Assignment#17: Invention, Intellectual Property, and Income
This assignment is about documenting what I learned in the week of ' Invention, Intellectual Property, and Income'. I am of the belief that my invention will nourish in this society only if I take it ahead to a point, where it starts contributing towards society. As I have almost finished my final project, I am exploring different ways to convert it in to a product that can be used by mid-scale farmers to onion traders. At the same time, I am exploring ways and means to protect my project from infringements at the same.
Through this assignment, I have learned what is invention, what are different types of intellectual properties, etc. I have also documented my learning outcomes.
My Hero shots for this week
 |
 |
Click here to go back to the top
Individual Assignment
Objectives of Individual Assignment:
- Develop a plan for dissemination of your final project.
- Prepare drafts of your summary slide (presentation.png, 1920x1080) and
- Video clip (presentation.mp4, 1080p HTML5, < ~minute, < ~10 MB).
- Put them in your root directory
Basics of Invention and Intellectual Property
What is invention?
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition or process. The invention process is a process within an overall engineering and product development process. It may be an improvement upon a machine or product or a new process for creating an object or a result. An invention that achieves a completely unique function or result may be a radical breakthrough. Such works are novel and not obvious to others skilled in the same field. An inventor may be taking a big step toward success or failure.
Types of Inventions
Inventions are of three kinds: scientific-technological (including medicine), sociopolitical (including economics and law), and humanistic, or cultural. Scientific-technological inventions include- railroads, aviation, vaccination, hybridization, antibiotics, astronautics, holography, the atomic bomb, computing, the Internet, and the smartphone.
Sociopolitical inventions comprise new laws, institutions, and procedures that change modes of social behavior and establish new forms of human interaction and organization. Examples include the British Parliament, the US Constitution, the Manchester (UK) General Union of Trades, the Boy Scouts, the Red Cross, the Olympic Games, the United Nations, the European Union, and the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, as well as movements such as socialism, Zionism, suffragism, feminism, and animal-rights veganism.
Humanistic inventions encompass culture in its entirety and are as transformative and important as any in the sciences, although people tend to take them for granted. In the domain of linguistics, for example, many alphabets have been inventions, as are all neologisms (Shakespeare invented about 1,700 words).
Credits and Reference: Click here.
What is Intellectual Property (IP)?
Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The best-known types are copyrights, patents, trademarks, and trade secrets. The modern concept of intellectual property developed in England in the 17th and 18th centuries. The term "intellectual property" began to be used in the 19th century, though it was not until the late 20th century that intellectual property became commonplace in the majority of the world's legal systems.
The main purpose of intellectual property law is to encourage the creation of a wide variety of intellectual goods. To achieve this, the law gives people and businesses property rights to the information and intellectual goods they create, usually for a limited period of time. This gives economic incentive for their creation, because it allows people to benefit from the information and intellectual goods they create, and allows them to protect their ideas and prevent copying. These economic incentives are expected to stimulate innovation and contribute to the technological progress of countries, which depends on the extent of protection granted to innovators.
Types of Intellectual Property Rights
Intellectual property rights include patents, copyright, industrial design rights, trademarks, plant variety rights, trade dress, geographical indications, and in some jurisdictions trade secrets.
Patents: A patent is a form of right granted by the government to an inventor or their successor-in-title, giving the owner the right to exclude others from making, using, selling, offering to sell, and importing an invention for a limited period of time, in exchange for the public disclosure of the invention. An invention is a solution to a specific technological problem, which may be a product or a process and generally has to fulfil three main requirements: it has to be new, not obvious and there needs to be an industrial applicability. To enrich the body of knowledge and stimulate innovation, it is an obligation for patent owners to disclose valuable information about their inventions to the public.
Copyright: A copyright gives the creator of an original work exclusive rights to it, usually for a limited time. Copyright may apply to a wide range of creative, intellectual, or artistic forms, or "works". Copyright does not cover ideas and information themselves, only the form or manner in which they are expressed.
Industrial Design rights: An industrial design right (sometimes called "design right" or design patent) protects the visual design of objects that are not purely utilitarian. An industrial design consists of the creation of a shape, configuration or composition of pattern or color, or combination of pattern and color in three-dimensional form containing aesthetic value. An industrial design can be a two- or three-dimensional pattern used to produce a product, industrial commodity or handicraft. Generally speaking, it is what makes a product look appealing, and as such, it increases the commercial value of goods.
Trademarks: A trademark is a recognizable sign, design or expression which distinguishes products or services of a particular trader from similar products or services of other traders.
Plant varieties: Plant breeders' rights or plant variety rights are the rights to commercially use a new variety of a plant. The variety must amongst others be novel and distinct and for registration the evaluation of propagating material of the variety is considered.
Trade dress: Trade dress is a legal term of art that generally refers to characteristics of the visual and aesthetic appearance of a product or its packaging (or even the design of a building) that signify the source of the product to consumers.
Trade secrets: A trade secret is a formula, practice, process, design, instrument, pattern, or compilation of information which is not generally known or reasonably ascertainable, by which a business can obtain an economic advantage over competitors and customers. There is no formal government protection granted; each business must take measures to guard its own trade secrets (e.g., Formula of its soft drinks is a trade secret for Coca-Cola.)
Credits and Reference: Click here.
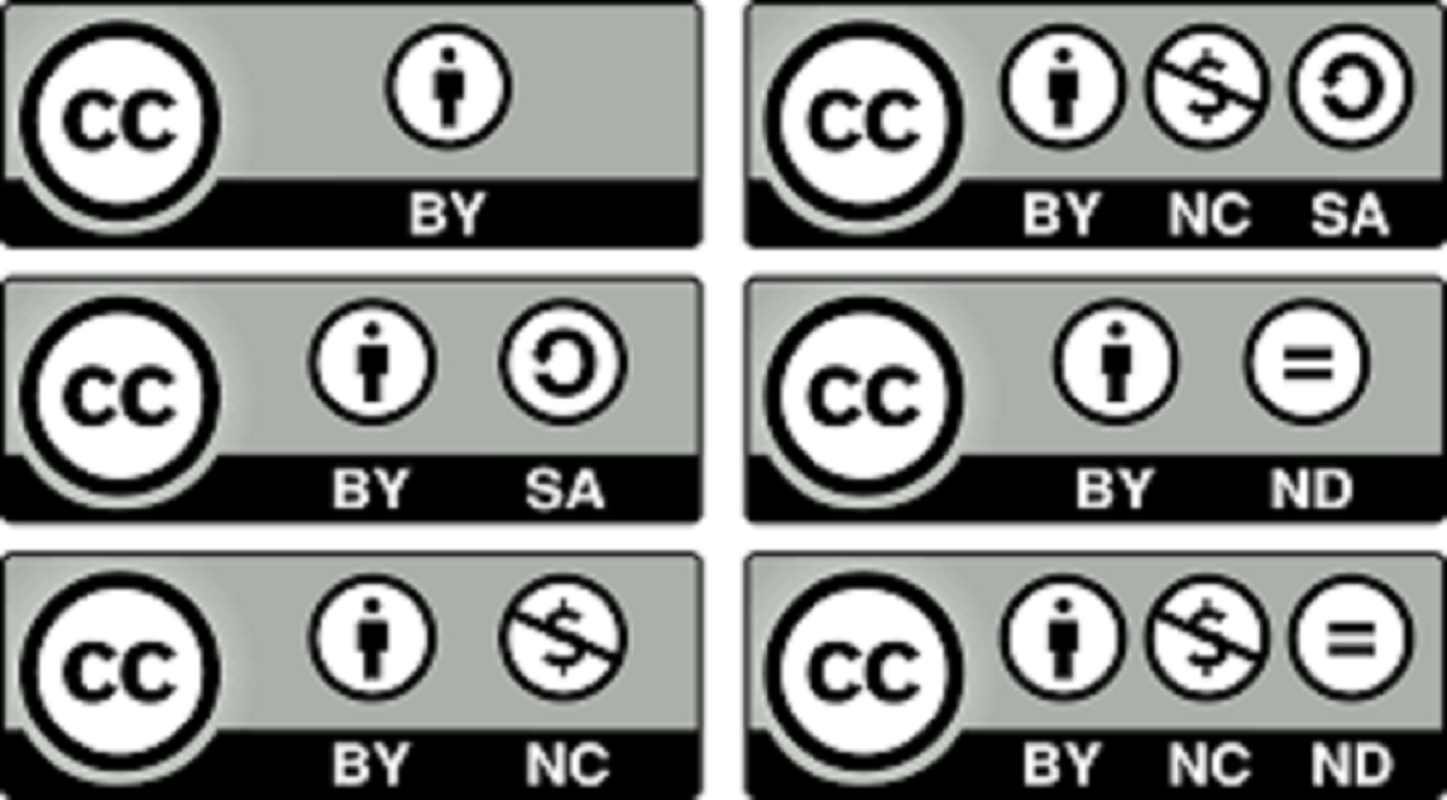
Different Copyright Licenses
 |
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
Click here to go back to the top
Dissemination plan for my Final project:
Who is my project for:
My final project 'Low cost IoT based Smart storage for onions' is for small to medium-scale farmers and traders, restaurant owners, organizations having a community kitchen, etc.
How is it funded:
My final project is currently not being funded apart from what we have spent on developing the same. However, for further development, we will seek funds from some organizations, institutes working in the area of onions and post-harvest storage of onions.
Business plan and funding for scaling up:
Yes, we are currently working on drafting a business plan for developing this project as a commercial product.We will also include the funding plans for scaling up the process of converting it to a product.
License chosen or something else to protect intellectual properties of my project:
Yes, I have chosen license from Creative Commons. Details of, which are given below in this assignment itself.
How will I raise awareness of my project amongst the target group:
I have already contacted 3-4 farmers nearby Pabal to spread awareness of the project. I initially wanted to install my project at their farms for onion storage. However, we later changed the plan and implemented in at Vigyan Ashram. We will keep introducing this project to the visitors, farmers, traders, whoever visits Vigyan Ashram. We will also create awareness through our social media, websites, blogs, newsletters, etc.
Click here to go back to the topFuture Possibilities for my Final project:
As I have already mentioned, m final project is designed for small to medium-scale farmers and traders, restaurant owners, organizations having a community kitchen, etc., I am implementing it at our community farm that I am a part of. This farm is situated at around 65 KMs from Vigyan Ashram. I will continue to develop my project board and add more features as we conduct more tests and do data analysis from that set-up.
Click here to go back to the topCreating license on Creative Common for Final project:
I started with going to creativecommons.org
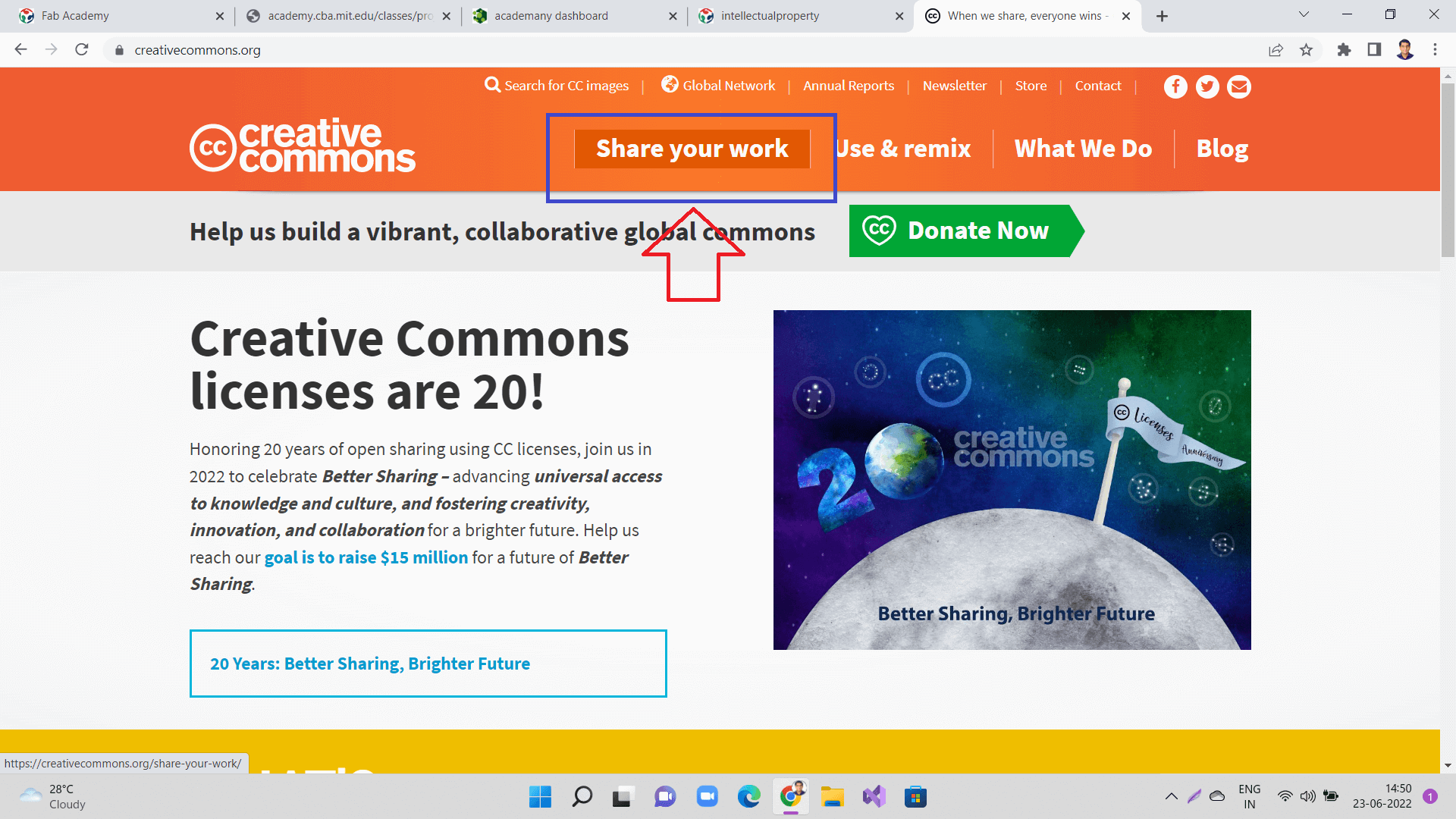 |
Here you will find options to share your work as seen in the image below. Click on 'Get Started' button.
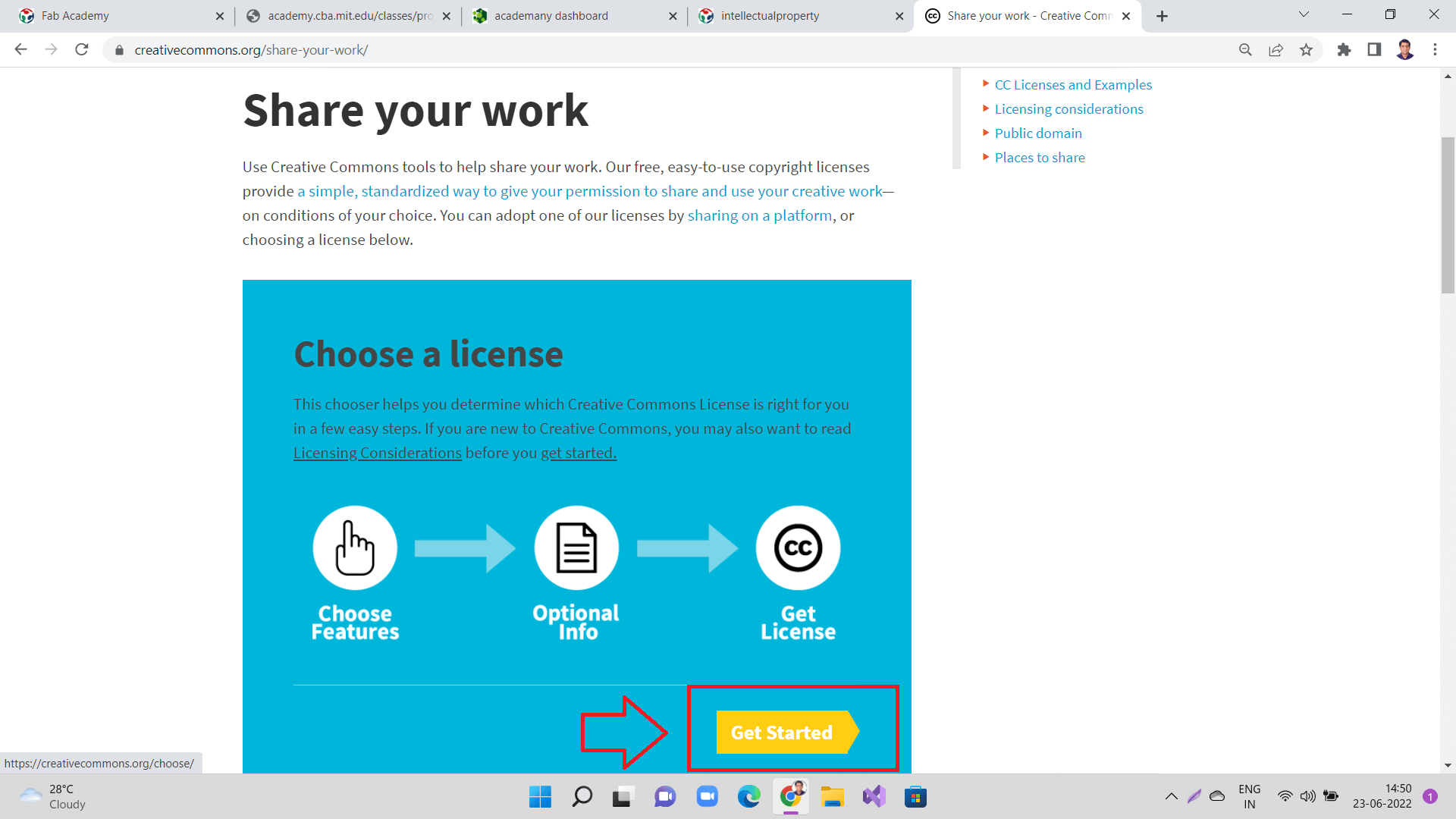 |
After clicking 'Get Started', it will move you to the next step asking you to select license chooser. Here, click on 'chooser beta' version as shown in the image below.
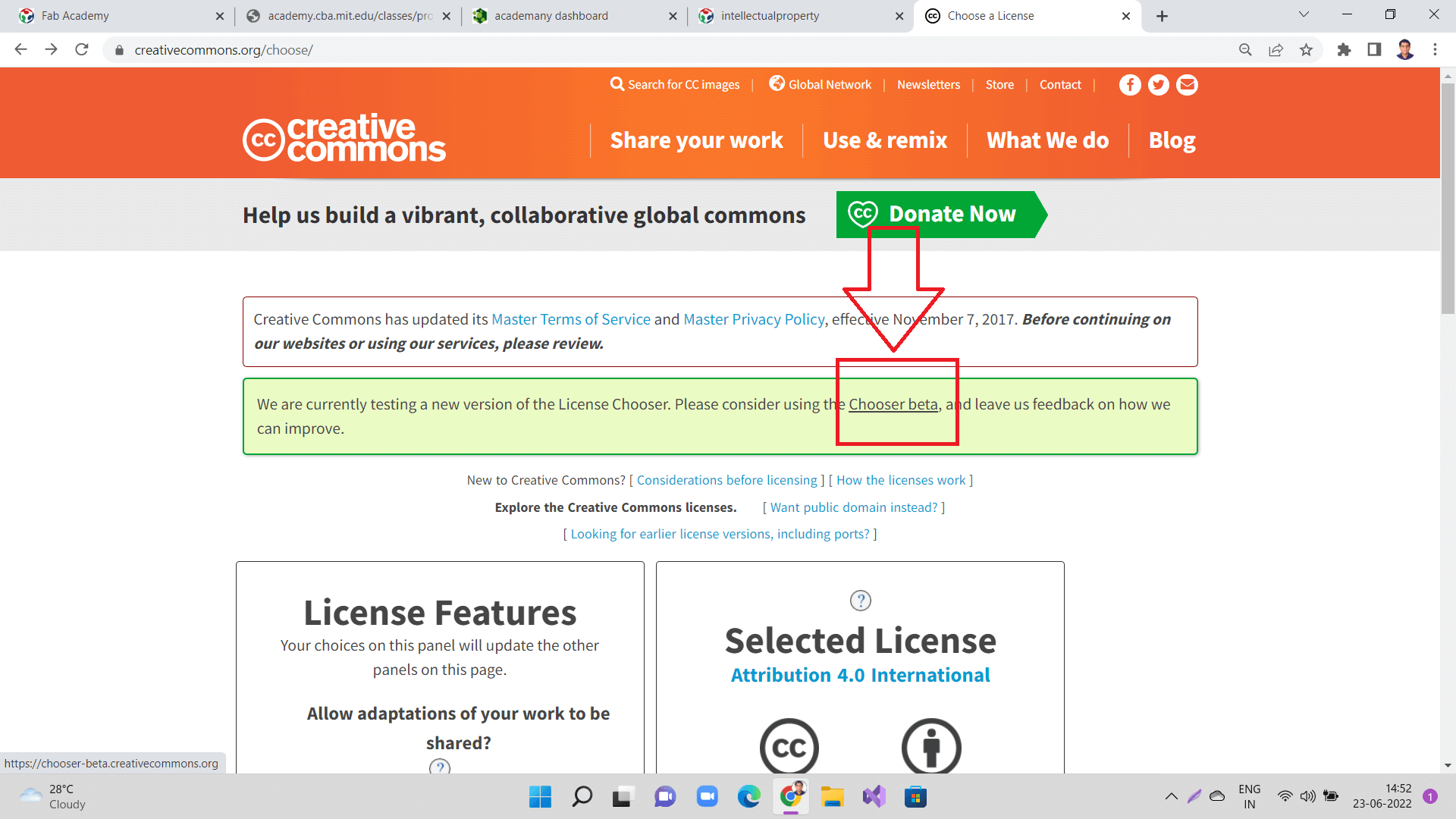 |
Now next part is to select options as shown in the images below and keep clicking next. Click "No, I need help selecting a license.".
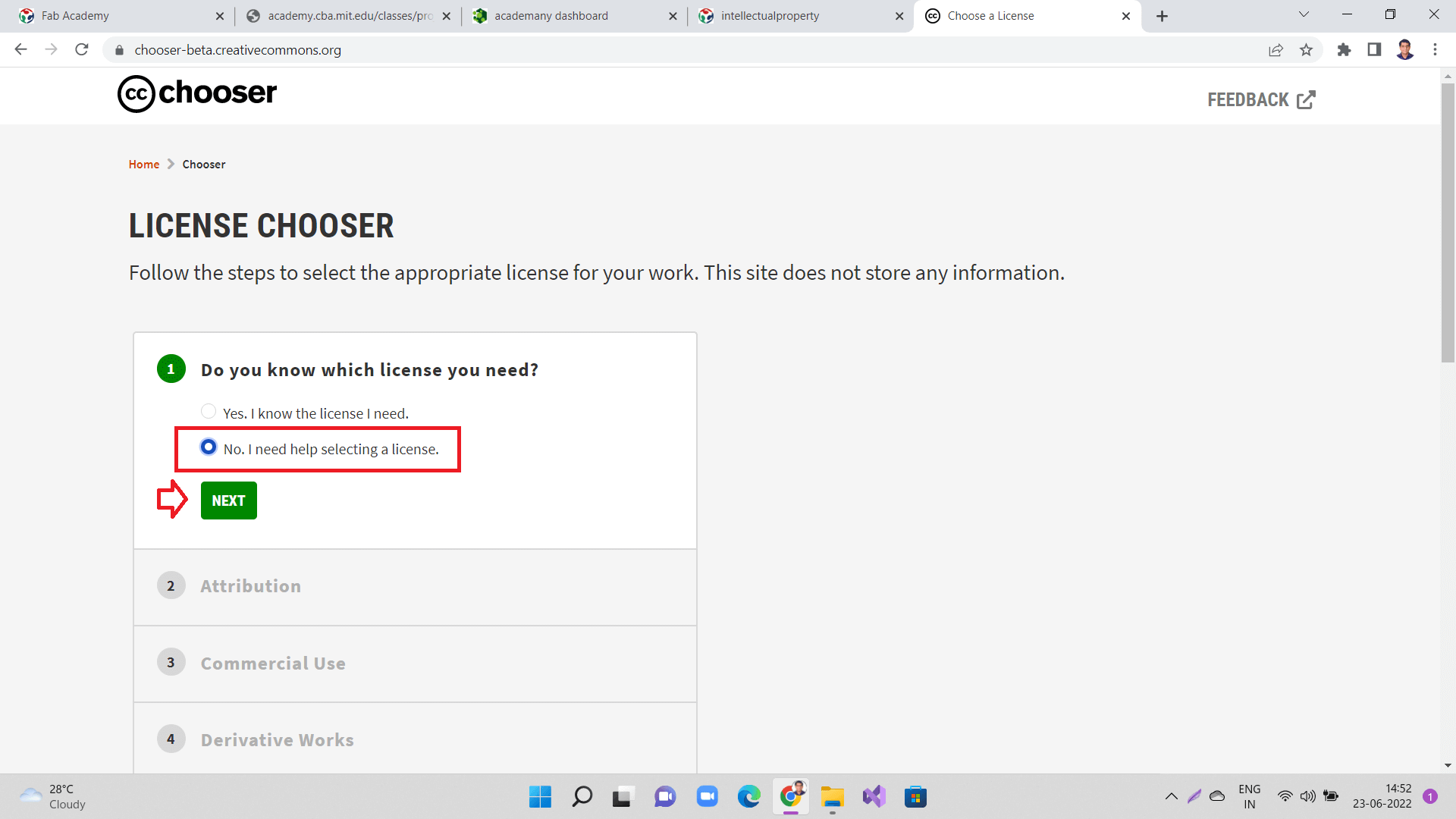 |
Next, click "Yes. Anyone using my work must include proper attribution." and click 'Next' as shown below.
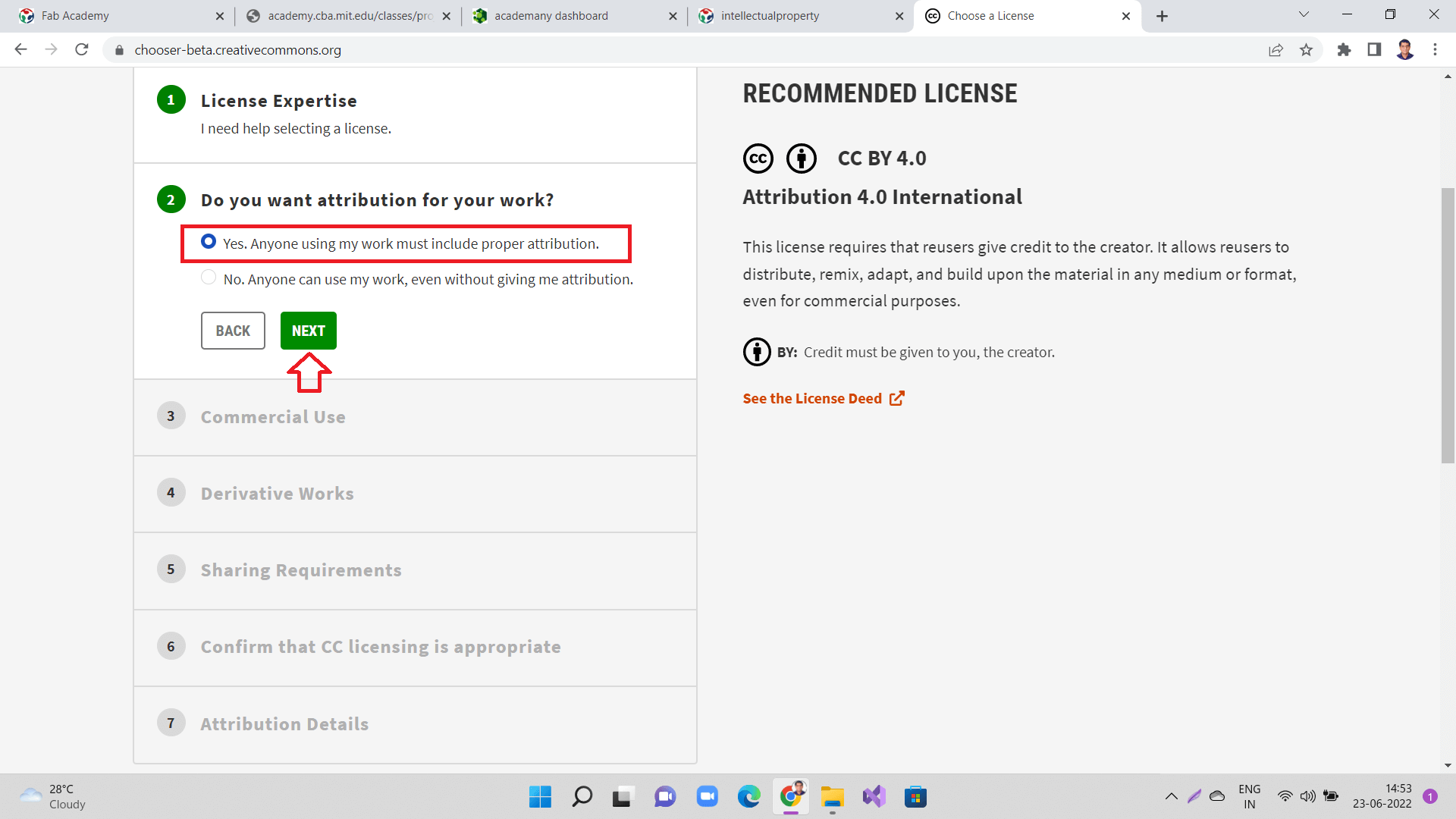 |
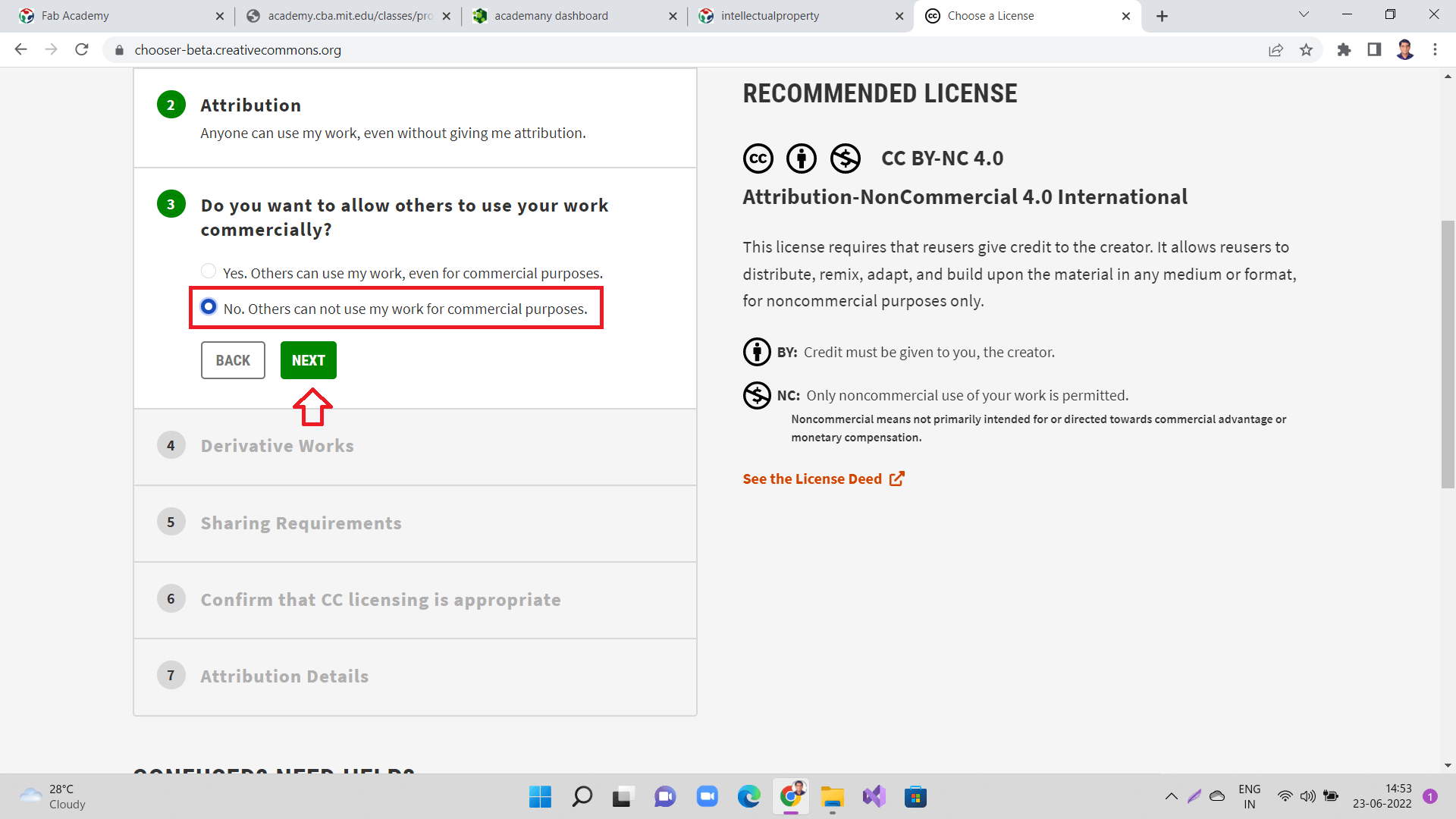
Next, click "No. Others can not use my work for commercial purposes." and click 'Next' as shown below.
 |
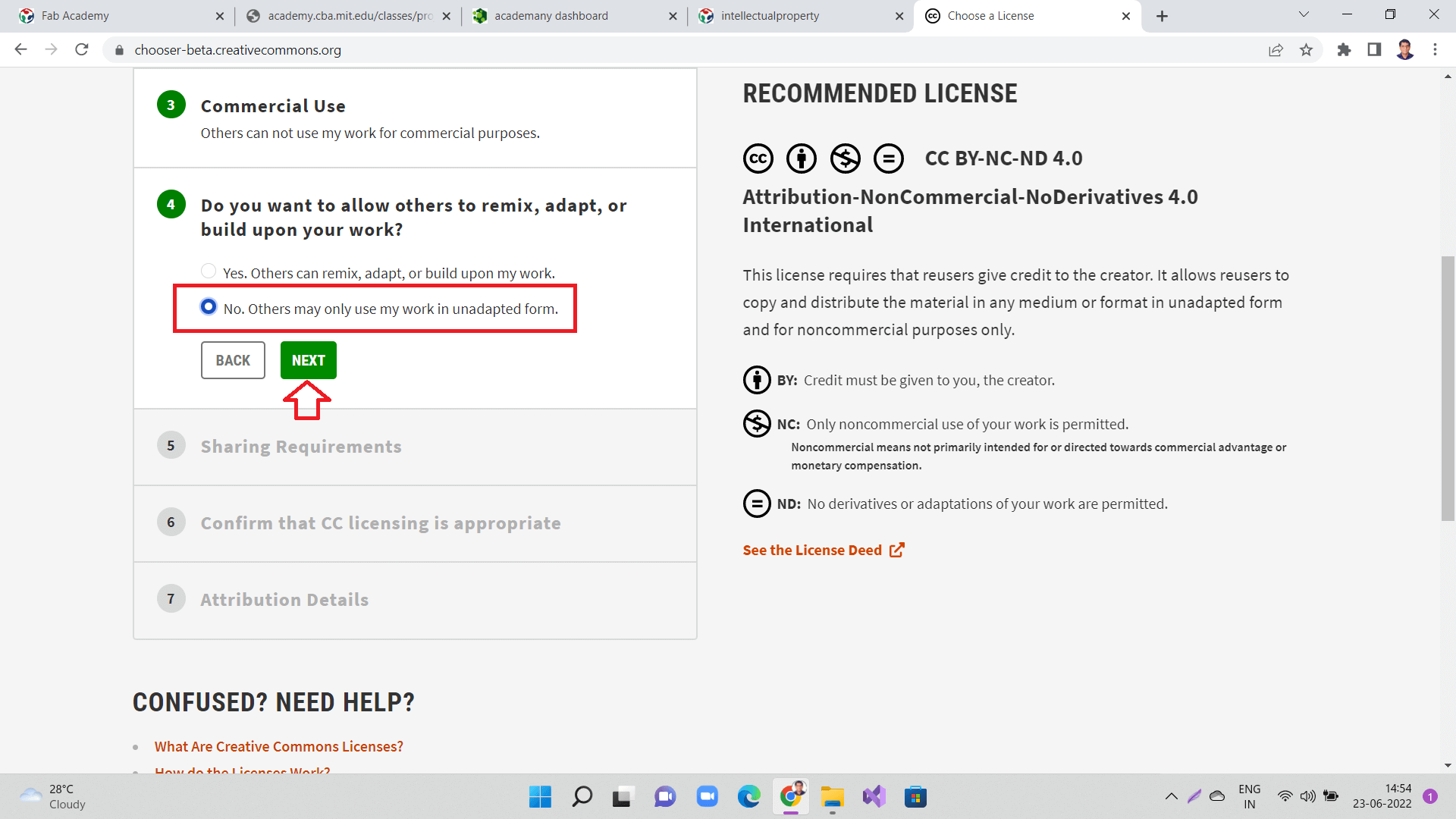
Next, click "No. Others may only use my work in unadapted form." and click 'Next' as shown below.
 |
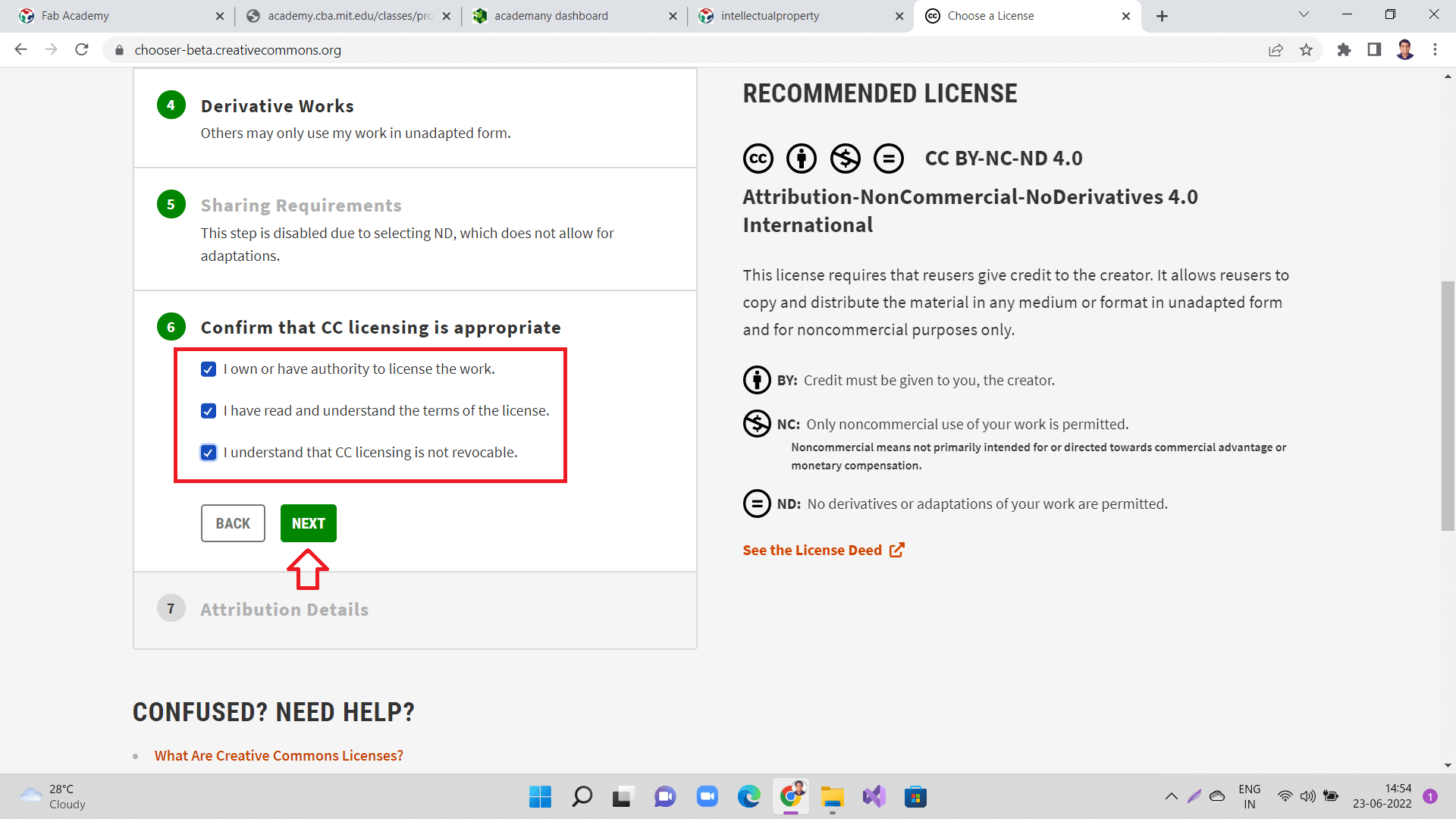
Next, check all the boxes and click 'Next' as shown.
 |
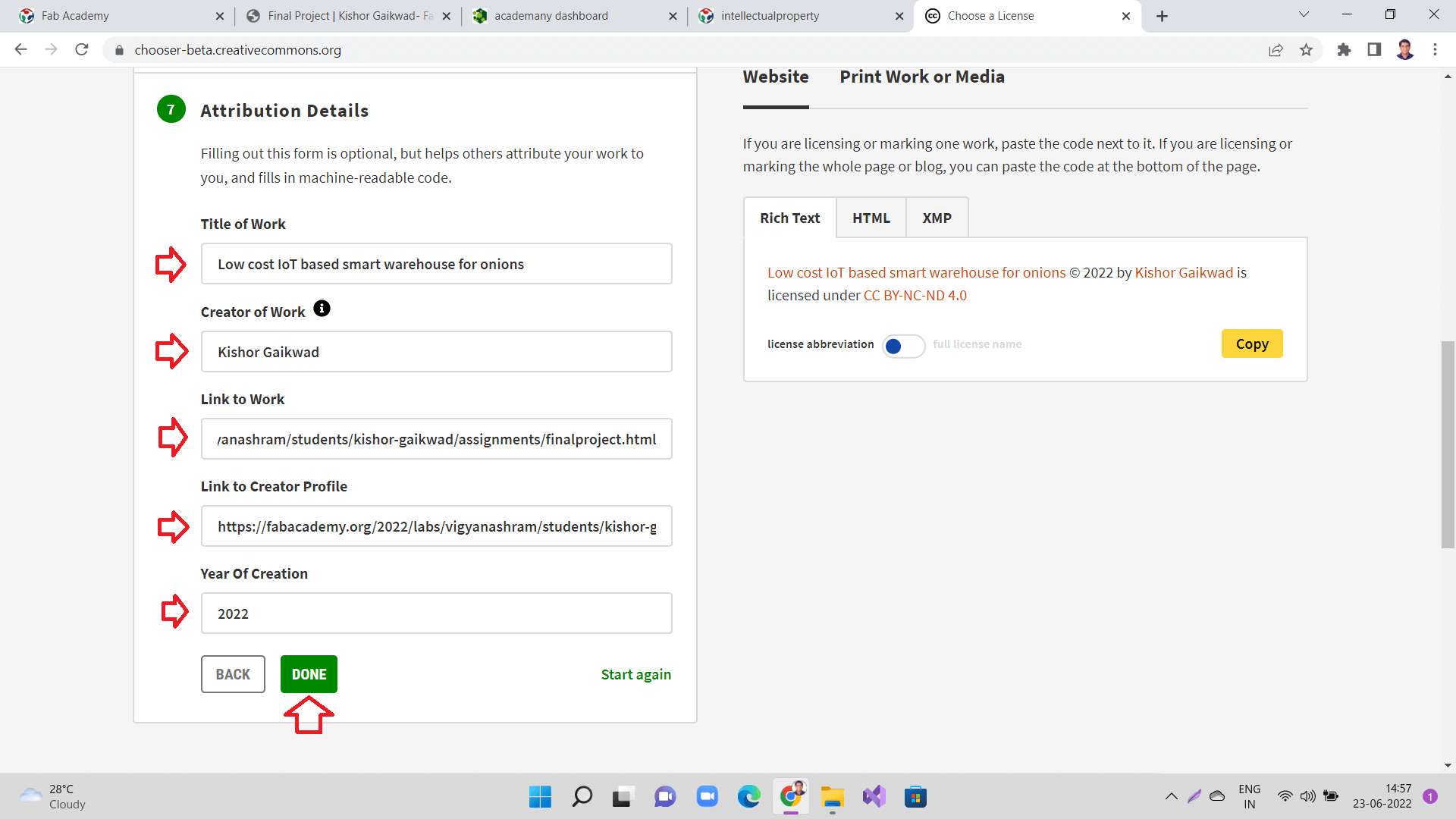
Add all the details like 'Title of Work', 'Creator of Work', etc., and click 'Done' as shown.
 |
You are almost done. Copy license details as a 'Rich text' as shown.
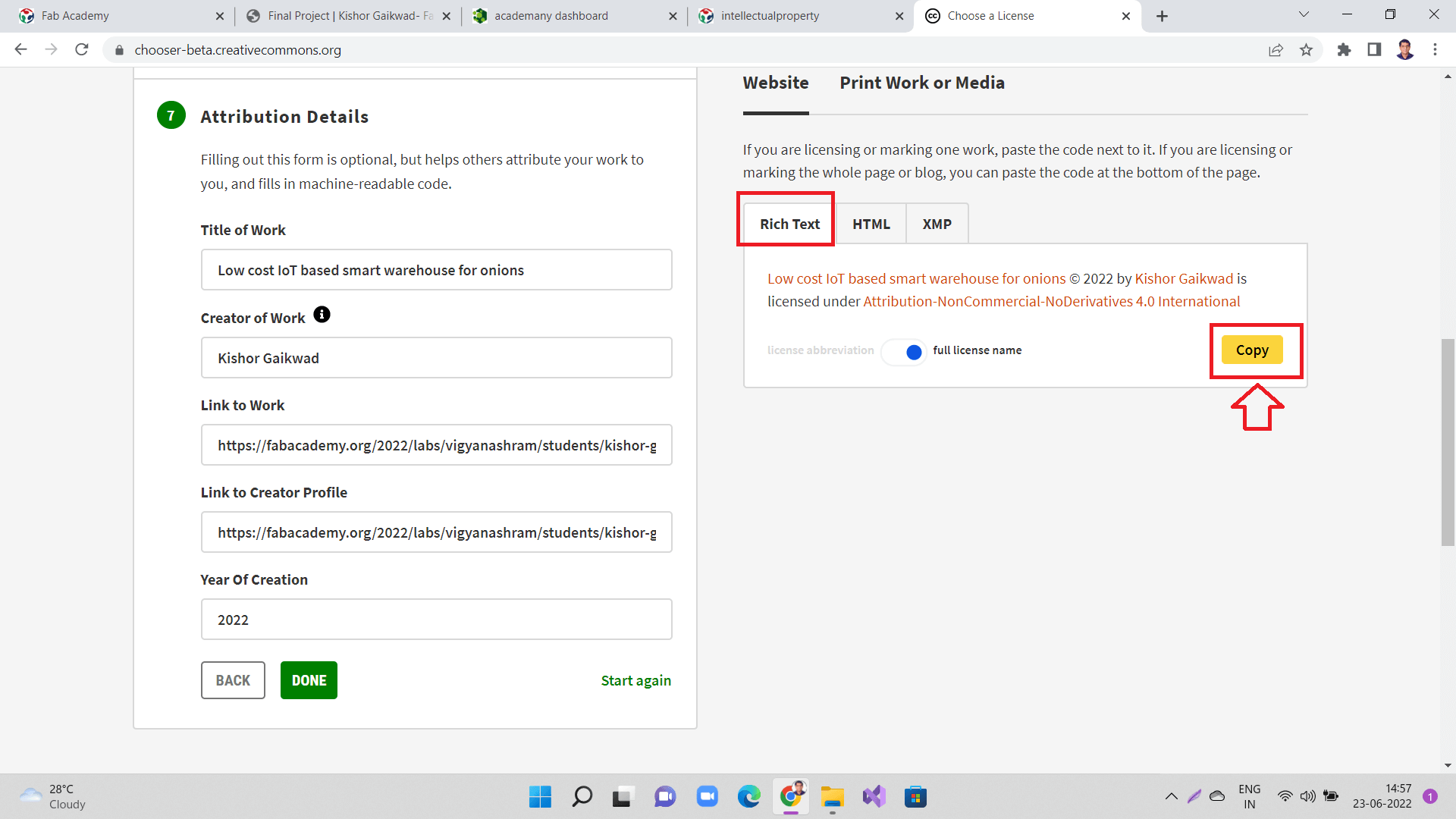 |
Alternatively, copy license details as a 'HTML' format as shown.
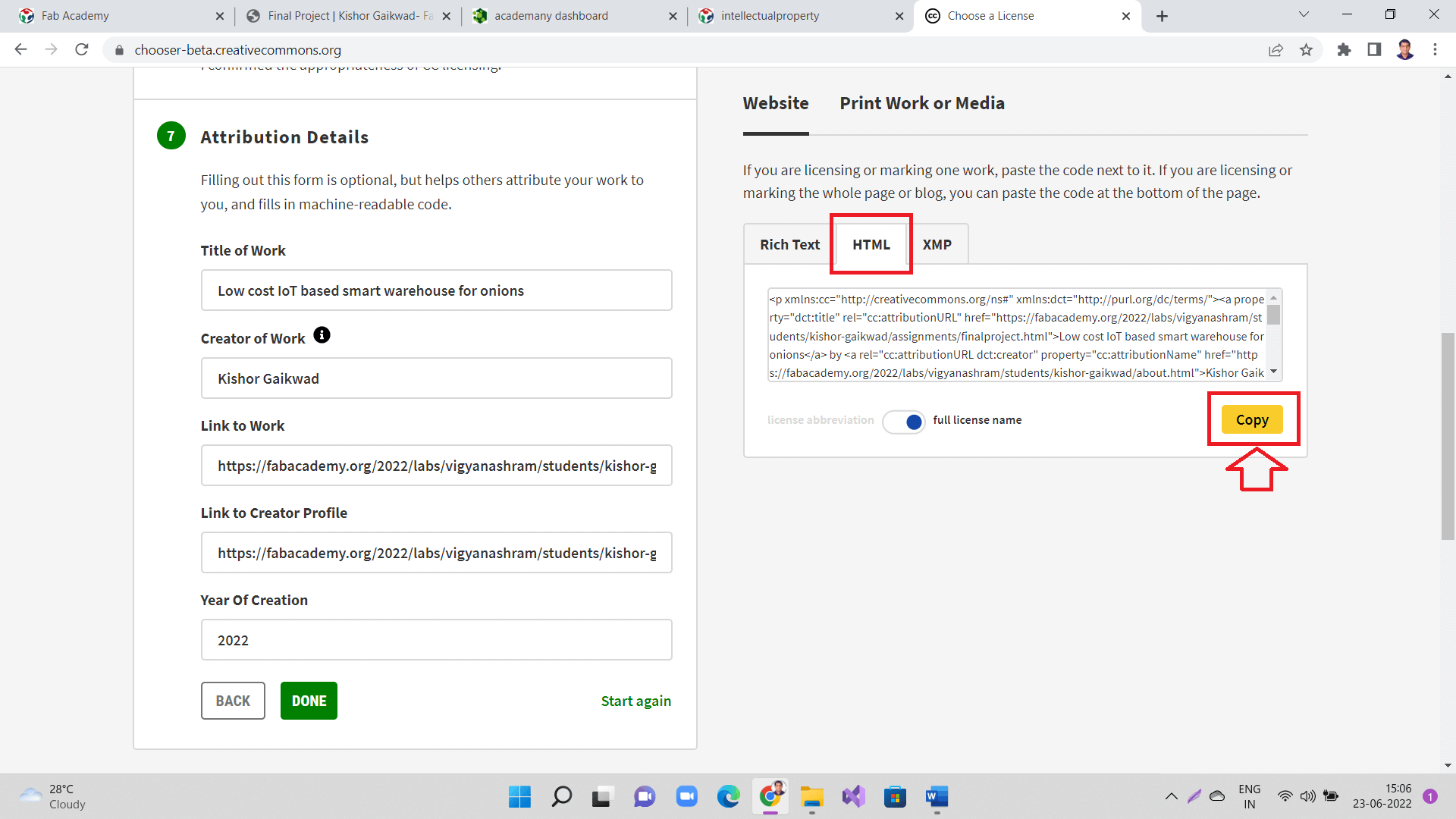 |
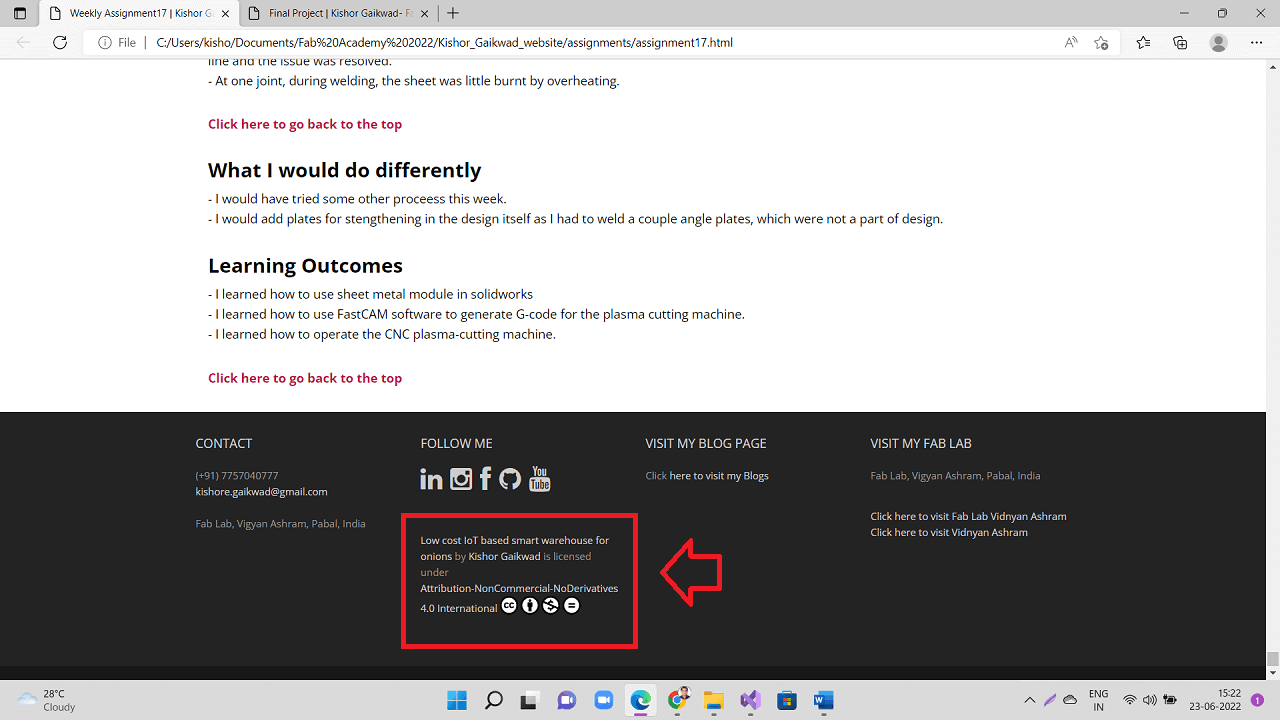
I used this HTML format and added to the footer of my final project page as shown below.
 |
Also, copy license details as a 'Plain text' format as shown.
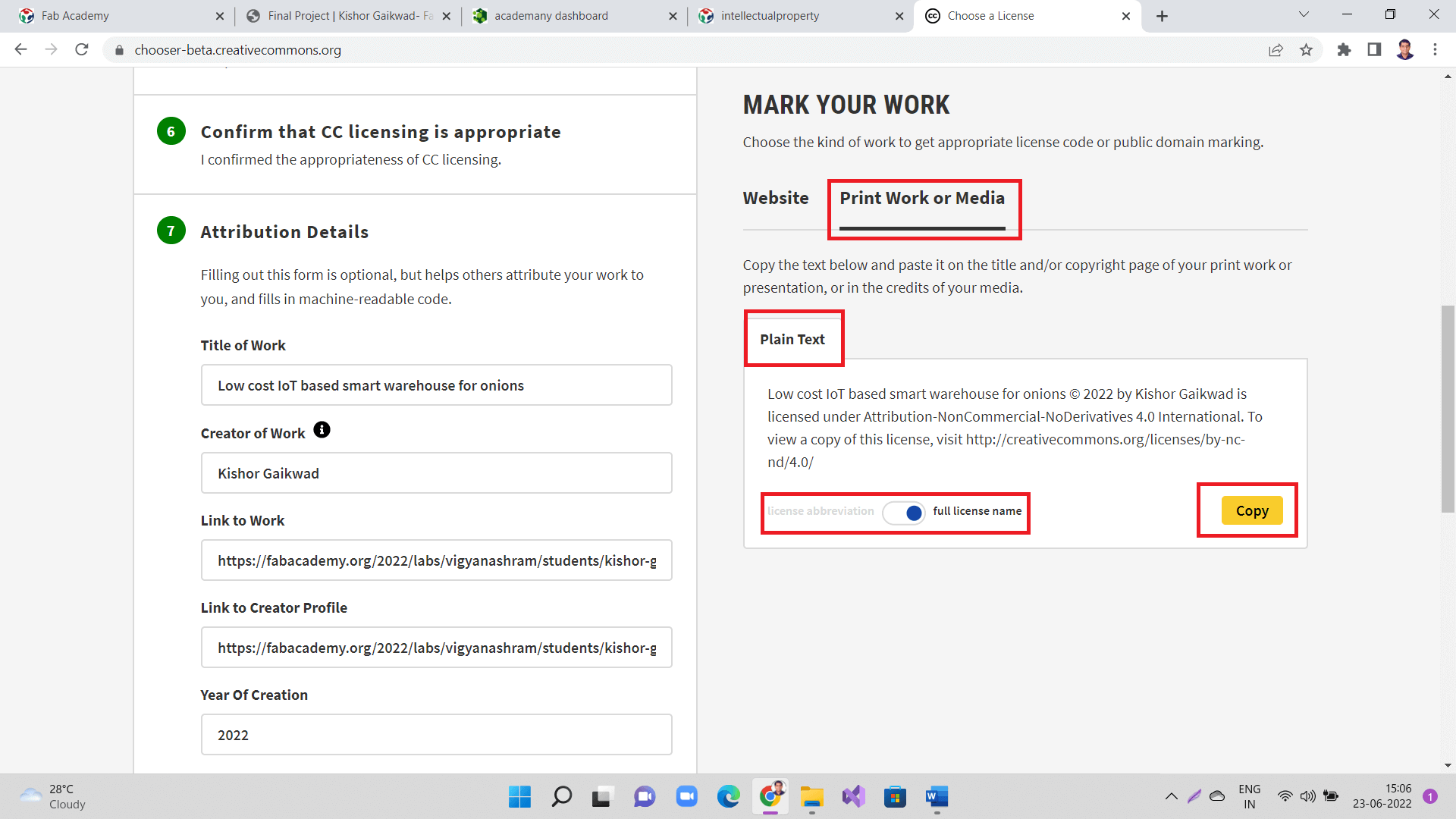 |
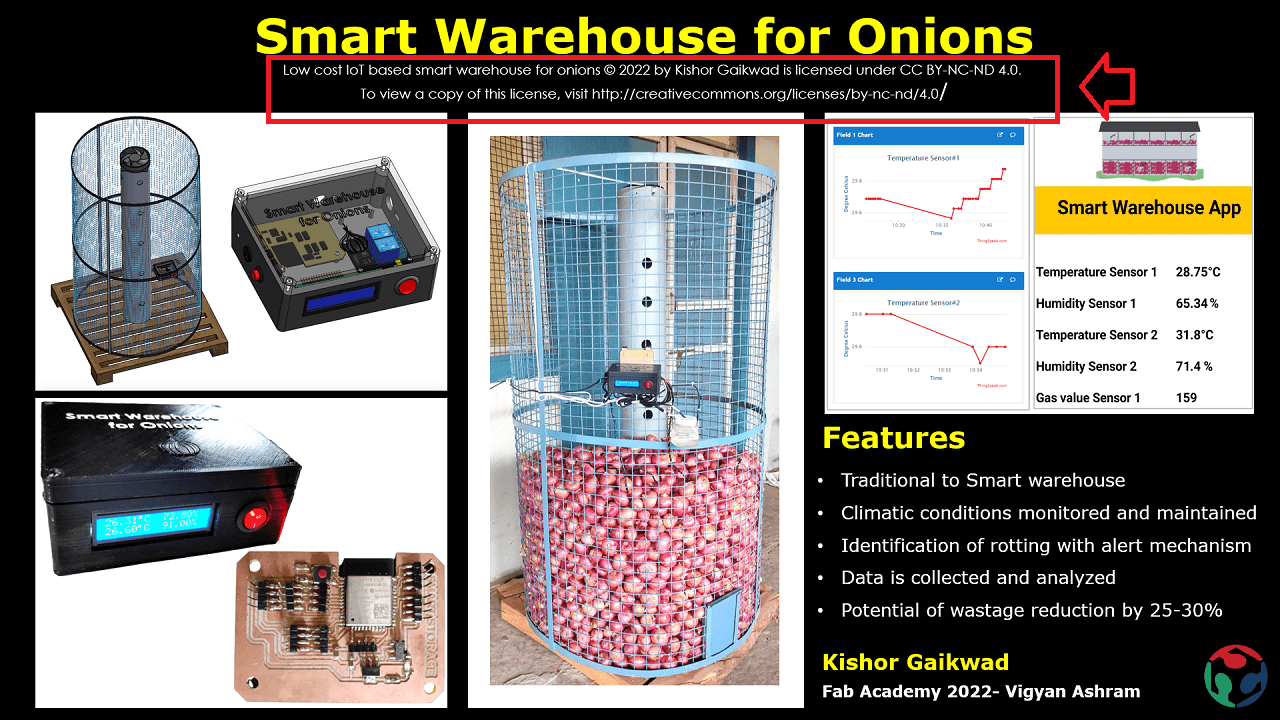
I added this Plain text format of my license just below the project tile on final slide as shown below.
 |
Click here to go back to the top
Final Presentation Slide
 |
Final Presentation Video
Click here to go back to the top
Learning Outcomes
- I learned different types of inventions and Intellectual Property Rights and when to use which one amongst them.
- I learned how choose license from various portals.
- I learned how to document dissemination plan for my final project.
