Appearance
Week 14 - Molding and casting
Assignments
Group Assignment
- Rreview the safety data sheets for each of your molding and casting materials,then make and compare test casts with each of them compare mold making processes
Individual Assignment
- Design a mold around the process you'll be using,produce it with a smooth surface finish that does not show the production process toolpath,and use it to cast parts
- Extra credit: use more then two mold parts
Group Working
My group work is attached here: https://fabacademy.org/2025/labs/unnc/assignments/week14/week14.html
Individual Working
This week, I experimented with two mold-making methods: one using silicone to create molds, and the other using CNC machining to produce steel molds.
Silicone mold production
Keychain Modeling
I first completed the 3D modeling of the keychain using Fusion 360. The design features a simple geometric outline, with a reserved hole for attaching a strap.
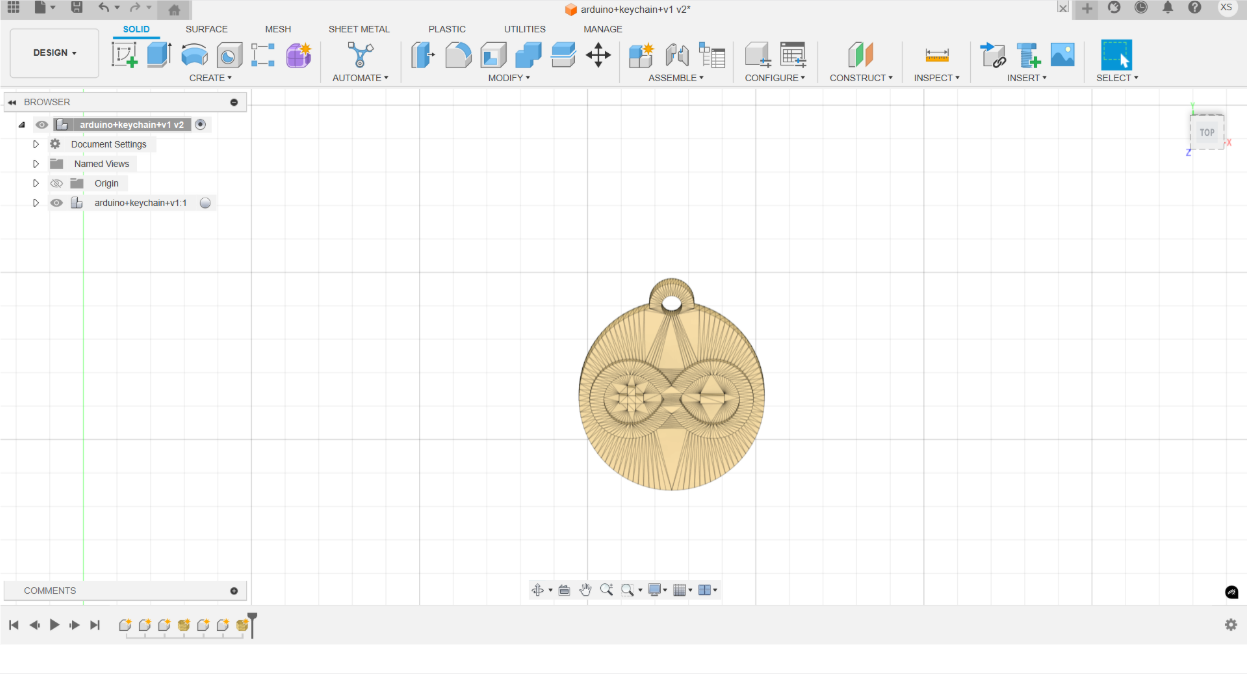
3D Printing
Once the design was finalized, I printed the keychain model using a 3D printer. The resulting object had a good surface finish and clearly defined details. 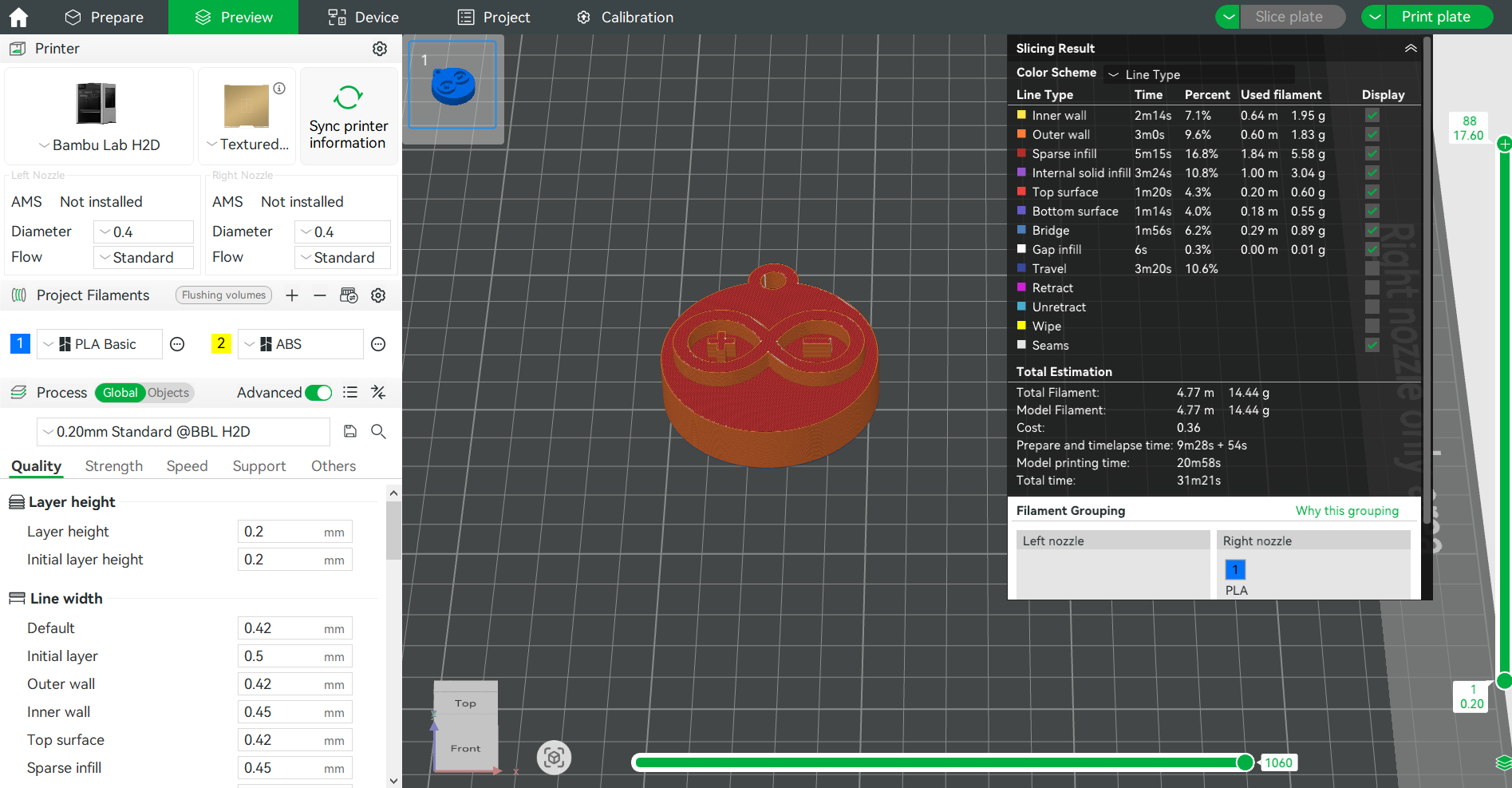
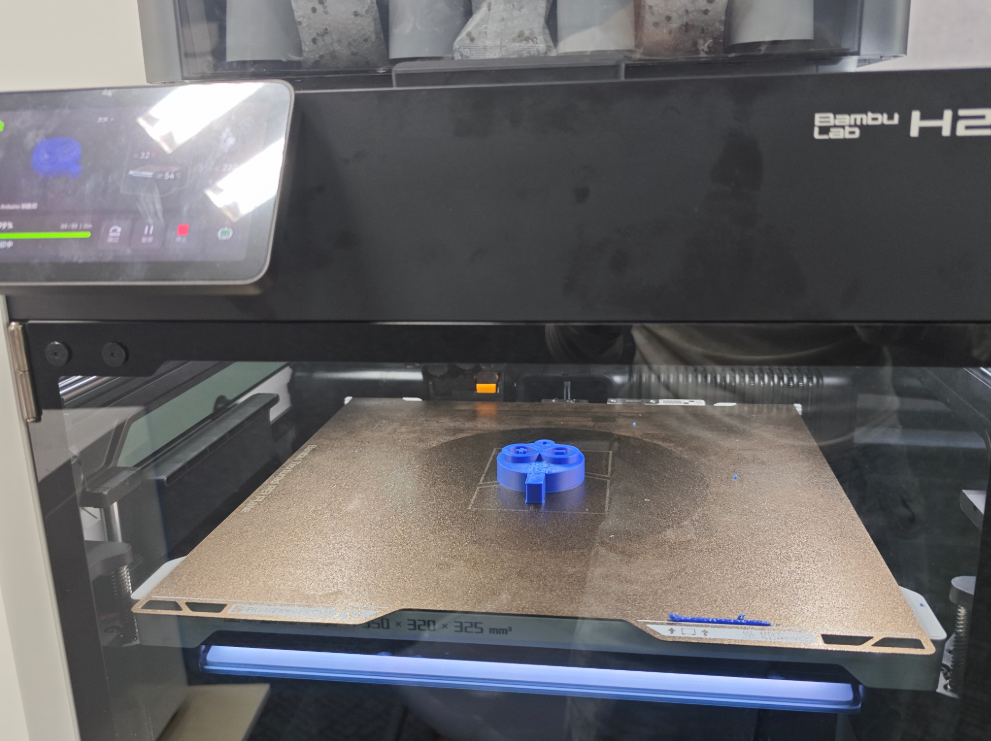
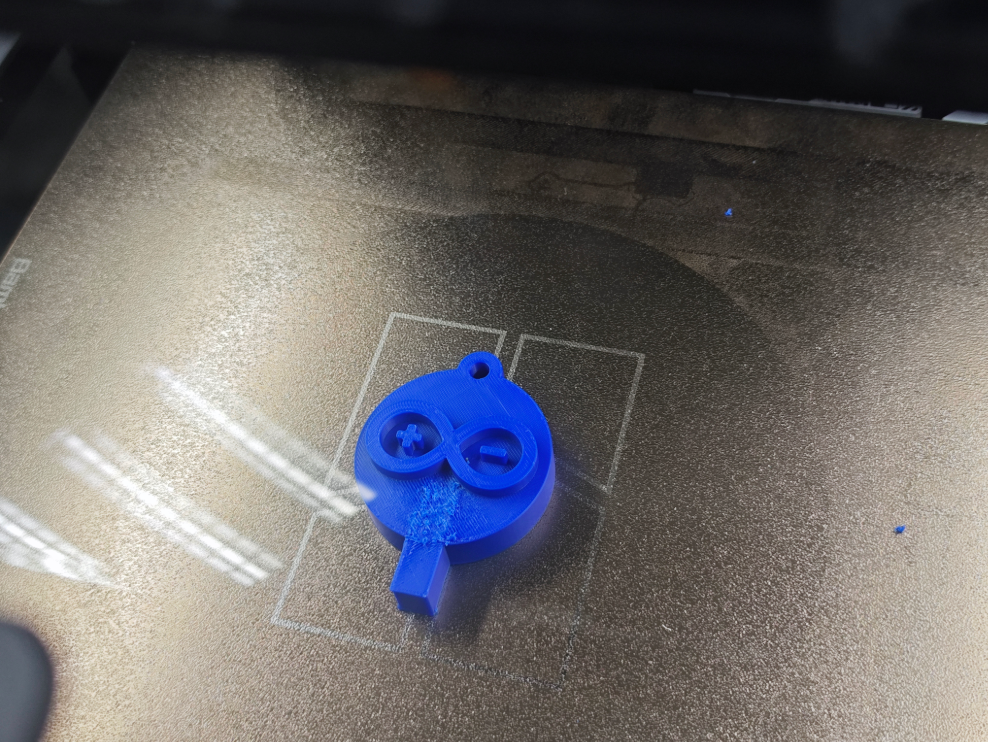
Testing 8015AB
I planned to use 8015AB (a silicone surface treatment agent) to improve surface adhesion before coating or printing.

Mixing Test:
- Mixed 8015A and 8015B in a 1:1 ratio.
- Stirred evenly and observed the surface reaction and film-forming properties.
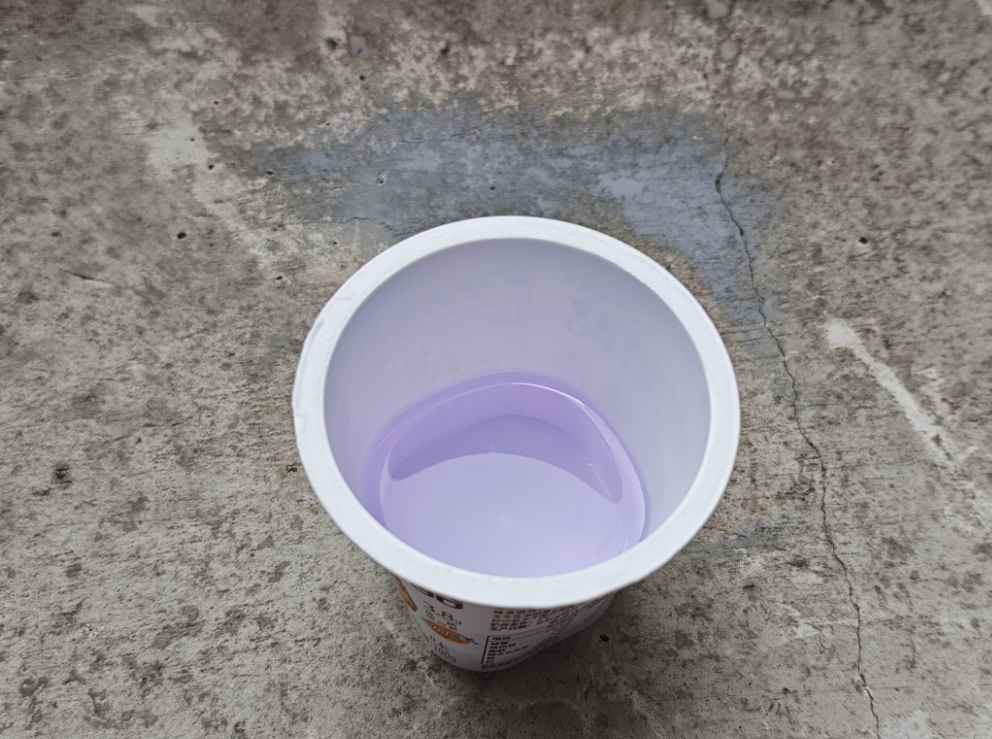
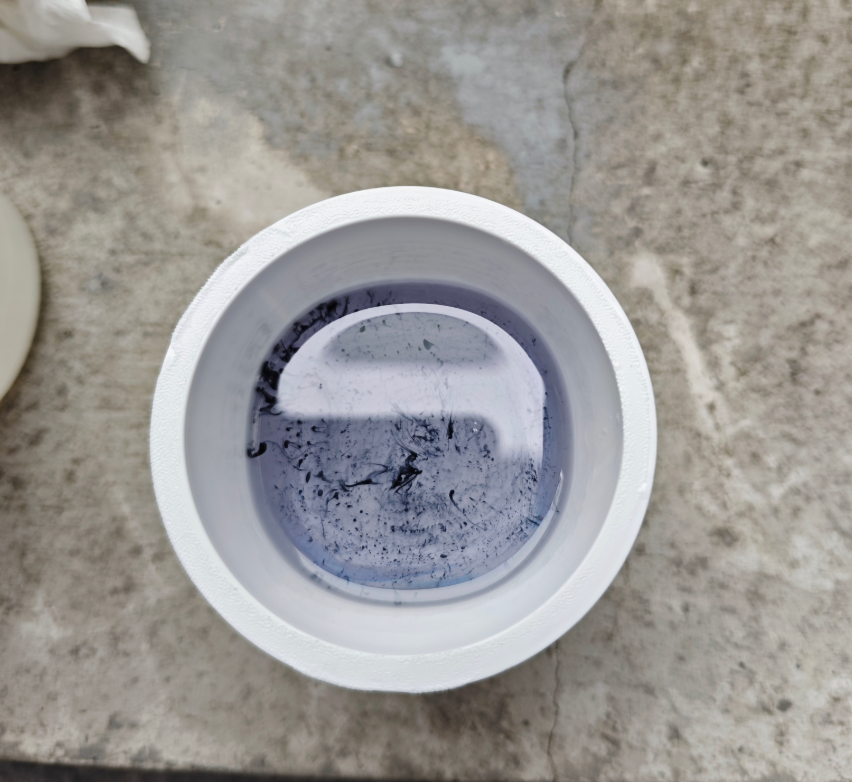
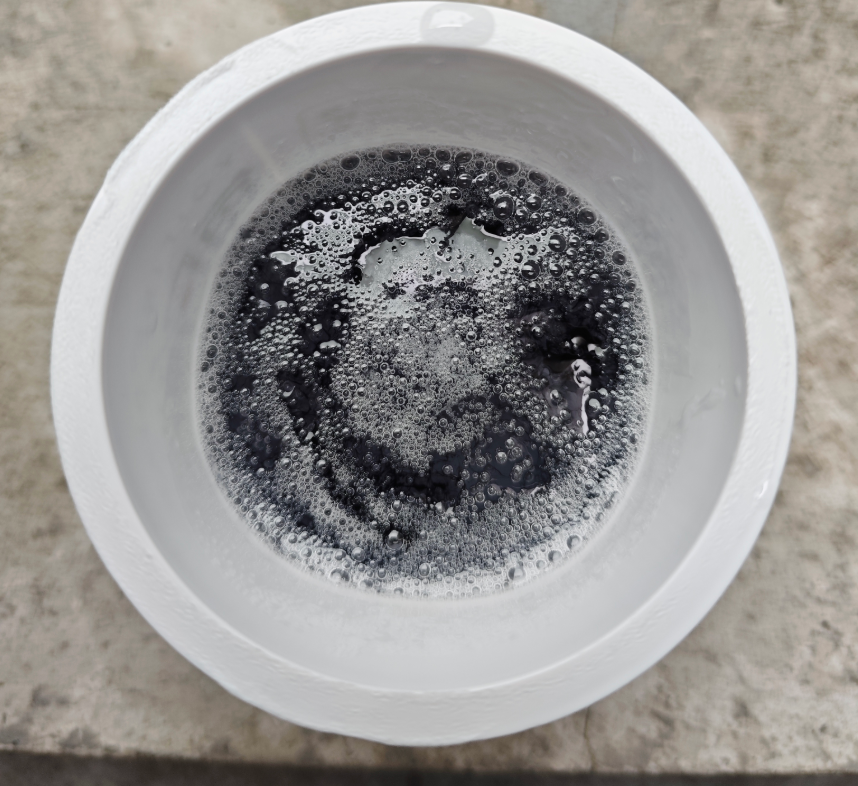



- After the AB resin was fully cured and demolded, a large number of bubbles were present on the surface.

- To improve the final finish and reduce air entrapment, I plan to use a vacuum pump for degassing in future tests.
Experiment Issues:
Due to the lack of a precise electronic scale, the mix ratio was inaccurate. As a result, the mixture failed to solidify or form a proper film — the surface remained sticky, indicating a significant deviation from the optimal AB ratio.
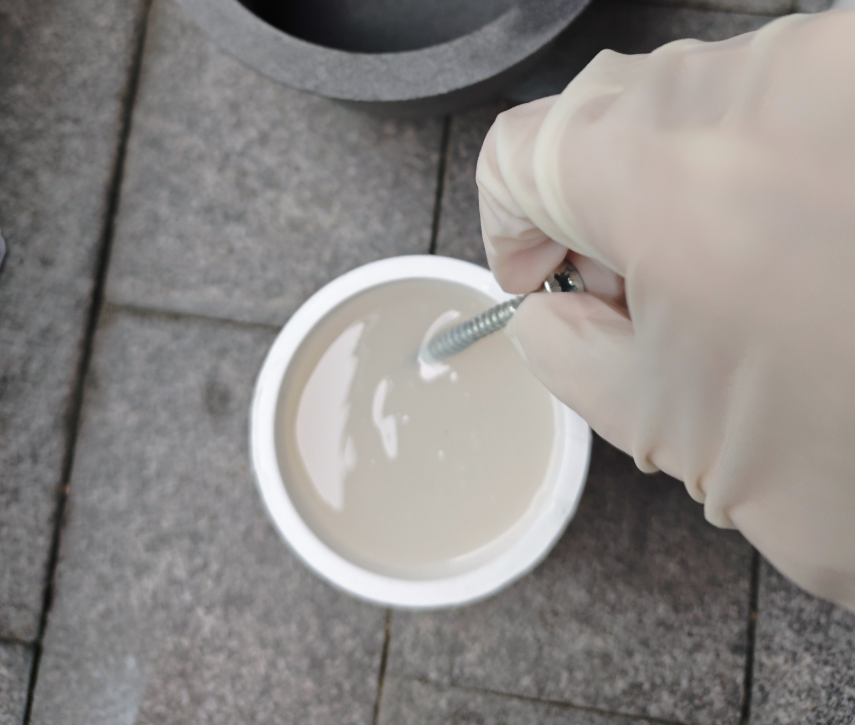

Silicone mold making
To further process the keychain, I attempted to make a negative mold using silicone, for replication or casting.
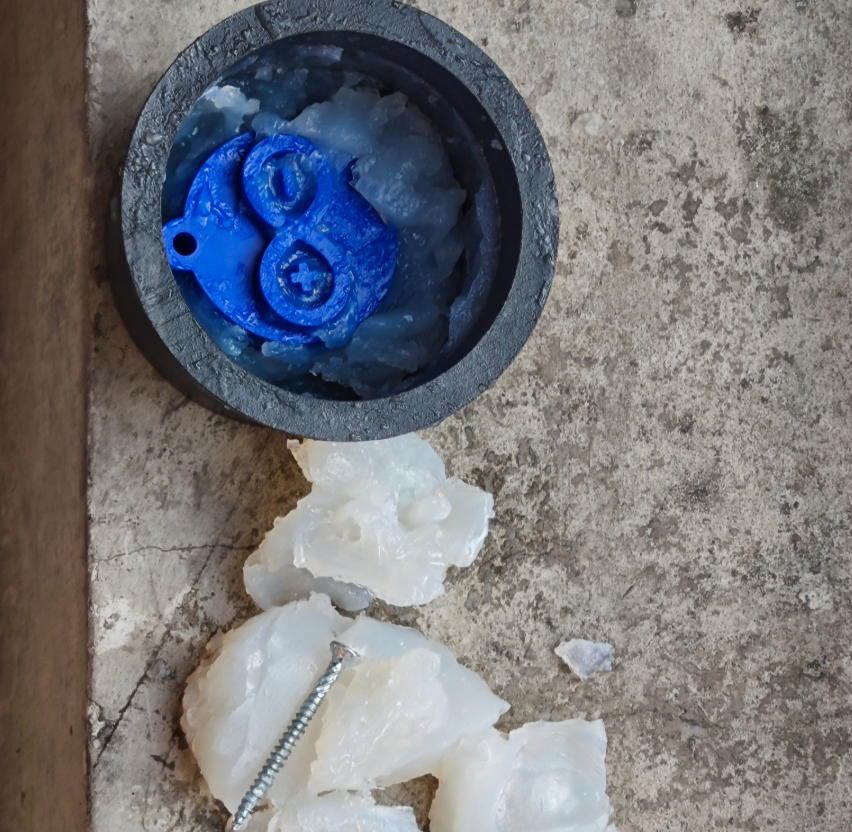

Reflection on failure
- The curing agent was insufficient, resulting in prolonged uncured silicone.
- Severe flow and bubble formation occurred.
- Lessons Learned:
- Always use a measuring cup or electronic scale to ensure accurate proportions.
- Enhance defoaming steps during silicone preparation.
I experimented with a new process that combines 3D printing technology with hot press molding to fabricate a composite material of polycarbonate (PC) and high-temperature carbon fiber.
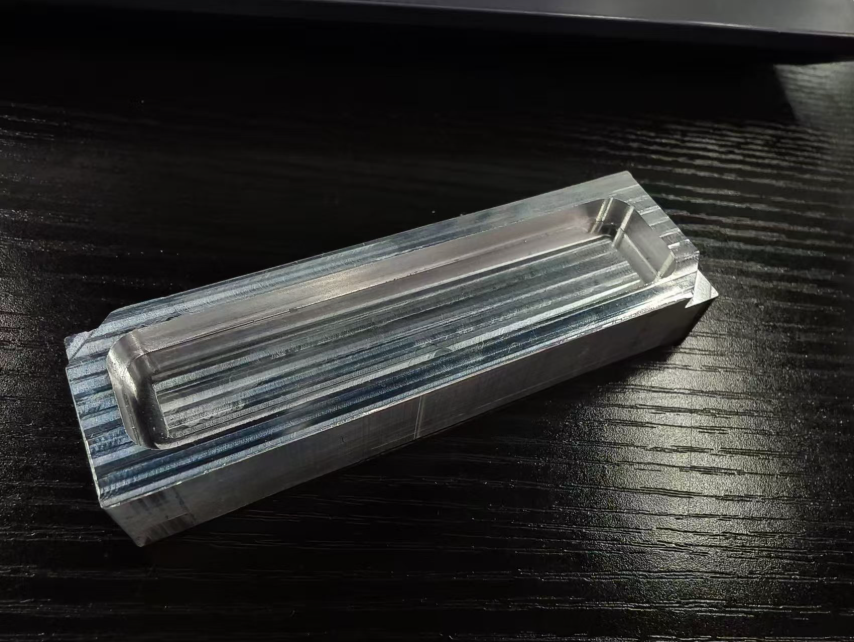
Metal mold
Material Introduction
Polycarbonate (PC) is a colorless, transparent thermoplastic engineering plastic known for its high impact strength, excellent heat resistance, and good molding processability. Its glass transition temperature is approximately 147°C, with a melting point between 220–230°C, making it suitable for secondary processing via hot press molding.
High-temperature-resistant carbon fiber (24K) is a high-strength carbon fiber bundle with outstanding mechanical properties and heat resistance, widely used in reinforced composite materials.
Experimental Steps:
- Mould processing
The processing results are as follows:

- PC Sheet Preparation
First, FDM 3D printing technology was used to print two flat PC sheets.
- Model slicing and uploading:
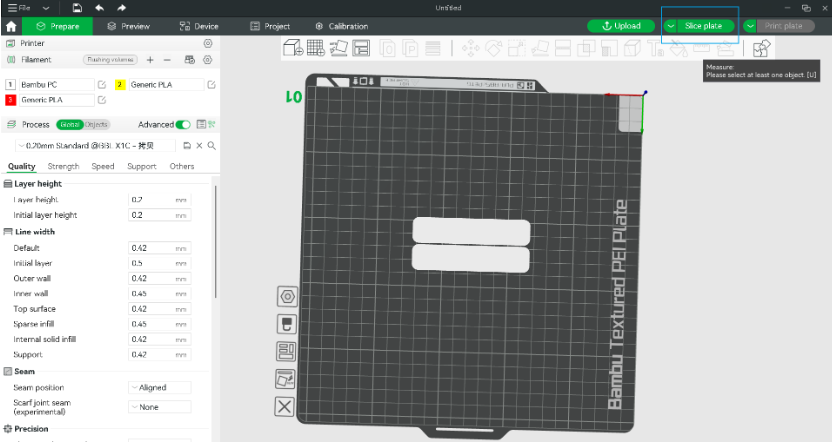
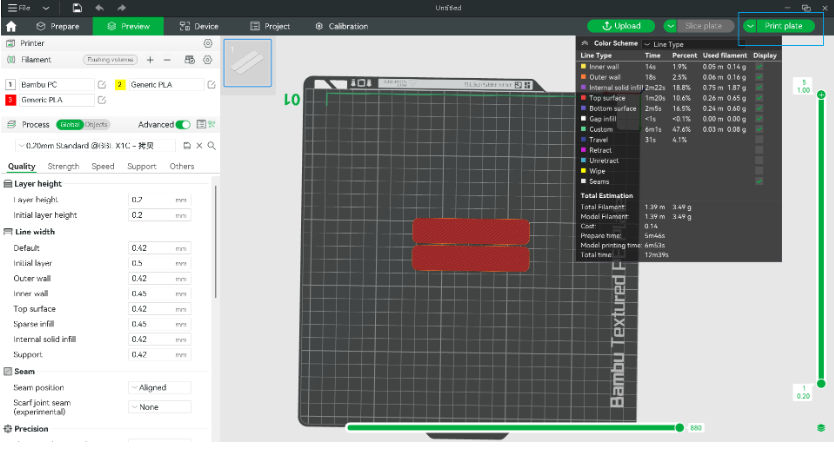
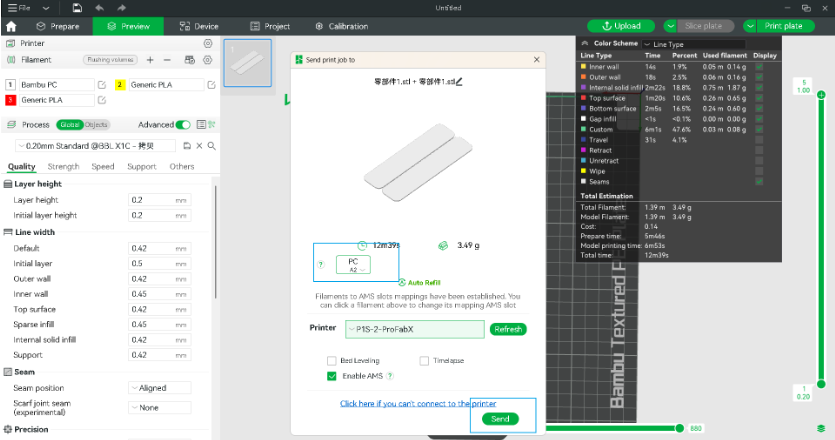
- After printing, uniformly thick and smooth PC sheets were obtained:
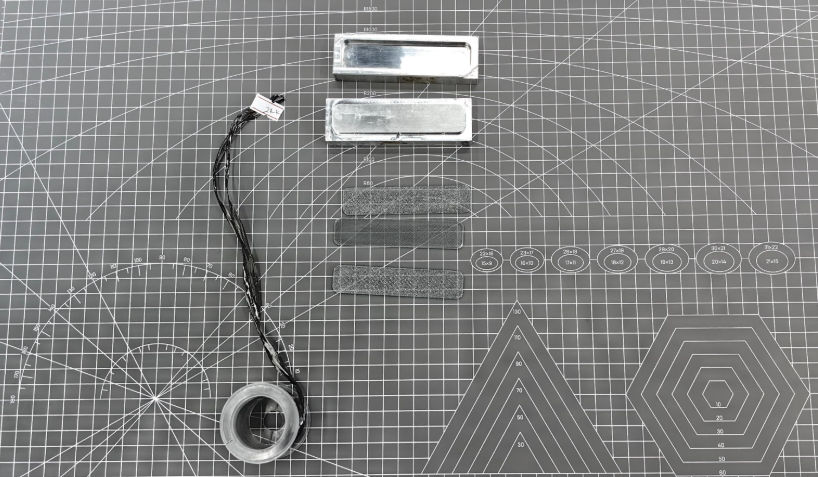
 2. Material Preparation
2. Material Preparation
The required materials included molds, PC sheets, carbon fiber, and clamps:
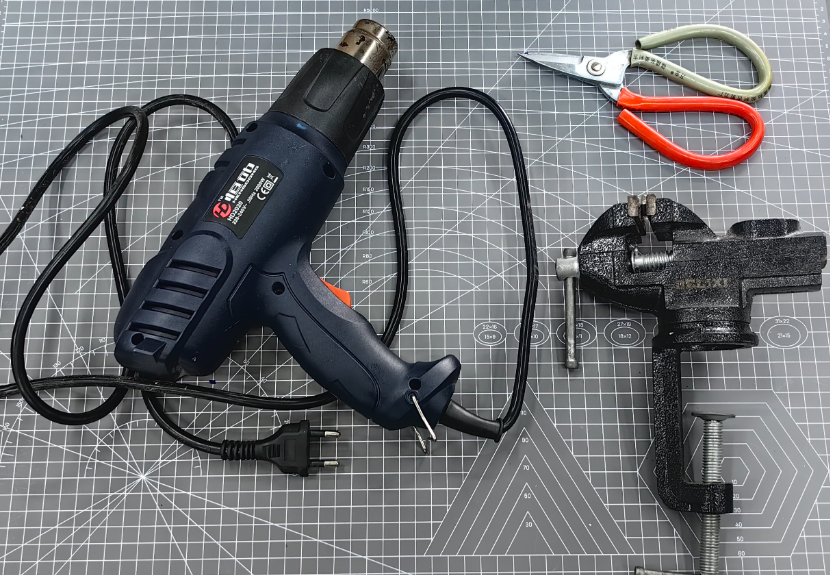
 3. Hot Press Molding
3. Hot Press Molding
The carbon fiber was evenly arranged between the two PC sheets to form a "sandwich structure." The assembly was then placed into the mold and secured with clamps to ensure tight bonding during heating. A heat gun was used to heat the mold for 3–5 minutes, allowing the PC material to fully soften and fuse with the carbon fiber:
- Cooling and Demolding
After heating for 3–5 minutes, molten material was observed overflowing from the mold surface, indicating that the PC had reached a softened state and begun to flow:

- After cooling for a period, the mold was disassembled, revealing the fully formed material:
- Comparison between finished product and PC material after processing:
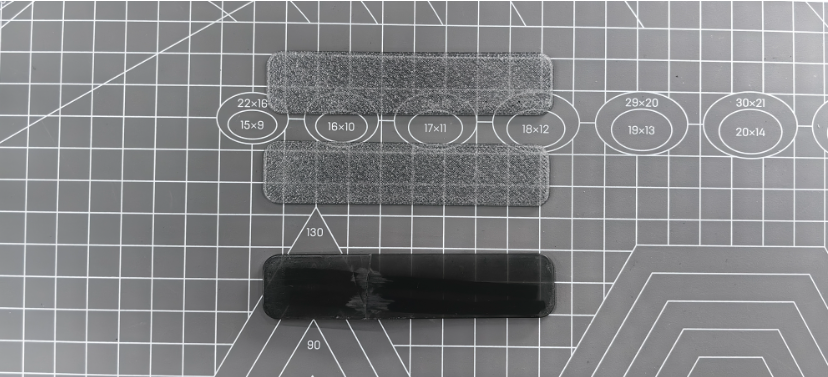 It can be observed that the originally opaque material became transparent after processing, with significantly improved hardness and no internal bubbles.
It can be observed that the originally opaque material became transparent after processing, with significantly improved hardness and no internal bubbles.
Reference:
The reference and design files are listed below:
The .3mf file for Keychain Modeling can be found in my repository:https://gitlab.fabcloud.org/academany/fabacademy/2025/labs/unnc/students/xu-sun/-/blob/main/docs/assignments/week14/resource-week14/week14-arduinokeychain.f3d?ref_type=heads
Metal mold's .stp files can be found in my repository:https://gitlab.fabcloud.org/academany/fabacademy/2025/labs/unnc/students/xu-sun/-/blob/main/docs/assignments/week14/resource-week14/mould.stp?ref_type=heads