Week 09 - Group assignment
The goal of the group assignment is to measure the power consumption of an output device.
We used a simple small DC motor, which we powered with a power supply.
To measure the power consumption, we first need to measure the power, and to measure the power, we need to measure the current intensity. For this measure we will use a multimeter.
Important! Though the voltage is measured by connecting the multimeter in parallel, the current is measure by placing it in series.
The circuit should thus be as the following:
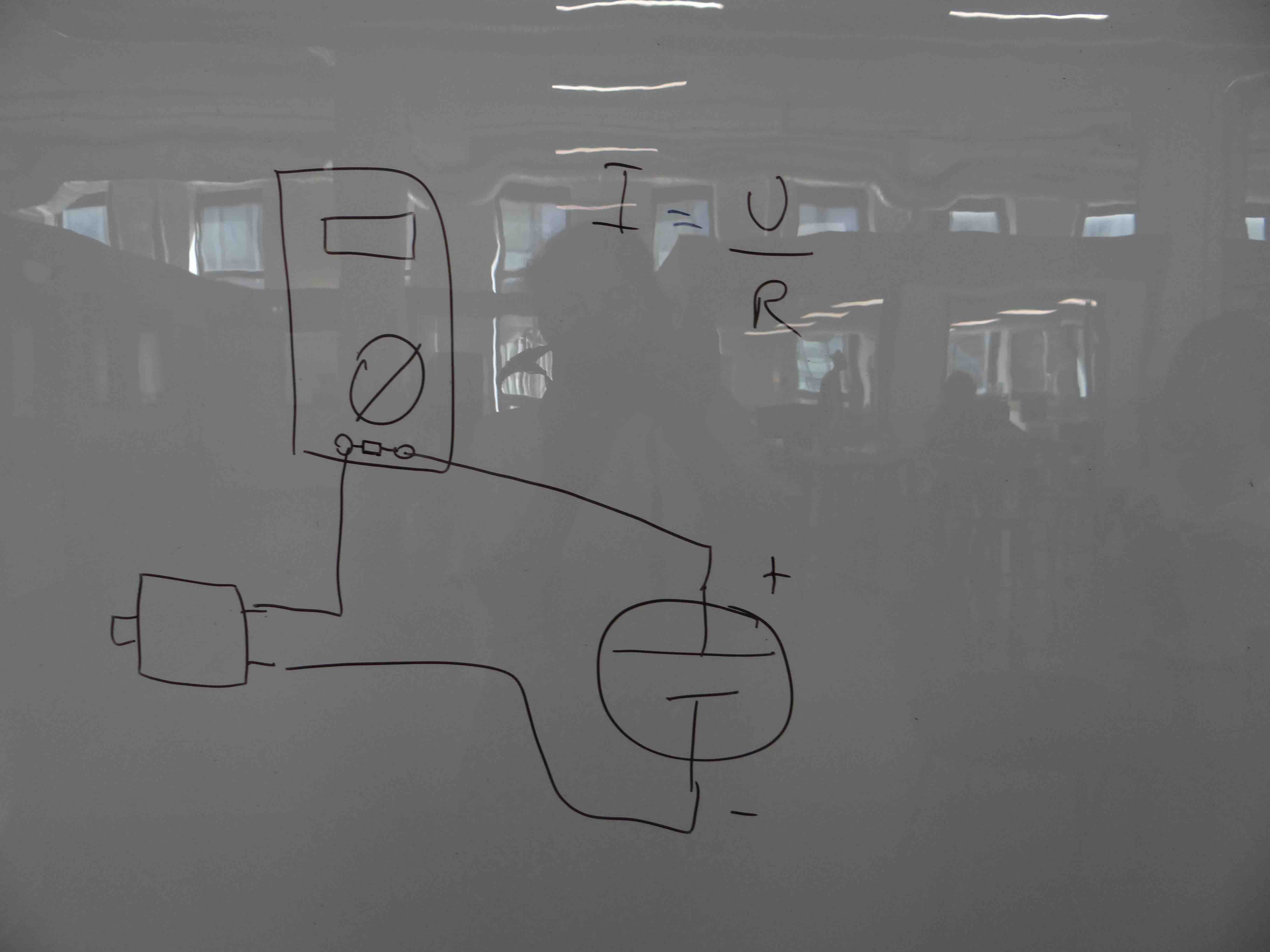
Note the small resistor drawn on the multimeter: it's our instruction explanations about how the multimeter can measure current: using a small resistor with a known resistance value
We first set a voltage a bit below 5V (4.1V) and measure the current.
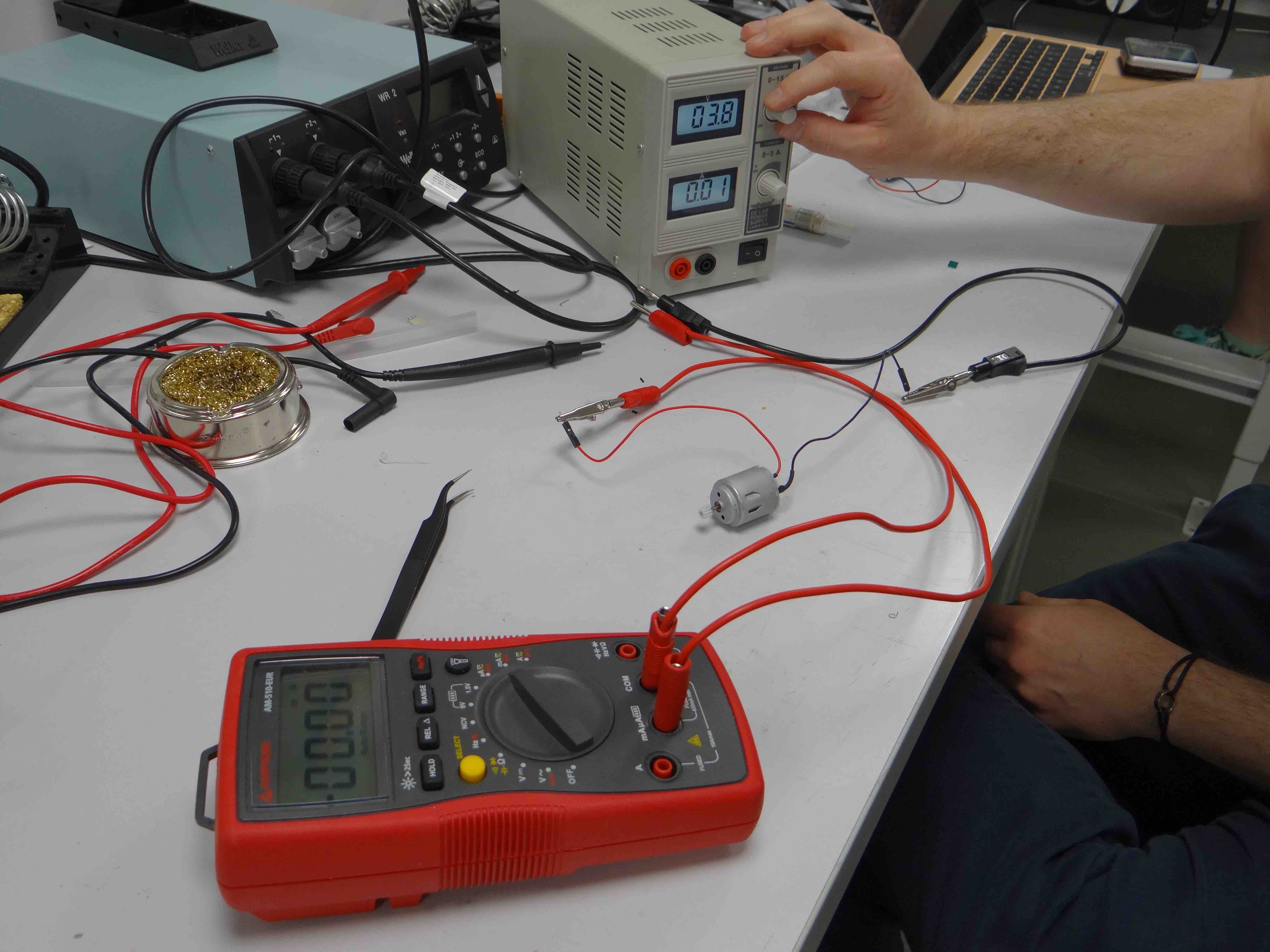

When the motor axis can spin freely, the measured current is approximatively 74 mA (consistent with what's indicated by the power supply).
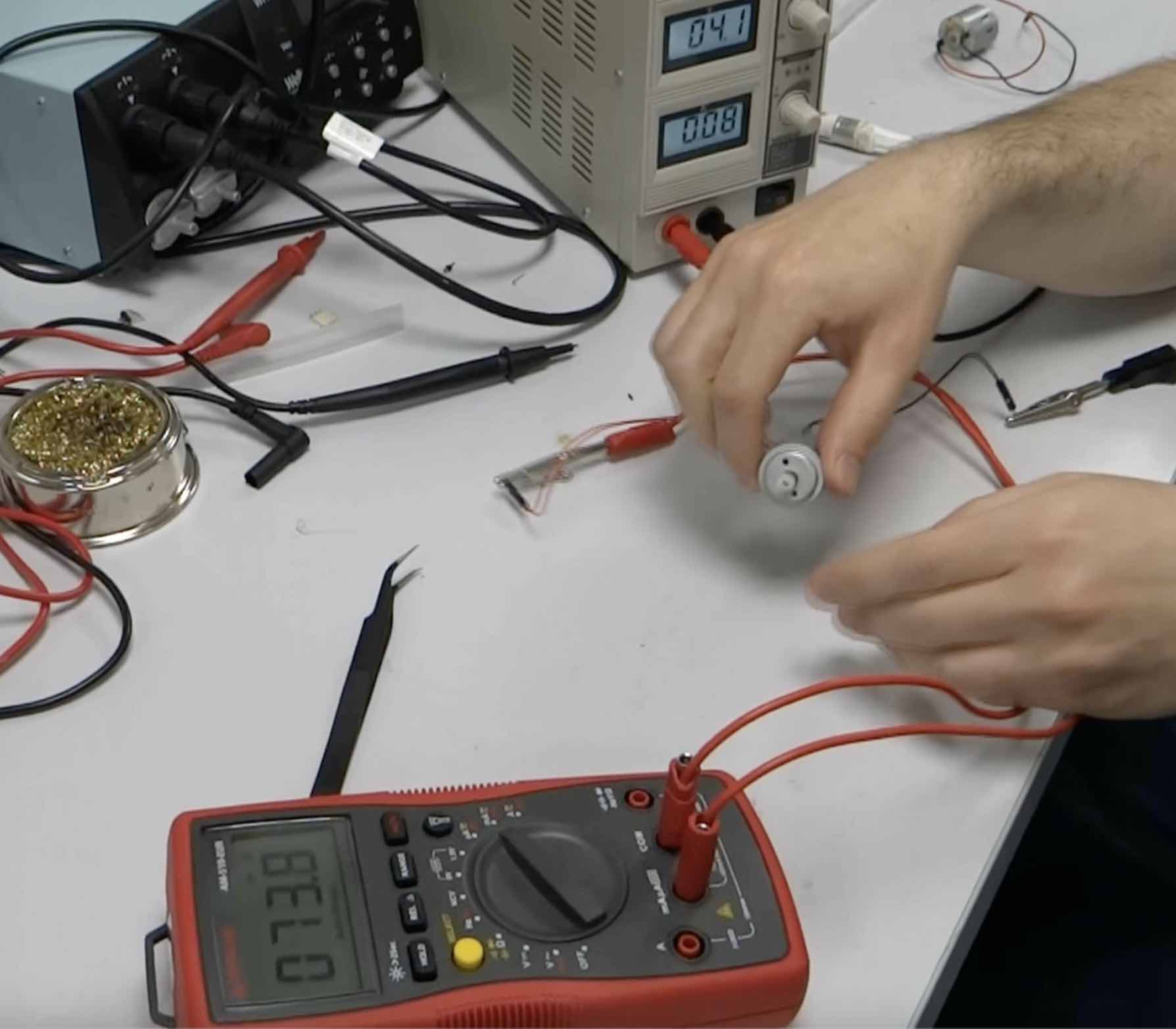

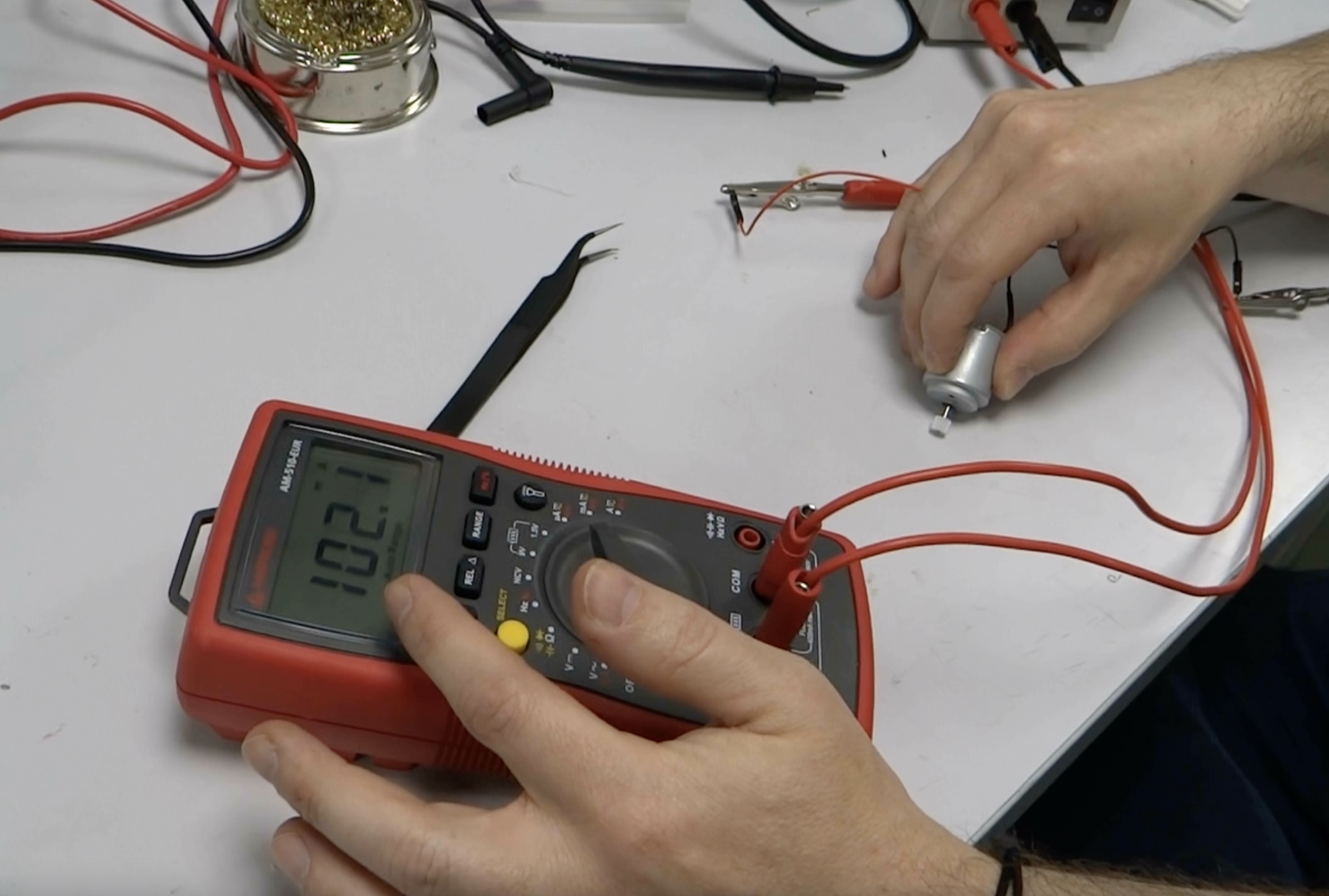
When we apply friction to the motor axis, the measured current elevates: more current is necessary to compensate the friction effort.

We can finally calculate the instant power with the formula P = U * I where U is the voltage and I the current:
- Without friction:
P = 4.1 * 0.074 = 0.3 W
- With moderate friction:
P = 4.1 * 0.102 = 0.42 W
To measure the power consumption in Wh or kWh, power must finally be multiplied by time, e.g. the duration you want your circuit to run.