Moulding and Casting
Overview of week 13
Group Assignment
- Review the safety data sheets for each of our molding and casting materials
- Make and compare test casts with each of them
- Compare printing vs milling molds
Individual Assignment
- Design a mold around the process we'll be using, produce it with a smooth surface finish that does not show the production process, and use it to cast parts.
Group Assignment :
I referred to each material’s datasheet to understand the correct mixing ratios, curing times, and safety precautions.
Individual Assignment :
Moulding and Casting
Moulding
Moulding is a manufacturing process used to shape materials like plastic, metal, or rubber by placing them into a hollow cavity. The material is heated, injected or pressed into the mould, and then cooled to form a solid shape. It is widely used in mass production due to its efficiency and repeatability. The quality of the mould directly affects the accuracy and surface finish of the final product.
Types
Injection moulding
Molten plastic is injected into a mould to form complex plastic parts.
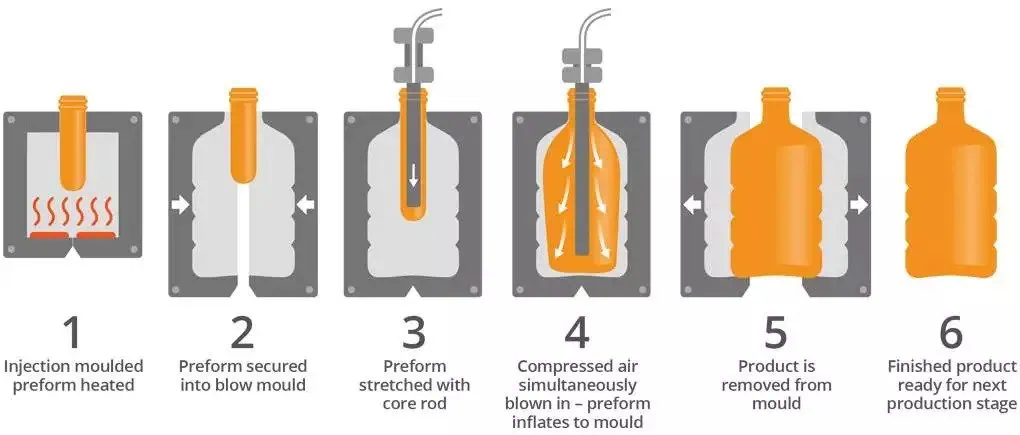
Blow moulding
Used for making hollow plastic parts like bottles using air pressure.
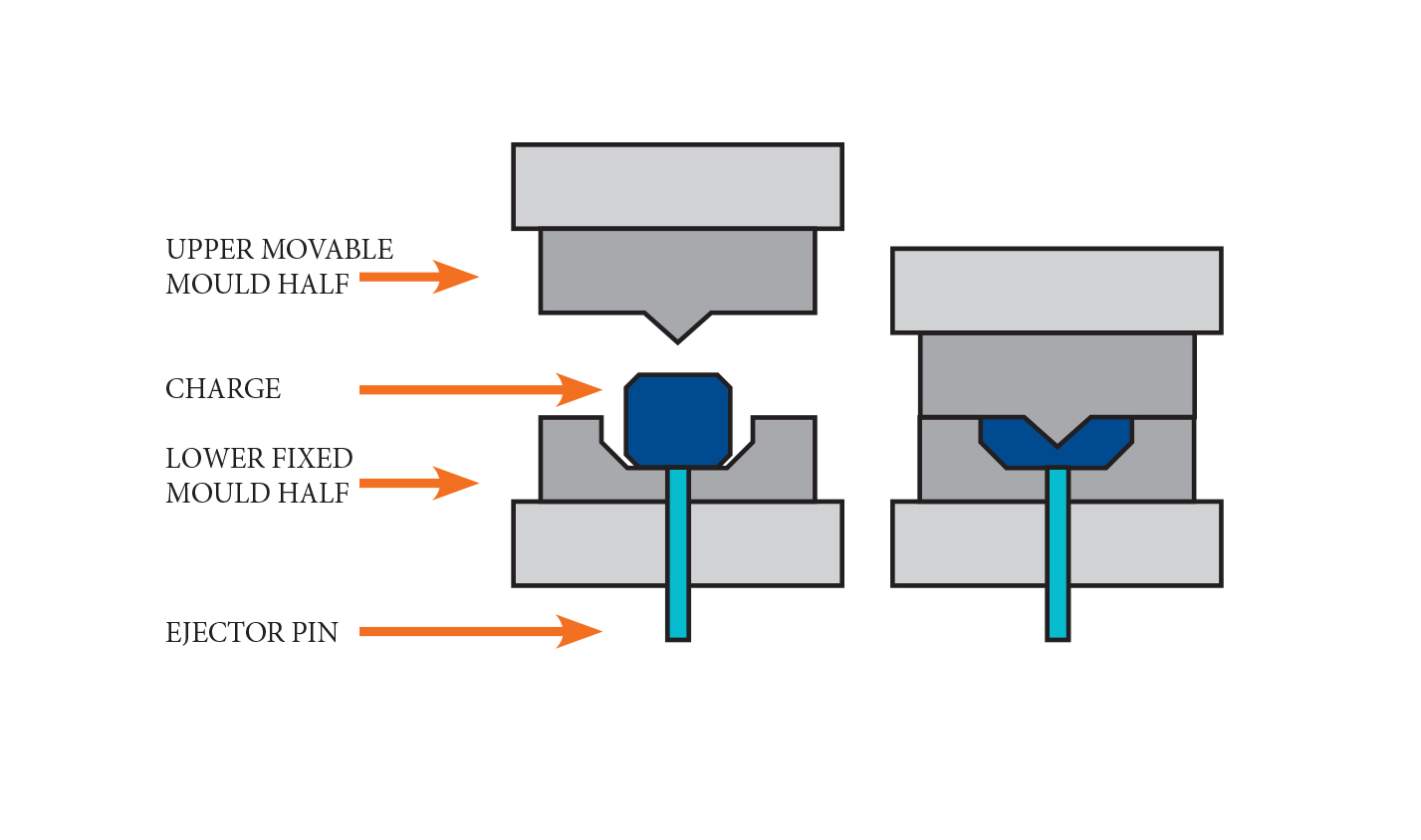
Compression molding
Preheated material is placed into a heated mould and compressed into shape.
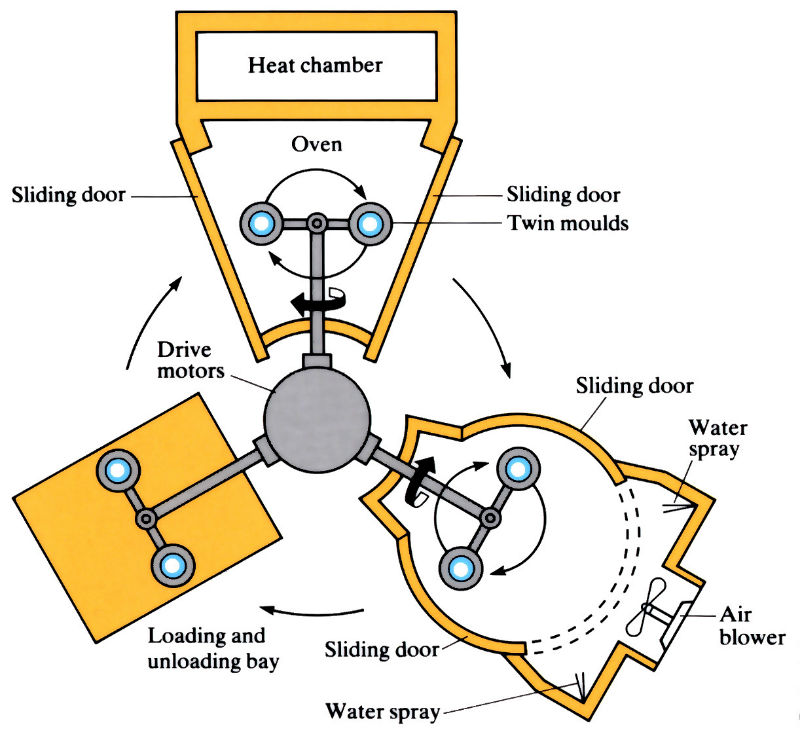
Rotational molding
Mould is rotated in multiple axes to coat and form hollow plastic products.
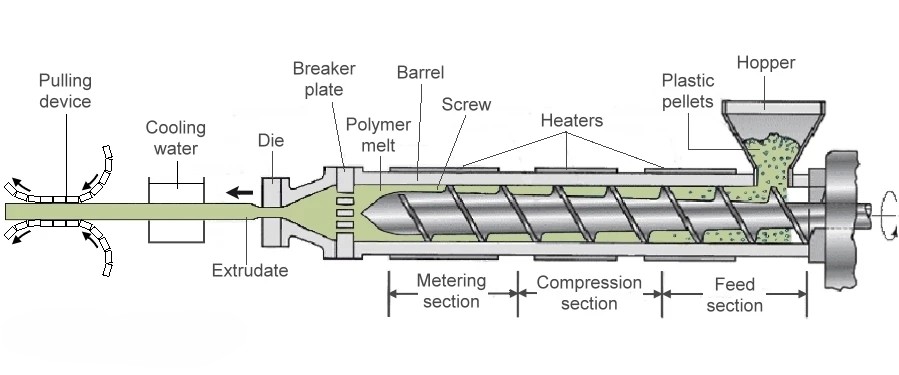
Extrusion moulding
Material is forced through a die to form long shapes like pipes and tubes.
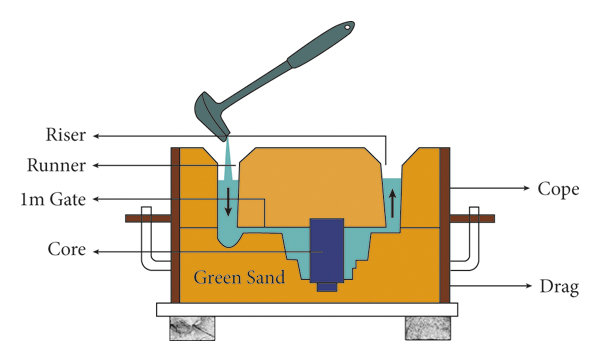
Sand Moulding
Uses sand to create moulds for metal casting (common in foundries)
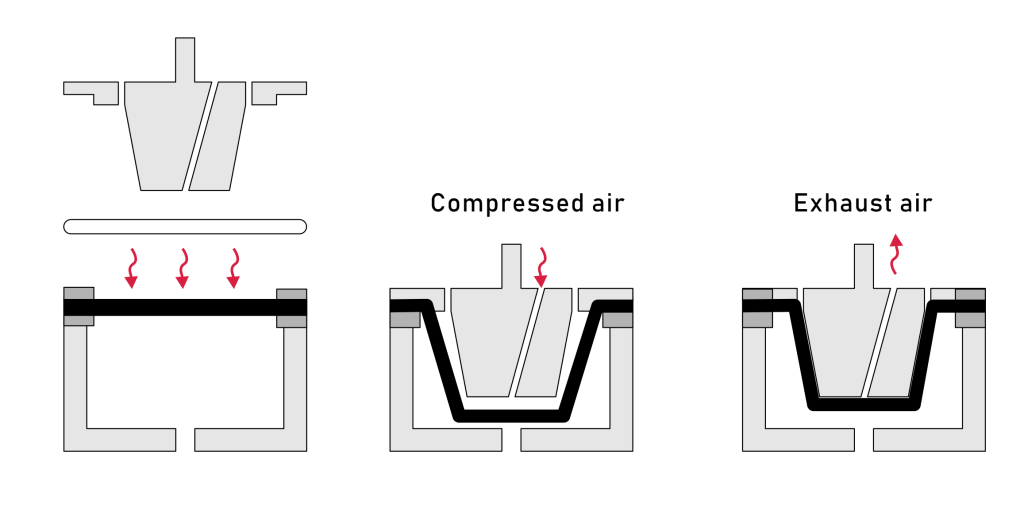
Vacuum forming
Heated plastic sheet is shaped over a mould using vacuum pressure.
Transfer moulding
Material is heated, then transferred into a mould cavity (used for electronics)
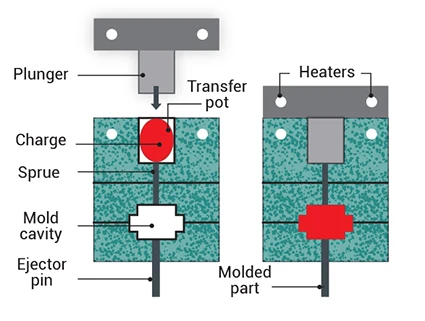
Casting
Casting is a manufacturing process where molten metal is poured into a mould cavity to take its shape upon cooling and solidification. It is one of the oldest and most versatile methods for making complex metal parts.
Types
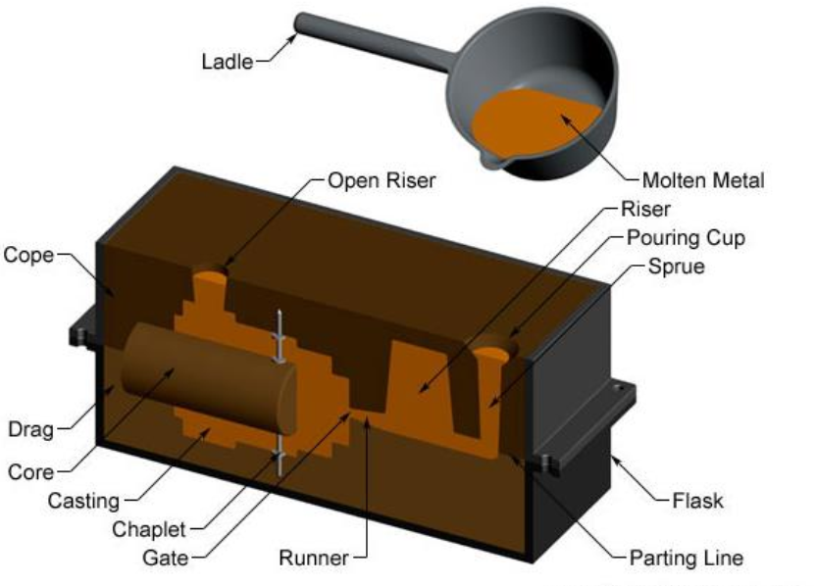
Sand Casting
Uses a sand-based mould, ideal for large, simple castings and quick production.
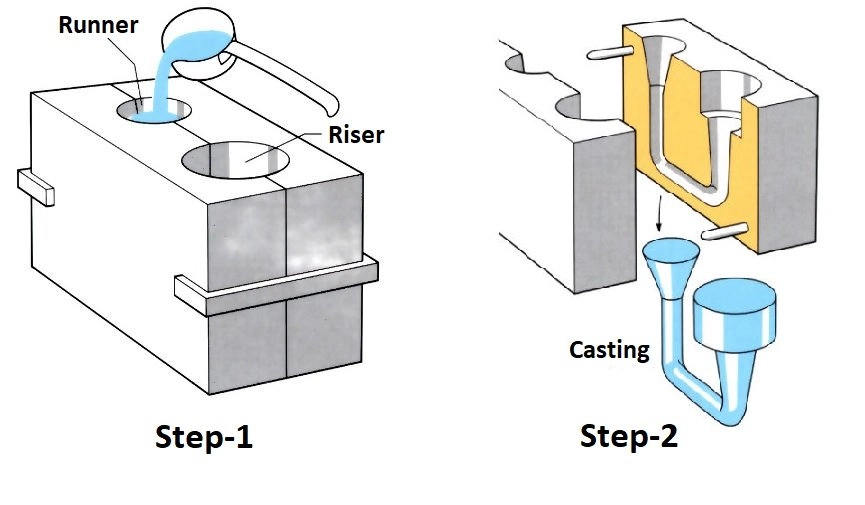
Die Casting
Forces molten metal under high pressure into a metal mould for high precision and smooth finishes.
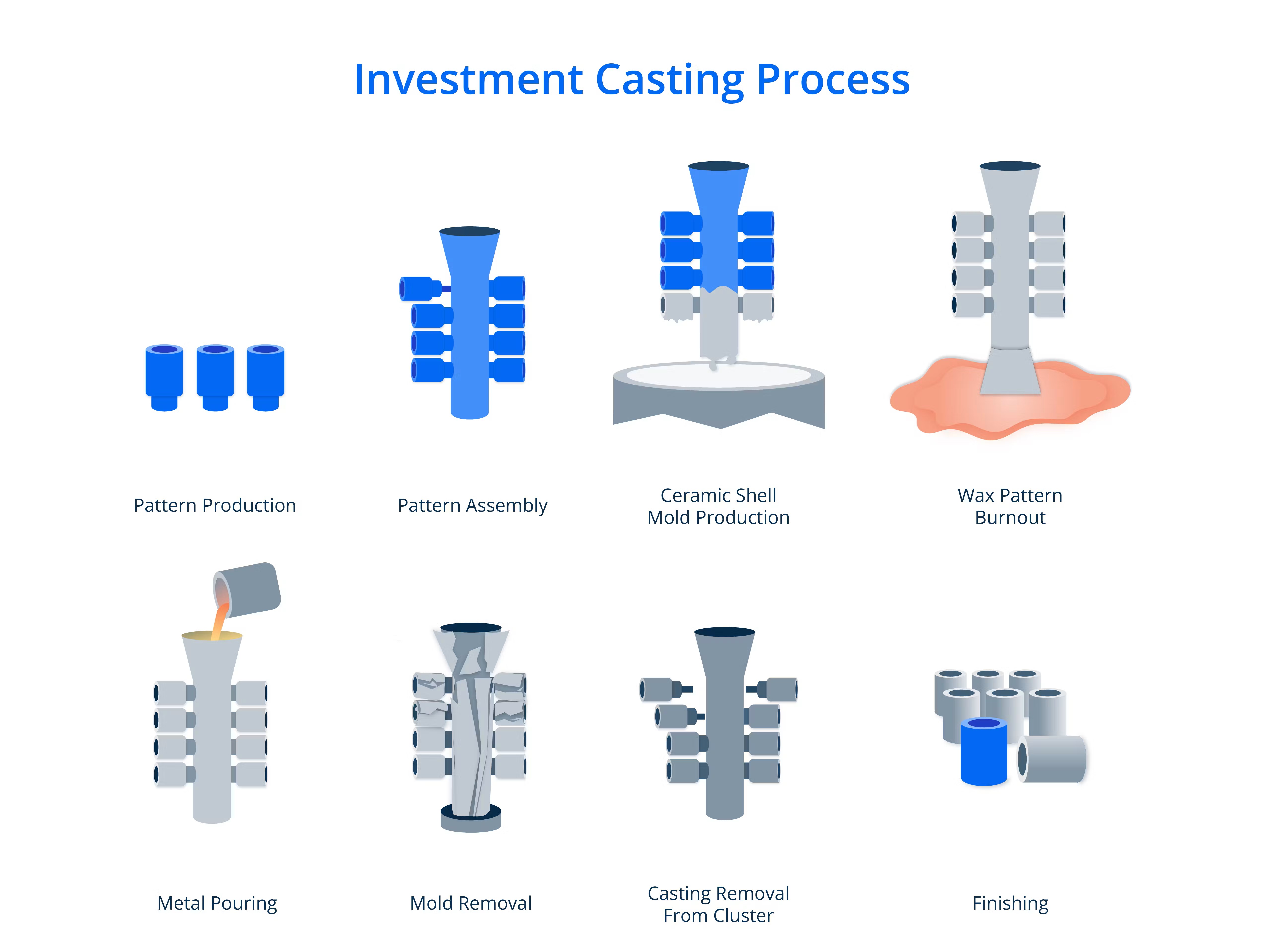
Investment Casting
Involves a wax pattern covered by ceramic, yielding high-detail, intricate parts.
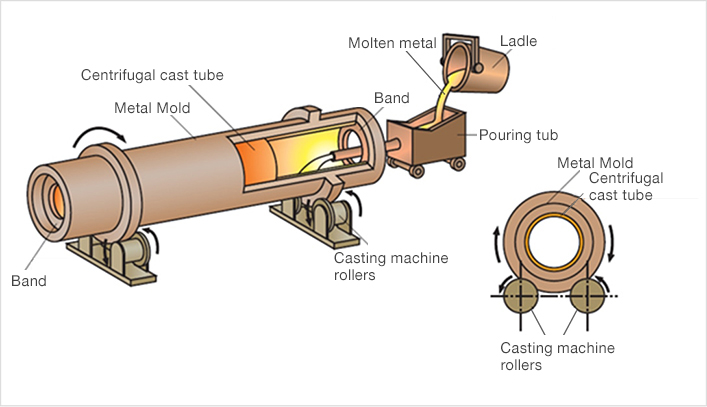
Centrifugal Casting
Rotates the mould to evenly distribute the molten metal, effective for cylindrical parts.
3D Design
Fusion 360
I start my assignment in 3D design, I create the sketch and give the dimensions respectively. For the dimension I using the parametric, if any changes need in future.
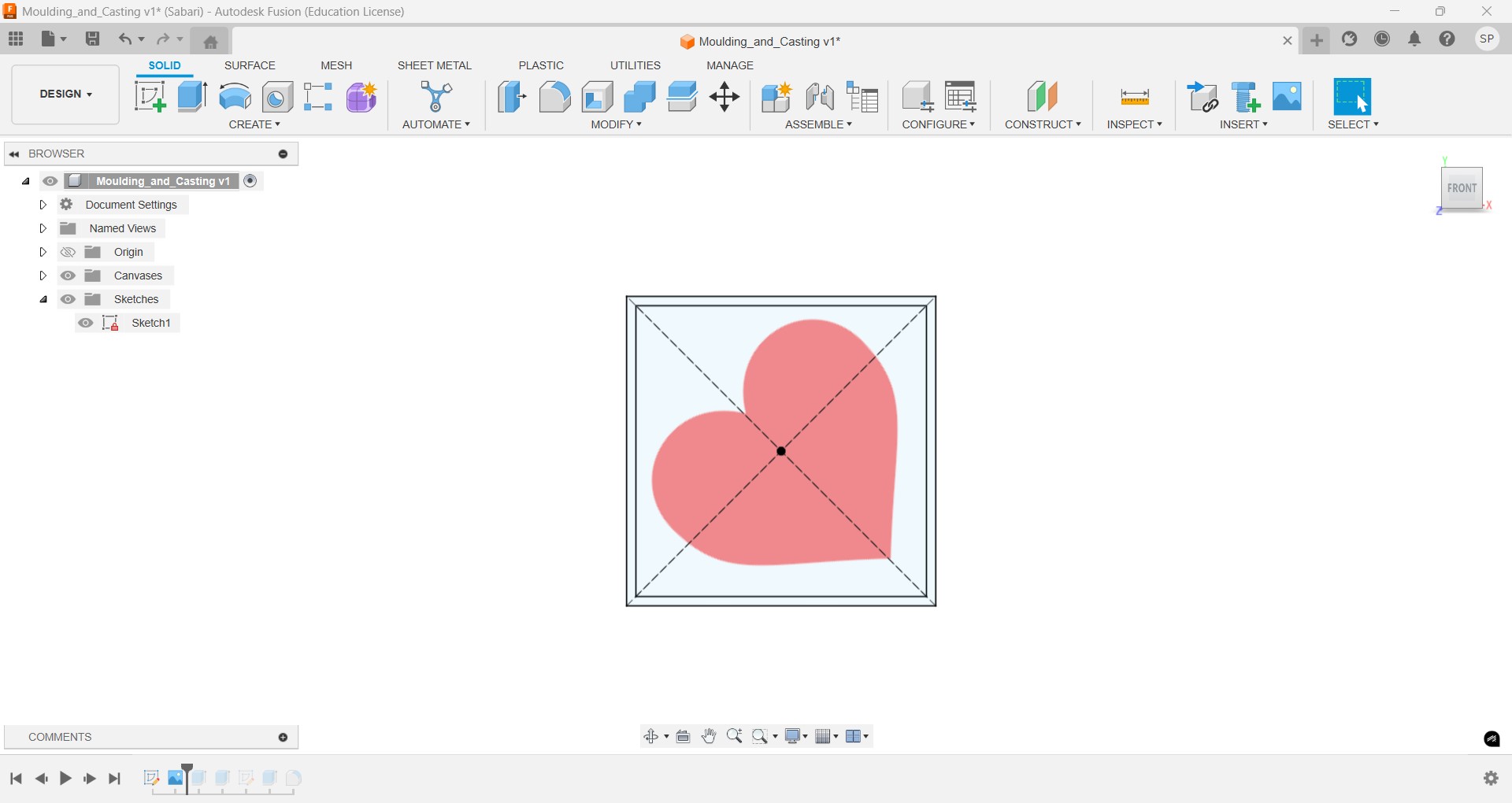
To draw the heart desing properly I take one reference image from online and attached it through canva option.

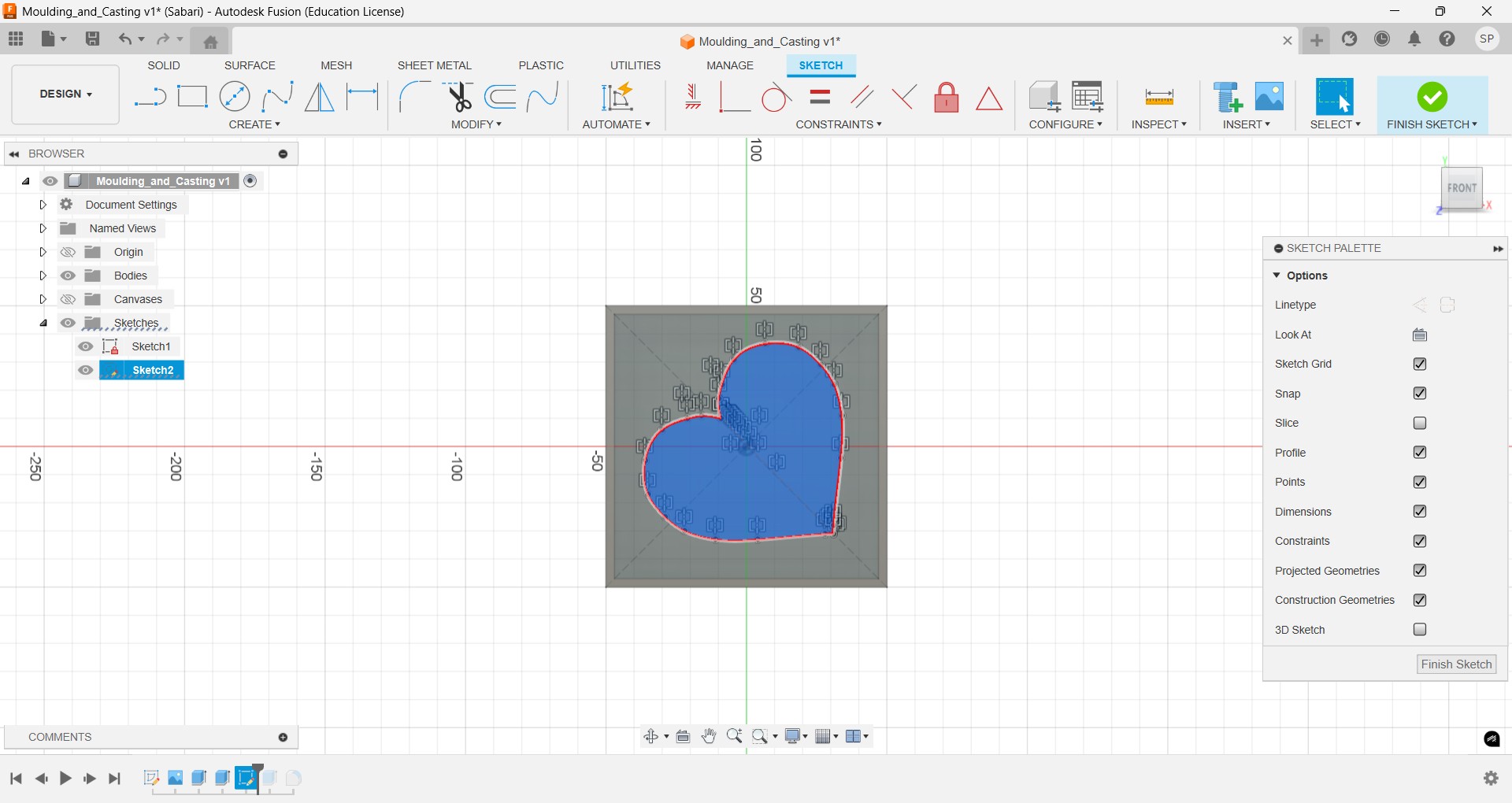
Then by using the extruder command I extrude it upto my required lenght which is I set in the parametersnand draw the line of heart by the help of reference image on above the extruder body.
Slicing
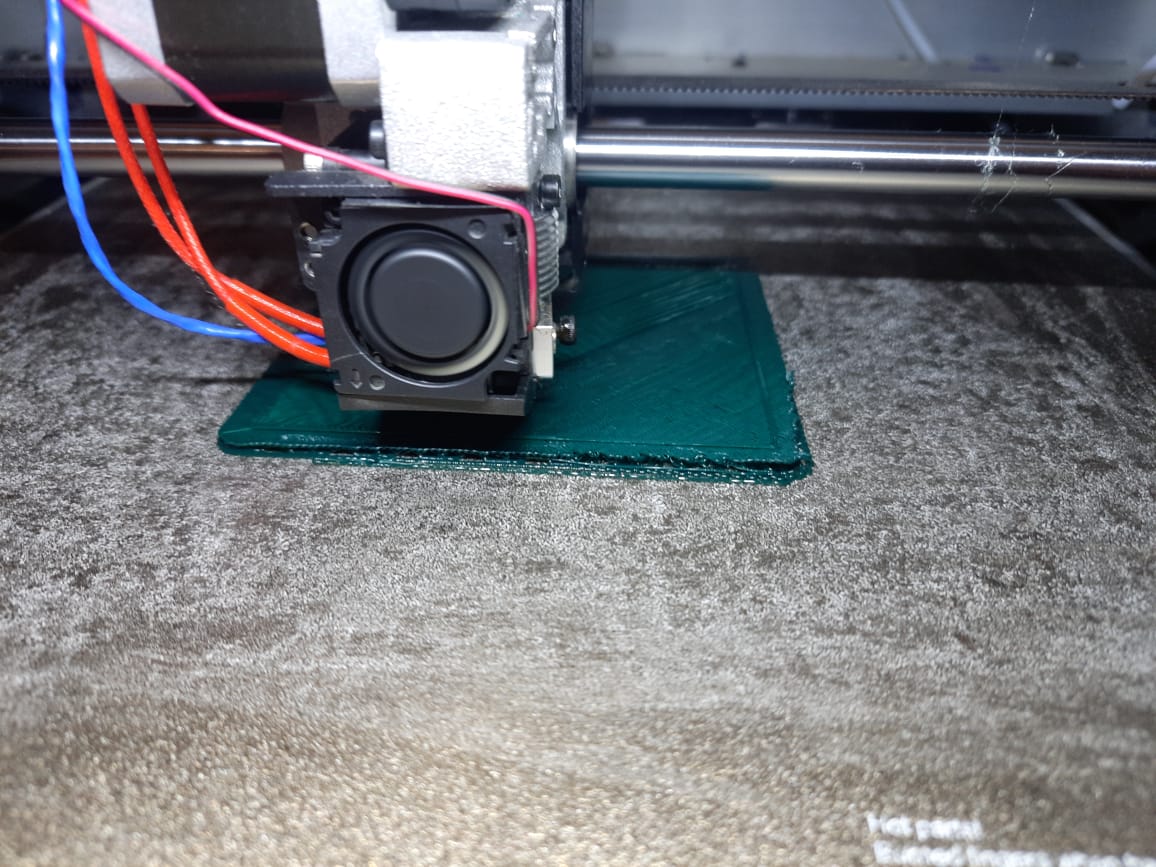
After done everything I moved to do slicing so I uses the Flash print software, I load the STL file in the software.
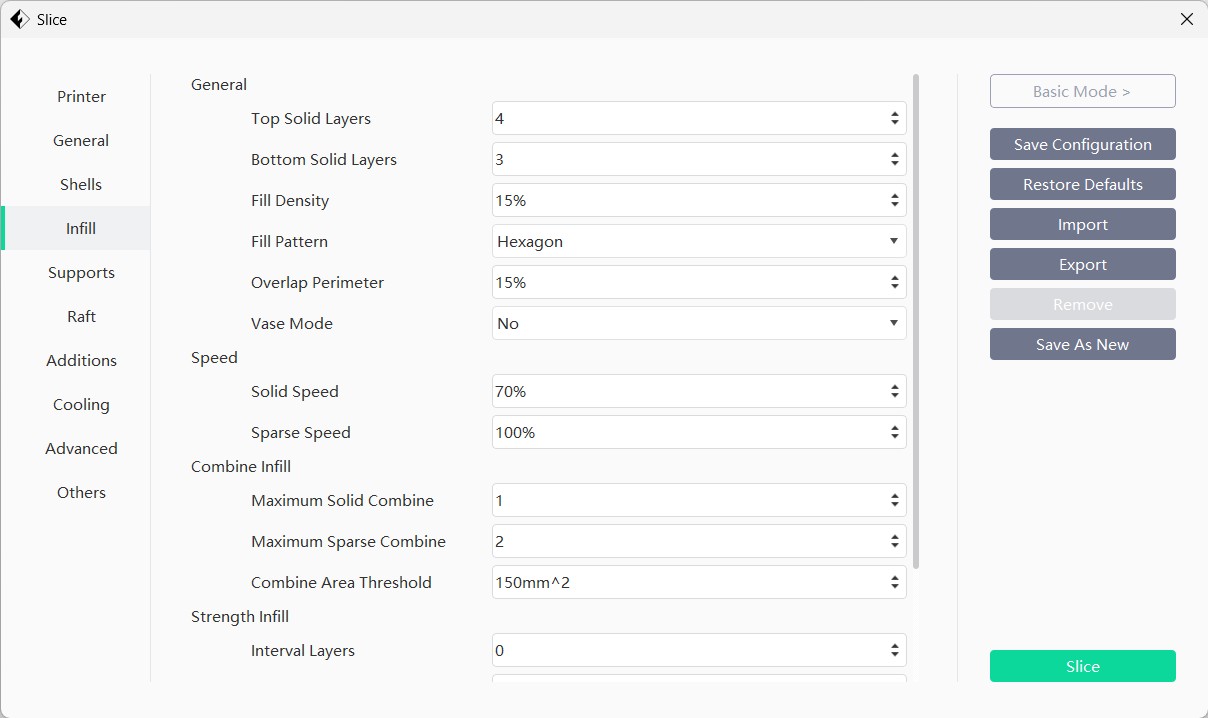
I uses the PLA material - Nozzle temp : 205 degree celcius, Bed temp : 55 degree celcius, Infill pattern - Hexagon, Infill density : 15 %
Then I slicing it, opent the preview tap and check the printing time as well, it look lie it will take around 5 hrs.
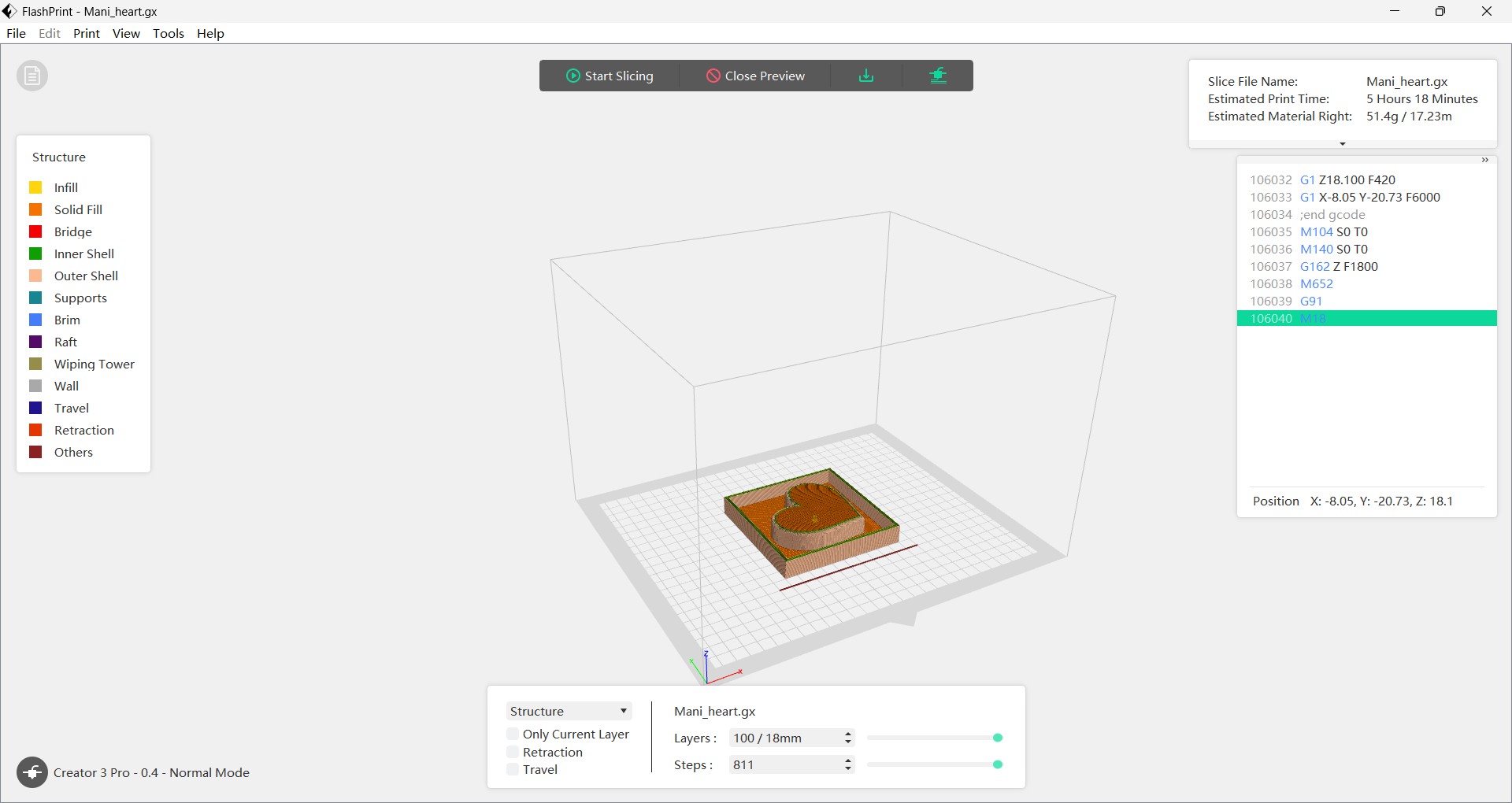
Then I download it into the gcode file.
Moulding Process


To prepare the mold, the initial step involved determining the required quantity of silicone for the negative mold. This was achieved by filling the 3D-printed cavity with water and measuring the volume used. The measured water volume provided an accurate estimate of the silicone material needed for casting.
The water was then transferred into a measuring beaker to determine its volume precisely. This step ensured an accurate calculation of the silicone required for mold making. Based on the measured volume, the silicone mixture was prepared accordingly to achieve a proper fill, avoiding both excess and shortage.
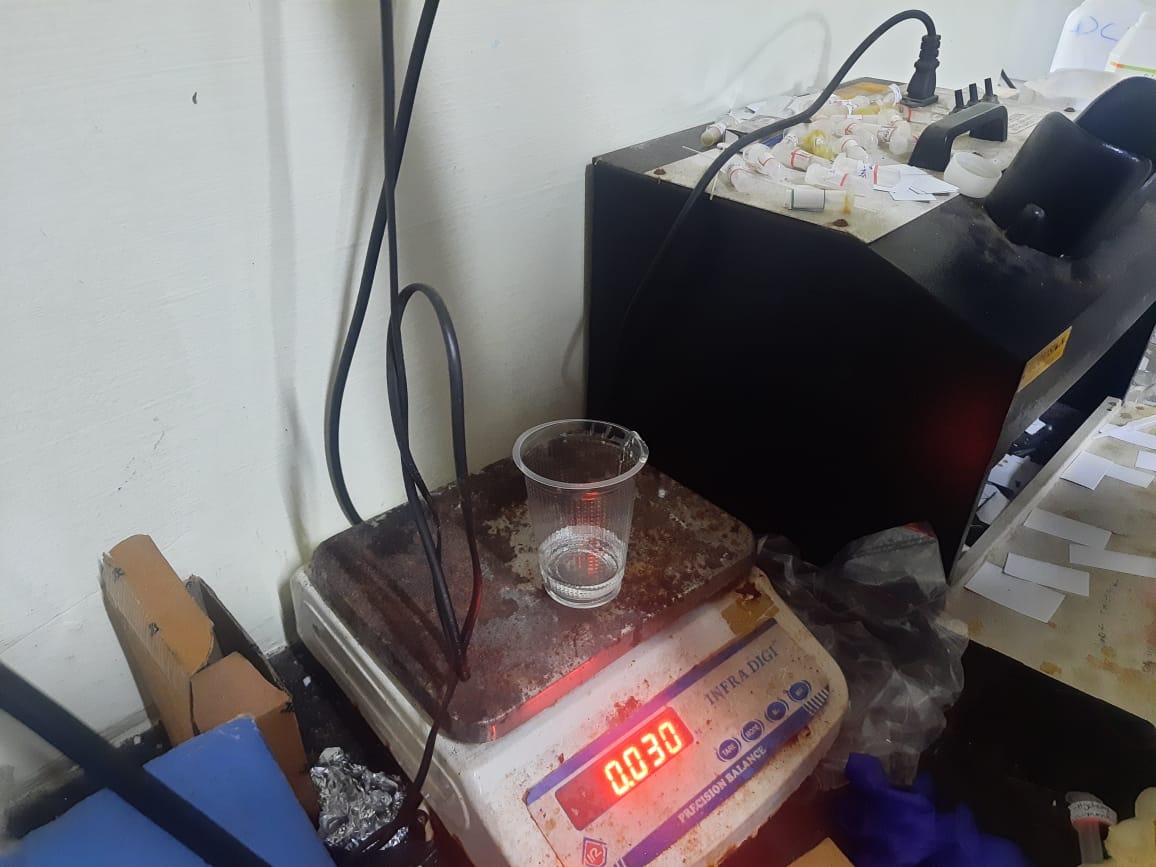

Prior to measuring the water volume, the beaker was tared by recording its empty weight. This ensured that only the actual volume of water was measured accurately. After taring, the water from the mold cavity was poured into the beaker to determine the precise amount of silicone required.
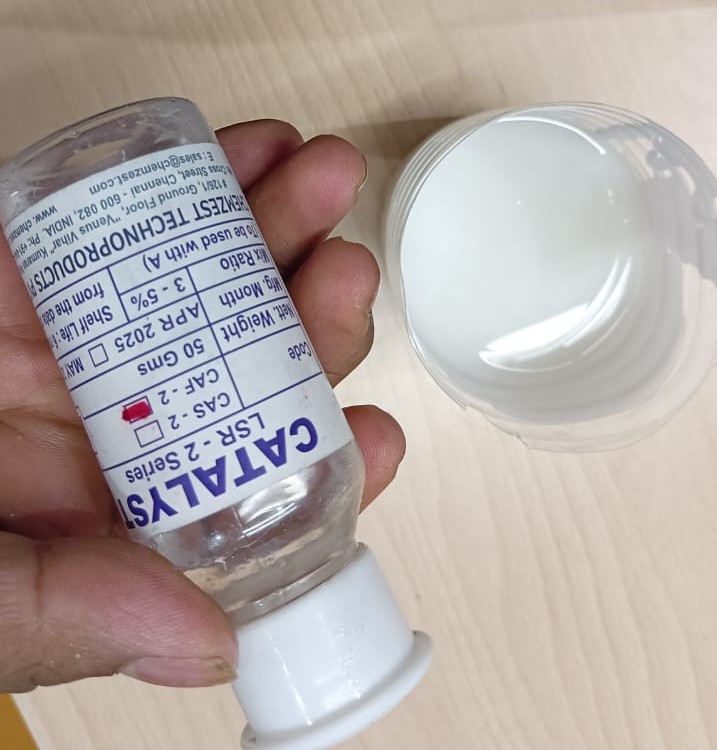
Using the measured volume and an online silicone mold calculator, I calculated the required amounts of silicone base and catalyst. The calculator provided the precise ratio and quantities needed for both components based on the water volume. This ensured accurate mixing and proper curing, resulting in a durable, bubble-free mold.
The silicone base and catalyst were slowly poured into a plastic beaker to begin the mixing process.
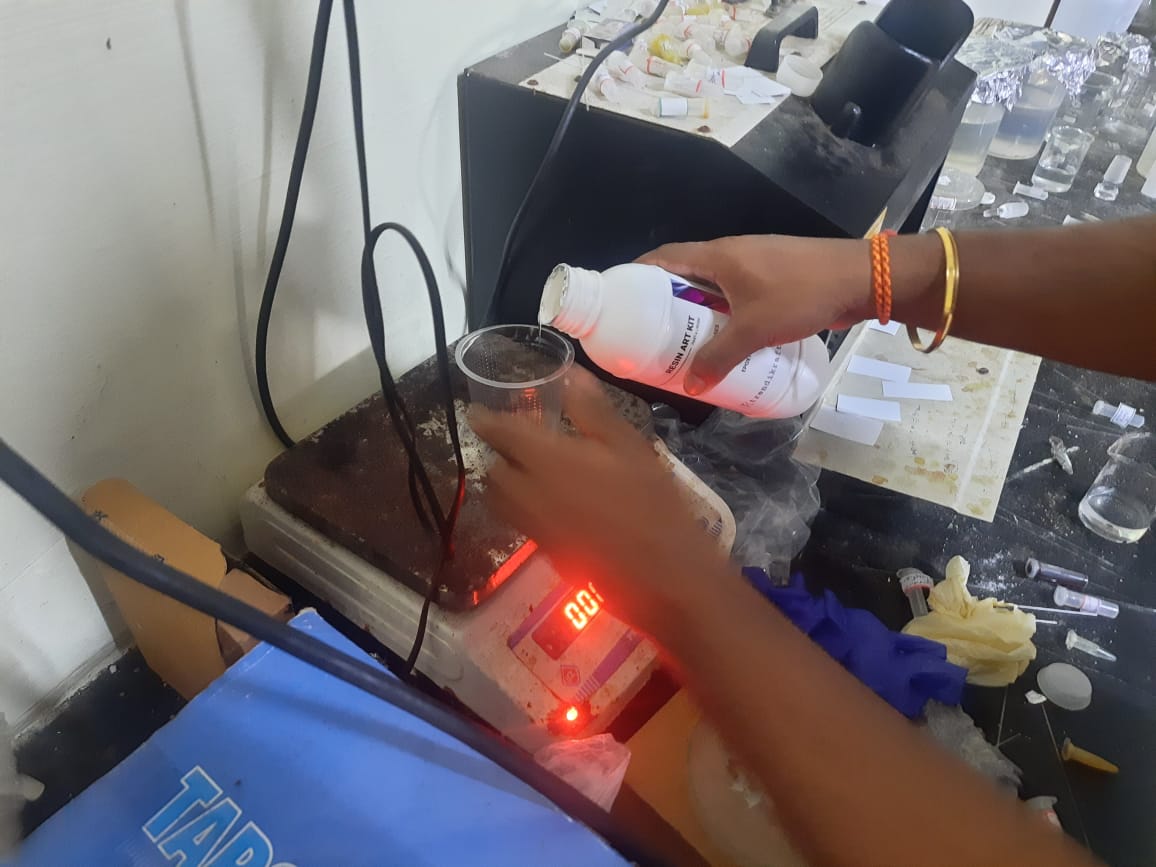

After pouring the silicone base, the plastic beaker was tared again to zero the scale, ensuring accurate measurement of the catalyst. Based on the required ratio, 2 grams of catalyst were added. This precise measurement was essential for proper curing and for producing a strong, detailed negative silicone mold.
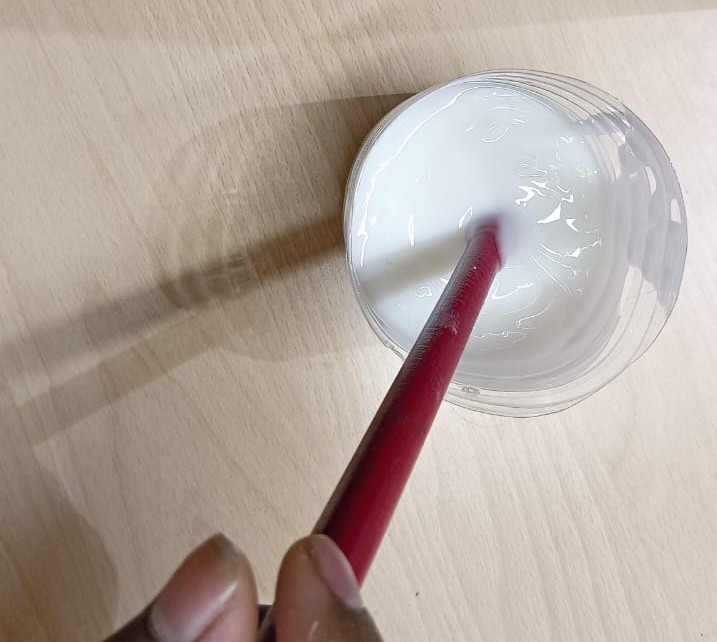
Then adding the catalyst, the silicone was thoroughly mixed to ensure an even and consistent blend, which is essential for uniformly activating the curing process. The mixture was stirred slowly to minimize the formation of air bubbles and was allowed to settle before being poured into the mold.

A release agent was applied to the 3D-printed mold cavity prior to pouring to facilitate easy demolding. The mixed silicone was then carefully poured into the cavity, starting from one side to allow the material to flow evenly and enable air bubbles to escape naturally. This approach ensured that the silicone captured all the fine details of the mold.
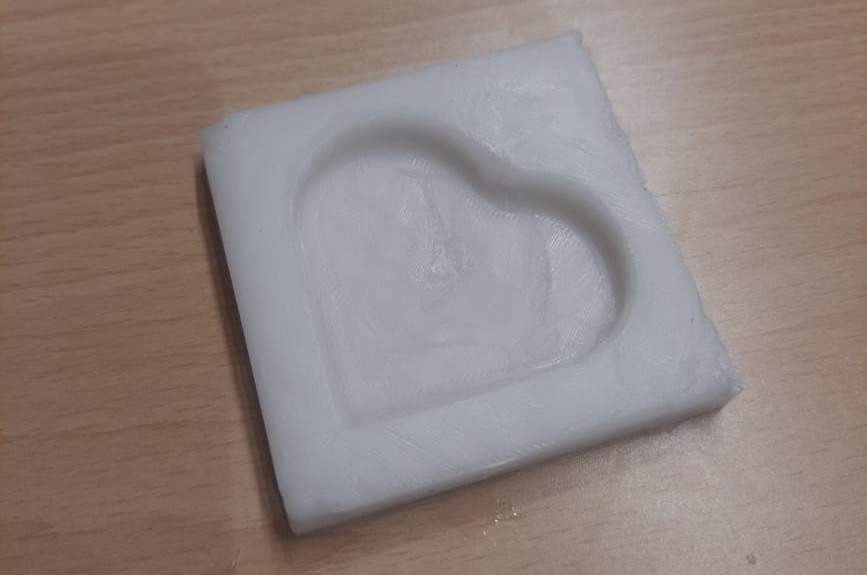


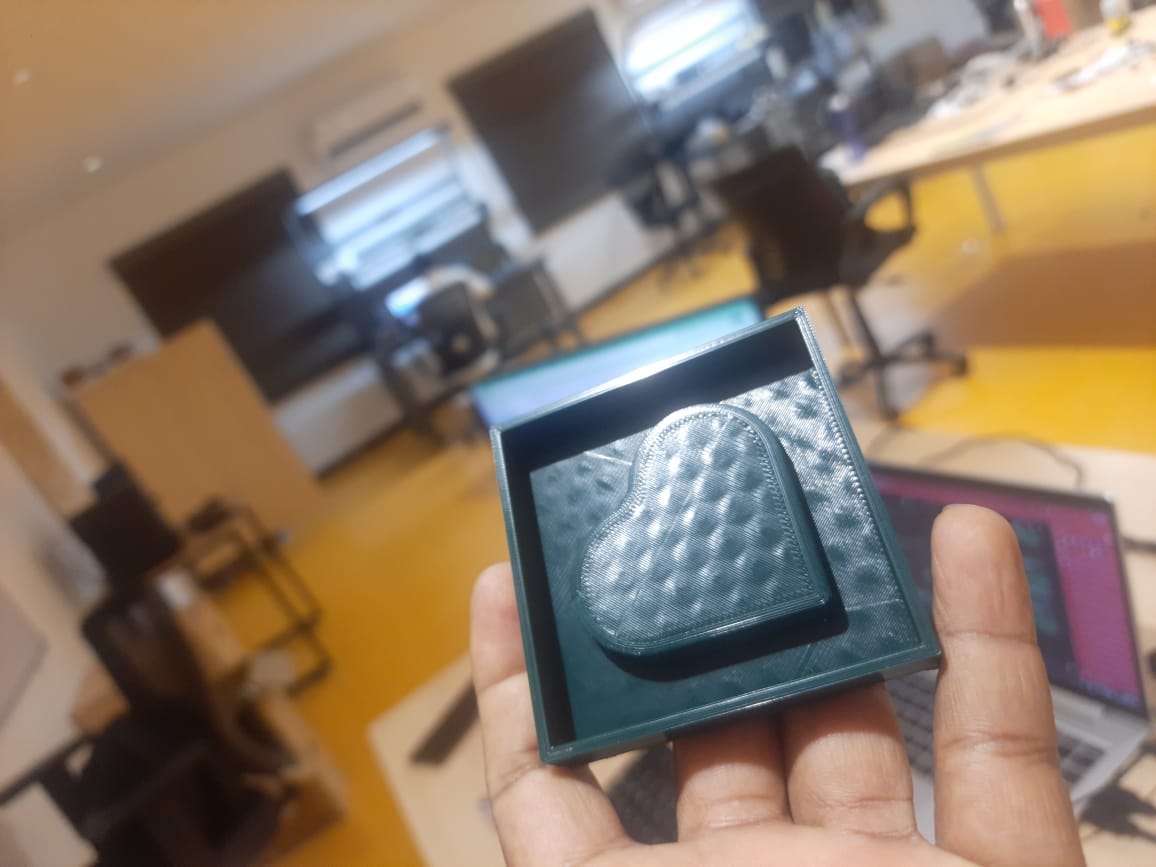
Once the curing process was complete, the silicone mold set perfectly, exhibiting a clean and detailed finish. The surface was smooth, and all features from the 3D-printed mold were accurately replicated. The final product was a high-quality negative mold, suitable for casting chocolate or other materials.
The 250 ml beaker was tared again prior to measuring the resin to ensure accurate weight, excluding the beaker’s mass. This step was essential for precise mixing with the hardener. The resin quantities were then calculated based on a 2:1 mixing ratio (Part A: Resin, Part B: Hardener). After measuring the required amount of Part A, half that quantity of Part B was added. Maintaining this precise ratio is critical to achieving proper curing, optimal strength, and clarity in the final cast
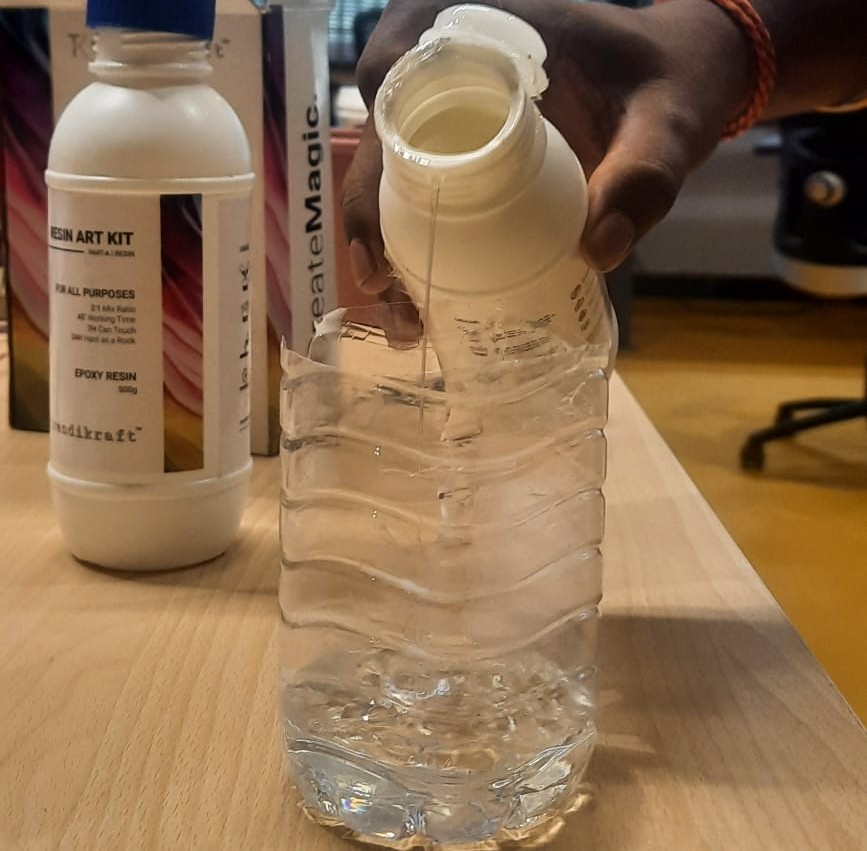

Part A (resin) was added in double the quantity of Part B (hardener), adhering to the specified 2:1 mixing ratio. This ensures the correct chemical reaction required for proper curing. Accurate measurement is essential to prevent issues such as incomplete curing or a tacky surface finish.
After measuring Part A (resin), Part B (hardener) was added in the correct proportion—exactly half the amount of Part A—maintaining the 2:1 mixing ratio required for proper curing.
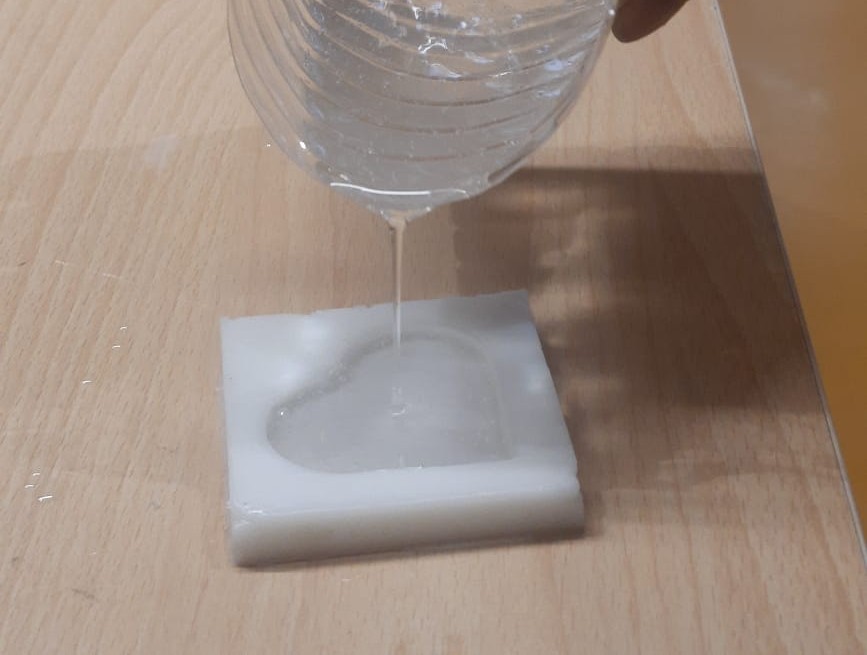

The mixed resin was then slowly poured into the cured silicone mold, beginning from one side to promote even flow and minimize air bubble formation. Care was taken to ensure the resin filled all the intricate details of the mold cavity accurately.
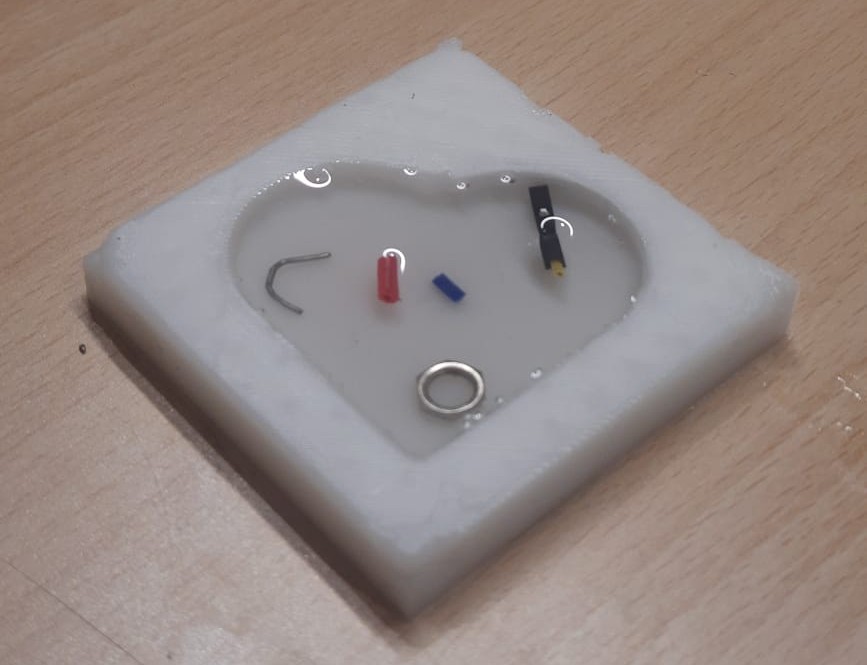
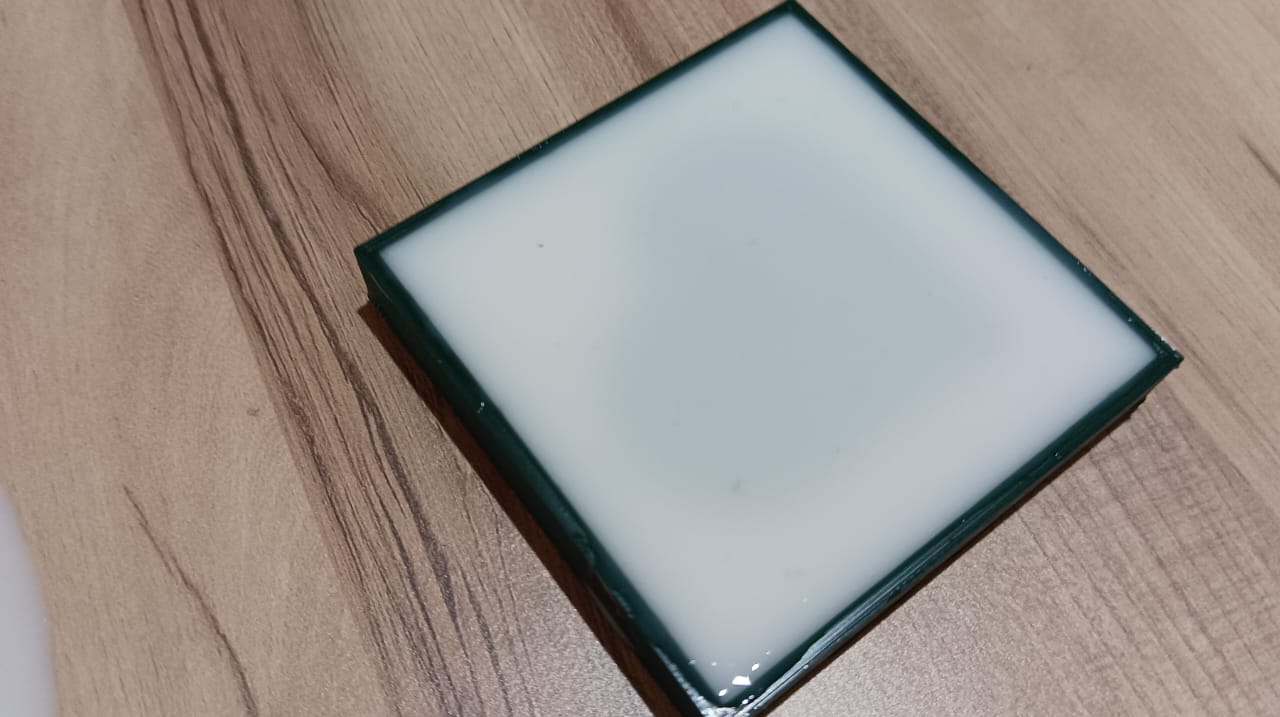
The resin was then left to rest and cure undisturbed for the recommended duration, allowing it to solidify completely. This step is essential to ensure that the final cast achieves optimal strength, clarity, and accurately retains the intended shape.
Once the resin had fully cured, it was carefully demolded from the silicone mold. The casting emerged with smooth surfaces and finely captured details, accurately reflecting the mold’s design. The final product was solid, well-formed, and demonstrated the effectiveness of both the mold preparation and casting process.
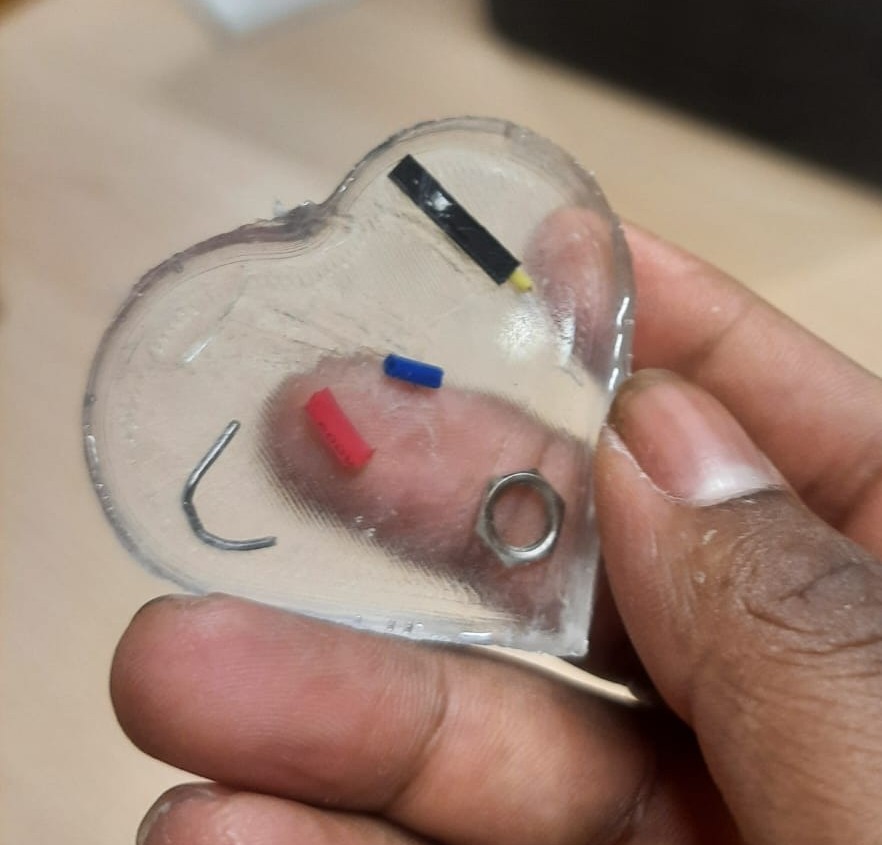
Conclusion
Learning outcomes
- Learnt about what are the types are available in Moulding and Casting
- Know more about pro and cons of them individually
- For the design rules of moulding how much draft angle we will give it
- Gained knowledge on utilizing 3D printing and milling techniques for parent material fabrication and production
- Understood the method of estimating silicone volume using water displacement for precise mold preparation
- Gained hands-on experience in using silicone mold calculators to determine accurate base-to-catalyst ratios