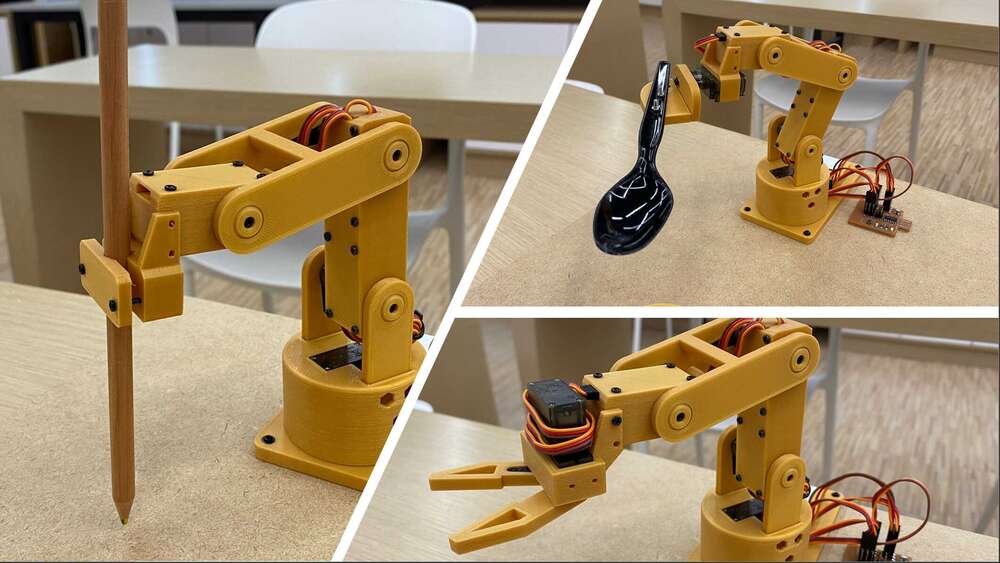
// System value
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
const int numberOfServos = 5; // Number of servos
const int numberOfACE = 6; // Number of action code elements
int servoCal[] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, }; // Servo calibration data
int servoCurrentPos[] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, }; // Servo current position
int servoOldPos[] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, }; // Servo old position
int servoPrgPeriod = 20; // 20 ms
int servoPin[] = {5, 8, 9, 14, 15 }; // Initializing servo pin ( head to base )
int runProgram = false; // Flag for run program
const int buttonPin = 2; // The number of the pushbutton pin
int buttonState = 0; // Variable for reading the pushbutton status
const int ledPin = 4; // The number of the LED pin
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Action code
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Zero
int servoPrg00step = 1;
int servoPrg00 [][numberOfACE] PROGMEM = {
// P05, P08, P09, P14, P15, ms
{ 90, 90, 90, 90, 90, 1000 }, // zero position
};
// Bread
int servoPrg01step = 12;
int servoPrg01 [][numberOfACE] PROGMEM = {
// P05, P08, P09, P14, P15, ms
{ 90, 90, 90, 90, 40, 1000 }, // 轉向白碗
{ 90, 70, 10, 70, 40, 1000 }, // 放下機械臂
{ 70, 70, 15, 80, 45, 1000 }, // 放下湯匙
{ 80, 75, 10, 60, 45, 1000 }, // 升起湯匙
{ 85, 60, 10, 70, 110, 1000 }, // 轉向黃碗
{ 30, 100, 75, 100, 120, 1000 }, // 倒糖漿
{ 50, 100, 115, 140, 125, 1000 }, // 移到面包左上角
{ 50, 100, 100, 130, 140, 1000 }, // 移到面包左下角
{ 50, 100, 10, 30, 115, 1000 }, // 移到面包右下角
{ 50, 100, 50, 90, 100, 1000 }, // 移到面包右上角
{ 85, 60, 10, 70, 110, 1000 }, // 轉向黃碗
{ 90, 70, 10, 70, 40, 1000 }, // 轉向白碗放下機械臂
};
// Setup
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setup() {
// Declaring servo pin as an output mode
for(int s = 0; s < 5; s++){
pinMode(servoPin[s], OUTPUT);
}
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT); // Initialize the pushbutton pin as an input mode
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Initialize the LED pin as an output mode
servoPos(90, 90, 90, 90, 90);
runServoPrg(servoPrg00, servoPrg00step); // zero position
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Loop
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void loop () {
buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin); // read the state of the pushbutton value
// check if the pushbutton is pressed
if (buttonState == LOW) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
runServoPrg(servoPrg01, servoPrg01step); // bread action
} else {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
}
delay(100);
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Function
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void servoPos(int a1, int a2, int a3, int a4, int a5) {
servoPulse(servoPin[0], a1);
servoPulse(servoPin[1], a2);
servoPulse(servoPin[2], a3);
servoPulse(servoPin[3], a4);
servoPulse(servoPin[4], a5);
servoOldPos[0] = a1;
servoOldPos[1] = a2;
servoOldPos[2] = a3;
servoOldPos[3] = a4;
servoOldPos[4] = a5;
delay(400);
}
void servoPulse (int servo, int angle) {
int pwm = (angle*11) + 500; // Convert angle to microseconds
digitalWrite(servo, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(pwm);
digitalWrite(servo, LOW);
}
void runServoPrg(int servoPrg[][numberOfACE], int step)
{
for (int i = 0; i < step; i++) { // Loop for step
int totalTime = servoPrg[i][numberOfACE - 1]; // Total time of this step
// Get servo start position
for (int s = 0; s < numberOfServos; s++) {
servoCurrentPos[s] = servoOldPos[s] - servoCal[s];
}
for (int j = 0; j < totalTime / servoPrgPeriod; j++) { // Loop for time section
for (int k = 0; k < numberOfServos; k++) { // Loop for servo
servoPulse(servoPin[k], (map(j, 0, totalTime / servoPrgPeriod, servoCurrentPos[k], servoPrg[i][k])) + servoCal[k]);
servoOldPos[k] = (map(j, 0, totalTime / servoPrgPeriod, servoCurrentPos[k], servoPrg[i][k])) + servoCal[k];
}
delay(servoPrgPeriod);
}
}
}