Group Assisnment Week 13
In this week, we are going to do these:
- Review the safety data sheets for each of your molding and casting materials, then make and compare test casts with each of them.
- Compare printing vs machining molds.
The Silicone materials in the Lab
We are making Silicone molds and here are the materials:
We have two different Silicone in the lab:

The brand of this is the HongDa

The brand of this is the ShinBon.
The usage details are shown in my individual assignment.
Safety Issues with Silicone
- Skin and Eye Irritation: Silicone can cause irritation if it comes into contact with the skin or eyes. It's important to wear protective gloves and safety goggles.
- Fume Inhalation: Some silicone products, especially those that cure using acetic acid, release fumes that can be irritating or harmful if inhaled. Use these products in a well-ventilated area.
- Fire Risk: Although silicone itself is generally non-flammable, the fumes can be hazardous near open flames or high heat sources. Chemical Sensitivity: Some individuals may have allergic reactions or sensitivities to the chemicals in silicone products.
Simple Preventative Measures
- Wear Protective Gear: Always wear gloves and goggles to protect your skin and eyes from direct contact with silicone. Ensure Good Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling any harmful fumes. Consider using an exhaust fan or working outdoors if possible.
- Avoid Contact with Sensitive Areas: Be cautious to prevent silicone from coming into contact with your eyes, mouth, and other sensitive body parts.
- Proper Storage: Store silicone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Ensure containers are tightly sealed to prevent the product from degrading.
- Follow Usage Instructions: Carefully read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application and curing times to achieve the best results and maintain safety.
- Safe Disposal: Dispose of any excess silicone or containers according to local regulations, ensuring that you minimize environmental impact.
Bad Habits
Not wearing any protection:

The AB Glue materials in the Lab
We are casting with AB Glue materials and here are:
We have two different AB glue in the lab:
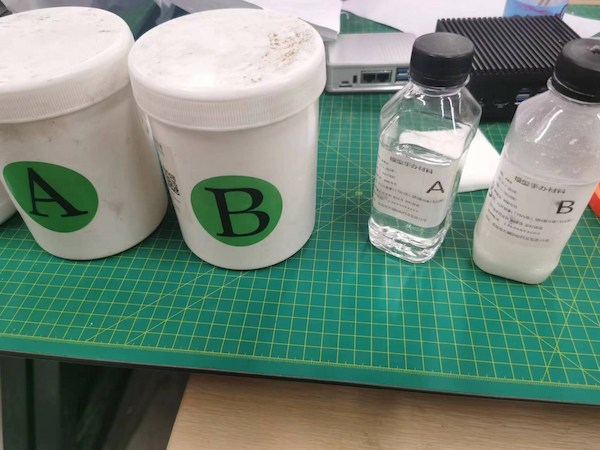

The one on the left is made by Silicon.
The one on the right is HongDa
The usage details are shown in my individual assignment.
Safety Issues with AB Glue
- Skin and Eye Irritation: AB glue can cause severe irritation if it comes in contact with the skin or eyes. Always wear gloves and safety goggles to protect yourself.
- Inhalation Hazards: The fumes from AB glue can be harmful if inhaled, especially in poorly ventilated areas. Use the glue in a well-ventilated space or wear a mask.
- Chemical Burns: Both components of AB glue can cause chemical burns upon contact with skin.
- Fire Risk: Some types of AB glue are flammable. Keep them away from open flames and heat sources.
- Toxicity: The components can be toxic, so avoid ingestion and prevent any food or drink from being contaminated during use.
Simple Preventative Measures
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and goggles.
- Work in a well-ventilated area.
- Keep the glue away from heat and open flames.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for safe use and disposal.
- Store the glue properly in a cool, dry place and ensure containers are tightly closed.
Good Habits
Wearing protection:

Methods of Modelling
3D Printing directly printing a mold
3D printing offers a contemporary approach to mold creation, excelling at producing molds with complex geometries. This method’s strength lies in its ability to construct detailed features layer-by-layer, achieving high precision. However, it also presents challenges; surfaces of the final products can display layer lines, reflecting the layered construction process. Additionally, 3D-printed molds may lack the necessary robustness for applications involving high temperatures or pressures. Thus, when choosing 3D printing for mold-making, one must weigh the complexity of the design against the required surface quality.
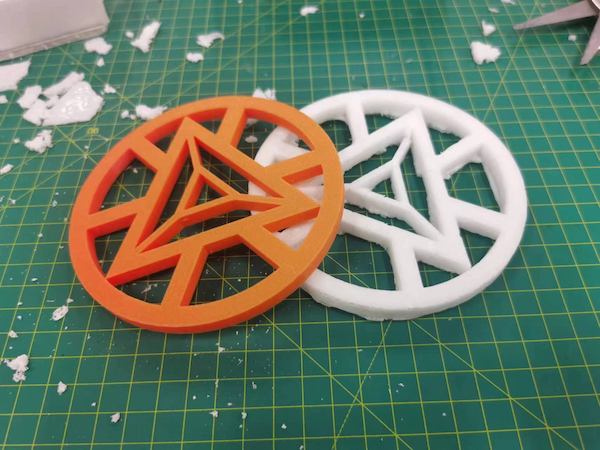
My group have directly designed a mold:
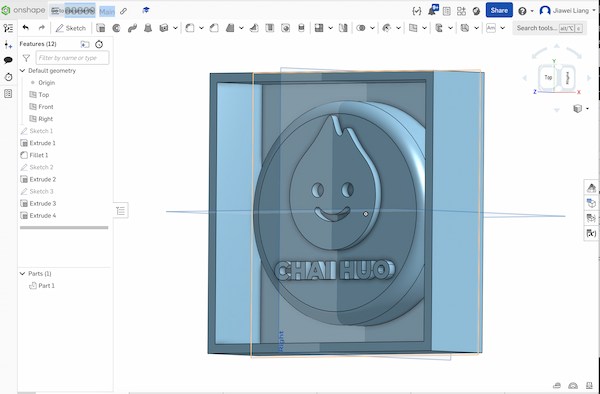
And Print it out:

Milling directly milling a mold
Milling, a traditional technique in mold-making, is noted for its capability to produce molds with smooth finishes and sharp outlines, making it ideal for larger or simpler shapes. The key benefit of milling is its superior surface finishing and clear design depiction. Its limitation, however, is in handling intricate details that are smaller than the milling bit itself, making it less suitable for highly detailed or complex mold designs.
After completing our group assignment, we evaluated the merits and limitations of both milling and 3D printing for mold production.
My group have directly designed a mold:
And mill it out:

My Method
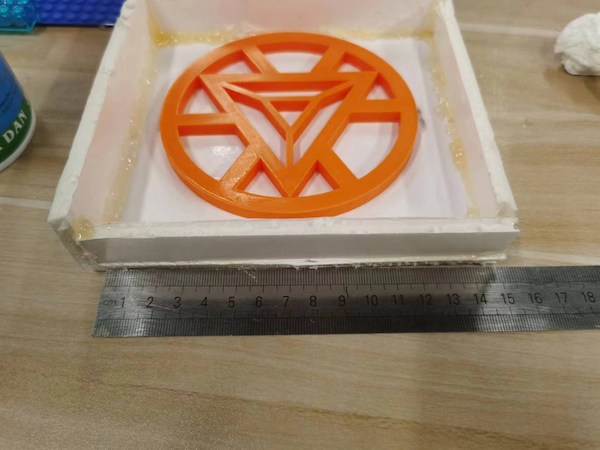
I am designing a module that is already formed, and use 3D printing to print it out:

Then I use a simple foam board to build a simple mold:

Method of Casting
Our group is all using AB Glue materials to cast the modules:
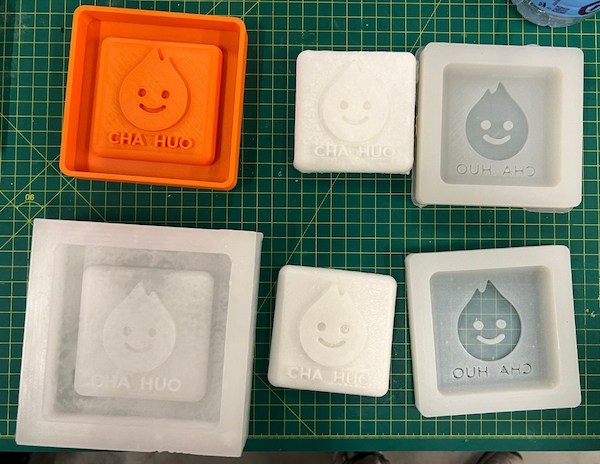

And mine is as well:
