Week 10
Molding and Casting
This week's group assignment was to review the safety data sheets for each of the molding and casting materials at our lab, and then to make and compare test casts with each of them. In addition to the group activity, we had to individullay design a 3D mold and use it to cast parts.
Materials & Safety
The materials we have at our lab are Mold Max 60, Liquid Silicon Rubber, High Gloss and Transparent Epoxy Resin etc.
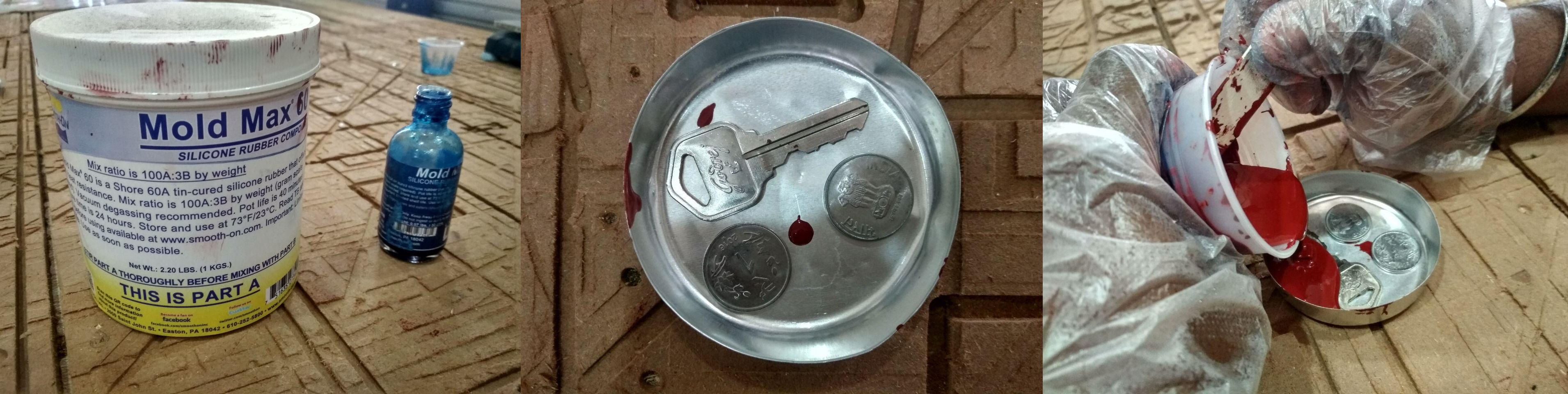
Mold Max 60
Mold Max 60 is a tin catalysed silicone rubber formulated for applications requiring high heat resistance. It comes in two parts which are to be mixed in the ratio of 100:3 by weight. Pot Life and cure time is 40 minutes and 24 hours respectively.
Below is the information Bulletin and material safety data sheet of Mold Max 60 which is arranged into 16 sections.
Section 4 of the data sheet specifies the first aid measures to be taken in case of inhalation, eye contact, skin contact and ingestion. Subsequently,guidelines to be adopted for fire fighting measures, accidental release measures, handling and storage, exposure control and personal protection etc are provided in detail in the safety data sheet.

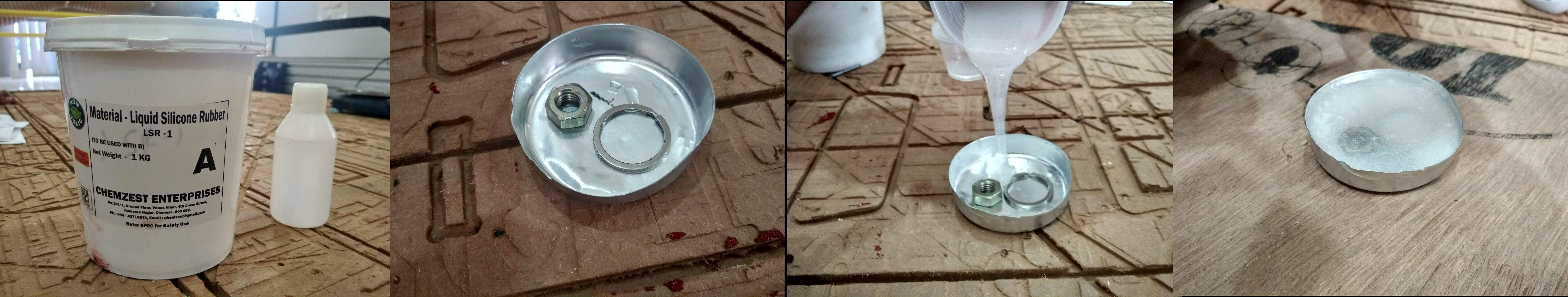
Liquid Silicone Rubber
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR-1) is a two-component, addition cure liquid silicone rubber designed for mold making. LSR-1 cures at room temperature to a translucent high strength elastic rubber with the addition of curing agents. Below is the data sheet of Liquid Silicone Rubber.

High Gloss & Transparent Epoxy Resin
This is a two part epoxy system (Resin & Hardner) with High Glossy, Transparent, low viscosity and UV stable liquid epoxy resin for casting, coatings, and adhesive applications. The resin and hardner is to be mixed in the ratio of 10:6 by weight. Below is the data sheet of Epoxy Resin.
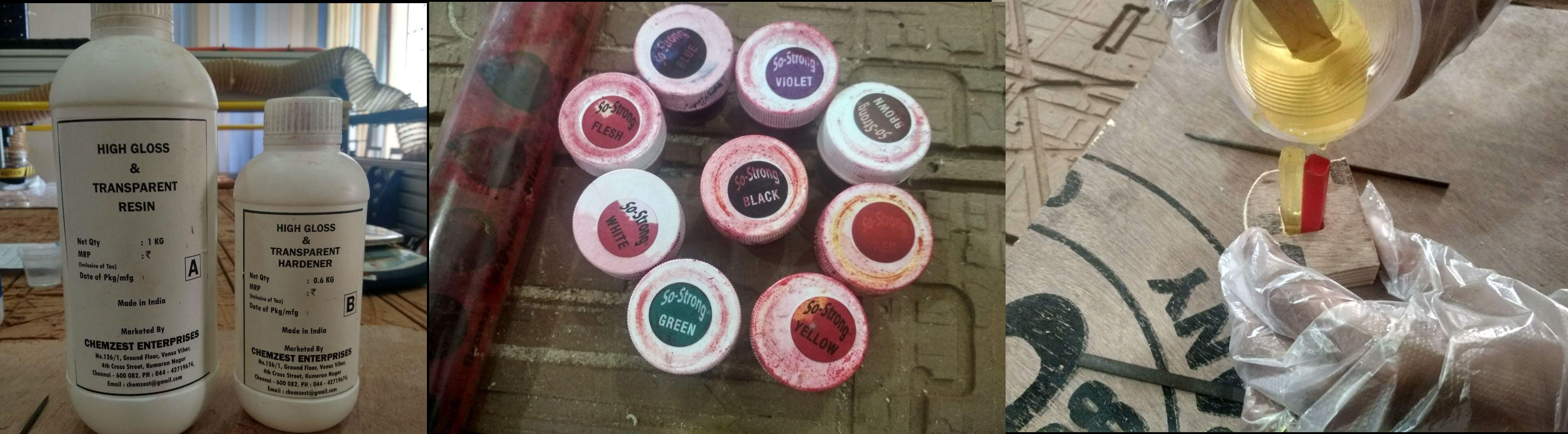


Designing and making a 3D Mold
The design skills developed during the Computer Aided Design week and the Computer Controlled Cuting week was put to use. To mold and cast a lamp shade, a two part mold was designed in SOLIDWORKS. The object was designed in soliworks using the revolve function. Below image is the lamp shade which was designed.
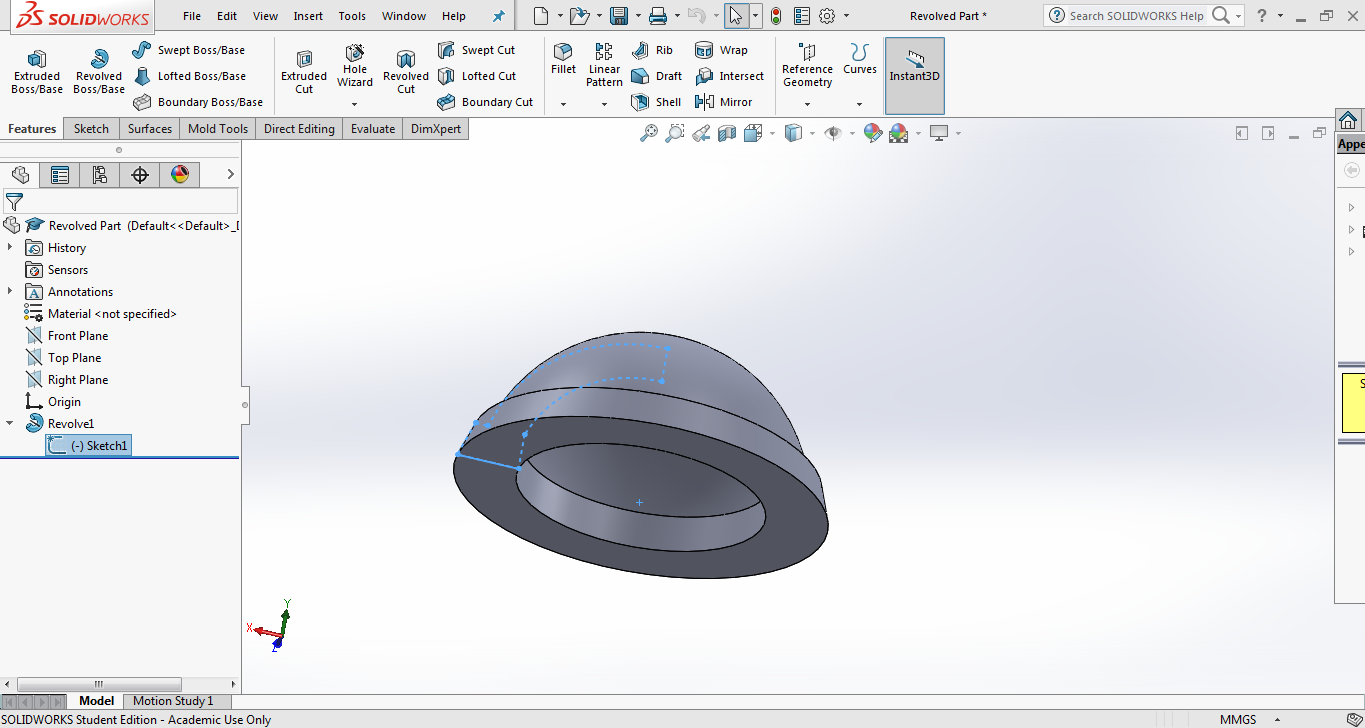
Using the "Mold Tools" available in SolidWorks, the female and male parts of the mold were designed. Below image shows the part along with the male and female mold's.
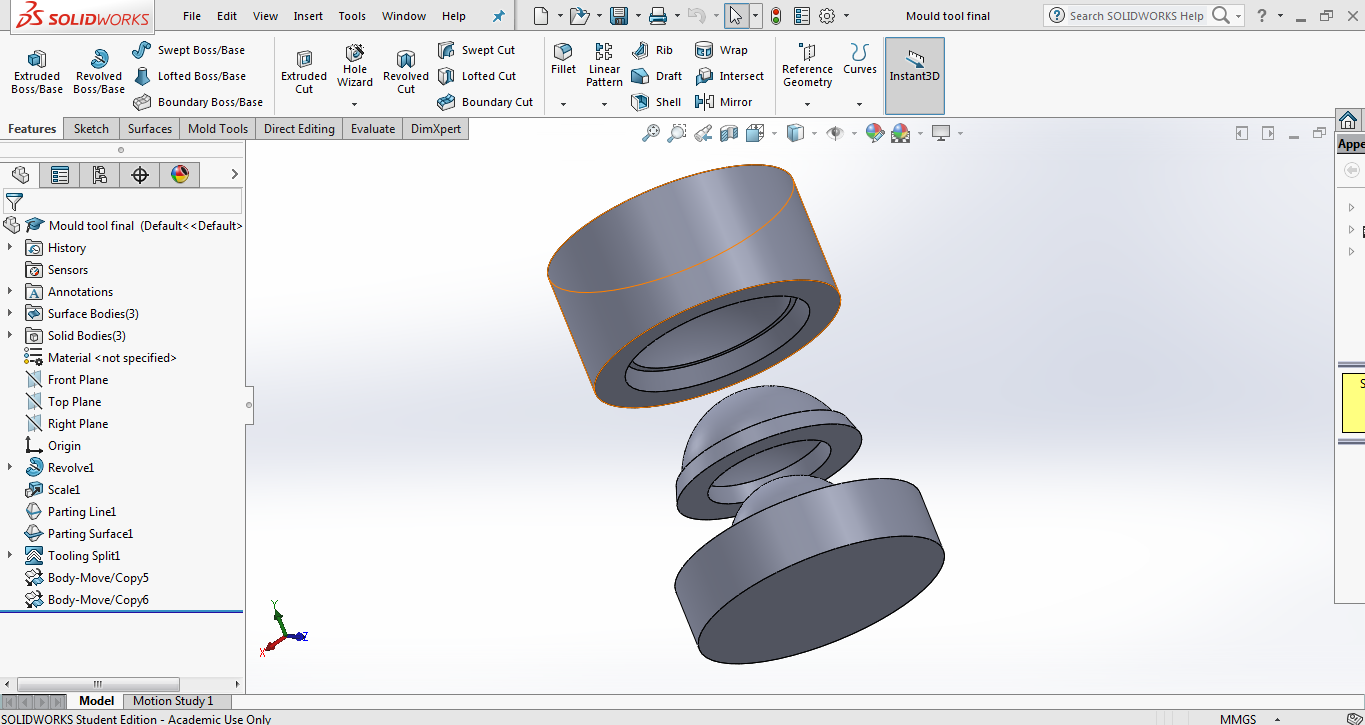
Below image shows the female and male molds seperated.
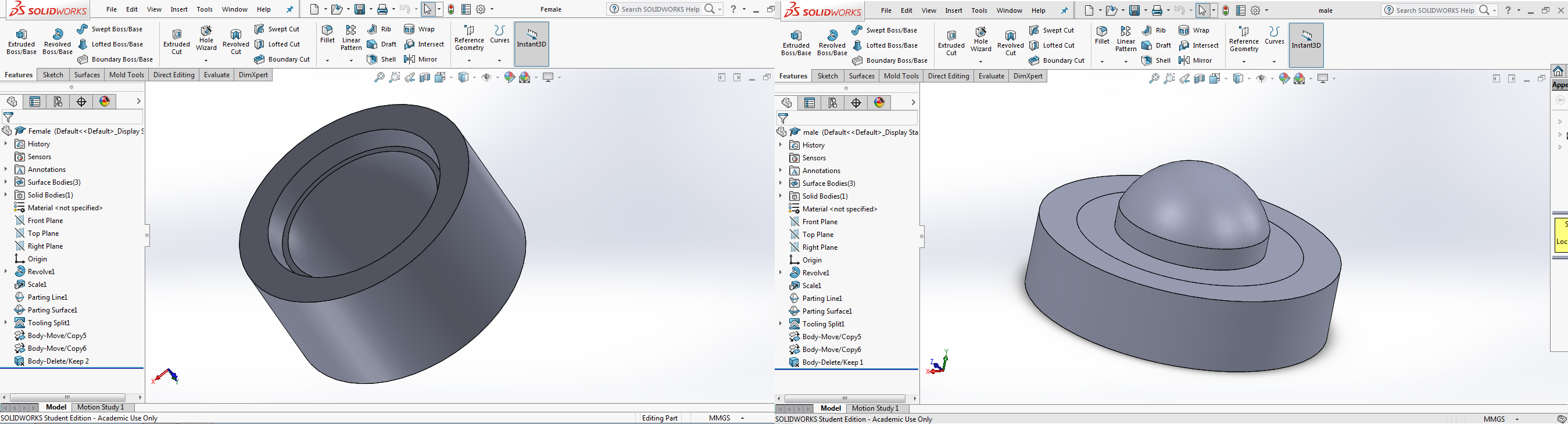
To make the molds, wax is to be milled. Since, milling is a subtractive process, the inverse(Boolean Operation) of the parts were to be made. The below two images shows the female and male molds subtracted from a cube.
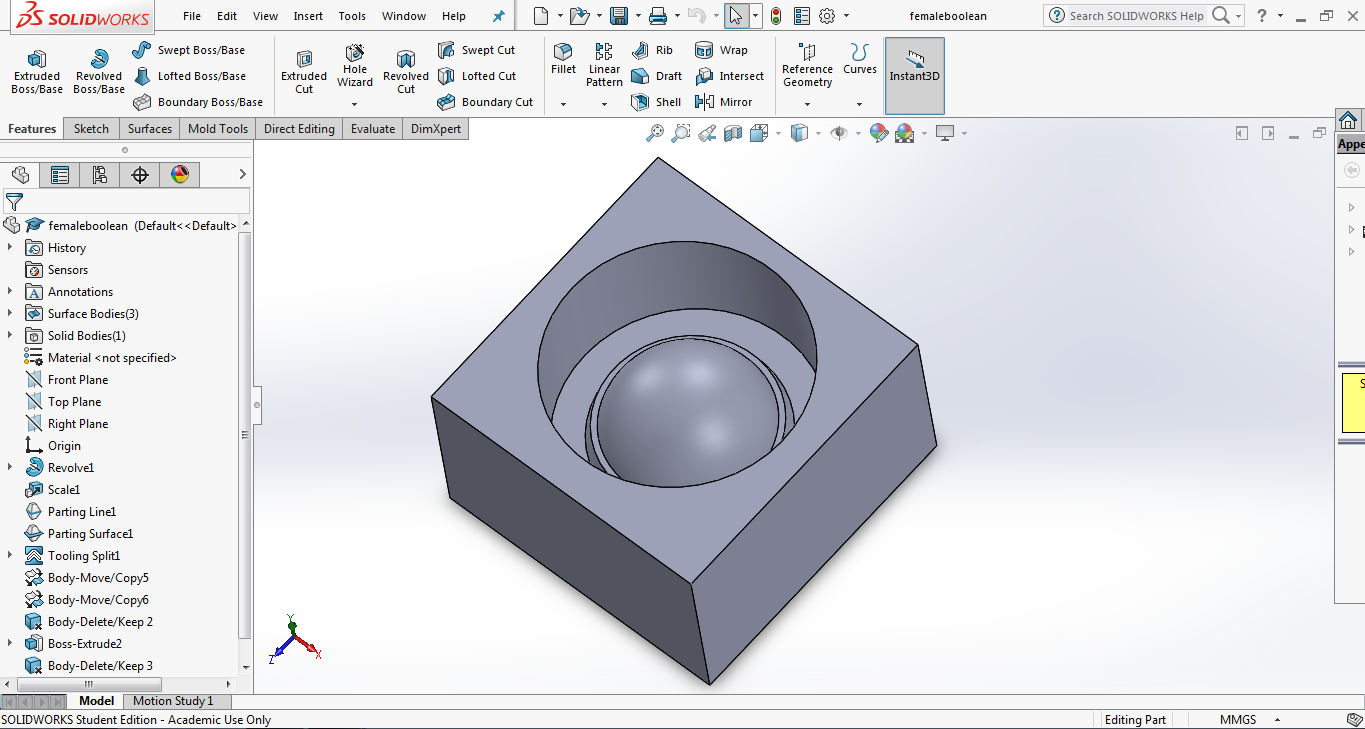
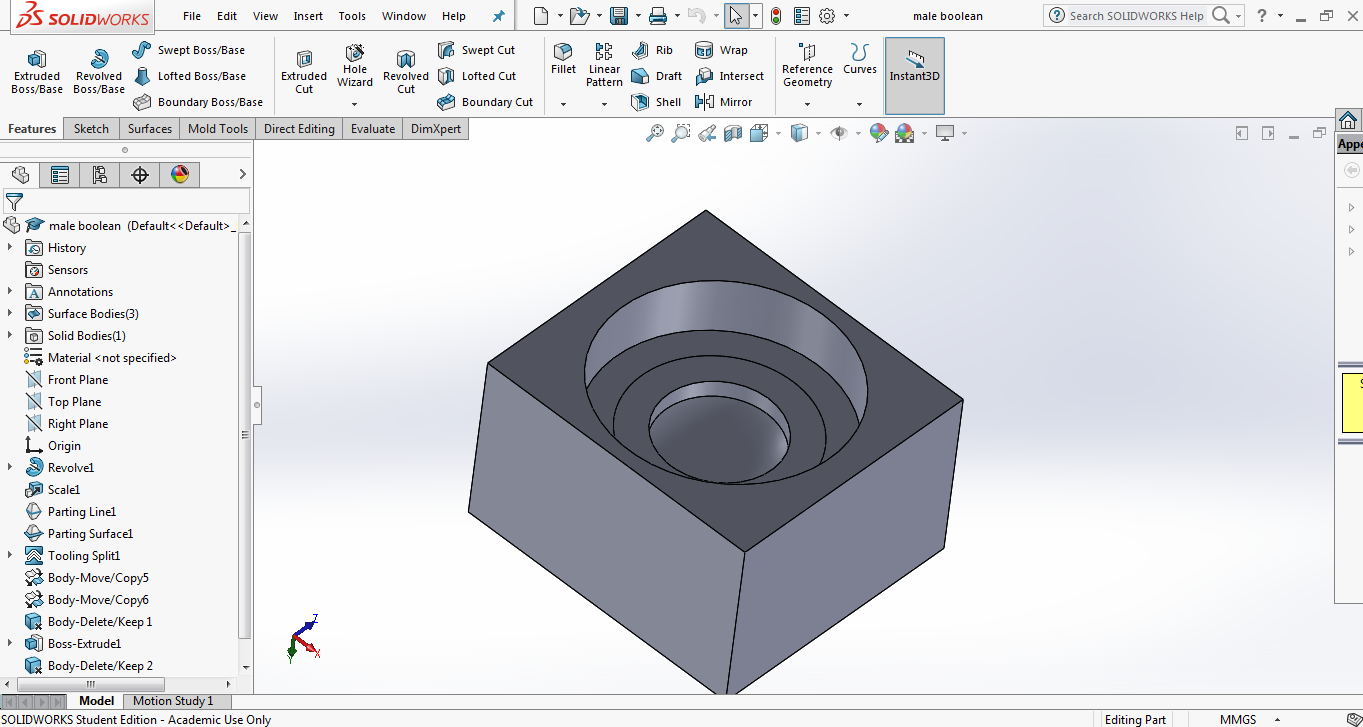
The STL files of the object's after the boolean operation was exported from SolidWorks so that wax can be milled using the Modella MDX 20.
Download the design files
The milling operation is to be done in two steps. First a rough cut is made followed by a finish cut. A Ball nose end mill is to be used for the milling operation for getting a smooth contour. While installing the end mill, it has to be taken care that sufficient length is availble for the end mill to move upto the vertical extreme of the model. A 3mm end mill and "Mods" software was used for the milling operation. Below image shows the mill bit used for the operation.

The milling operation of the female part of the mold was first done. Below image shows the settings during the rough cut.
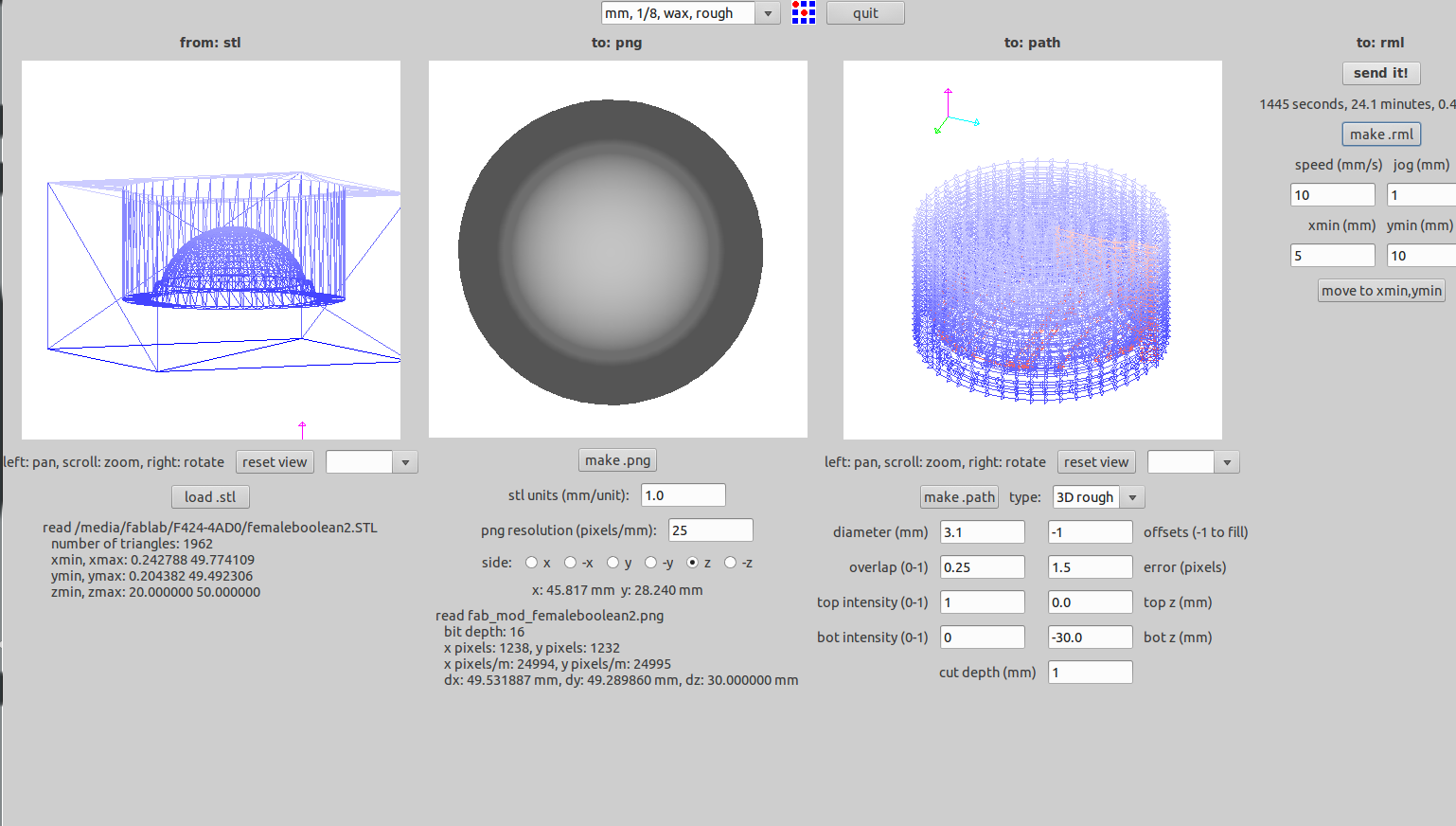
The below image shows the settings during the finish cut.
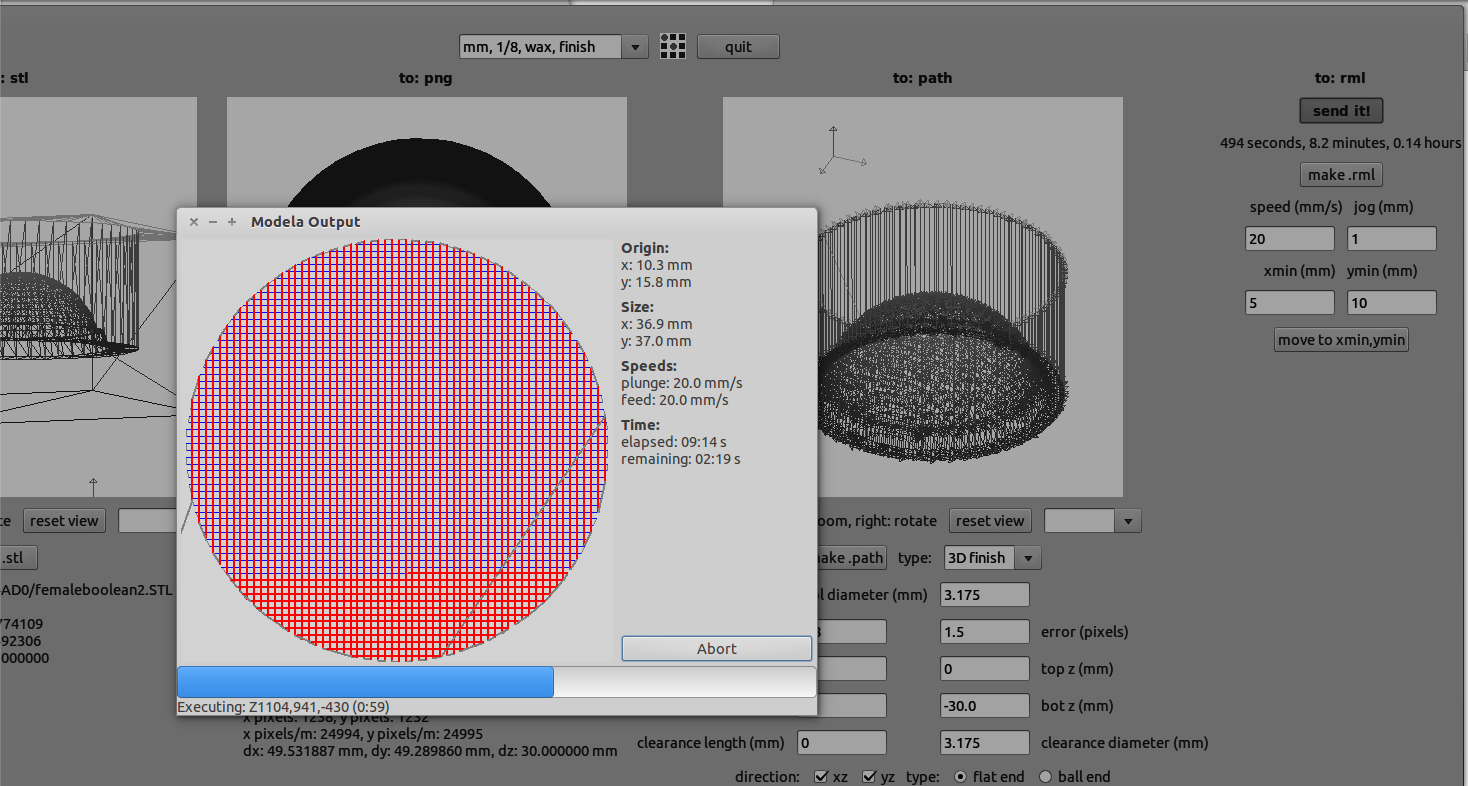
It can be observed that the tool path created during the two operations are entirely different and the below image shows the difference in the surface finish of a rough and smooth cut.
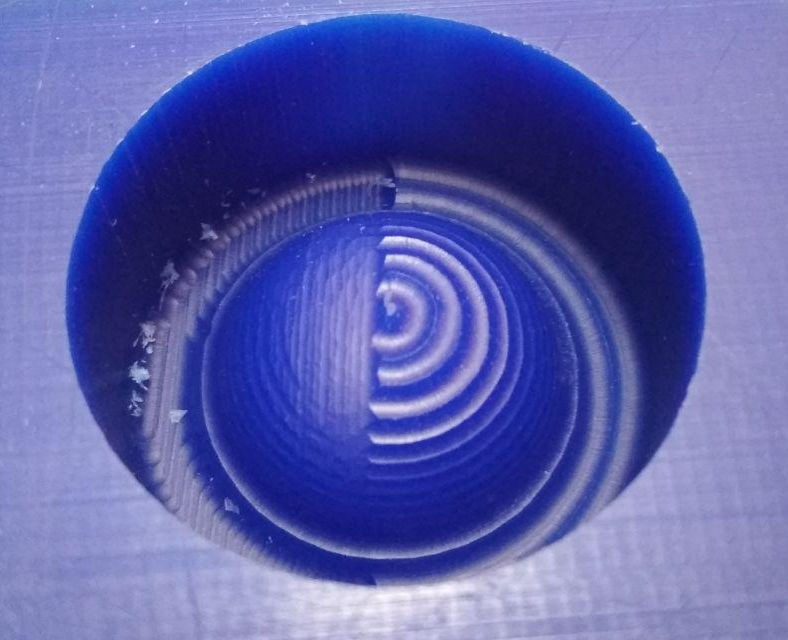

The milling operation for the male part of the mold was done next using the settings as in the images below.
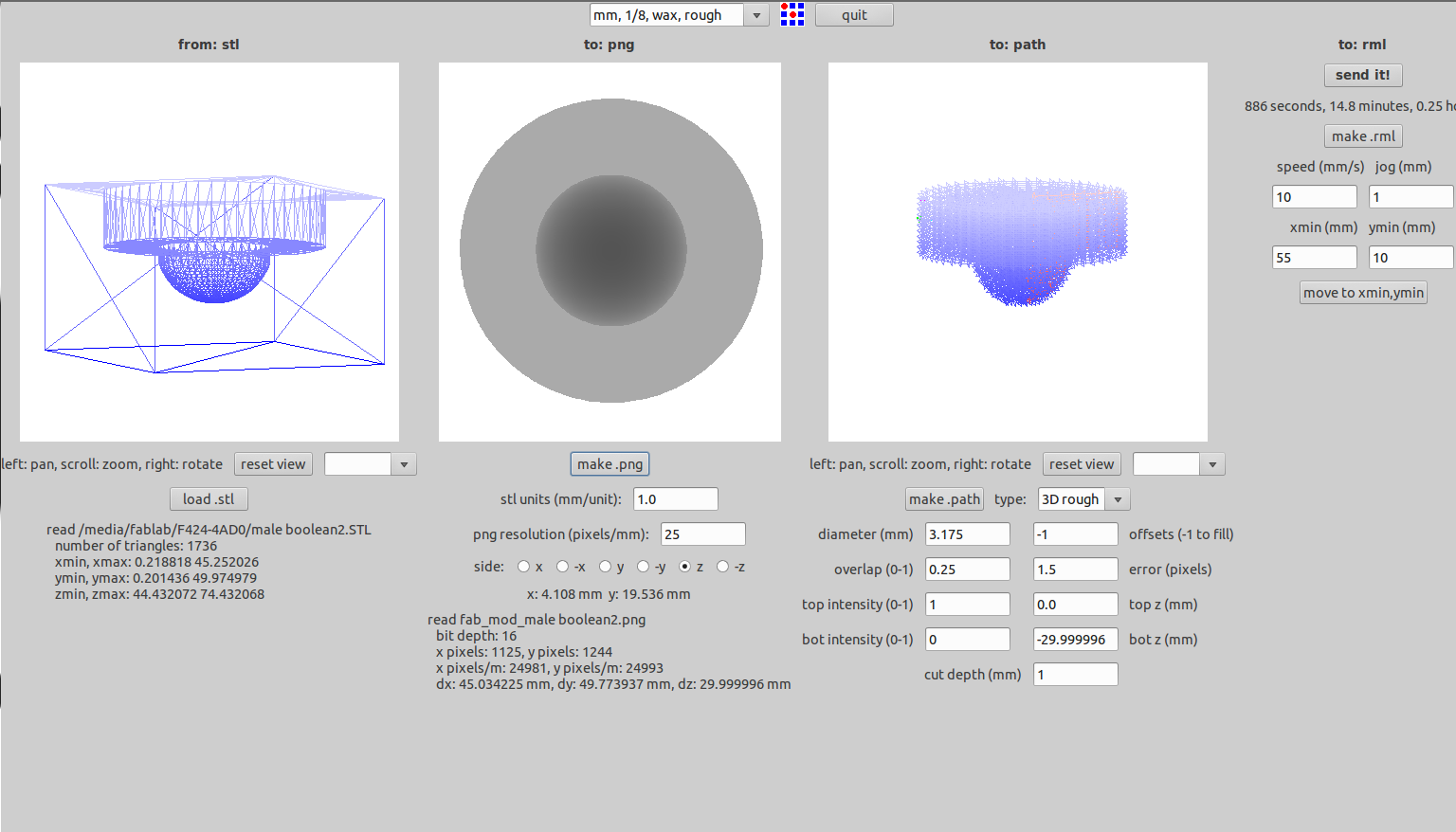
Making of Mold & Casting Parts
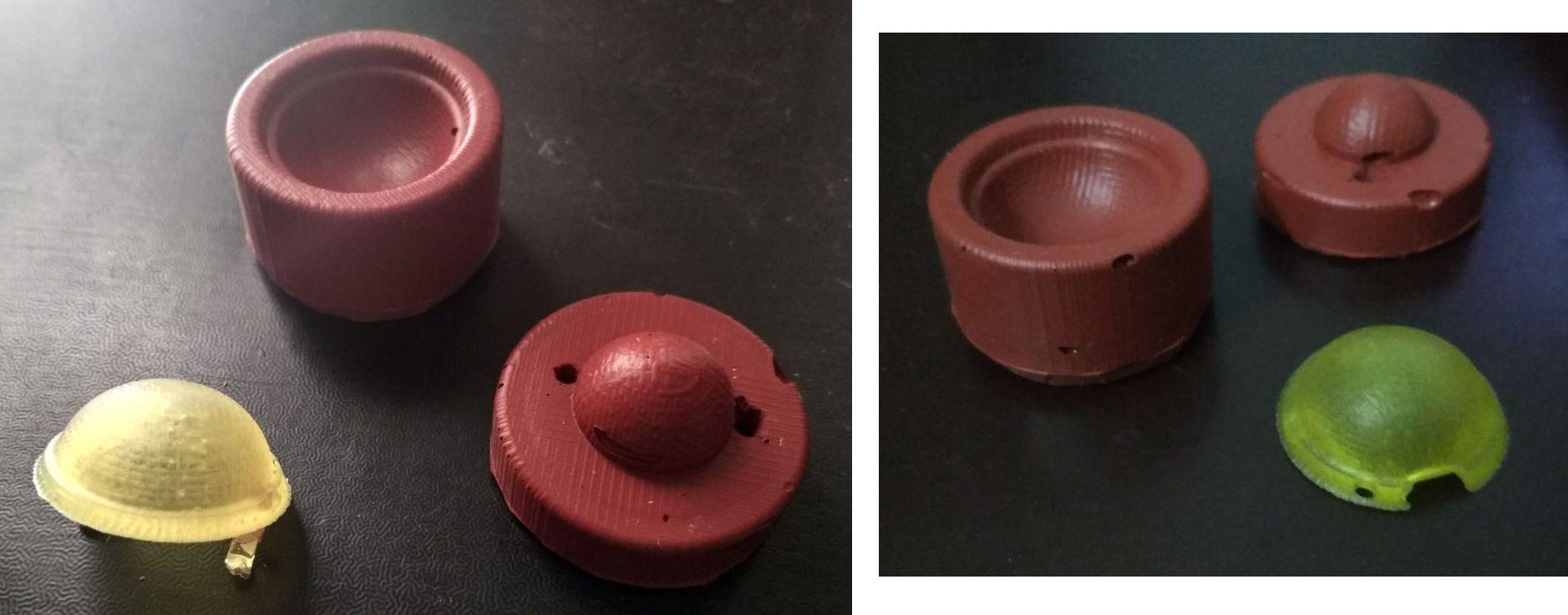
Mold Max 60 was used to make the mold. The volume of the male and female parts of the mold was obtained from SOLIDWORKS with which the quanity of Mold Max 60 required was calculated. More quantity than required was mixed to account for wastage and for creating a thin top cover for easy removal after setting. The two parts were mixed in the ration 100:3 and was poured into the mold made by the milling operation. The compound has to be poured from a sufficient height to flow as thin threads so as to avoid entrapping air and formation of air bubbles. After pouring, the wax block was gently vibrated for proper compaction of the compound. It was allowed to cure for 24 hours and was pulled out to get the two part mold.Below image shows the stages of operation.
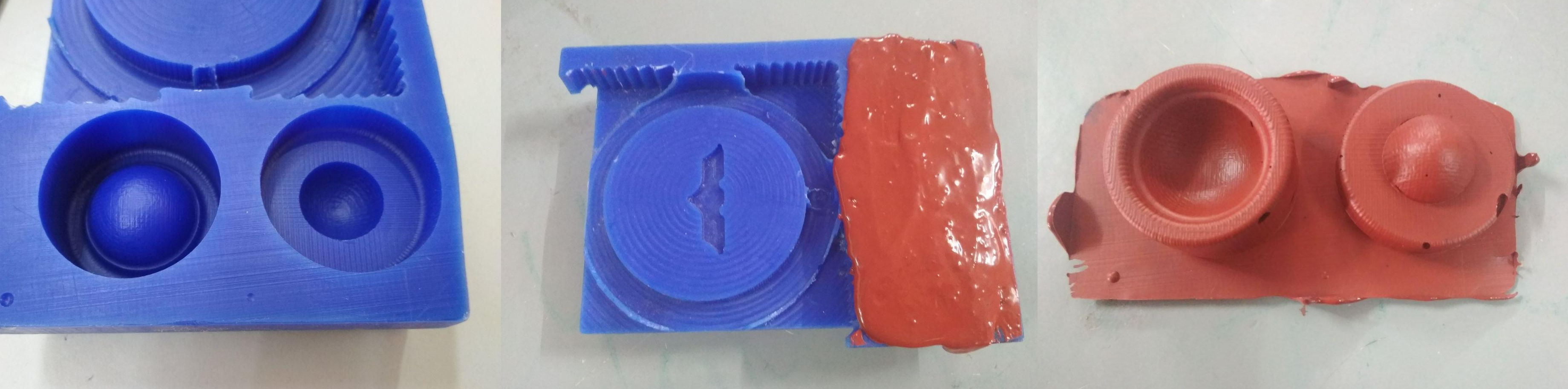

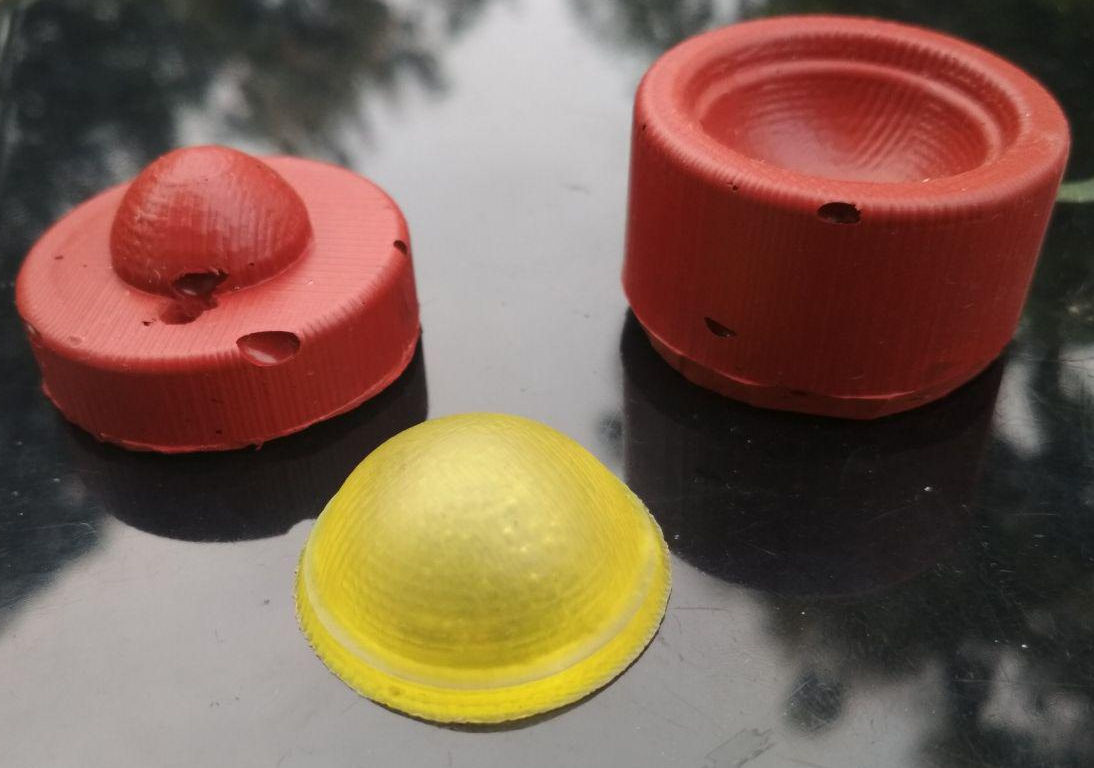
The two parts of the mold were seperated by using a knife. It had imperfections formed due to entrapped air bubbles. It is at this point where i realised that, grave mistakes were committed by not including the sprue, air vent and also the locking arrangement between the two parts. To overcome the shortcomings, two holes were drilled for pouring the compound and to act as an air vent. The mouth of the sprue was made wider for easy pouring of the compound. Below image shows the final mold ready to cast parts.
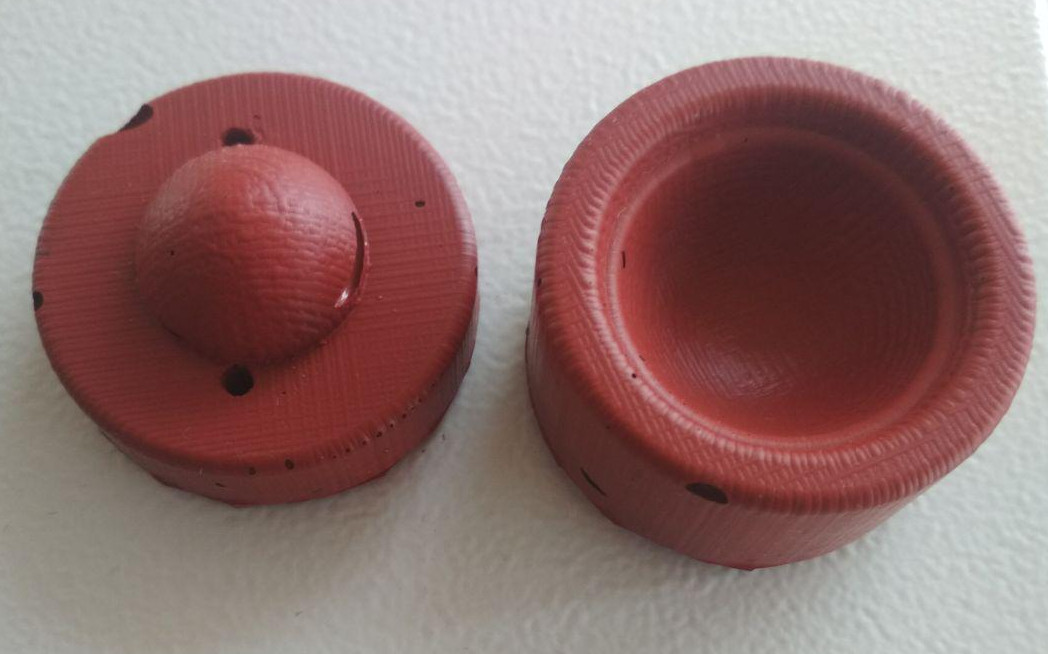

High Gloss & Transparent Epoxy Resin was used to cast parts. Slightly more quantity than what was required was mixed and a tiny drop of yellow colour pigment was added. The two parts of the mold were held together using a clamp and the resin was gently poured into the mold through the sprue. The resin was poured until it came out through the air vent and was then allowed to cure for 24 hours
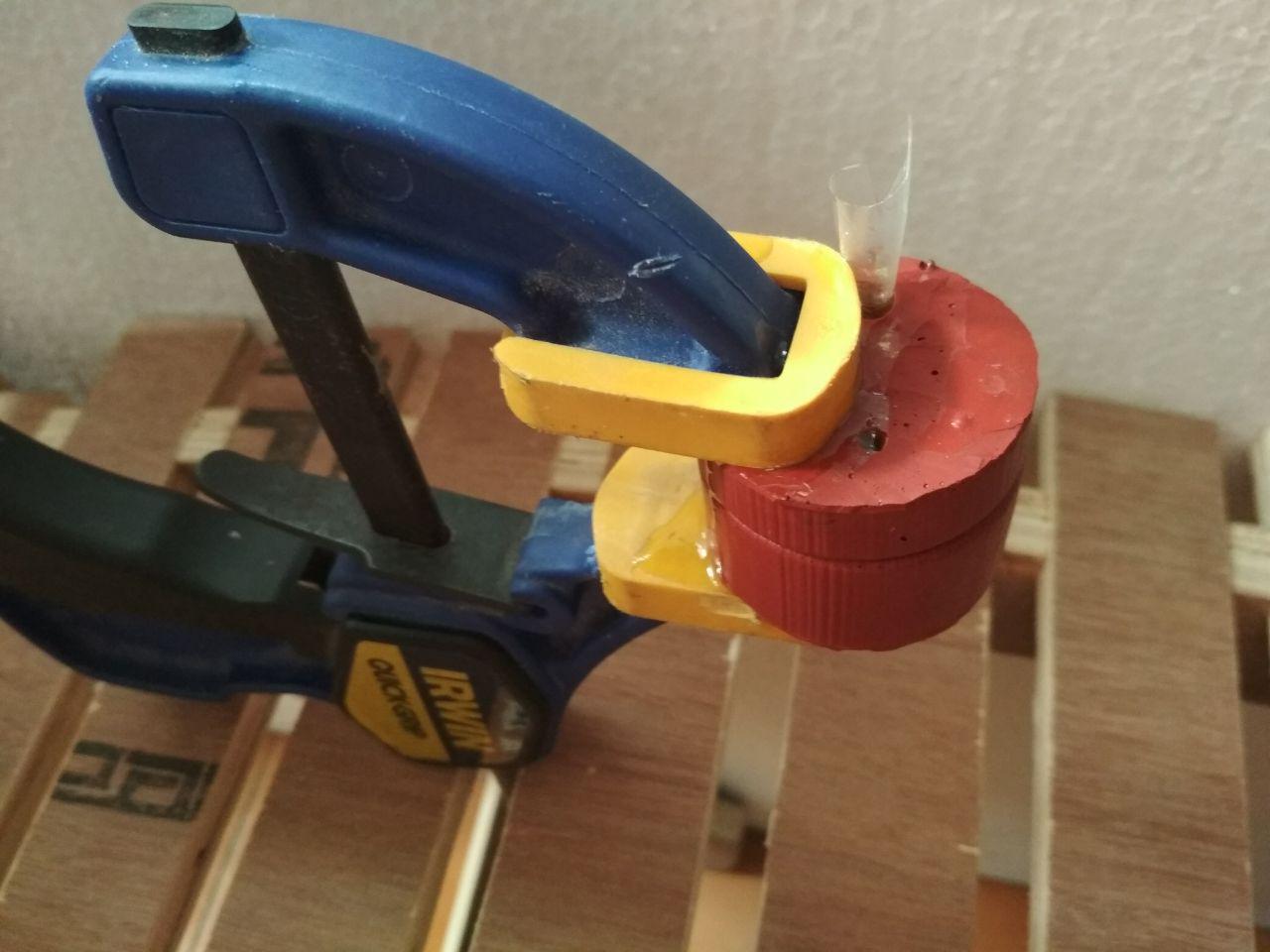

Below image shows the part casted. The resin at the sprue and air vent portion was broken and filed to a smooth finish. The part had imperfection at exactly 90 degree from the line connecting the sprue and air vent. The resin did not flow completely due to entraped air, leaving a hole in the part.

