Appearance
In-Vehicle Mood Mastery Robot: Multi-Sensor Biotech System for Driving Wellness
Idea Sketch
Input:Heart Rate(HR), Salivary
Output:Music, Screen
The diagram below illustrates the initial concept of input and output sketches. v1: 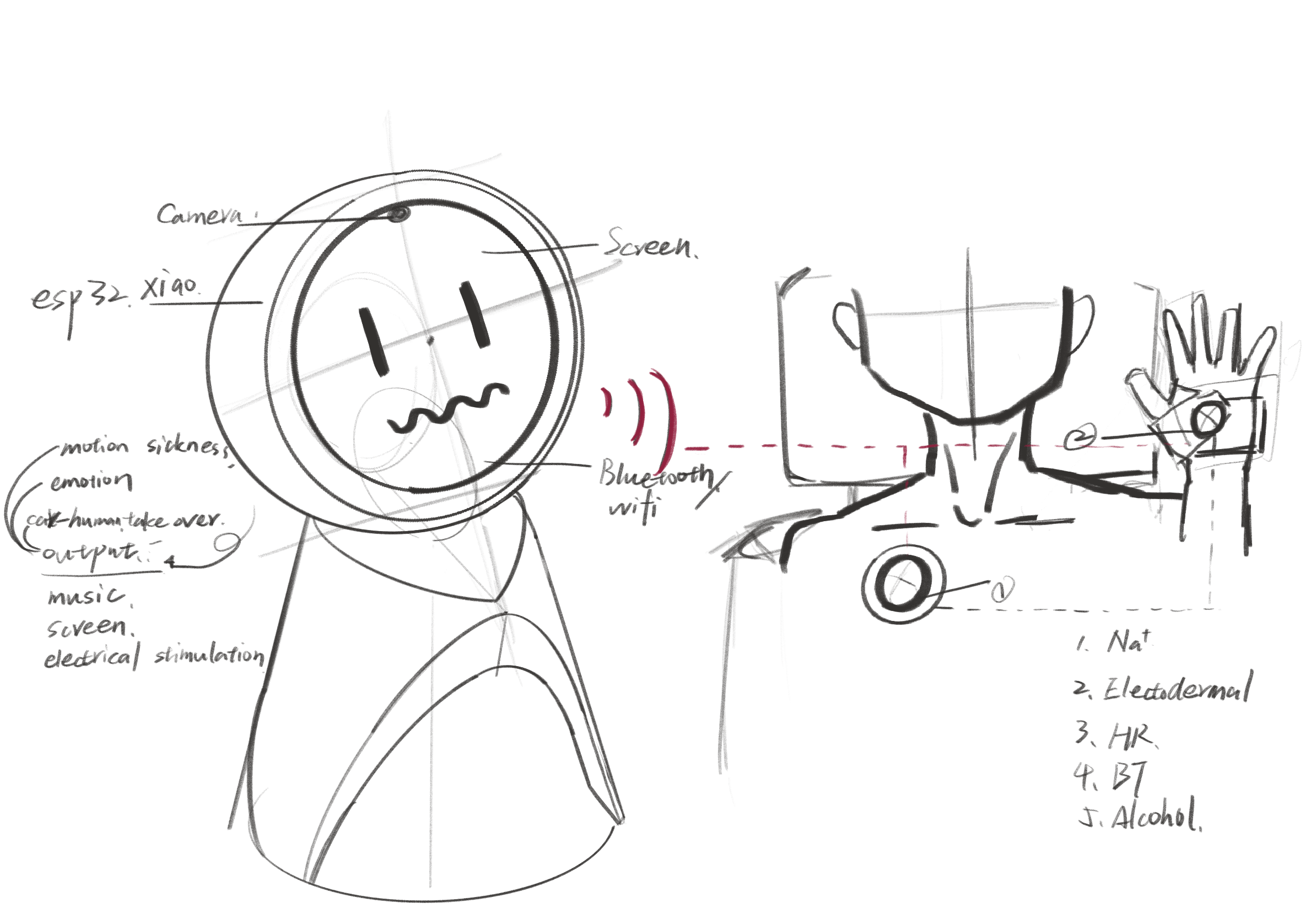 v2:
v2:  After studying relevant microcontroller and sensor technologies, we decided to utilize ultrasonic sensors , sodium ion sensors , WiFi modules , Raspberry Pi data processing modules , and an LCD screen to develop an in-vehicle autonomous driving assistant.
After studying relevant microcontroller and sensor technologies, we decided to utilize ultrasonic sensors , sodium ion sensors , WiFi modules , Raspberry Pi data processing modules , and an LCD screen to develop an in-vehicle autonomous driving assistant.
Key Components Explained:
Millimeter-wave radar: Non-contact heart rate monitoring, achieving precise measurement through high-frequency electromagnetic wave penetration of clothing.
Sodium Ion Sensors: Ensuring real-time monitoring of driver health or environmental conditions.
WiFi Modules: Enable wireless communication and integration with cloud platforms for data transmission and remote control . Raspberry Pi: Acts as the central processing unit, supporting edge computing for tasks like sensor data fusion, AI inference, and system control .
LCD Screen: Likely an LCD display for user interaction, providing visual feedback on navigation, sensor status, or alerts.
This integration combines low-cost hardware (ultrasonic sensors, Raspberry Pi) with advanced sensing (sodium ion detection) and connectivity (dual-band WiFi) to create a robust, multifunctional autonomous driving assistant.
After finalizing the sensor selection, detailed sketches were created to facilitate subsequent 3D modeling and the 3D printing of the enclosure.
Sodium Ion Sensor Fabrication and Usage:
- Preparation of Sodium Ion-Selective Membrane Solution (Na+ ISE)
The preparation of the sodium ion-selective membrane solution is as follows:
- Tetrahydrofuran (THF) 1 mL
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) 33 mg
- 2-Nitrophenyl octyl ether (2-NPOE) 63 μL
- Sodium tetraphenylborate 0.55 mg
First, dissolve Sodium Ionophore VI (1 mg/mL) and 2-NPOE in THF, then stir for 30 minutes to ensure complete homogeneity. Next, add the weighed PVC and continue stirring for another 30 minutes until the PVC is fully dissolved. After preparation, store the mixed solution in a refrigerator at 4°C for later use.
- Using a pipette gun, evenly drop the sodium ion-selective membrane solution onto the surface of the ChPBN-coated SPE electrode, ensuring uniform membrane layer formation. After coating, allow the electrode to air-dry for 12-24 hours, ultimately forming the SPE/ChPBN/Na+ ISE structure.


- Electrode appearance after sodium ion-selective membrane coating:

- Sodium ion concentration detection in NaCl solution,After immersing the sensor in the prepared NaCl solution, the electrode continuously measures the potential in real-time and converts it into sodium ion concentration. The MATLAB plots demonstrate a stepwise increase in measured potential corresponding to changes in sodium ion concentration.

