1. Principles and practices¶
The task assigned for this week consists of planning and sketching a possible final project and some characteristics and requirements to develop this idea.
Potential final project¶
The project consists in design a cart that allows to follow the collection process, to monitoring the route of work, so as the data to establish the relation between the quantity, the harvest zone, and the time used to each one. The data will be sent to a receiving device to keep track of the entire process in real times.
Sketch¶
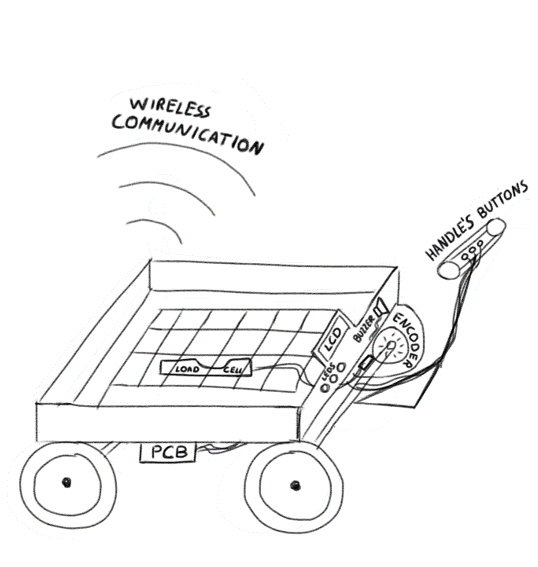
The idea¶
The proposed solution to solve the problem is a mechanism that facilitates the process of harvesting fruits to the worker, and simultaneously allows to relate the product collected with the specific area from where it was harvested. It allows to identify the mayor and least productive areas of the land. I will use this cart as a reference of my idea.

The cart will also have an integrated scale to keep tracking of the collected product weight in kg in each sector, last but not least (yet to be defined) it will use a positioning system based on an encoder or a GPS to be able to correctly map the worked area. This information will allow to know the production in each site so that you can solve some doubts such as: - Where is the less production?. - How many products did each worker collect?. (based on the weight) - How much time is spent collecting on each zone?.
Components¶
Next I will proceed to detail the necessary components for the elaboration of the cart.
Hardware / Mechanical pieces:¶
- Electronics housing made out of acrylic. (Computer-Controlled Cutting)
- Custom actuators and sensors housings. (3D Scanning and Printing)
- Cart made out of plywood. (Computer-Controlled Machining)
- Custom handle grip with buttons and leds compartments. (Molding and Casting)
Sensors (Input Devices):¶
- Load cell: Integrated in the cart to register the weight of the collected products.
- Tactile buttons: Counter to determine the number of points harvested.
- Optical encoder: Allowing to keep track of the distance traveled.
Actuators (Output Devices):¶
- LCD screen: Necessary to show all the information collected.
- Leds: Visual indicator of task progress.
- Buzzer: Alarm for maximum weight reached or waypoint completed.
Control board (Electronics Production):¶
- Design of a board with all the inputs and outputs necessary to control the functions of the cart.
Extras:¶
- Wireless communication. (Networking and Communications)
- Data displaying. (Interface and Application Programming)
To send the information collected by the sensors to a receiving device and display a graph and keep a constant monitoring of the area in which the harvesting is taking place.
Fab charter¶
What is a fab lab?
Fab labs are a global network of local labs, enabling invention by providing access to tools for digital fabrication
What’s in a fab lab?
Fab labs share an evolving inventory of core capabilities to make (almost) anything, allowing people and projects to be shared
What does the fab lab network provide?
Operational, educational, technical, financial, and logistical assistance beyond what’s available within one lab
Who can use a fab lab?
Fab labs are available as a community resource, offering open access for individuals as well as scheduled access for programs
What are your responsibilities?
- safety: not hurting people or machines
- operations: assisting with cleaning, maintaining, and improving the lab
- knowledge: contributing to documentation and instruction
Who owns fab lab inventions?
Designs and processes developed in fab labs can be protected and sold however an inventor chooses, but should remain available for individuals to use and learn from
How can businesses use a fab lab?
Commercial activities can be prototyped and incubated in a fab lab, but they must not conflict with other uses, they should grow beyond rather than within the lab, and they are expected to benefit the inventors, labs, and networks that contribute to their success
Week Assessment¶
During this week, have I :
-
[ ] Read the Fab Charter http://fab.cba.mit.edu/about/charter/? Yes, I learnt the basic philosophiy behind the word “Fablab”.
-
[ ] Sketched my final project idea ? Yes, have a look at the Final Project page.
-
[ ] Described what it will do and who will use it ? Yes, right above.