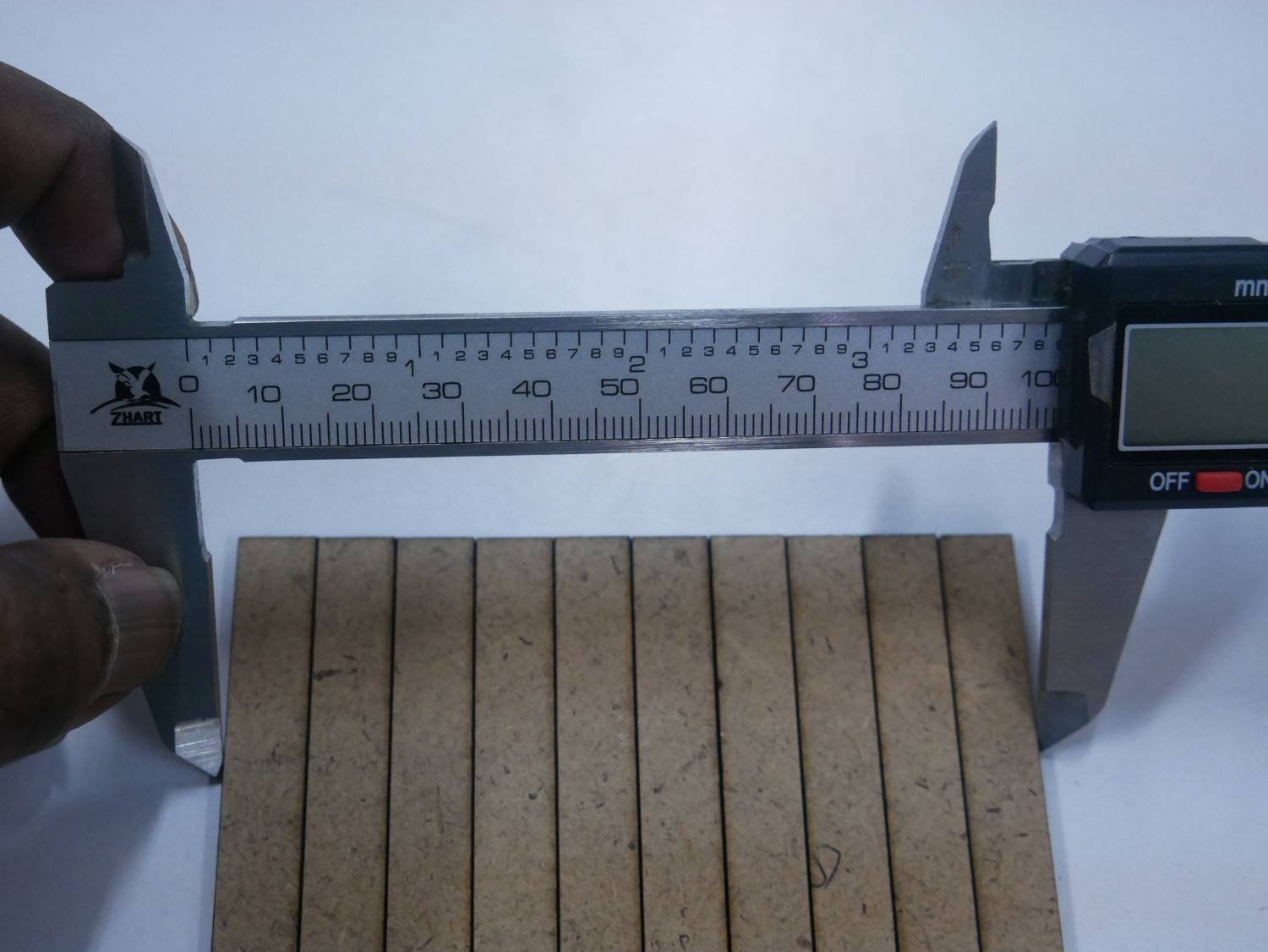
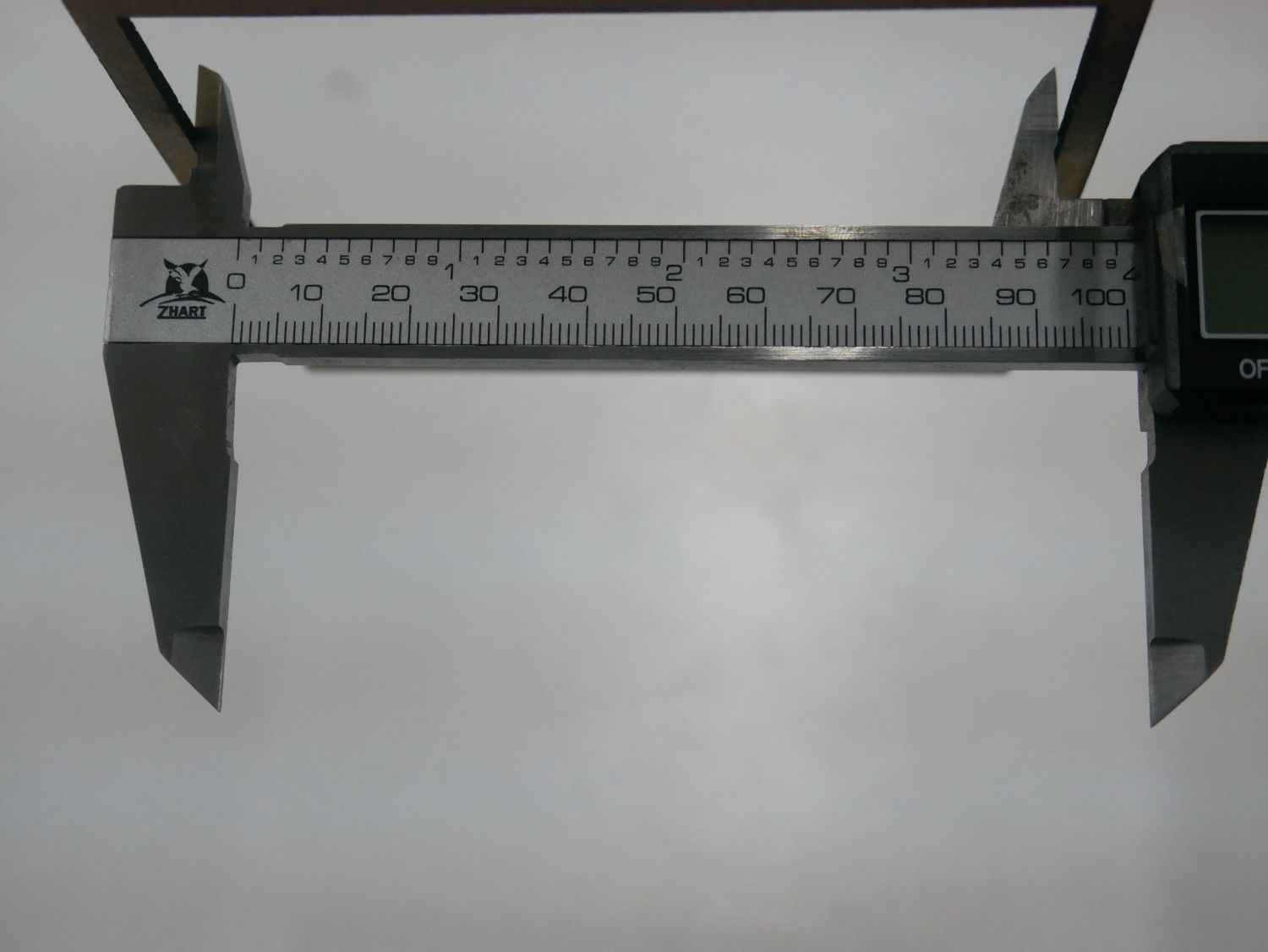
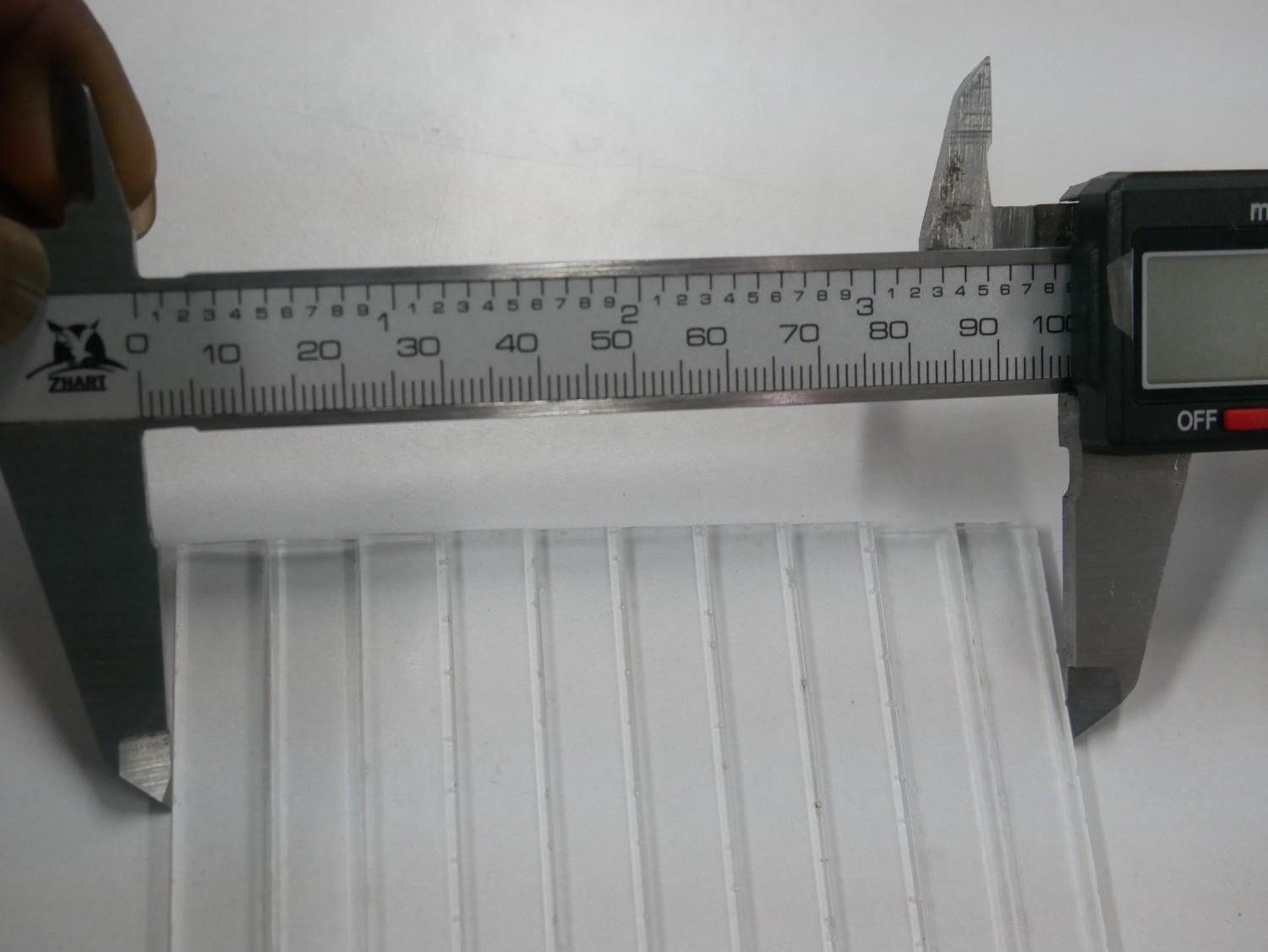
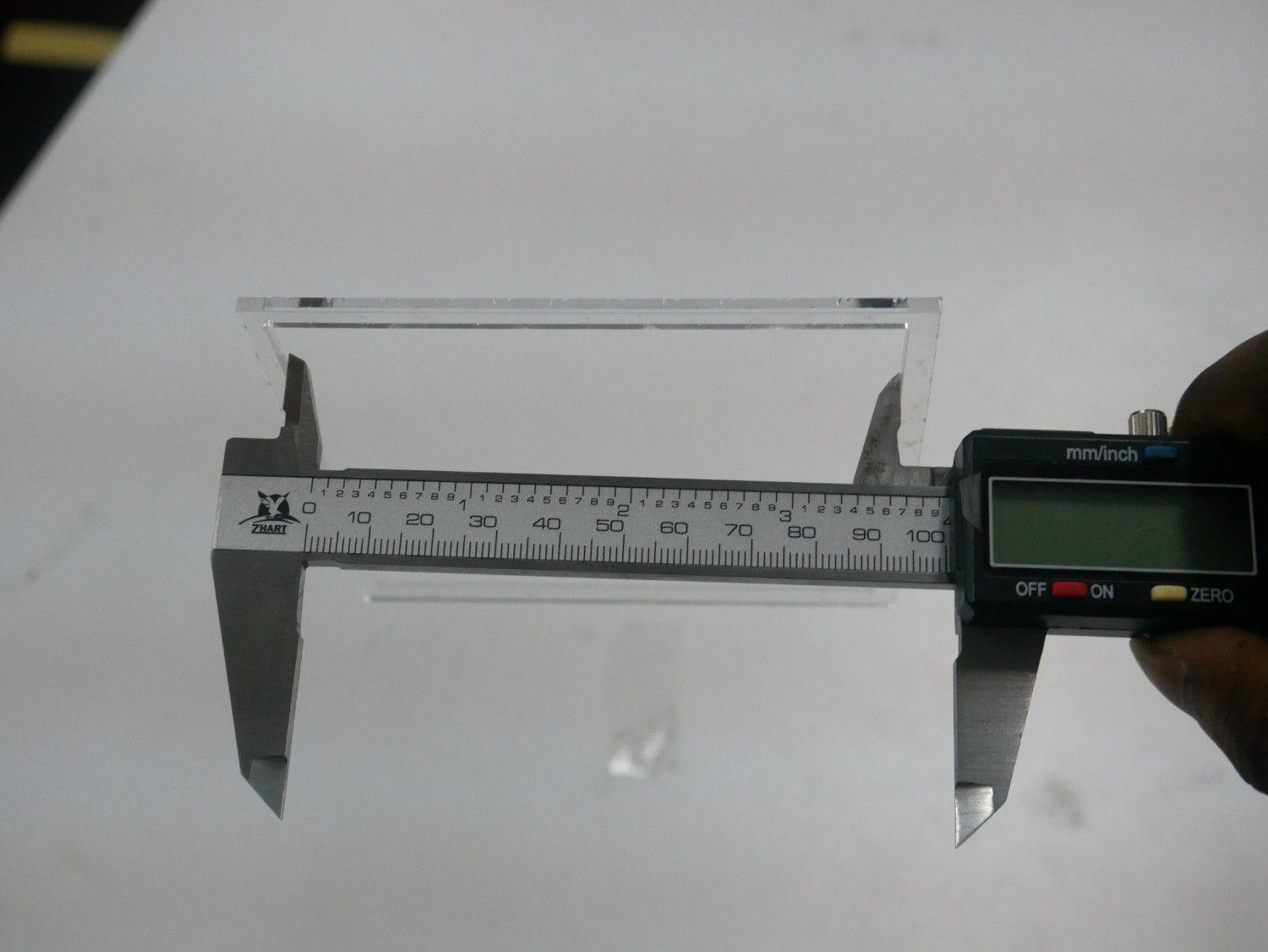




Results
| Material | Designed Size | Measured Slot (mm) | Measured Piece (mm) | Kerf (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDF | 100 × 100 | 100.30 | 99.70 | 0.30 |
| Acrylic | 100 × 100 | 100.25 | 99.75 | 0.25 |
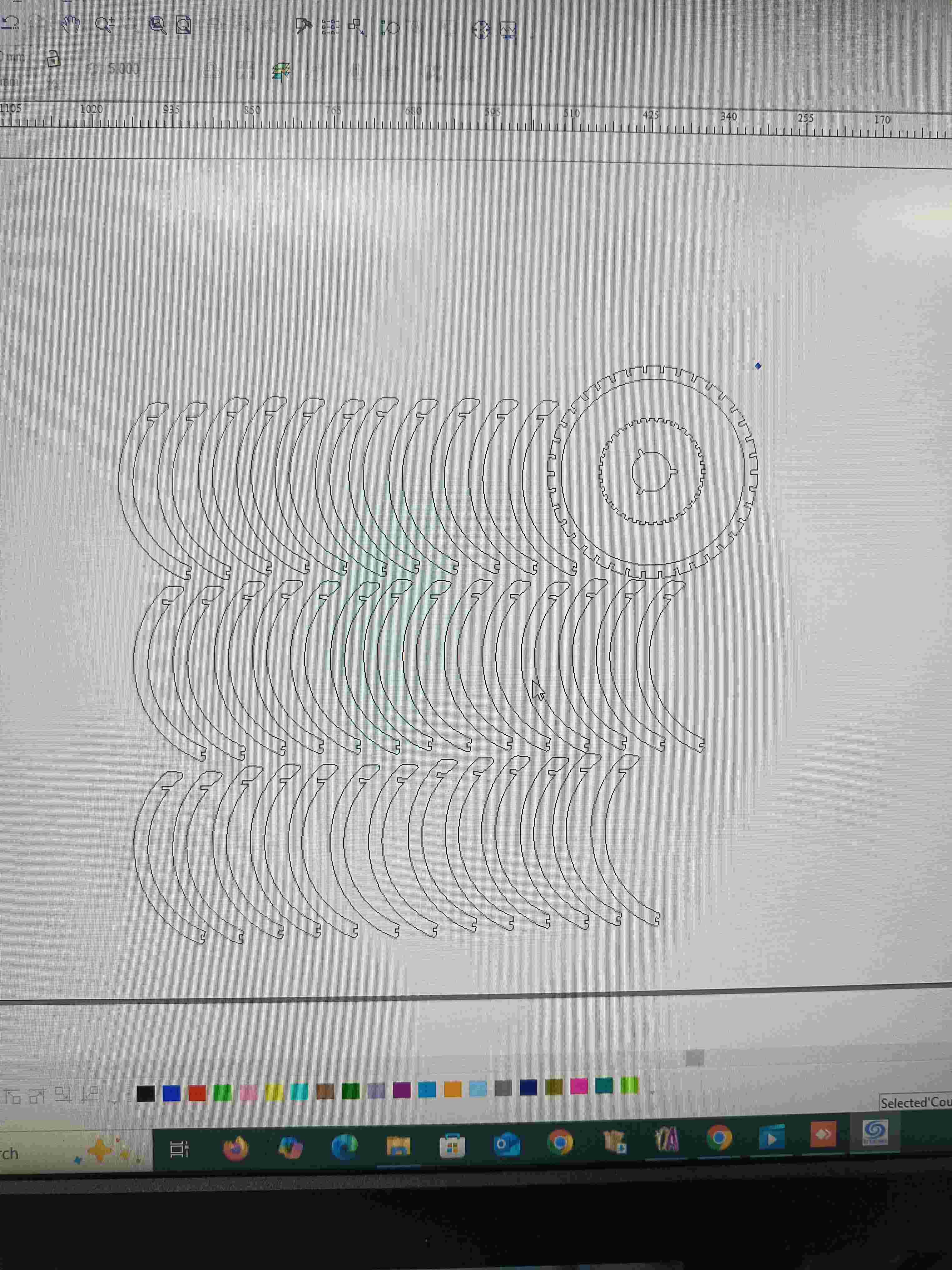
Parametric Lamp Design Kit
For the Paramaetic Lamp design I have refered this video
2D laser-cuttable design with customizable dimensions
I planned to design the lamp in three strucutres one is that, The Connectors Which I done Initial design in 2D drafting and then designing the base plate which connecting all the hands and then conecting the hands to the base plate
Parametric Design in Fusion 360
Parametric design in Fusion 360 involves creating models where key dimensions and parameters drive the geometry. This approach allows for easy modifications and fine-tuning, as changes to the parameters automatically update the entire model.
- Defining Parameters: Parameters are defined at the start, such as the length, width, or diameter. These parameters can be used throughout the design to maintain consistency and allow for quick adjustments.
- Using Constraints: Constraints are used to maintain relationships between different parts of the model. For example, ensuring that two lines remain parallel or that a circle stays concentric with another shape.
- Advantages: Parametric design allows for efficient iteration, as changes can be made quickly by altering parameter values. This is particularly useful for prototyping and testing different design configurations.
- Example: When designing a lamp in Fusion 360, you can set parameters for the lamp's height, base diameter, and connector thickness. Adjusting these parameters will automatically resize and redefine the lamp's components, providing flexibility in design exploration.
By leveraging parametric design, designers can create adaptable and scalable models that meet specific requirements and constraints.
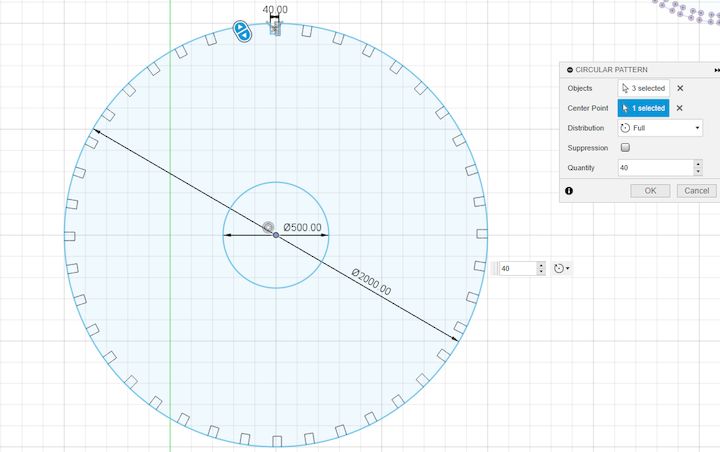
For the Parametric Design
I Initially fixed a Dimension of d5 to the common for all dimensions
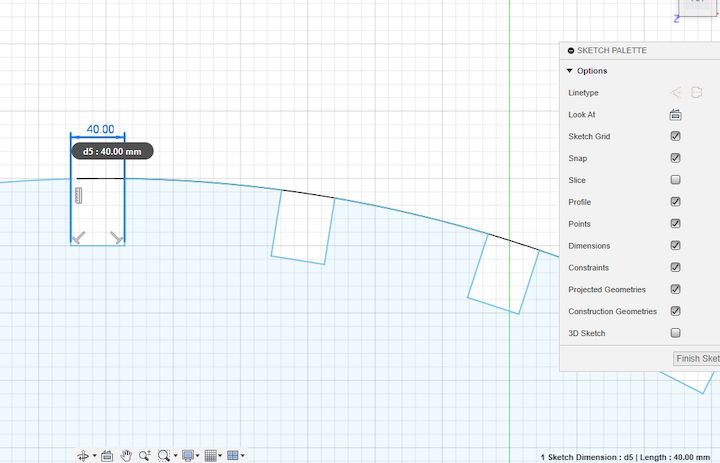
Next I have taken the same value for the Hands Design to and then changed its value too
Similarly I have used this for all of my areas where I am Connecting one with Each other
br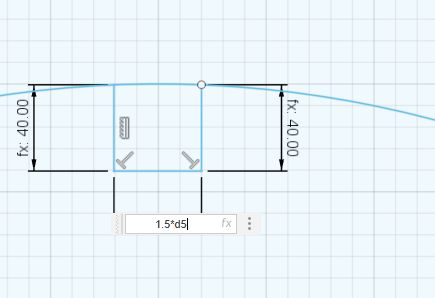
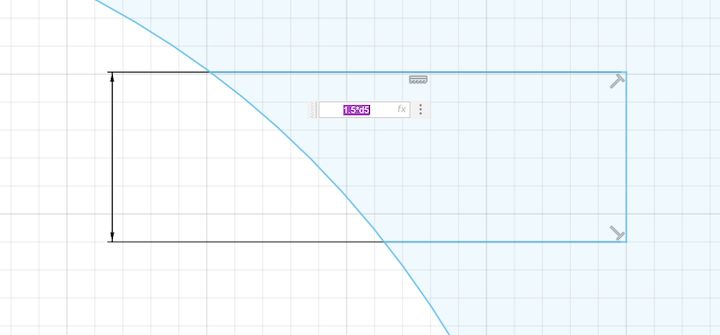
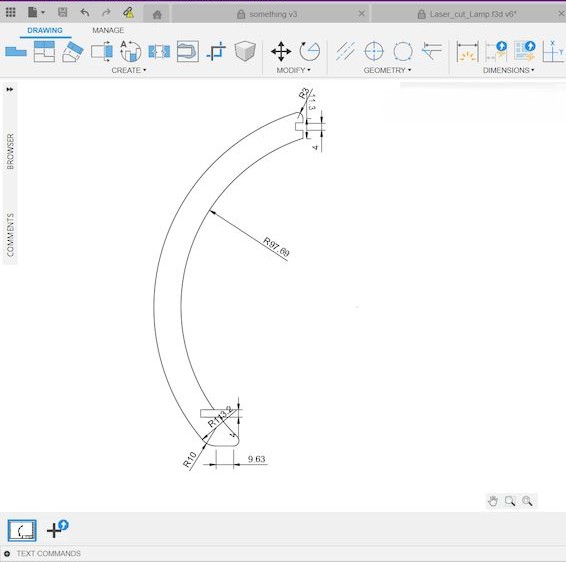
Hand Design
Initially I considered all the aspects and then having the edges of the connectors as 4mm and as there two connectors will be have and I assigned the 4mm as both ends as a parametric.
Base Plate Design
And then considering the common 4mm connectors as parametric constraint for the base plate cuts
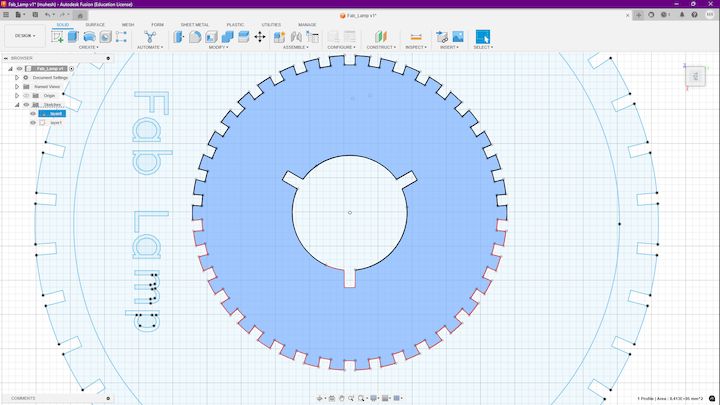
As we have to connect the hands to the base plate, so I used the same parametric as the connector, which is 4mm.
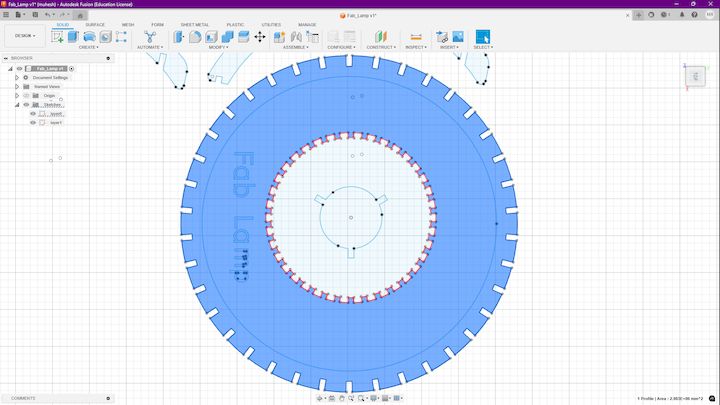
Intial parameters
I have done the initial parametric design in Fusion 360 and the below listed are the initial parameters that came along with the design
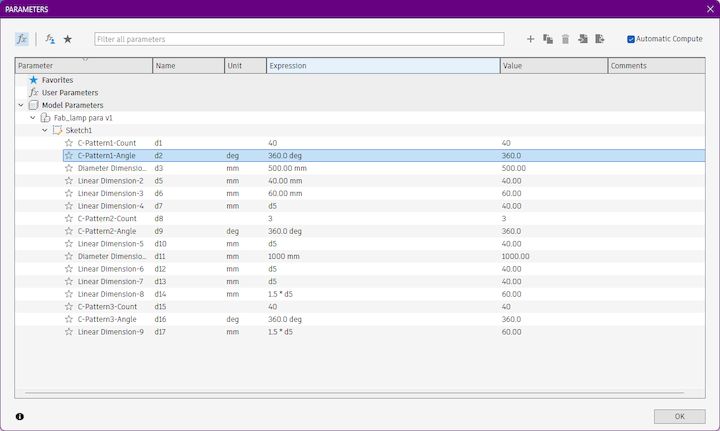
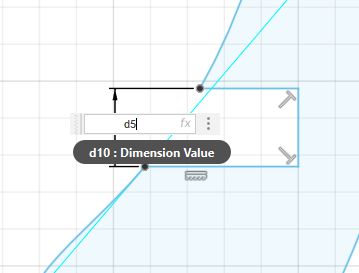
Now what I am going to do is chaning the inital design that I have done in Fusion 360, Initially I have taken a d5 as my Initially measuring thing
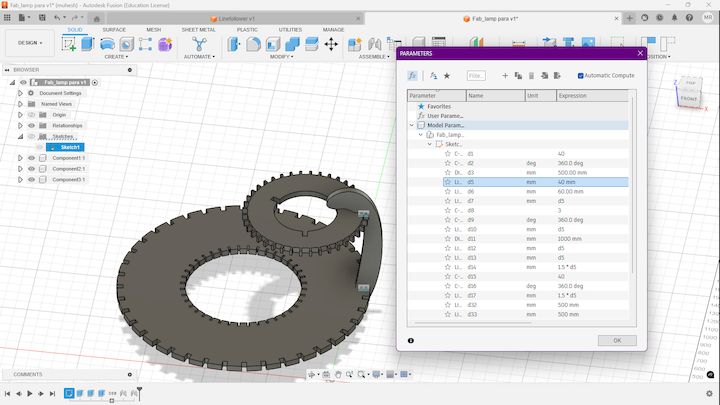
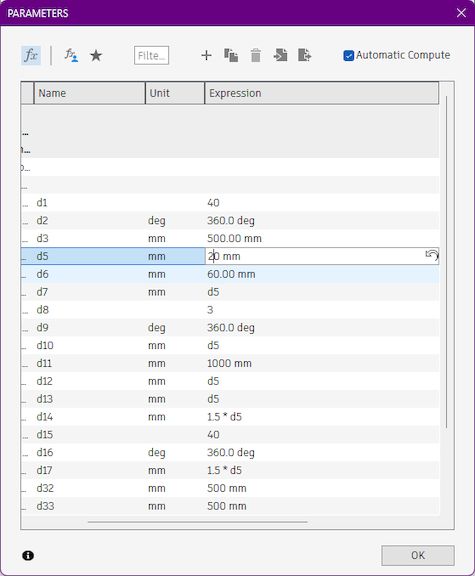
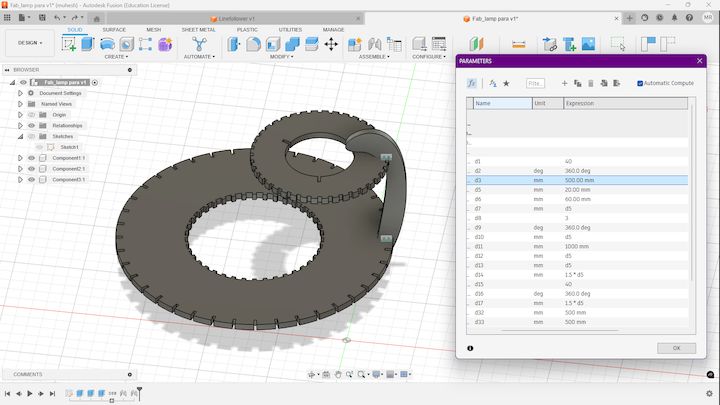
Initally you can see here the design is much more what we initially had, Now I going to change that value from 40mm to 20 mm, Let's see how its affecting the design
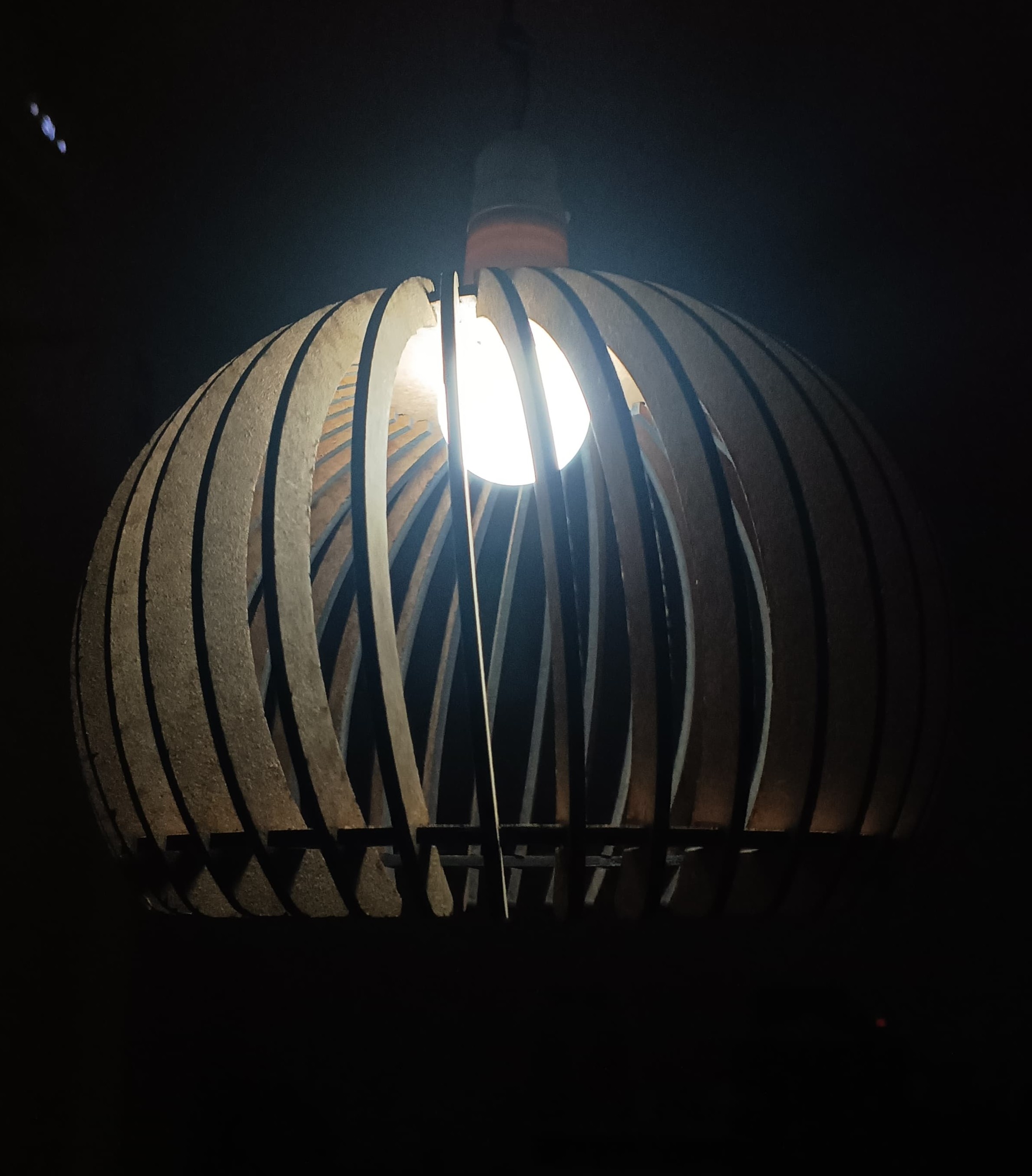
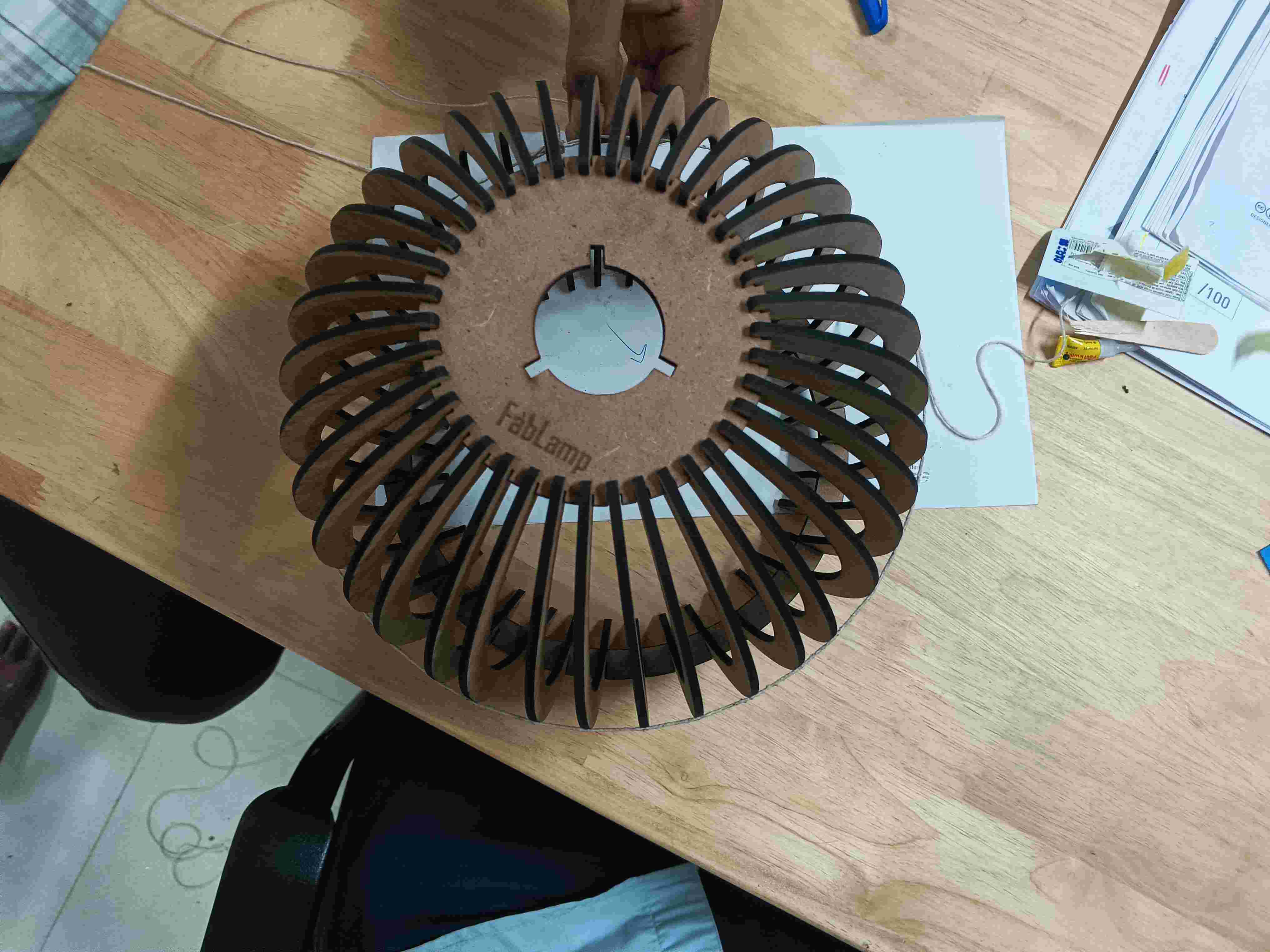
Hero Shot
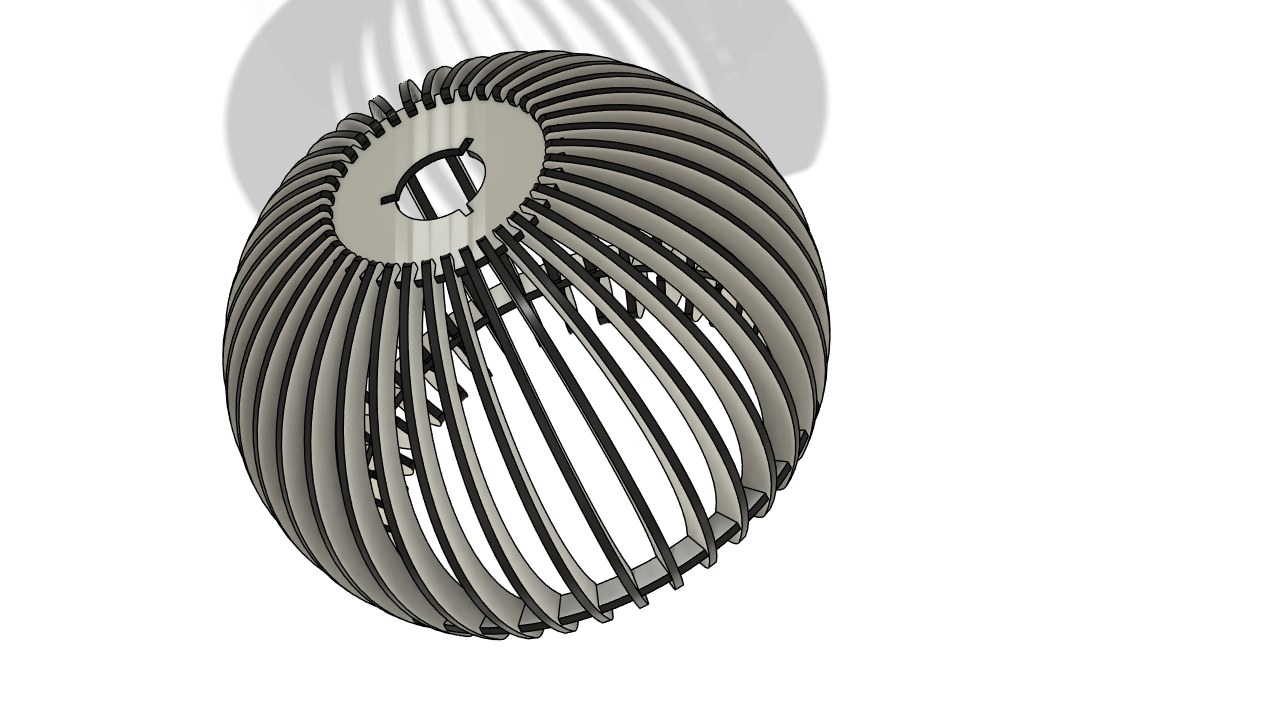

LaserCAD
Laser Cutting Guide
Recommended Settings:
| Material | Speed | Power |
|---|---|---|
| 3mm Plywood | 8mm/s | 85% |
| 6mm Plywood | 5mm/s | 90% |
Cut interior features first, then outer contours
Assembly Steps

- Connect base components
- Insert vertical supports
- Attach shade panels
Hero Shot
Viny Cutting
For this week's computer-controlled cutting assignment, I made a personalized vinyl sticker with my name "MUHESH | FAB LAB MADURAI". The goal was to understand the full workflow of designing, preparing, cutting, and transferring vinyl using a SkyCut C24 machine along with the SignMaster software suite, which includes the Vinyl Spooler, where the actual cutting job is processed.
This documentation explains each step in detail, from digital design to final application.
Design Process
Choosing the Design Software
- I used a vector-based design tool (Inkscape / Illustrator / CorelDRAW)
- Vinyl cutters require vector paths, so the design must be created using scalable vector graphics
Creating Text for the Sticker
- I created the following text:
- MUHESH
- FAB LAB MADURAI
- I used a bold, easy-to-weed font to ensure smooth cutting and clean readability

Converting Text to Vector Paths
Since vinyl cutters cannot interpret text formats:
- I converted the text to paths/outlines/curves
- This prevents font errors and ensures clean blade tracing
Final Design Dimensions
- I scaled the design to the desired size:
- Width: ~14.93 cm
- Height: ~8.3 cm
- This ensures easy weeding and efficient material usage
Exporting the File
- To prepare the file for cutting, I exported it as:
- SVG (recommended)
- The SVG file was then imported into SignMaster
Sign Master
Sign Master is a software used to create and customize vinyl cutting designs. It is a free software that can be downloaded online. This software allows the user to create their own designs or modify existing ones. It also provides a variety of tools and features to help the user to create their design.
- Create and customize vinyl cutting designs
- Modify existing designs
- Provides a variety of tools and features
Using SignMaster for Vinyl Cutting
Importing the Design into SignMaster
- I opened SignMaster and chose:
- File → Import → (Select SVG file)
- The design loaded into the workspace where I could verify:
- Dimensions
- Alignment
- Path accuracy
Sending the Job to Vinyl Spooler
- SignMaster uses a built-in tool called Vinyl Spooler to communicate with the SkyCut machine
- I clicked:
- Cut → Send to Cutter (Vinyl Spooler)
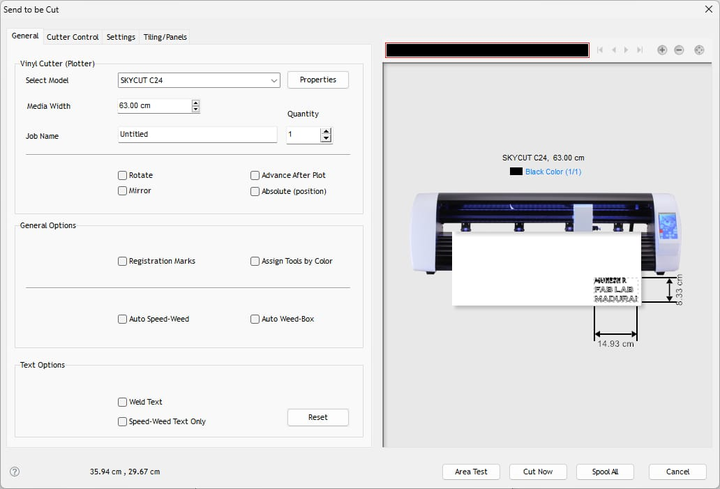
- This opened the Vinyl Spooler window
Job Preview in Vinyl Spooler
In Vinyl Spooler, I checked:
- Correct orientation
- Path preview
- Cutting boundaries
- Actual size (14.93 cm × 8.3 cm)
- Selected cutter: SkyCut C24
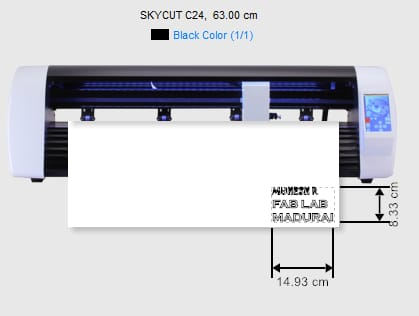
This step ensures that the vinyl will be cut accurately.
Machine Settings in Vinyl Spooler
In the Cut Options tab, I configured:
| Parameter | Setting |
|---|---|
| Speed | 300 mm/s |
| Force/Pressure | 120–150 g |
| Mode | Cutting/Contour Cut |
| Passes | 1 |
| Blade | 45° blade |
These settings are ideal for thin-to-medium vinyl.
I also used the Test Cut option to verify the blade depth.
Preparing the Vinyl Material
Selecting Vinyl Sheet
- I used standard adhesive vinyl:
- Top: colored vinyl
- Middle: adhesive layer
- Back: paper backing sheet
Cutting the Vinyl to Size
- I cut a piece slightly larger than my design area to allow margin for alignment and origin setting
Checking the Vinyl Surface
Before loading:
- Ensured the sheet was flat
- Checked for dust or wrinkles
- Confirmed backing paper was intact
This ensures smooth feeding inside the cutter.
Loading Vinyl into the SkyCut C24
Aligning and Securing the Material
Steps:
- Lifted pinch rollers
- Inserted vinyl sheet
- Aligned it parallel to the machine guide
- Positioned pinch rollers over the grit wheels
- Locked them in place


Proper alignment prevents shifting during cutting.
Setting the Origin
- Using the machine controls, I positioned the blade at the lower-left corner and pressed:
- Set Origin
- This tells the machine exactly where to start cutting
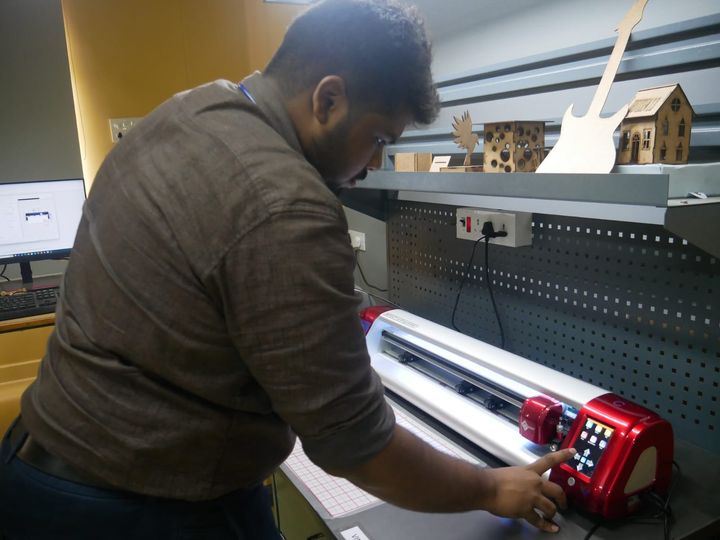

Cutting the Vinyl
Executing the Cutting Job
- Back in Vinyl Spooler, I clicked Cut Now
- The SkyCut C24 began cutting the sticker precisely following the vector paths
- During the process, I monitored:
- Material feed
- Blade movement
- Any lifting or tearing
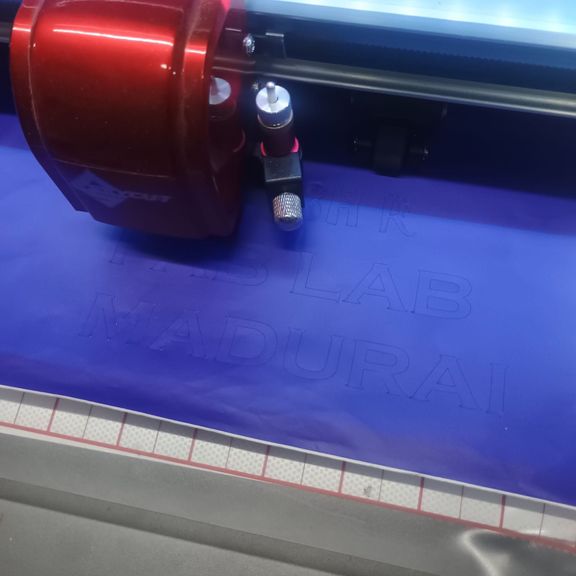

Weeding the Vinyl
Removing Excess Vinyl
- Using a weeding tool or tweezer:
- I peeled away the unwanted outer vinyl
- Removed internal pieces inside letters (A, R, B, D, etc.)
- Weeding requires patience, especially for small text
Inspecting the Results
After weeding, I checked:
- Cleanly cut edges
- No tears
- All letters intact
- Proper spacing maintained
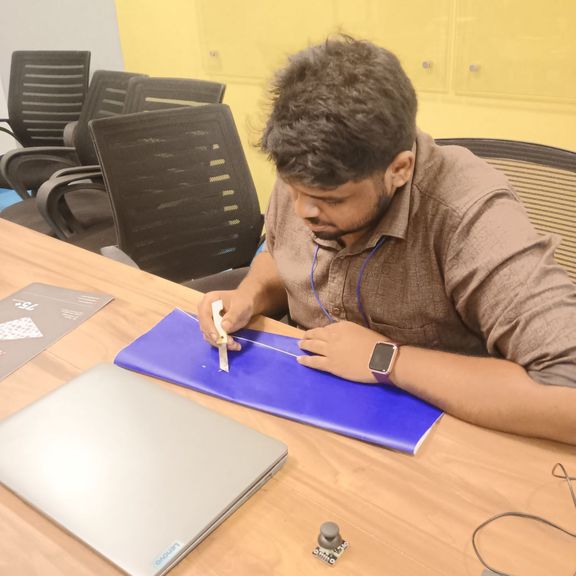

Applying Transfer Tape
Preparing the Tape
- I cut a transfer tape piece slightly larger than the sticker
Applying the Tape Over the Vinyl
Steps:
- Placed tape over the weeded design
- Pressed it firmly using a squeegee
- Ensured bubble-free adhesion
The tape helps lift the design cleanly for application.
Lifting the Sticker
- I slowly peeled the tape, ensuring the vinyl letters stuck to it completely
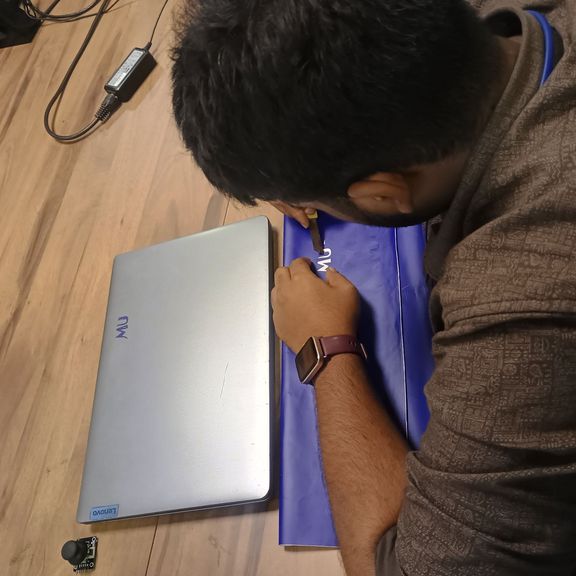

Applying the Final Sticker
Preparing the Target Surface
- I cleaned the surface using a dry cloth and ensured it was dust-free
Transferring the Vinyl
Steps:
- Placed the tape (with vinyl) on the target surface
- Reseated it with a squeegee
- Slowly peeled away the transfer tape
- The vinyl lettering remained cleanly on the surface, forming the final sticker
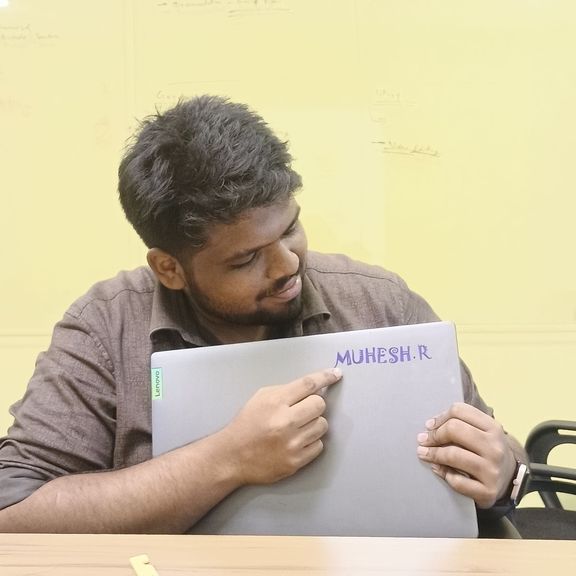
Final Output
The final vinyl sticker: "MUHESH R"
was successfully cut, weeded, and applied.
It has sharp edges, proper alignment, and professional finish.

Download the files
You can download the encoded model by clicking on the following links.