Computer-Aided Design
CAD Design & Parametric Modeling
📌 Assignment Overview
This week focused on two main tasks: designing a 6-axis robotic arm prototype (Final Project Draft) and revisiting the modular box from Week 3. Used Fusion 360 with parametric modeling to make design changes easier.
📋 Assignment Process
This section documents the step-by-step process of completing this week's assignment.
1. Technical Workflow & AI Assistance
Environment Setup
- Operating System: macOS
- CAD Software: Fusion 360
- AI Tool: Gemini (for troubleshooting)
AI-Assisted Problem Solving
Used Gemini to solve these issues:
- Constraint Issues: Sketch constraints didn't update when parameters changed. Fixed by using "Update" command.
- Joint Alignment: Revolute Joints were misaligned. Used construction geometry and "Align" tool to fix.
- Parameter Organization: Grouped related parameters and used clear names for easier management.
2. Parametric Robotic Arm Design
Design Strategy
Started a new Fusion 360 file and:
- Created 6 empty components first
- Set the height of two cylinders and the circle diameter, shown in the parameter diagram below
- Made each component independent but connected
Component 1: Base
Design Process: Created a circular sketch with mounting holes. Used Extrude to make a cylindrical base. Added a central shaft for the joint connection.
Joint & Motion: Applied a Revolute Joint between Base and Link 1 for 360° rotation (first DOF).
Parameters:
Base_Diameter: Overall sizeBase_Height: HeightMount_Hole_Diameter: Hole sizesJoint_Shaft_Diameter: Connection size
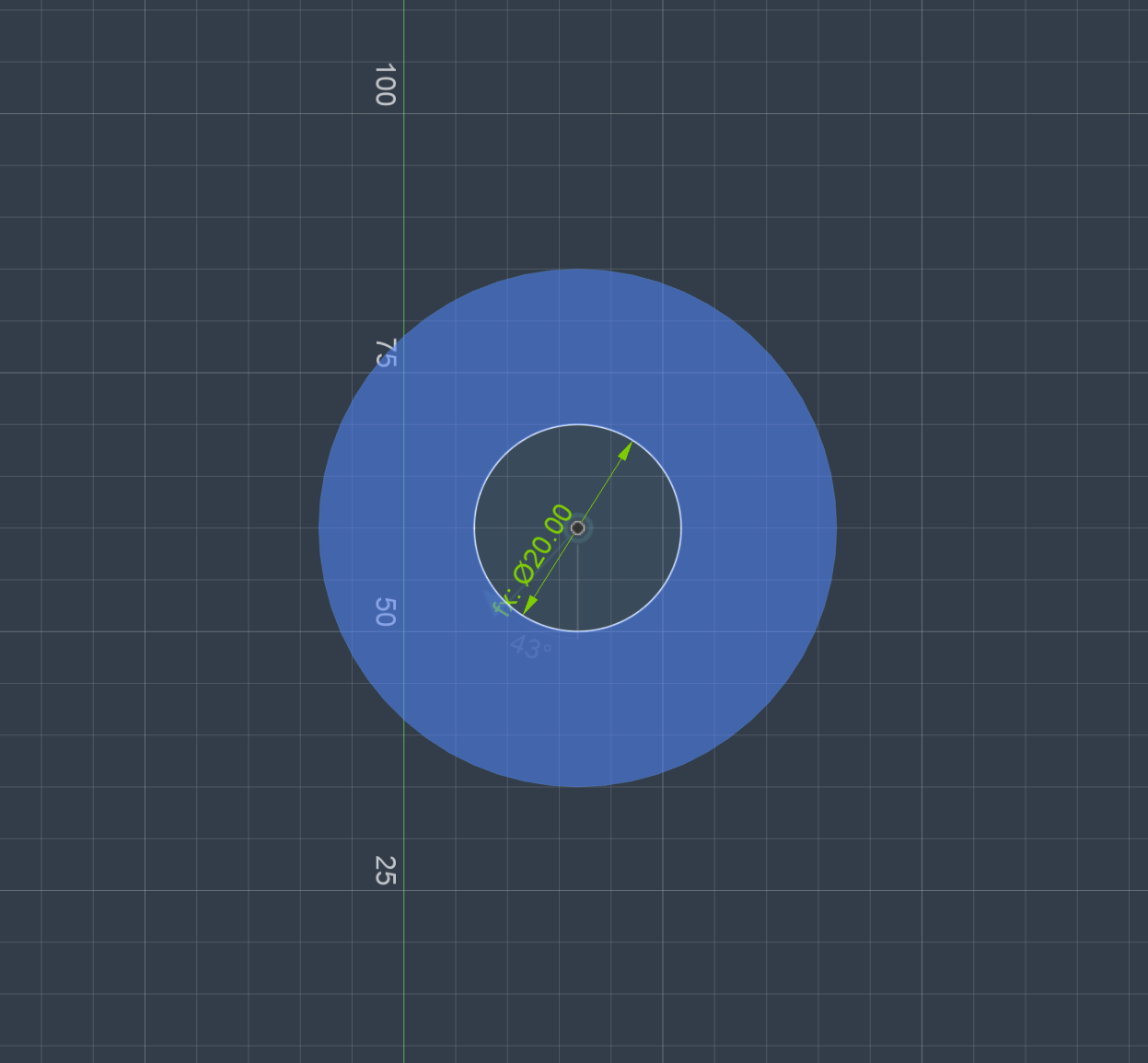
Component 1 Side Sketch
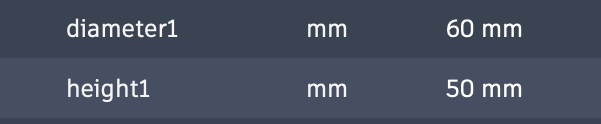
Component 1 Parameters
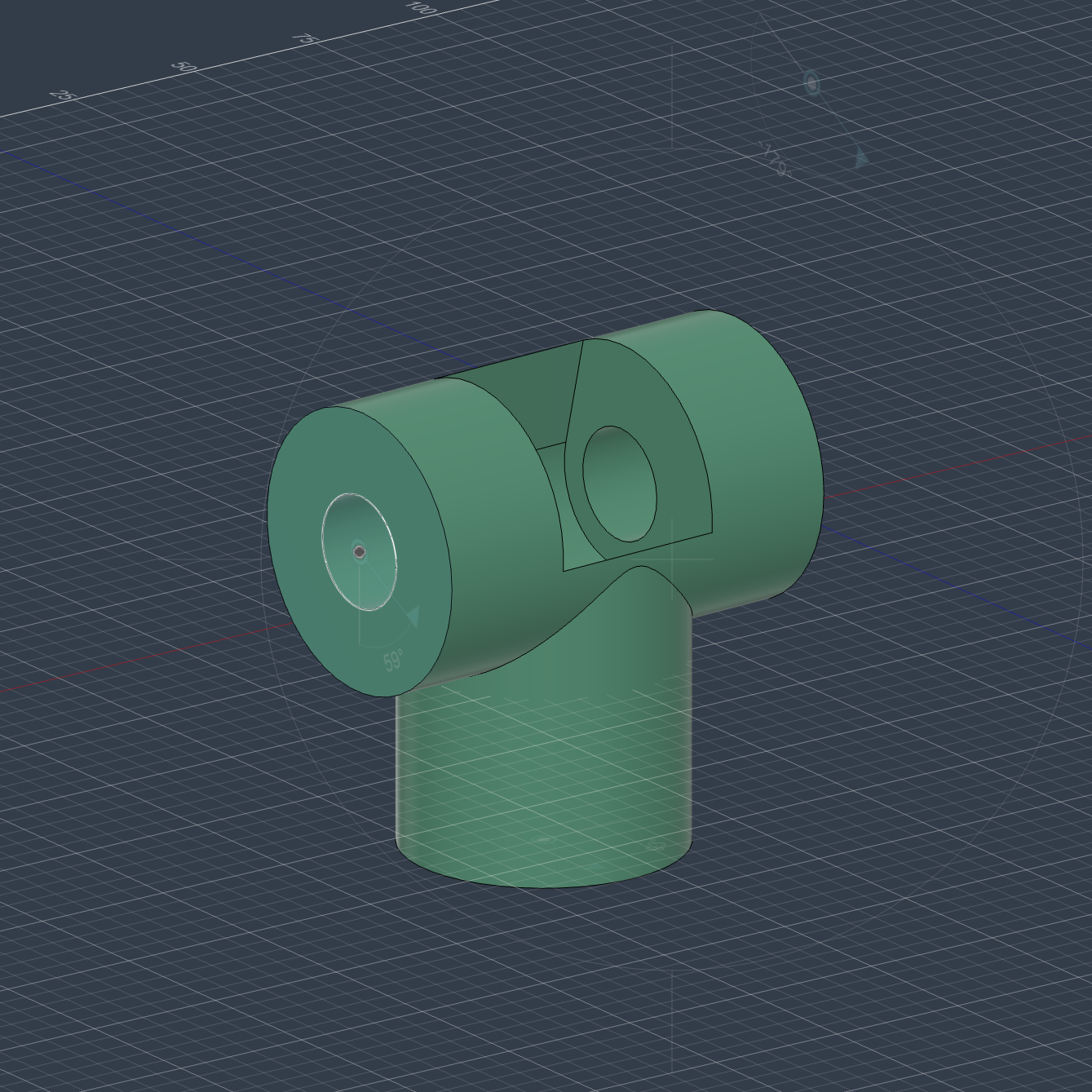
Component 1 Final Result
Component 2: Link 1 (Shoulder)
Design Process: Created a U-shaped bracket sketch. Used Extrude to make the 3D part. Added reinforcement at stress points.
Joint & Motion: Two Revolute Joints:
- To Base: Horizontal rotation
- To Link 2: Vertical rotation
Provides two DOF.
Parameters:
Link1_Length: Horizontal reachLink1_Thickness: Material thicknessJoint_Spacing: Distance between jointsBracket_Width: U-shape size
Component 2 Sketch
Component 2 Parameters
Component 2 Final Result
Component 3: Link 2 (Upper Arm)
Design Process: Made a rectangular sketch with rounded corners. Used Extrude to create a beam with internal ribs to reduce weight.
Joint & Motion: Revolute Joint to Link 1 for elbow bend/straighten motion.
Parameters:
Link2_Length: LengthLink2_Width: WidthLink2_Height: HeightRib_Thickness: Rib sizeElbow_Max_Angle: Max rotation
Component 3 Sketch
Component 3 Parameters
Component 3 Final Result
Component 4: Link 3 (Forearm)
Design Process: Similar to Link 2 but smaller to reduce weight. Added wrist mounting and cable channels. Used Extrude for the main body.
Joint & Motion: Revolute Joint at elbow for rotation. Prepared wrist connection point.
Parameters:
Link3_Length: LengthLink3_Width: WidthCable_Channel_Diameter: Cable spaceWrist_Mount_Offset: Wrist position
Component 4 Sketch
Component 4 Parameters
Component 4 Final Result
Component 5: Wrist Assembly
Design Process: Created a compact housing with two joints for pitch and roll. Added end effector mount and actuator space. Used Extrude for the housing.
Joint & Motion: Two Revolute Joints:
- Wrist Pitch: Up/down motion
- Wrist Roll: Rotation around forearm
Parameters:
Wrist_Housing_Diameter: SizeWrist_Pitch_Range: Pitch limitWrist_Roll_Range: Roll limitEnd_Effector_Mount_Diameter: Mount size
Component 5 Sketch
Component 5 Parameters
Component 5 Final Result
Component 6: End Effector Base
Design Process: Created a circular sketch for tool mounting. Used Extrude to make a cylindrical base with tool retention features. Added alignment and fastener holes.
Joint & Motion: Final Revolute Joint to wrist (6th DOF) for independent rotation.
Parameters:
End_Effector_Base_Diameter: Mount sizeTool_Mount_Pattern: Hole patternRetention_Feature_Depth: Lock depthRotation_Range: Max rotation
Component 6 Sketch
Component 6 Parameters
Component 6 Final Result
3. Modular Box Integration
Revisited the modular box from Week 3 and made it parametric:
- Fitment: Joint clearances controlled by parameters (
Joint_Clearance,Material_Thickness) - Scalability: Box size adjustable via parameters (
Box_Length,Box_Width,Box_Height) - Quick Changes: Can try different sizes without recalculating joints
📝 Assignment Notes
Parametric modeling worked well for this project. Key benefits:
- Quick Changes: Modify parameters instead of editing sketches
- Consistency: Related dimensions stay synchronized
- Easy to Maintain: Clear structure and naming
- Manufacturing Ready: Can quickly generate different sizes
All 6 components respond to parameter changes while keeping joints and assembly correct. This will help with future development.