Webpage building and design
Web Development and Setup
📌 Assignment Overview
This week focused on planning and sketching a potential final project and working through a git tutorial.
📋 Assignment Process
This section documents the step-by-step process of completing this week's assignment.
🖥️ Environment Configuration
Operating System: Mac
Environment Setup Software: Node.js
Download: https://nodejs.org/en
Tools Used: Cursor![]() , Gemini
, Gemini![]()
Stage 1
Create Repository
- Open
github, register, and create a newrepository - After naming, go to
settings,pages, selectmain, and create a static page
Download noteis to create environment
Enter cursor, open the folder created on desktop
Associate cursor with github
Set your GitHub username
git config --global user.name "your username"Set your GitHub registered email
git config --global user.email "your_email@gmail.com"Stage 2
- Enter the folder: In the
Cursorterminal, ensure the path is correct. - Initialize repository:
git init - Stage and commit files:
git add . git commit -m "version number" git push origin main
Stage 3: GitHub Remote Association
Generate Token
- Go to GitHub → Settings → Developer settings → Tokens (classic) → Generate new token
- Check
repopermission, save the generatedghp...string
1. Associate remote address
The address here should include your Token, so you won't need to enter your password repeatedly later.
git remote add origin https://YOUR_TOKEN@github.com/your_username/your_repository_name.git2. Set main branch and push to cloud
git branch -M main
git push -u origin main --forceStage 4
I used cursor's AI with the following prompt:
I now want to create a FabAcademy 2026 personal website,
style reference apple.com, needs to include Home, Dailywork,
Finalproject, Aboutme, where Dailywork has 20 assignments inside,
and needs two modes, dark mode and light mode, help me generate it.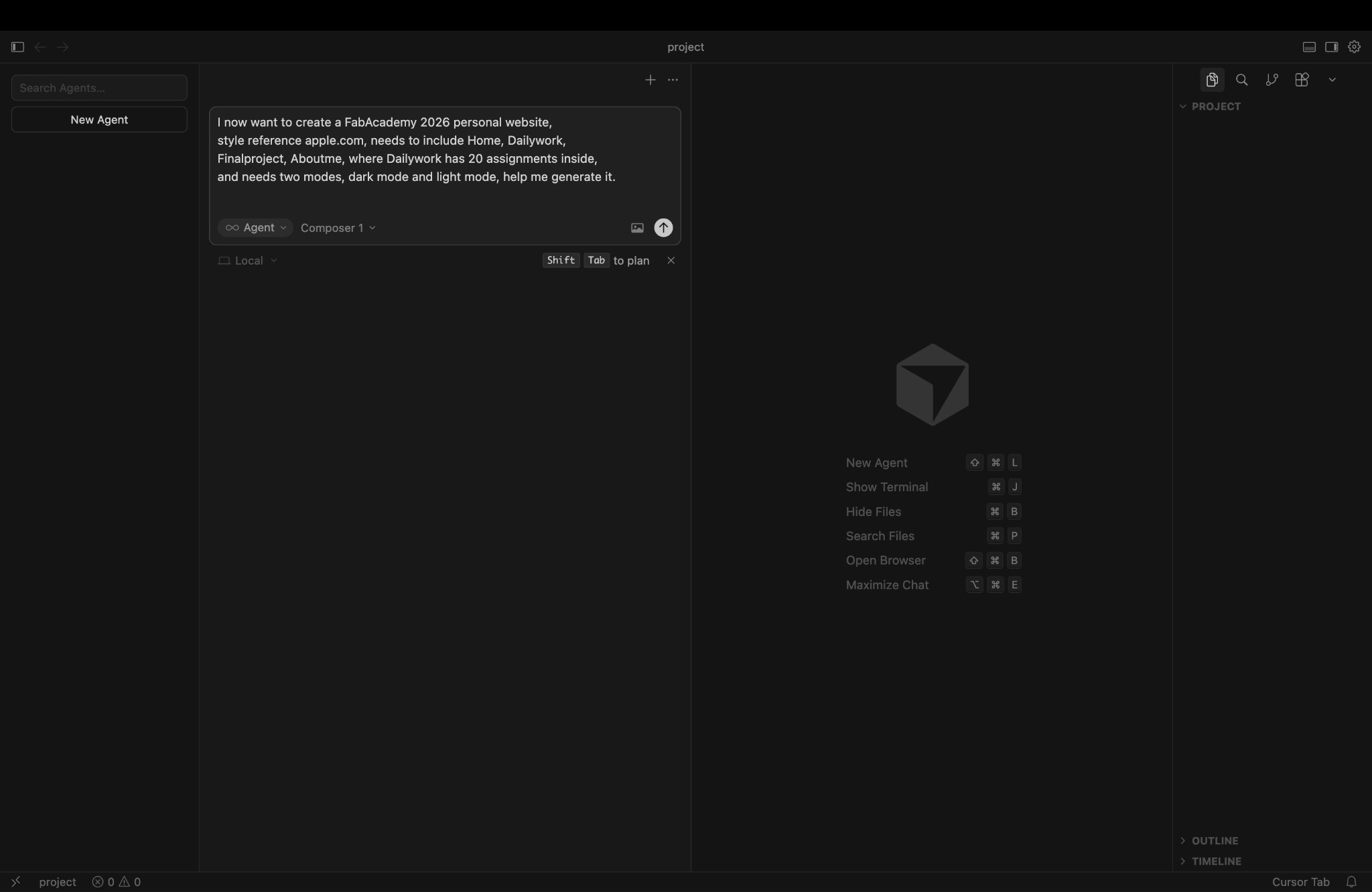
Cursor Generation Interface
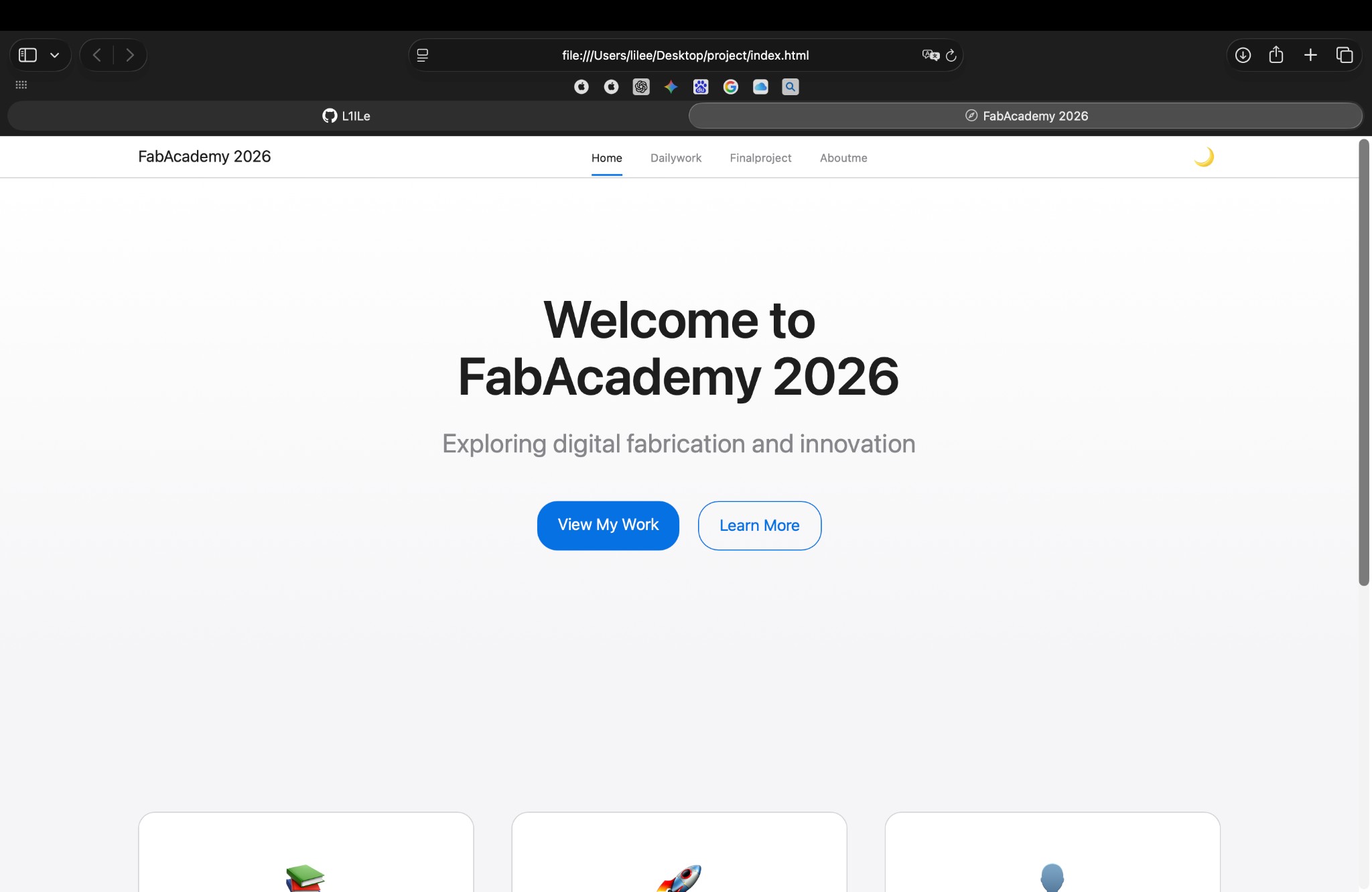
Prompt Generation Result
Subsequently used gemini for code troubleshooting, and continued to use cursor for optimization.
After completion, perform version upload
| Steps | Command |
|---|---|
| 1. Record changes | git add . |
| 2. Write commit message | git commit -m "update description" |
| 3. Send to cloud | git push origin main |
🖼️ Image Management
This section covers the process of managing images for the website using PicGo and GitHub.
Step 1: Download PicGo
Download PicGo from: https://github.com/Molunerfinn/PicGo
Install PicGo on your Mac system.
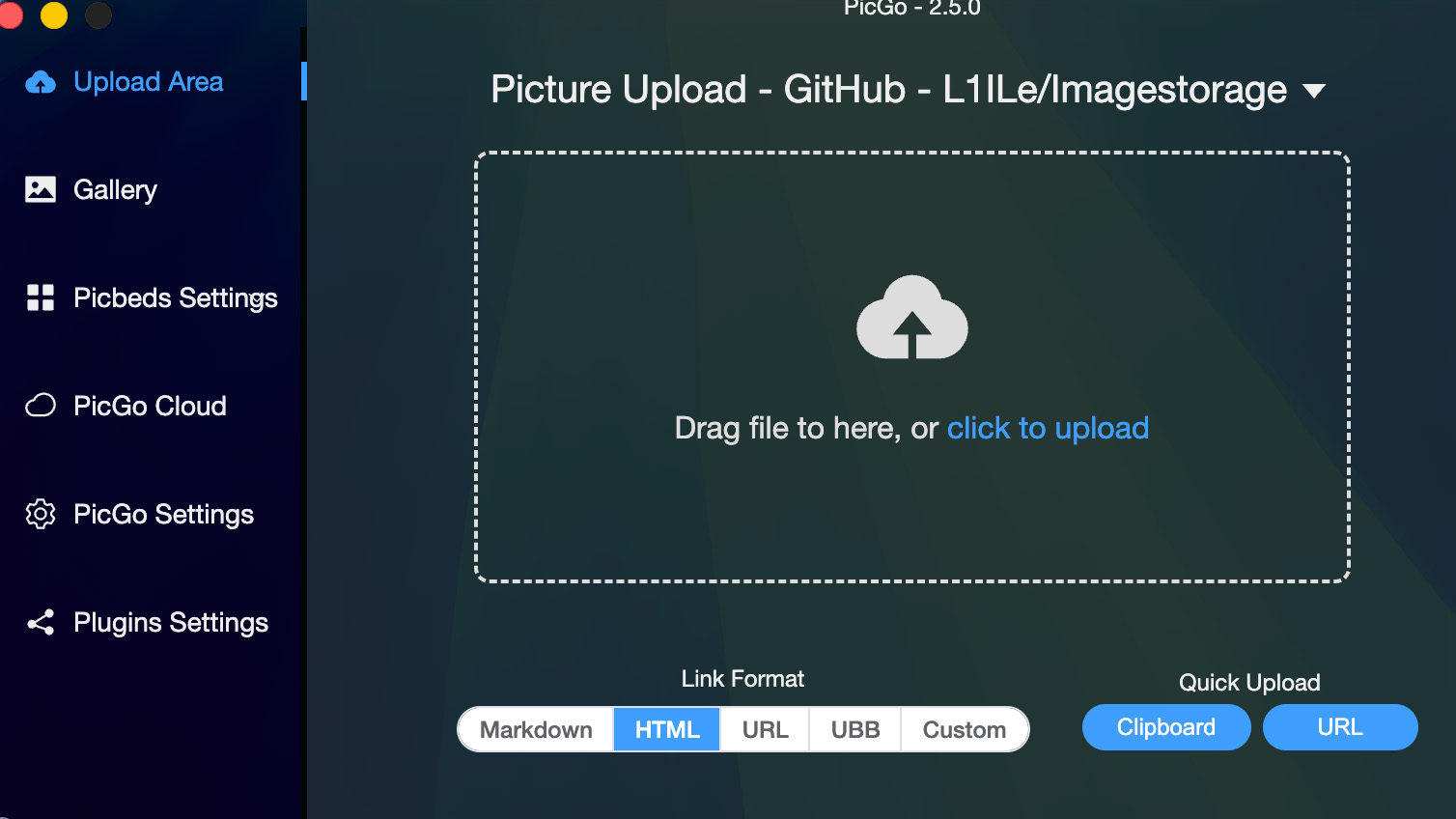
PicGo Application Interface
Step 2: Create GitHub Repository for Image Storage
Go to GitHub and create a new repository named Imagestorage (or any name you prefer).
- Make sure the repository is set to
Publicif you want to access images via public URLs - Initialize with a README file (optional)
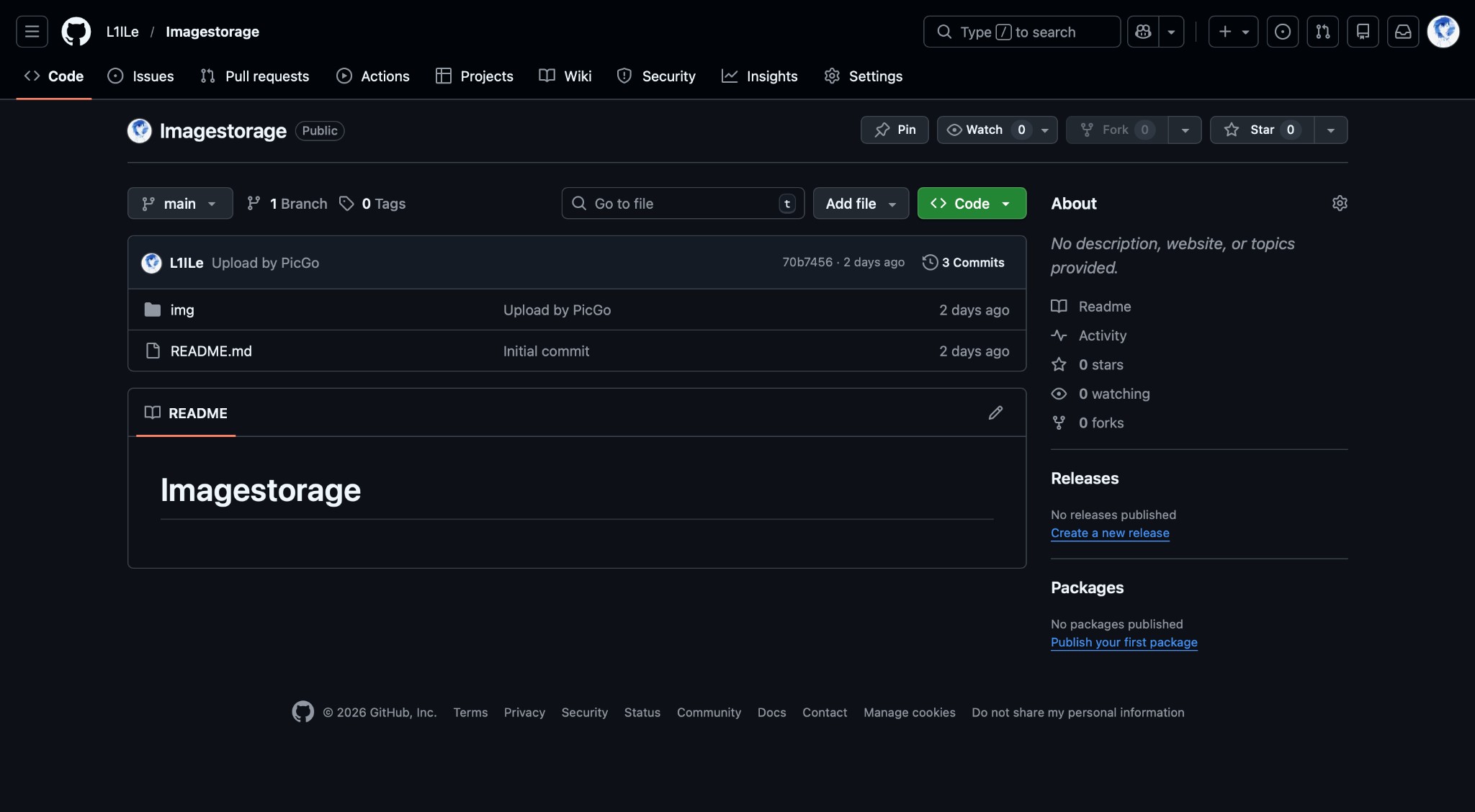
GitHub Imagestorage Repository
Step 3: Generate Personal Access Token
Go to GitHub → Settings → Developer settings → Personal access tokens → Tokens (classic)
- Click "Generate new token (classic)"
- Give it a descriptive name (e.g., "PicGo Image Upload")
- Select the
reposcope/permission - Click "Generate token"
- Important: Copy the token immediately - you won't be able to see it again!
Step 4: Configure PicGo
Open PicGo and configure it with the following settings:
- Go to
PicGo Settings→Picture Bed - Select
GitHubas your picture bed - Fill in the configuration:
- Repository:
your_username/Imagestorage - Branch:
main(ormaster) - Token: Paste your GitHub Personal Access Token
- Storage Path:
img/(optional, for organizing images) - Custom Domain: Leave empty or use GitHub Pages URL if configured
- Repository:
- Click "Confirm" or "Apply" to save settings
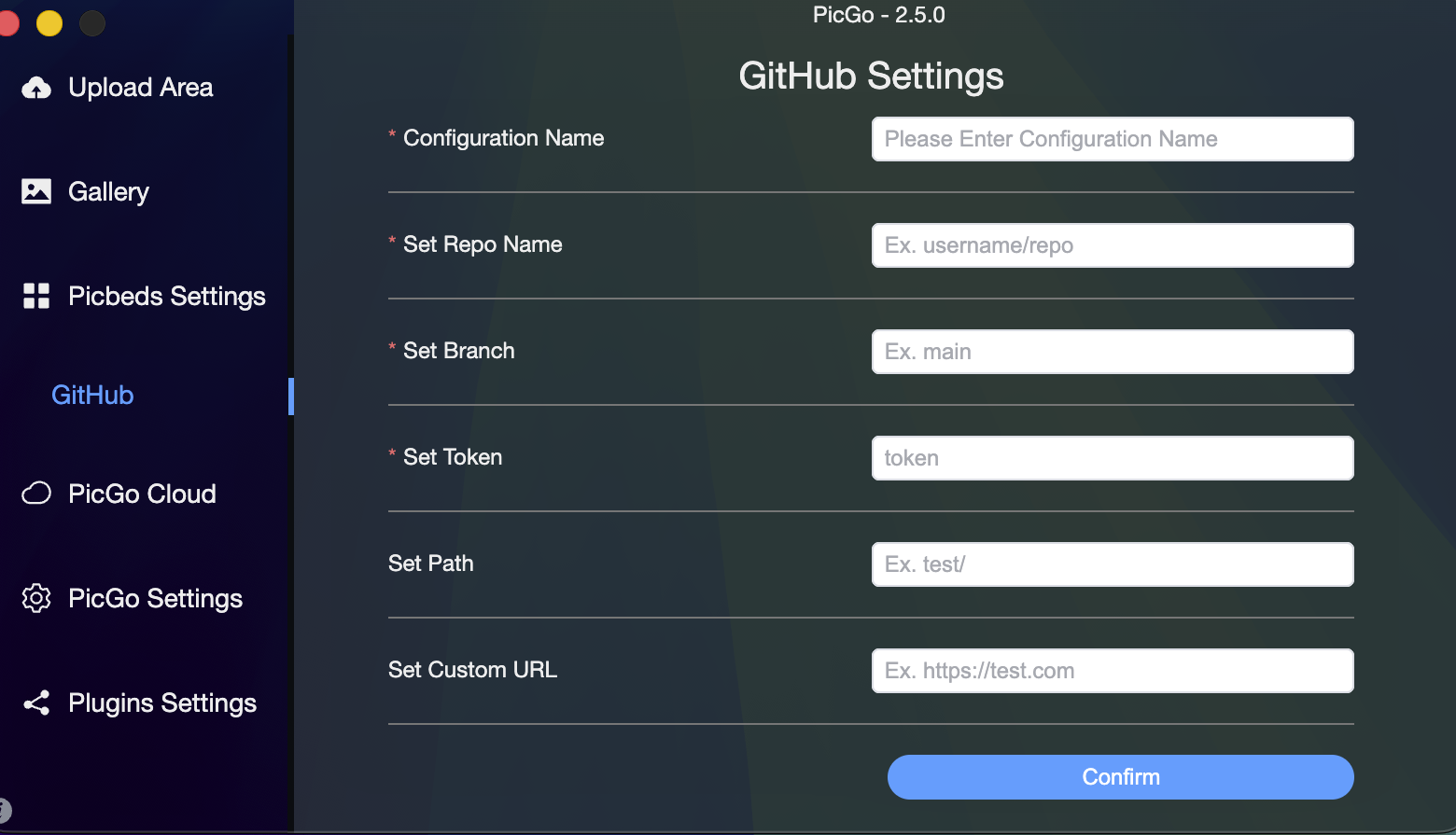
PicGo GitHub Settings Configuration
Step 5: Upload Images and Generate HTML Links
Once configured, you can upload images using PicGo:
- Drag and drop images into PicGo, or click "Upload" to select images
- PicGo will automatically upload images to your GitHub repository
- After upload, PicGo will copy the image URL to your clipboard
- Use the URL in your HTML code:
<img src="IMAGE_URL" alt="description">
Tips
- You can set PicGo to automatically copy URLs after upload in settings
- Use descriptive filenames for better organization
- Consider organizing images in subfolders using the Storage Path setting
- GitHub has a file size limit (usually 100MB per file), so compress large images if needed
📝 Assignment Notes
Any additional observations, tips, or resources that might be useful for future reference.