1. Principles and practices¶
Research¶
This week I worked on defining my final project idea
Revision of the definition and concept of Vestibular oculomotor reflex and introduction to the final project¶
Vestíbulo-ocular reflex (VOR):¶
The vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) is a reflex acting to stabilize gaze during head movement, with eye movement due to activation of the vestibular system. The reflex acts to stabilize images on the retinas of the eye during head movement. Gaze is held steadily on a location by producing eye movements in the direction opposite that of head movement. For example, when the head moves to the right, the eyes move to the left, meaning the image a person sees stays the same even though the head has turned. Since slight head movement is present all the time, VOR is necessary for stabilizing vision: people with an impaired reflex find it difficult to read using print, because the eyes do not stabilise during small head tremors, and also because damage to reflex can cause nystagmus (1)
Anatomical Funcional Scheme of the Vestibular ocular motor System
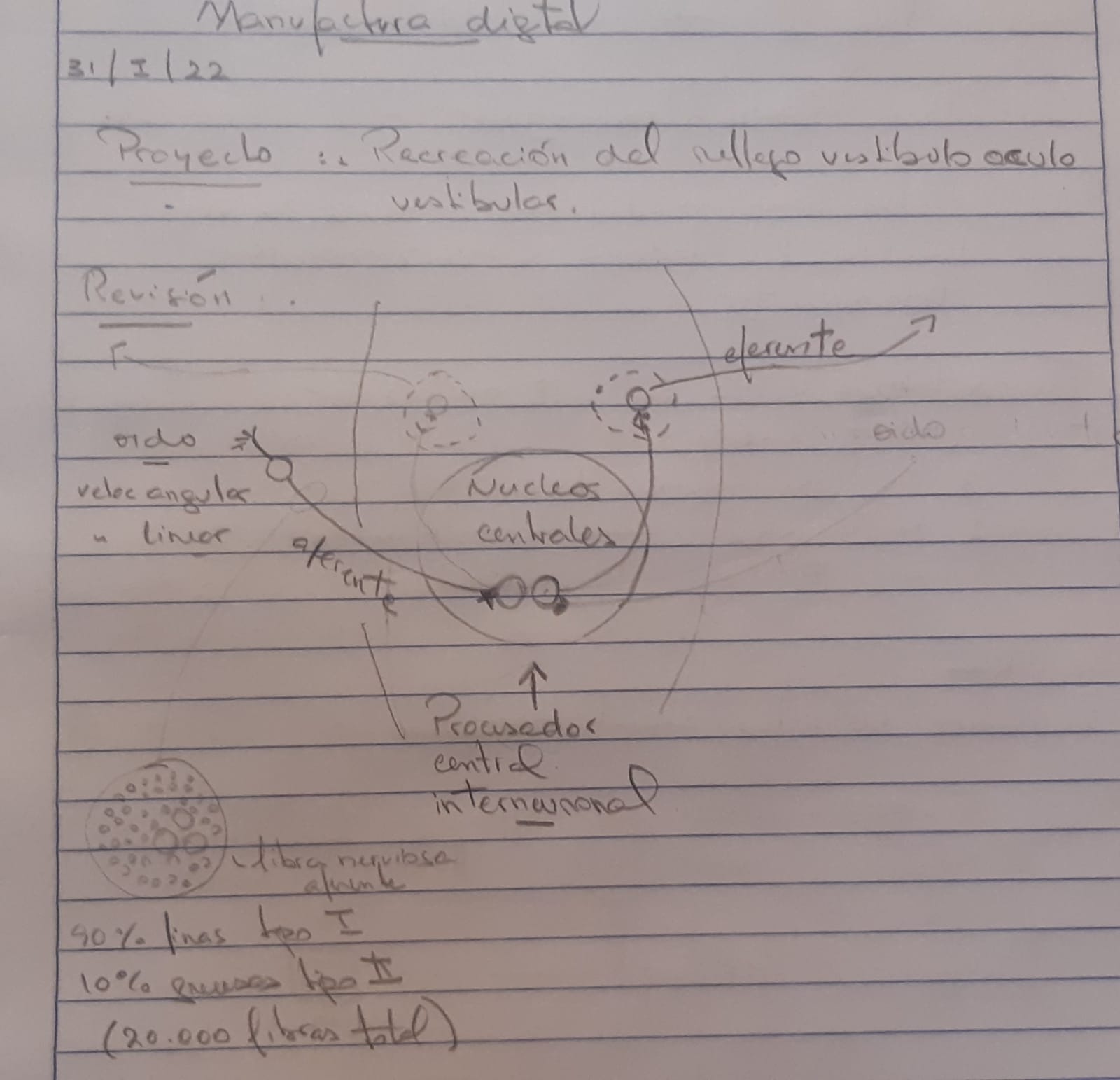
(HIT) Head Impuse Test¶
There is a very interesting semiological test that explores precisely this reflex and allows us to make more precise otoneurological diagnoses in a patient with some type of balance disorder and with it, the semiological test, to be able to differentiate where the causal problem could be. In the event that the semiological test is negative, it means with a normal reflex, we could orient ourselves to a cause of the central nervous system, in the opposite case, when the test is positive, it means with an abnormal reflex, it guides us that the cause could be peripheral, that is to say to be in the sensor of the ear or vestibule (see galery First and Second image).
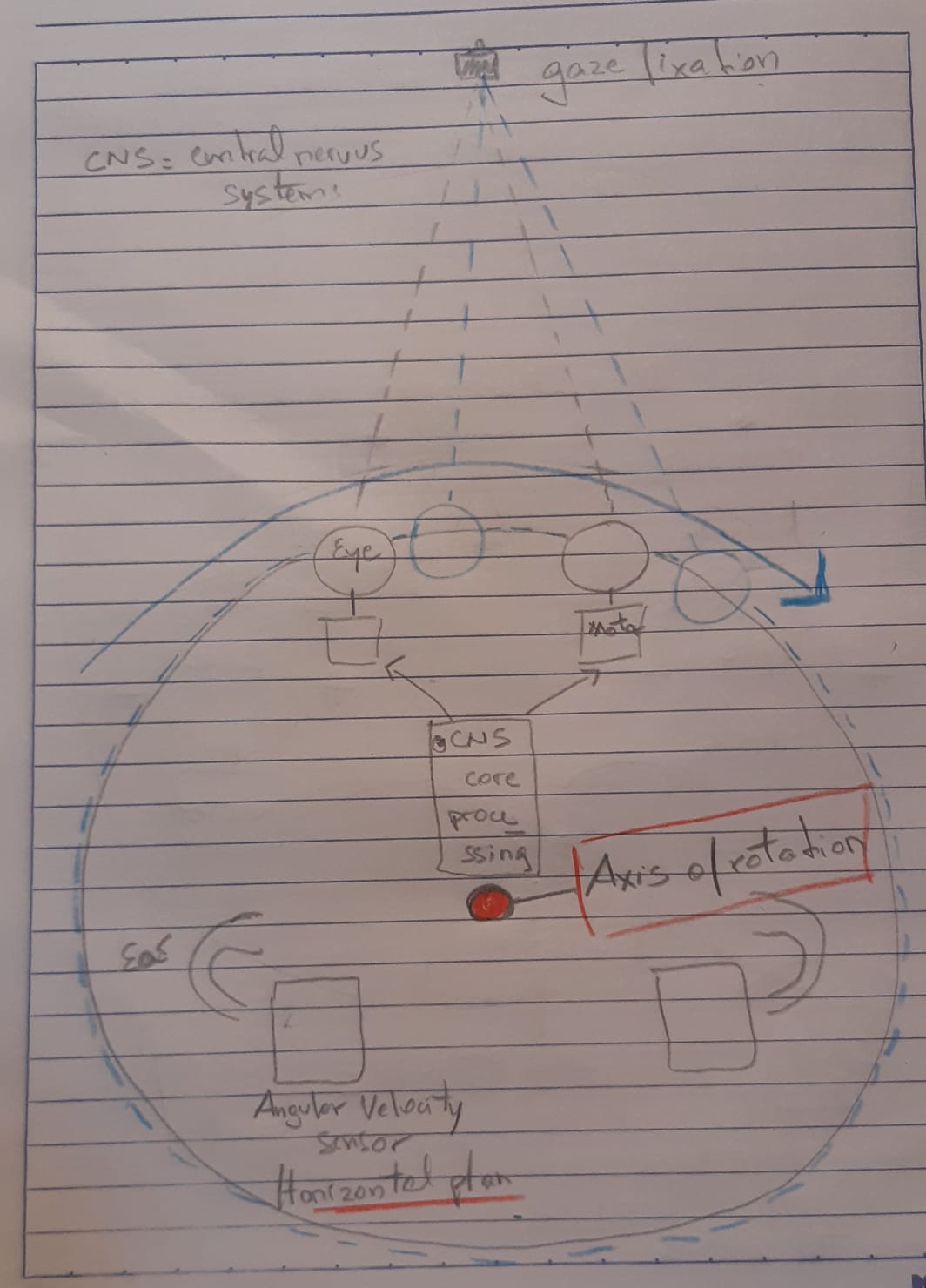
Esquema del VOR (Vestibular-ocularmotor reflex)
Balance¶
Balance is made up of a tripod: the ear, that is, the vestibule, the deep sensitivity of the muscles and tendons, and finally, as a third component, the sight. The three elements or sensors permanently send information to the brain, when one of them stops sending or does it in a defective way, it causes a disturbance at the level of the central nervous system and produces the sensation of imbalance. (2)
Here I present a video of a semiological examination where we can see the normal and abnormal réflex (see First video of youtube)
Introduction of the Final Proyect¶
What is the project and what is its use?¶
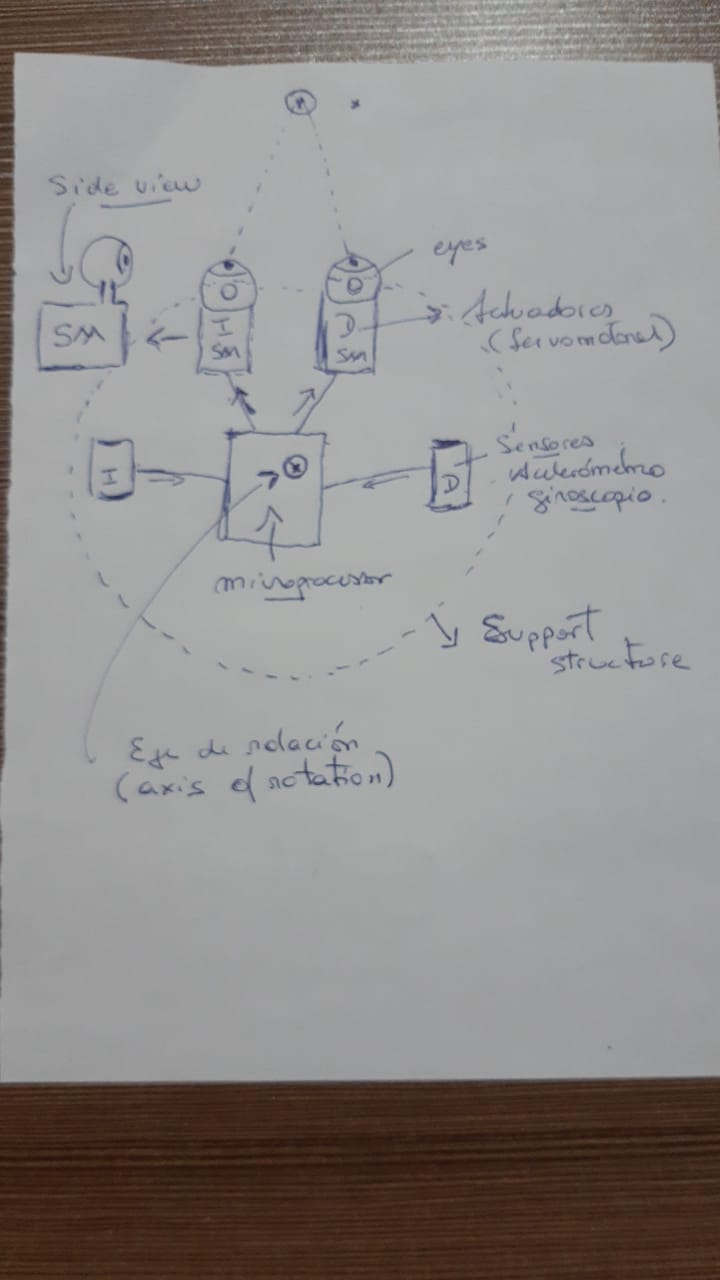
This project is one representation of the reflex function of the vestibule (ear) with the oculomotor system, call it the vestibulo-oculomotor reflex and will be usefull for educational and experimental purposes
Just as we can simulate normal functioning for educational purposes, we can also, through programming changes, recreate an abnormal or pathological response.
Proyect design VOR
References:¶
1- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vestibulo%E2%80%93ocular_reflex
2- Lonsbury-Martin, B. L., Martin, G. E., & Luebke, A. E. (2009). Physiology of the Auditory and Vestibular Systems. In Ballenger´s Otorhinolaryngology. Head and neck surgery. (Centennial, pp. 68–133). Connecticut: BC Decker Inc. https://orl.usmf.md/sites/default/files/inline-files/Ballehger%20ENT.pdf