Week 17. INVENTION, INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND INCOME

Intellectual property meaning and Tpes of IP
Intellectual property (IP) refers to legal rights that protect creations of the human mind
They usually give the creator an exclusive right over the use of his/her creation for a certain period of time
The following are common types of IP
Certainly! Here's a table outlining the types of intellectual property:| Type of Intellectual Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Copyright | Protects original works of authorship, such as literary, artistic, musical, and dramatic works. |
| Trademark | Protects brand names, logos, slogans, and other marks that distinguish goods or services. |
| Patent | Grants exclusive rights to inventors for their inventions, covering processes, machines, and compositions of matter. |
| Trade Secret | Protects confidential business information, such as formulas, customer lists, and marketing strategies. |
| Industrial Design | Protects the visual appearance and aesthetic aspects of a product. |
| Plant Variety Protection | Grants exclusive rights to breeders of new plant varieties. |
| Geographical Indication | Identifies products originating from a specific geographic region with certain qualities or reputation. |
invention
An invention is a novel and non-obvious creation or discovery that introduces a new process, product, composition of matter, or improvement to an existing process, product, or technology. It involves the development of a new and useful solution to a technical problem.
Inventions can be tangible, such as a new machine or device, or intangible, such as a new software algorithm or business method. They often involve a unique combination of ideas, concepts, or technologies to provide a solution or innovation.
To be considered an invention, the creation must meet certain criteria. It should be:
- Novelty: The invention must be new and not previously known or publicly disclosed anywhere in the world before the filing of a patent application.
- Inventive Step: The invention must involve an inventive or non-obvious step, meaning that it should not be an obvious solution to someone skilled in the relevant field.
- Industrial Applicability: The invention should have a practical use and be capable of being produced or used in an industry or commercial setting.
Inventions can have a significant impact on society and contribute to advancements in various fields, including technology, medicine, agriculture, and manufacturing. Patents are commonly used to protect and provide exclusive rights to inventors, enabling them to prevent others from making, using, selling, or importing their invention without permission for a limited period.
Types of Licenses and Grants of Rights for Software and Hardware
Software Licenses:
- End-User License Agreement (EULA): This license grants the end-user the right to use the software within the defined terms and conditions. users should adhere to this before use of my software
Hardware Licenses:
- Intellectual Property (IP) Licenses: project involves proprietary hardware components, so i need to secure licenses for any patented technology or designs incorporated into hardware.
Grants of Rights:
- User Access Rights: Define the rights granted to users of the access control system, including their ability to enter facilities, manage access permissions, and utilize system features.
- System Administration Rights: Grant system administrators the necessary rights to manage and configure the access control system, including user management, access rules, and system settings.
- Data Usage Rights: Specify the rights granted to the access control system provider regarding the collection, processing, and storage of user and system data.
LICENCE OF MY PROJECT
I choose to use open source licence . so my software and related hardware fall under MIT LICENCE on my project. Basically, you can do whatever you want with software licensed under the MIT license, as long as you add a copy of the original MIT license and copyright notice to it.
Busimess model learn convas
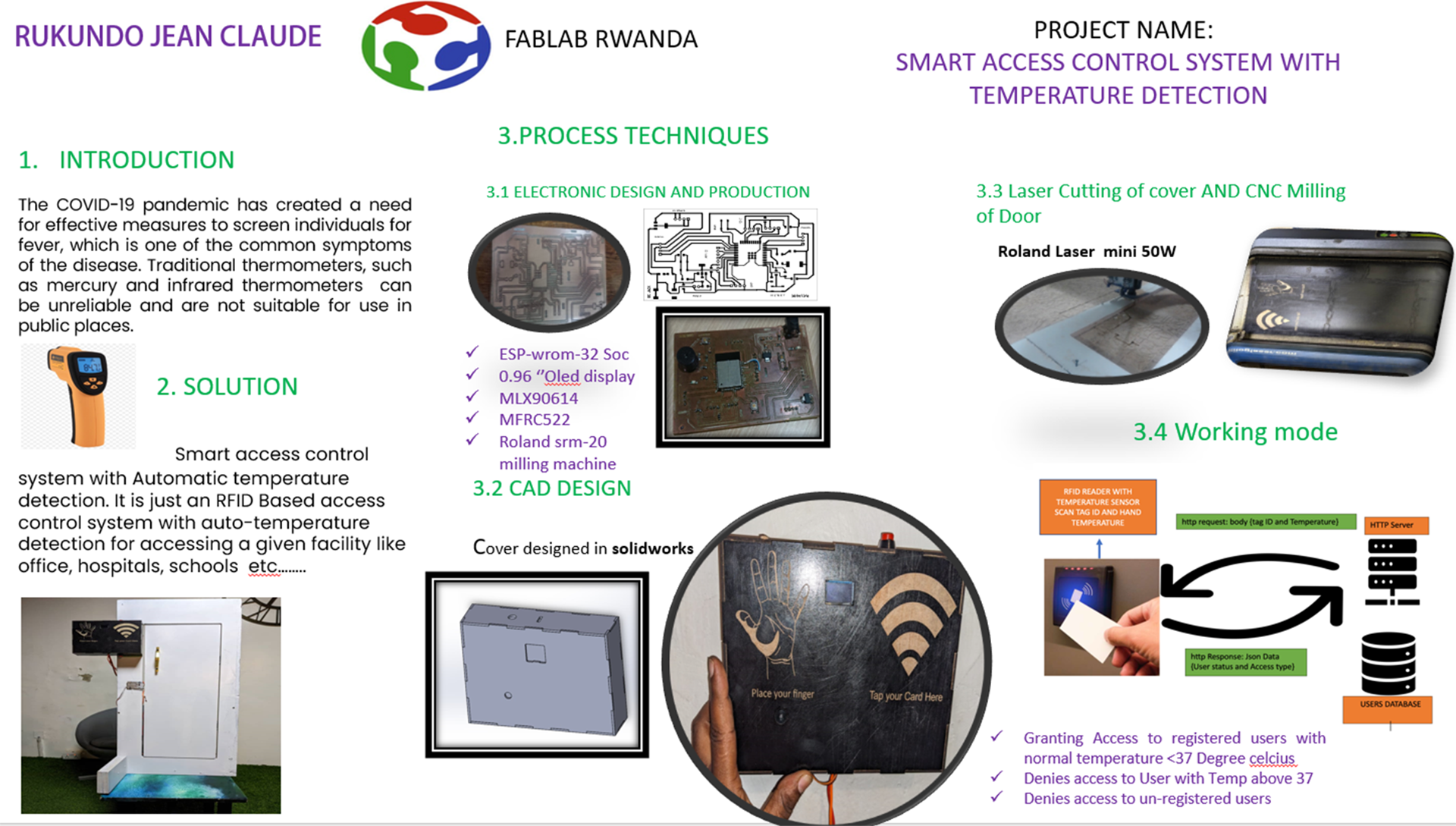
Project Name: Access Control System with RFID and Automatic Temperature Control
PROBLEM
- Limited access control measures and manual temperature monitoring in facilities
- Inefficient and time-consuming manual verification of users' access permissions
- Risk of unauthorized entry and potential health risks due to improper temperature control
CUSTOMER SEGMENTS
Offices, corporate buildings, educational institutions, healthcare facilities, event venues, etc.
UNIQUE VALUE PROPOSITION
- Integrated access control system with RFID technology for secure and efficient entry
- Automatic temperature control to ensure compliance with health and safety regulations
- Streamlined user verification process for seamless access management
SOLUTION
- RFID-based access control system integrated with temperature monitoring sensors
- User-friendly interface for administrators and users to manage access permissions
- Real-time temperature monitoring and automated control mechanisms
KEY METRICS
- Number of facilities using the access control system
- User satisfaction and feedback on ease of use and system reliability
- Reduction in unauthorized access incidents and improved security
- Compliance with health and safety regulations
CHANNELS
- Direct sales to facility owners and administrators
- Partnerships with security system integrators and access control vendors
- Online marketing and demonstrations through a dedicated website or social media
COST STRUCTURE
- Hardware costs for RFID readers, temperature sensors, and control devices
- Software development and maintenance
- Marketing and promotional expenses
- Support and customer service
REVENUE STREAMS
- Upfront sales revenue from hardware and software packages
- Recurring revenue from service contracts and maintenance fees
- Potential revenue from additional features, customization, and integration services
UNFAIR ADVANTAGE
- Strong expertise and experience in access control systems and IoT technology
- Patents or proprietary technology related to the integration of RFID and temperature control
- Strategic partnerships with key players in the security and access control industry
Dissemination Plan: Access Control System with RFID and Automatic Temperature Control
Target Audience
- Facility owners and administrators
- Security professionals
- Facility management companies
- Industry trade associations
Goals
- Generate awareness about the benefits of the access control system with RFID and automatic temperature control
- Showcase the innovative features and advantages of the system
- Build trust and credibility in the target audience
- Generate leads and potential customers
Dissemination Channels and Tactics
- Industry Events and Trade Shows:
- Participate in relevant industry events and trade shows to demonstrate the system and engage with potential customers.
- Set up an engaging booth with live demos, informational materials, and knowledgeable staff.
- Deliver presentations or participate in panel discussions to showcase the technology and its benefits.
- Online Presence:
- Create a dedicated website with detailed information about the access control system, its features, and case studies.
- Optimize the website for search engines to improve visibility.
- Utilize content marketing strategies such as blog posts, whitepapers, and videos to educate the audience about the system's benefits and industry trends.
- Engage with the audience through social media platforms, sharing relevant content and responding to inquiries.
- Collaborations and Partnerships:
- Establish strategic partnerships with security system integrators, access control vendors, and facility management companies.
- Jointly promote the system through co-marketing efforts, referrals, and bundled offerings.
- Leverage their existing customer base to expand reach and credibility.
- Case Studies and Success Stories:
- Create compelling case studies and success stories that highlight the positive impact of the access control system.
- Share these stories on the website, through industry publications, and in presentations to demonstrate real-world benefits and outcomes.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Number of leads generated through various channels
- Website traffic and engagement metrics (e.g., page views, time on site, conversion rate)
- Attendance and engagement at industry events and trade shows
- Number of partnerships and collaborations established
Budget
- Allocate a budget for participation in industry events, trade shows, and conferences
- Invest in online marketing efforts, including website development, content creation, and social media advertising
- Consider targeted advertising campaigns in relevant industry publications or online platforms
Project draft video and presentation
final video illustration
presentation banner