18. Invention, intellectual property and income¶
This week I worked on defining my final project idea and started to getting used to the documentation process.
- Develop a plan for dissemination of your final project
- Prepare drafts of your summary slide (presentation.png, 1920x1080) and video clip (presentation.mp4, 1080p HTML5, < ~minute, < ~10 MB) and put them in your root directory
Individual assignment¶
Dissemination plan for your final project¶
- The following activities were considered appropriate:
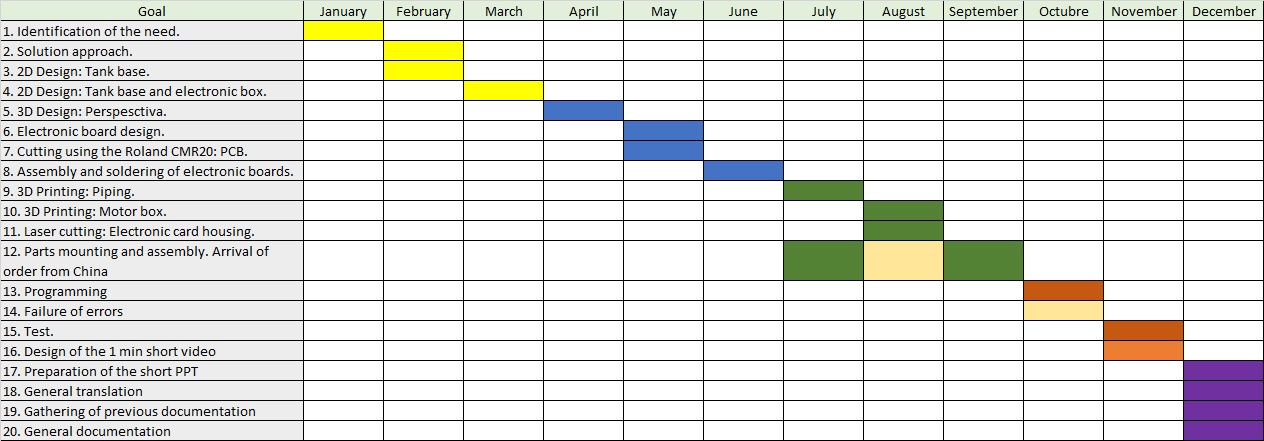
1. Identification of the need.
2. Solution approach.
3. 2D Design: Tank base.
4. 2D Design: Tank base and electronic box.
5. 3D Design: Perspesctiva.
6. Electronic board design.
7. Cutting using the Roland CMR20: PCB.
8. Assembly and soldering of electronic boards.
9. 3D Printing: Piping.
10. 3D Printing: Motor box.
11. Laser cutting: Electronic card housing.
12. Parts mounting and assembly.
13. Programming
14. Failure of errors
15. Test.
16. Design of the 1 min short video
17. Preparation of the short PPT
18. General translation
19. Gathering of previous documentation
20. General documentation
Diagrama de Gantt¶
- A picture of the trend over time using the Gantt Chart that I prepared is as follows:
Prepare drafts of my summary slide¶
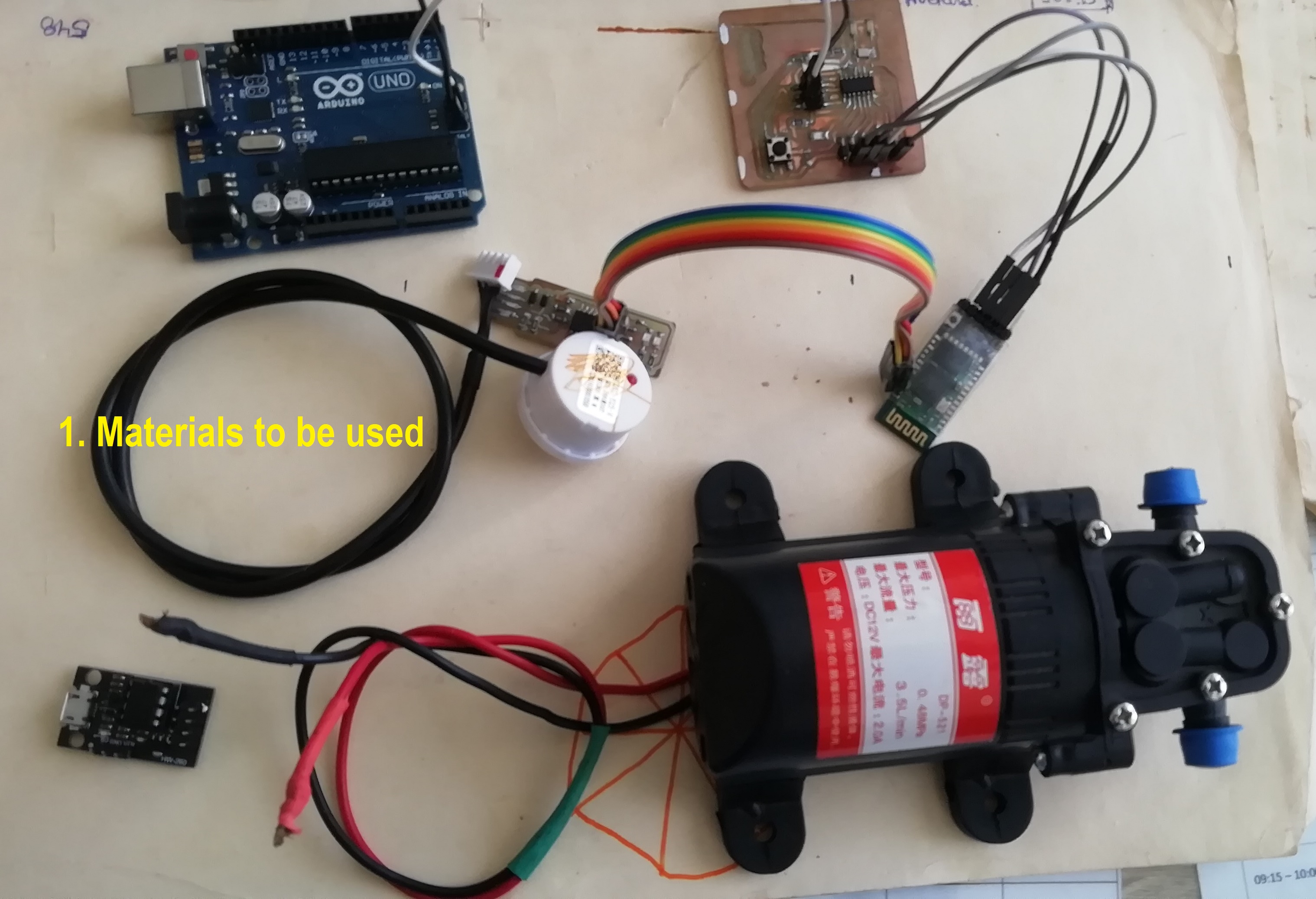
- Materials I will use that I cannot manufacture in FabLAB

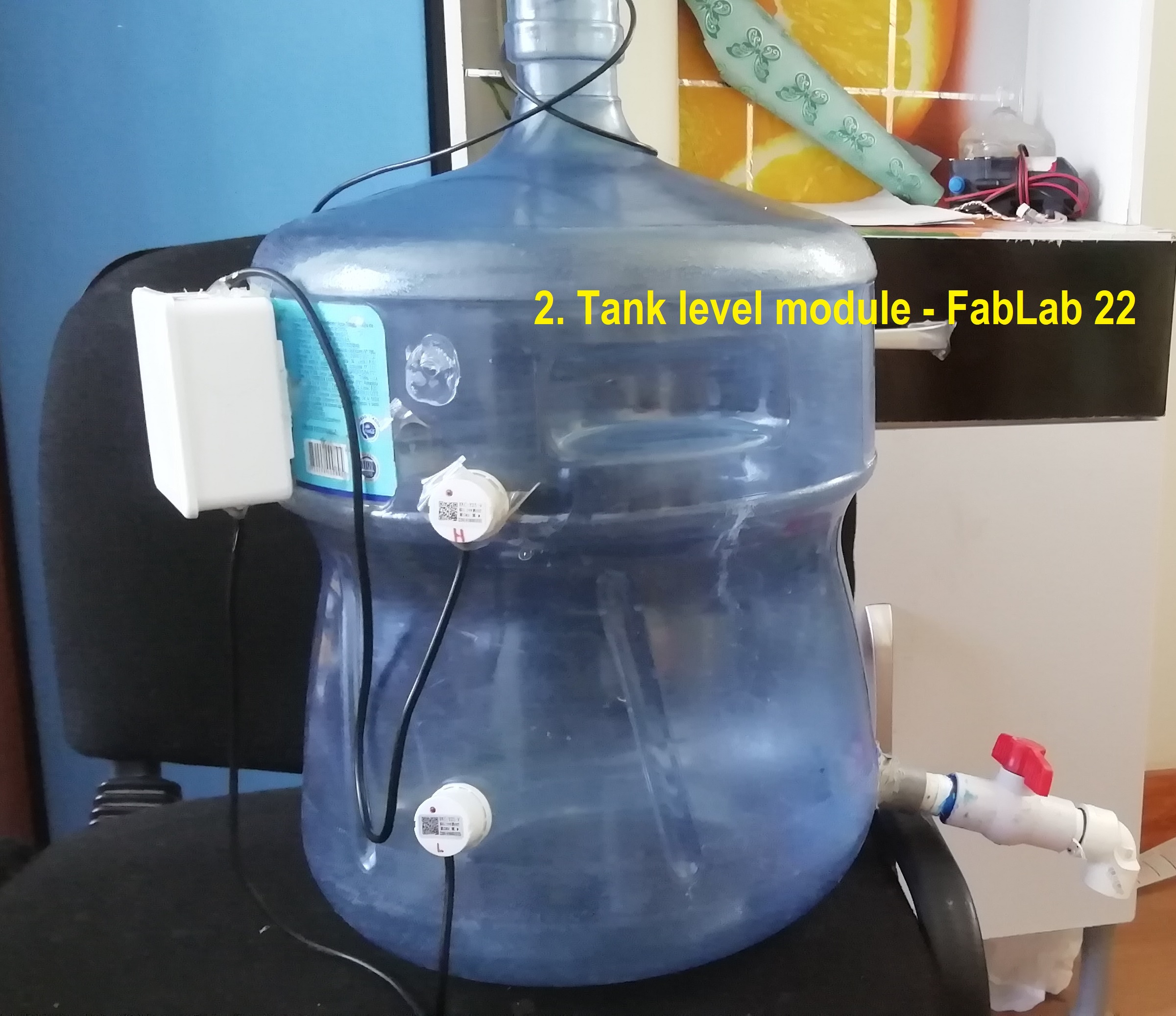
- Preliminary aspect before automation

- Digital project manufacturing cycle
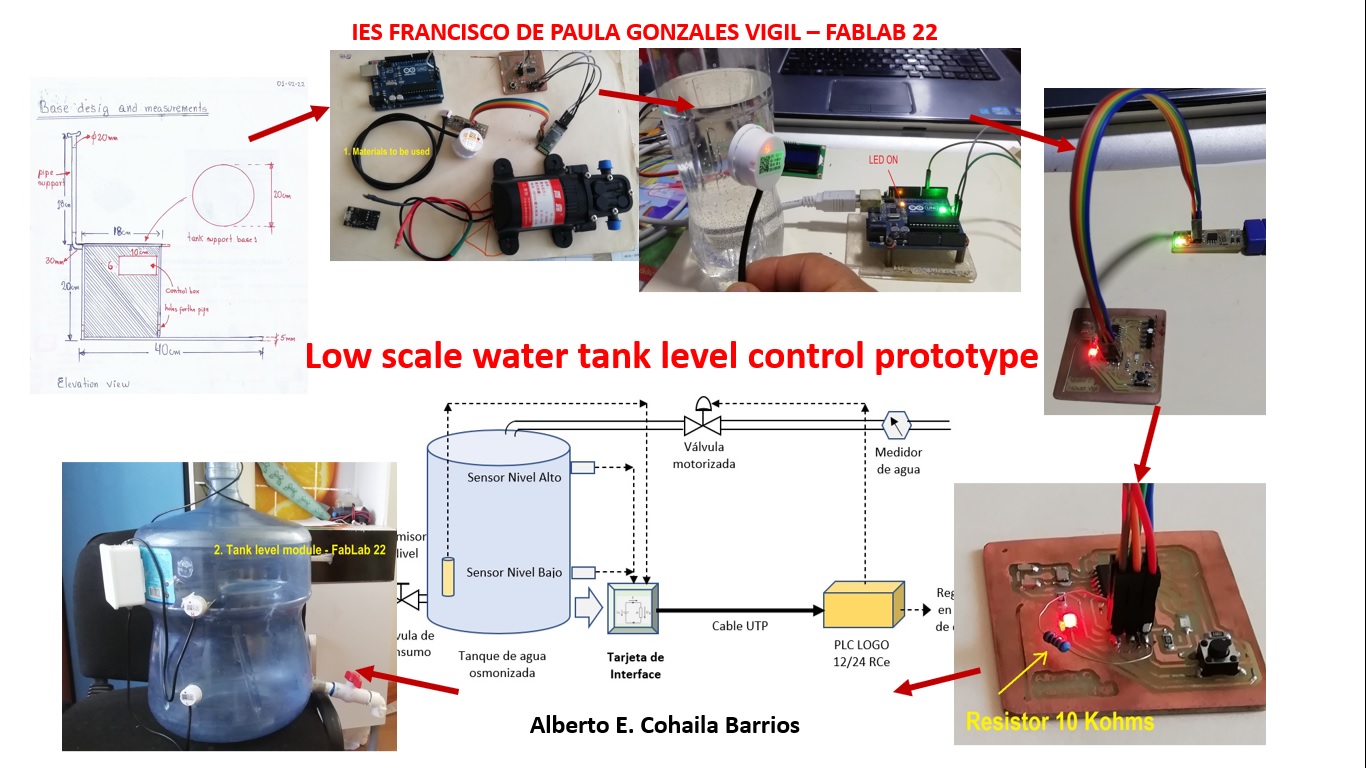
- You can see here a short video of the preview:
Intellectual property¶
It is the property right associated with any creation of the human mind that protects the rights of the authors of any work of a scientific, literary or artistic nature.
Free Licenses
They are licenses that defend a more free and shared use of works and grant authors the possibility of not exercising all the exploitation rights provided for in the intellectual property law: they can establish their own limits allowing authors to have greater control over rights to their works and easier management. In this way, they provide users with better access to the works and a use of them with fewer restrictions. At a general level, the most widely used free licenses currently for various creative works are the so-called Creative Commons licences.
Creative commons licenses
Creative Commons licenses allow authors to assign, under certain conditions, some of the rights to their works and keep another part of them.
Creative Commons
Each Creative Commons license details what rights the author gives up, under what conditions, and what users can do with the work, especially if they want to republish or modify it. There is no single license, but rather, at the will of the author, different combinations can be made. In all of them it is essential to acknowledge the authorship of the work.
Basic conditions
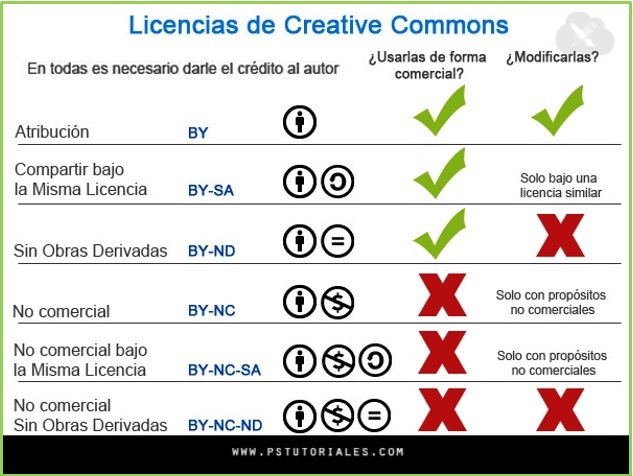
Four basic conditions are combined in the Creative Commons licenses: Attribution, Non-Commercial Use, No Derivatives, and Share Alike. • Attribution- Attribution (BY), by which the author allows others to copy, distribute and display his work (or works derived from it) as long as they cite his authorship. • Non-Commercial Use -Non Commercial (NC), the author limits the exploitation of the work to non-commercial uses, thus allowing others to copy, distribute and display his work (or works derived from it) without commercial purposes. • No Derivatives-No Derivatives (ND), allows the work to be reused, but not for the work to be modified, or for derivative works to be created from the original. The author allows others to copy, distribute and display his work as it was created, without modification. • Share Alike -Share Alike (SA), which allows reuse and modification of the work but includes the condition that the derivative works created are published under the same license. The author allows others to distribute derivative works of his work as long as they do so under a license equal to that of the original work.
CC License types
Combined the conditions can generate 6 different Creative Commons licenses:
- And click on Share your work.
Procedure for obtaining a license
In order to share my work, I go to the page Creative Commons

- And click on Share your work.
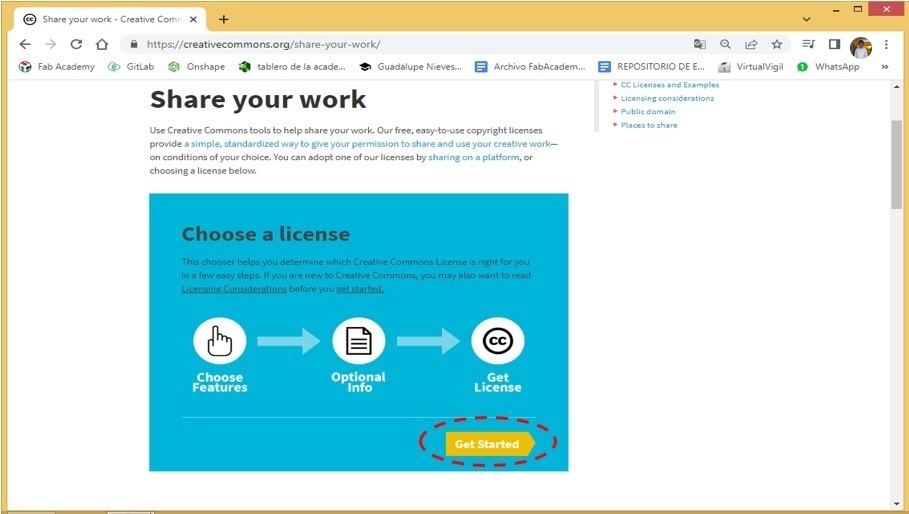
- Click Get Started.
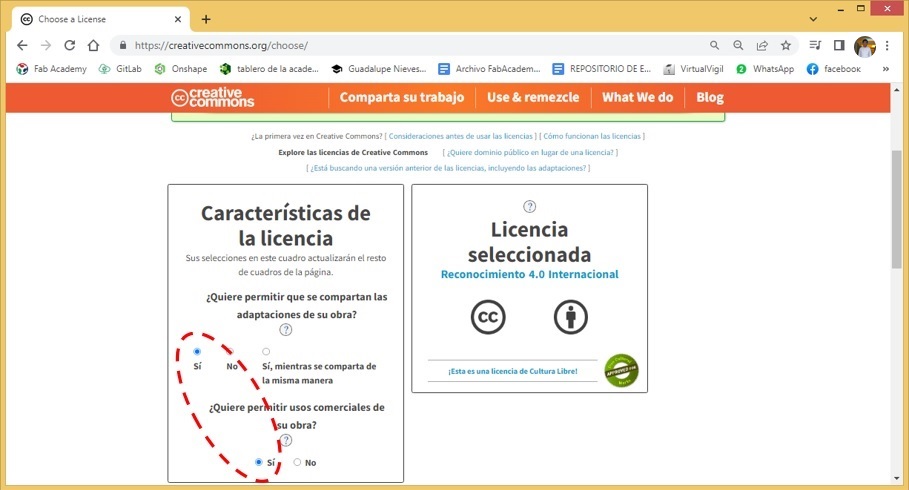
- We specify the characteristics of the license by simply activating the corresponding buttons. In my case, I want the adaptations of my work to be shared and I want their commercial use to be allowed.
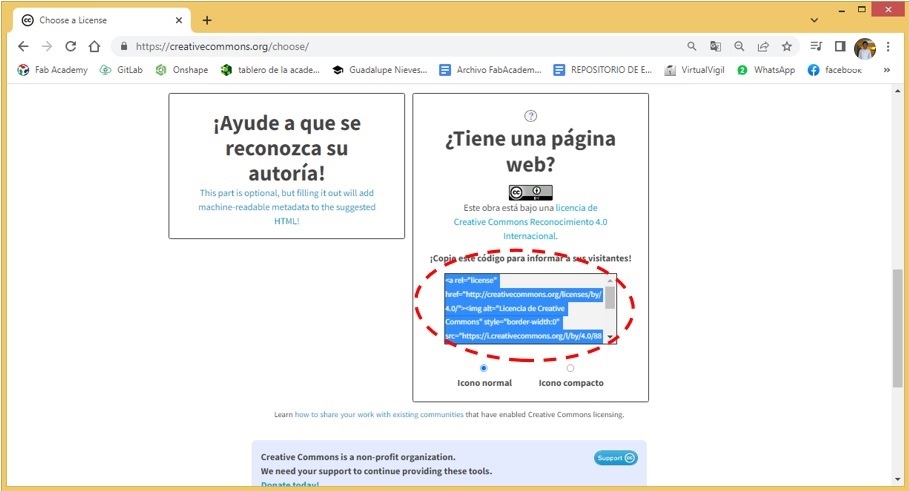
- Finally, the generated code must be copied and then pasted into the appropriate place on the FAB ACADEMY website.
Useful links¶

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.