In the realm of mechanical design, a deep understanding of stress-strain principles and material behavior is fundamental. Engineers leverage these principles to ensure that structures and components can withstand anticipated loads while maintaining desired performance criteria. Materials ranging from plastics and metals to rubbers and woods offer a diverse palette for designers to select from, each with its unique properties and suitability for specific applications. Adhesives and fasteners, including nuts, bolts, and washers, serve as the backbone of assembly, providing robust connections that withstand mechanical stresses and environmental conditions.
Drive mechanisms play a pivotal role in transferring motion and power within mechanical systems, with gears, belts, and chains offering efficient means of transmitting torque and facilitating precise movement. Meanwhile, guide components such as shafts and rails ensure smooth and accurate motion, contributing to the overall performance and reliability of the system. Couplers and bearings facilitate the connection and rotation of mechanical components, ensuring smooth operation and minimizing frictional losses. These foundational elements form the basis for the intricate and innovative designs that shape our mechanical world.
Machine design encompasses a broad array of components and systems, from individual mechanisms to complex structures and modules. Engineers meticulously analyze structural loops and error budgets, ensuring that designs meet stringent specifications while optimizing performance and reliability. Sensors and actuators play a crucial role in capturing and controlling motion, while end effectors enable machines to interact with their environment effectively. Power electronics and real-time networks provide the backbone for machine control, facilitating precise motion control and coordination of multiple subsystems.
In the realm of motion control, engineers employ a variety of techniques, including open-loop and closed-loop systems, and draw from control theory principles such as bang-bang, PID, and model predictive control. Timing mechanisms such as broadcast and time-stamp protocols ensure synchronization and coordination among distributed components. Machine control interfaces, path planning algorithms, and design representation tools aid in translating conceptual designs into functional machines. With a plethora of vendors, platforms, and file formats available, engineers have a rich ecosystem of resources to draw from, enabling them to bring their designs to life efficiently and effectively.
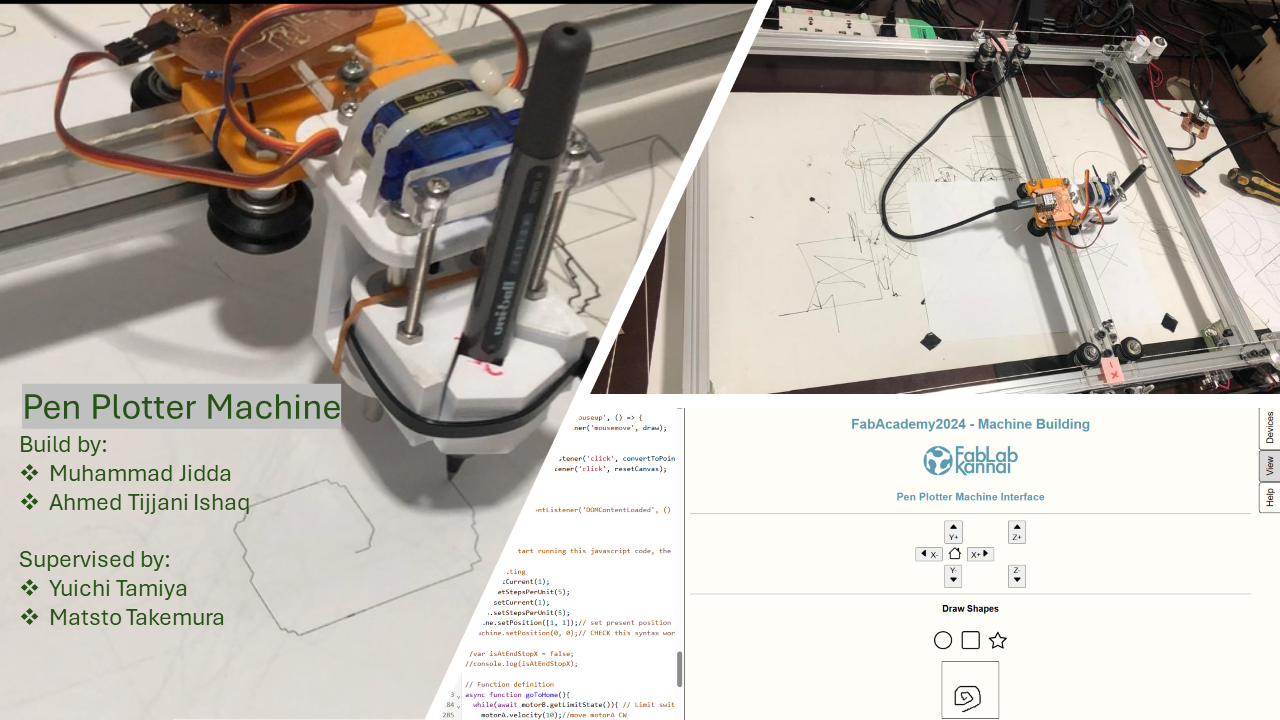
This week's assignment is about understanding how to design and build machine
For details on this assignment head to our Group assignment page
A complete detail on how we built, operate and automate our machine can be found on our group assignment page
I worked with Muhammed Jidda on this assignment. We assembled the machine and produced the control board which is well documented by Jidda's on his individual assignment page.
I am responsible for building the web interface using modular-things to automate the machine.
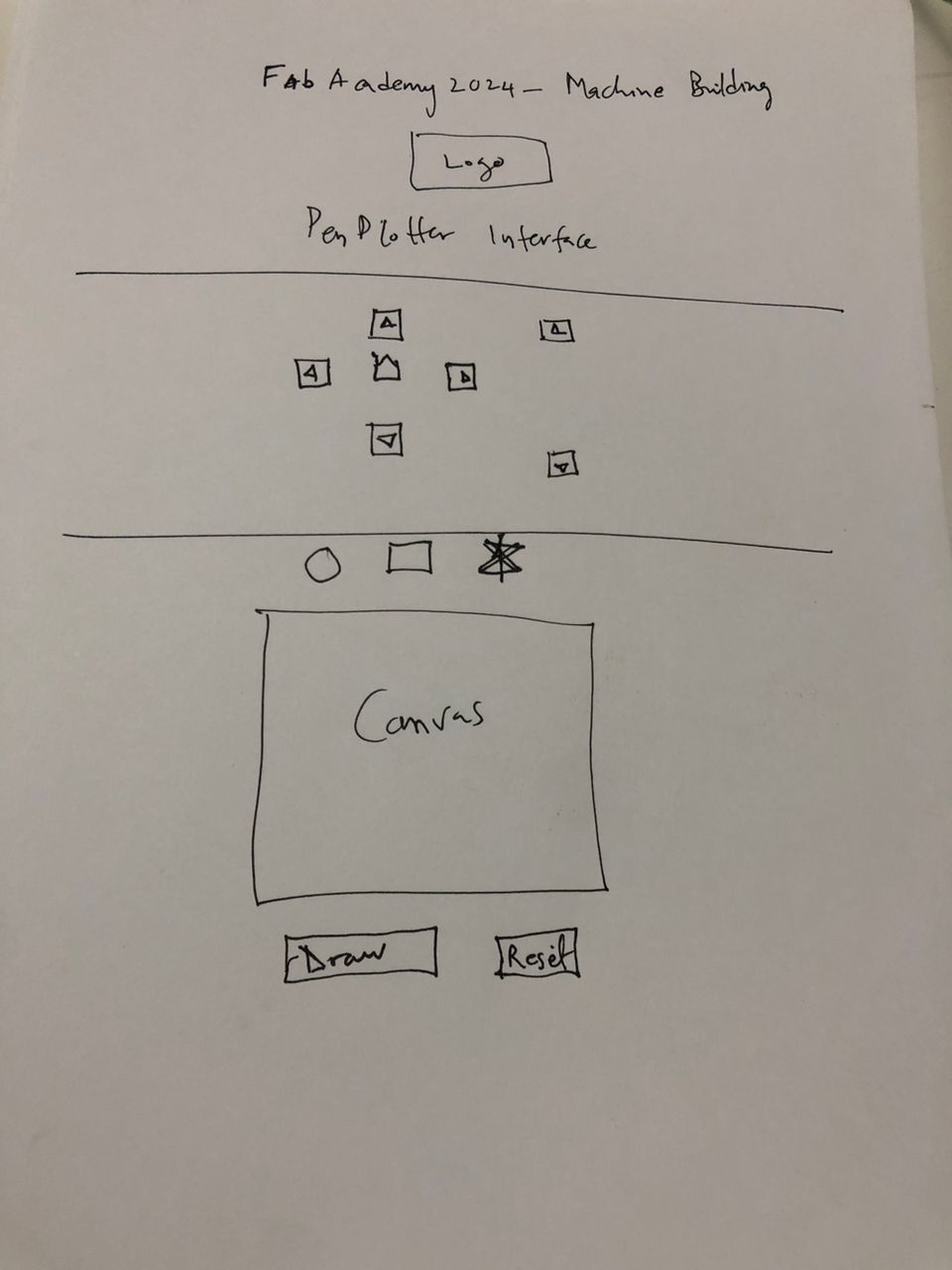
The machine is a CoreXY based pen plotter that works with a canvas so that anything that is drawn on the canvas can be plotted by the machine. Another feature added is the ability to draw shapes like circle, square and star easily by clicking on the shape.