10. Molding and casting¶
This week I worked with different materials to learn the techniques of moulding and casting.
Group Assignment¶
Molding and casting materials¶
Silicone F-10/F-20 Plus¶
The RTV Silicone Rubber F-10/F-20 plus uses a catalyst for its condensation and is the only non-imported domestic product on the market. It is excellent for making moulds resistant to tearing and stretching, as well as being very easy to demould.
The safety data sheets of this material stablish that handling and mixing require the following precautions: - Wear gloves & goggles. - Do not eat, drink or smoke. - Avoid swallowing, skin, or eye contact. - Use IPA Isopropyl to clean up any uncured material. - If contact does occur, wash with soap and clean water immediately & in the case of eye contact, consult a doctor.
![]()
Physical and usage characteristics:
- Silicone F-20 plus (Hardness 20) = for making plaster, resin and cement moulds.
- Silicone F-10 plus (hardness 10) = for making soap and candle moulds.
- Mixing ratio: 2-3 % Silicone catalyst (transparent)/100 gr Silicone (White)
- Manual mixing time: 60 sec
- Viscosity: medium
- Colour: White
- Working time: 15 to 40 minutes
- Curing time: 2 - 6 hours
- Shelf life: 1 year
Gypsum Stone Type III¶
Gypsum stone type III is for dental use. Therefore, under normal conditions of use and in its original form, the product does not have any other negative effects on health and the environment.
However, the safety data sheets of this material stablish:
- In case of inhalation: place the casualty in fresh air, keep warm and at rest, if breathing is irregular or stops, give artificial respiration. Do not administer anything by mouth. If unconscious, place in a suitable position and seek medical help.
- If in eyes: flush eyes thoroughly with clean, fresh water for at least 10 minutes, pulling up the eyelids and seek medical advice.
- If on skin: remove contaminated clothing. Wash skin vigorously with soap and water or a suitable skin cleanser. Never use solvents or thinners.
- If swallowed: seek medical attention immediately. Keep at rest. Never induce vomiting.
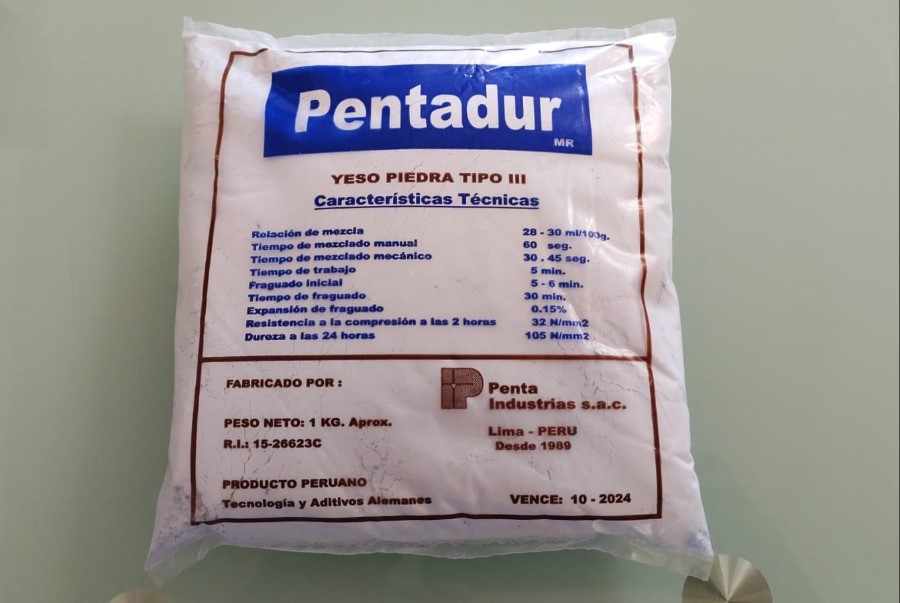
Physical Characteristics:
- Mixing ratio = 28-30 ml/100gr.
- Manual mixing time = 60 sec.
- Mechanical mixing time = 30 - 45 sec.
- Working time = 5min.
- Initial setting = 5-6 min.
- Set expansion = 0.15%
- Compressive strength at 2 hours = 32N/mm2
- Hardness at 24 hours = 105 N/mm2
Ceramic Gypsum¶
The semi-hydrated calcium sulphate, or ceramic gypsum, is used in the ceramic industry to manufacture high quality moulds, which provide adequate control of absorption, hardness, density and strength.
The safety data sheets of this material stablish that:
- When the gypsum is mixed with water, it will generate a chemical reaction that will raise the temperature, so do not apply the powder on any part of the body, as it may cause burns.
- If plaster or gypsum powder mixture is splashed in the eyes, rinse with plenty of water.
- This product should not be swallowed. If swallowed, consult a doctor.
- Dust from this product causes dry skin and mucous membranes, therefore the use of glasses, dust mask and gloves is recommended.

Physical and usage characteristics:
- Mixing ratio: 0.7 and 0.8 litres of water for 100 gr. of plaster.
- Absorption time: 1 min 22 sec (leave plaster in contact with water).
- Mixing time: 1 min 45 sec
- Flow time: 5 min
- Setting time: 7 min
- Unmoulding time without forcing the piece: 20-30 min depending on the amount of water.
Vegetable Glycerin in glass bar¶
This material is obtained from vegetable oils, such as coconut oil, through a process called hydrolysis, from which pure glycerin is extracted for its different uses, the main one being the manufacture of soaps.
Ingredients: Glycerin Usp, distilled water, sorbitol, sodium lauryl, coconut betaine, triethanolamine usp, vegetable stearin, preservatives, coconut oil, castor oil, saponifying agent. Free of parabens and sodium.

Instructions for use: Demolish, cut, dilute, pour, do not handle metal, keep out of reach of children.
Test casts¶
For the test, the security measures recommended by each product were taken. Gloves, safety glasses and a surgical mask were used. The workplace has good ventilation.
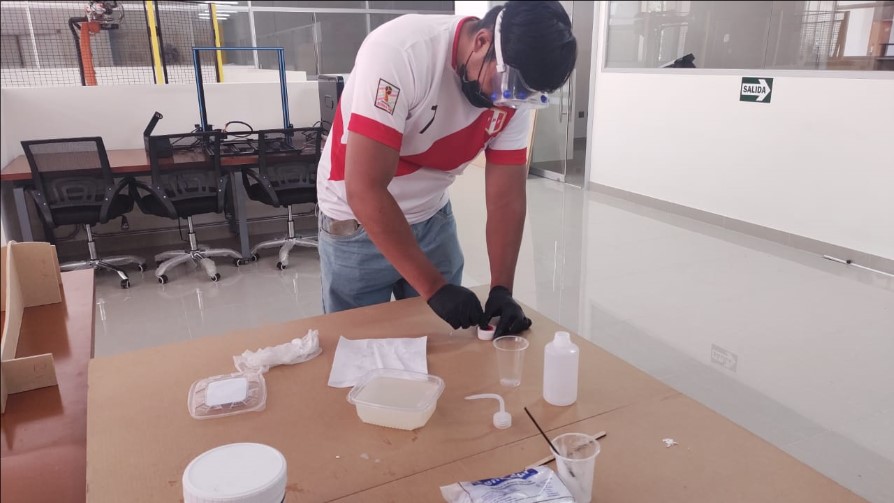

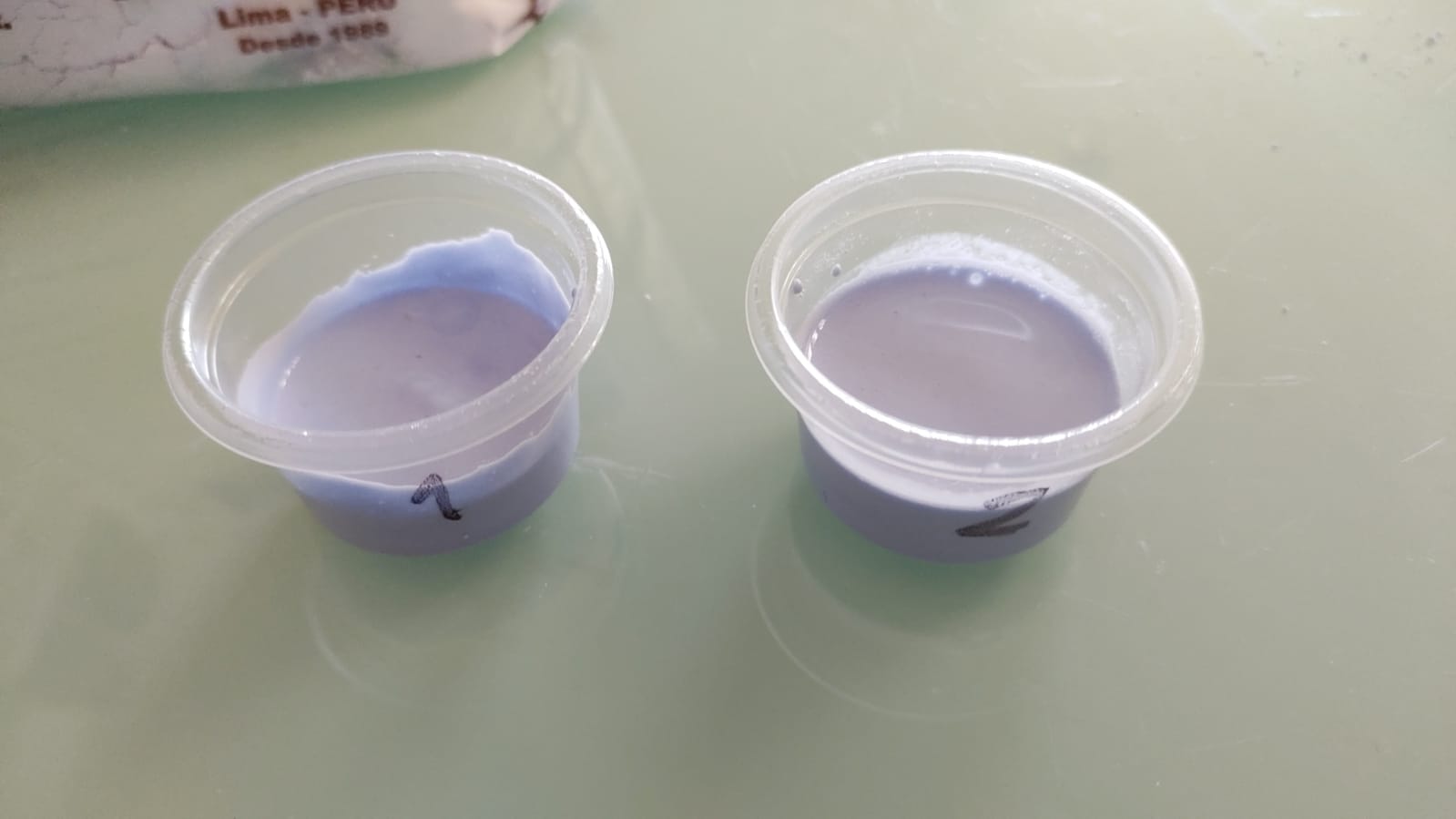
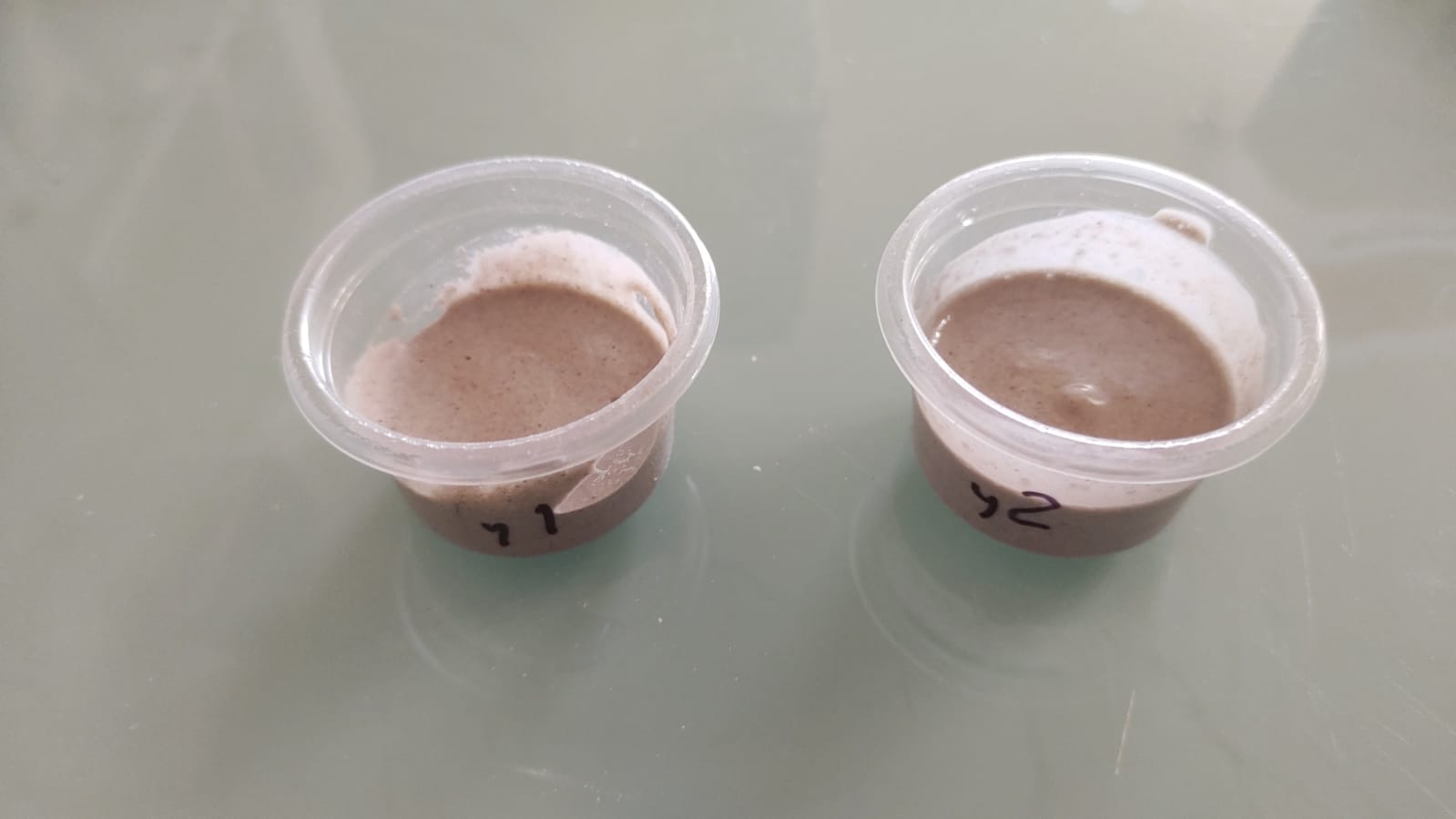
For the silicone, tests were made in small containers where in the first case (1) the recommended amount of catalyst was used and in the second case (2) half of the recommended amount of catalyst was used. After 2 hours, test 1 was very condensed and ready for use, while test 2 was still viscous.
![]()
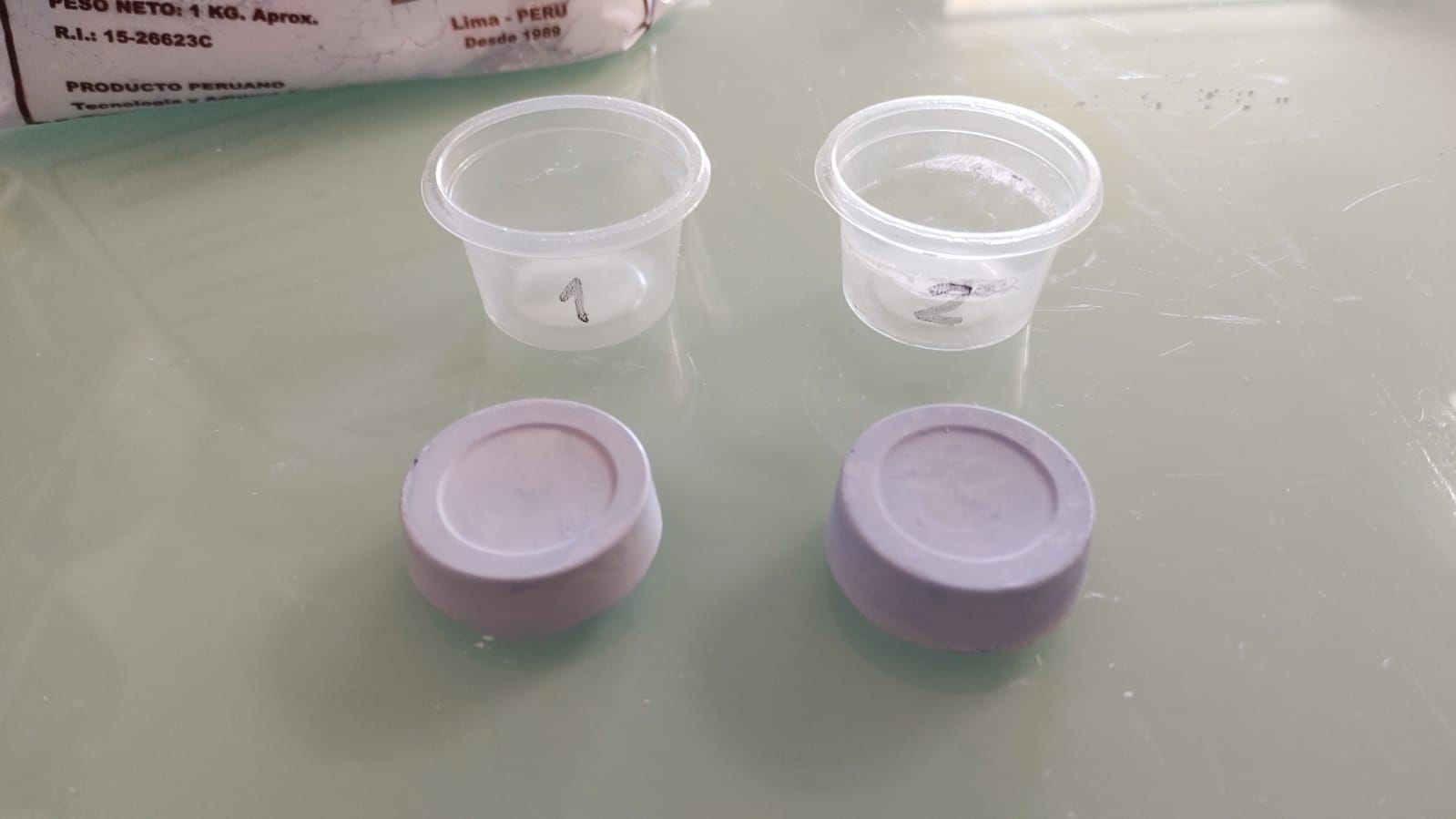
For the stone plaster, two tests were also carried out in small containers. For test 1 the recommended amount of water was used and for test 2 50% more water was used. After 30 minutes, both tests were very hard and perfect for use.
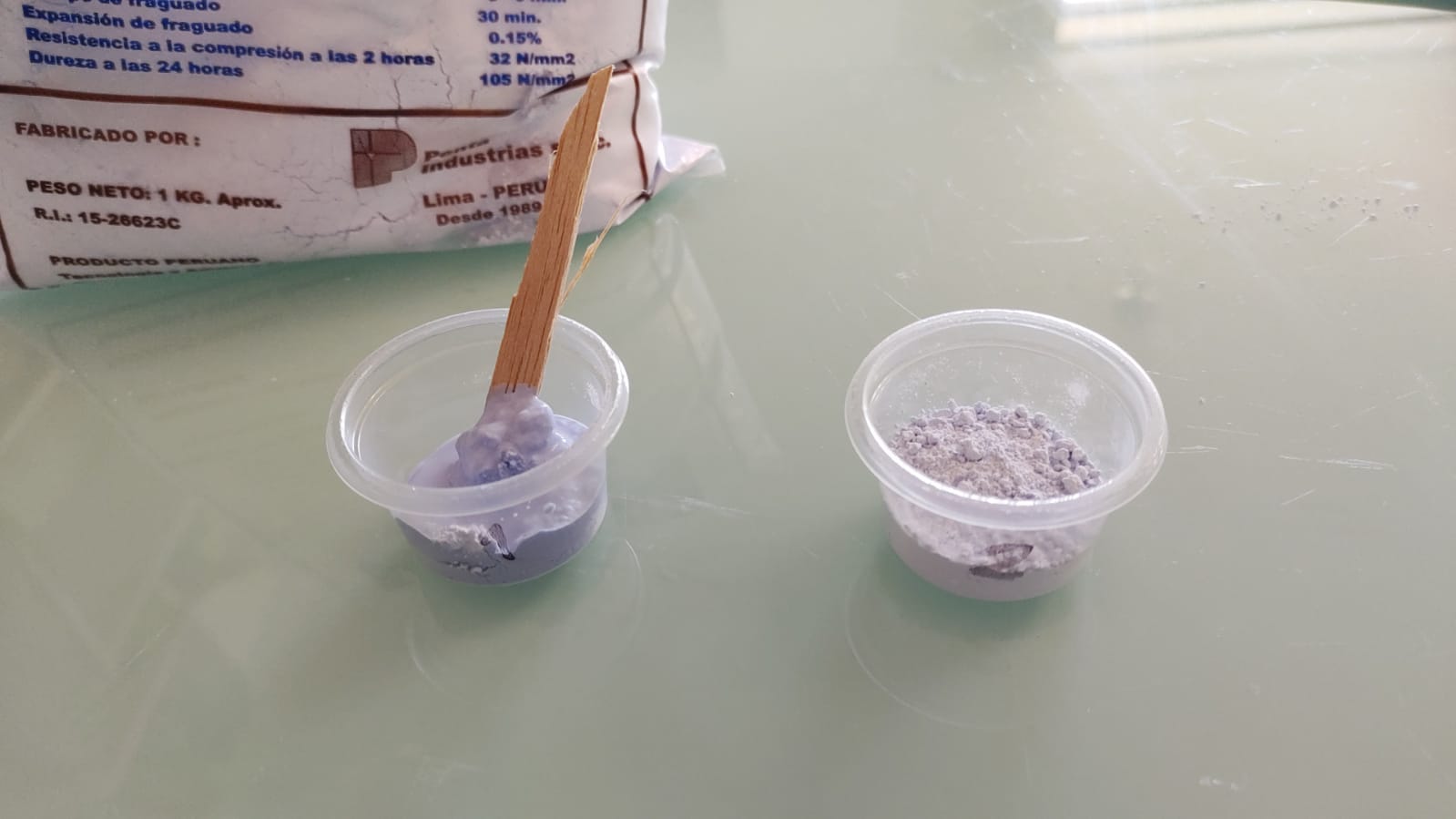



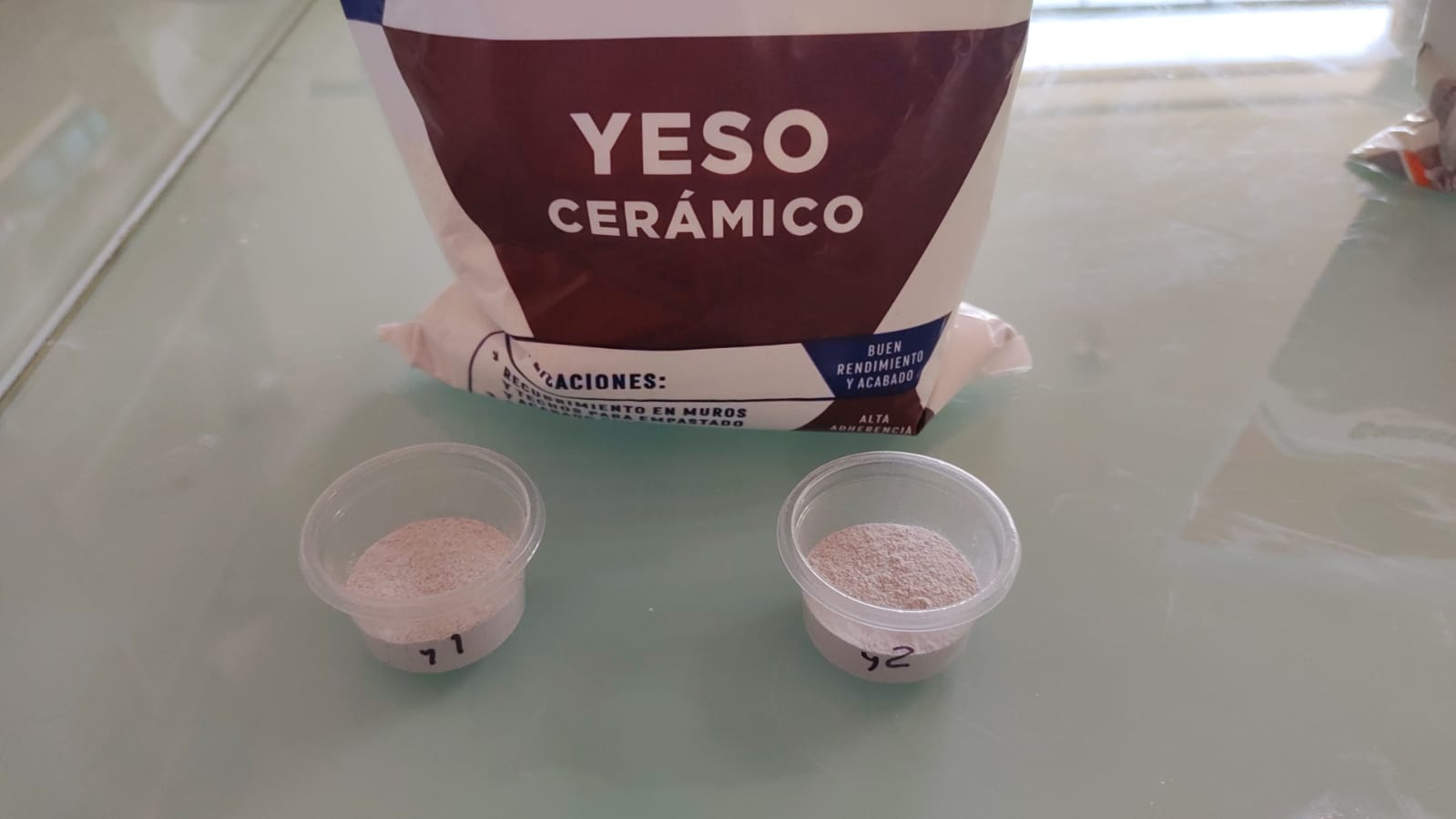
The same procedure was used for the ceramic plaster. In this case test 1 with less water and test 2 with more water. After 3 hours it was possible to demould both tests, but we realised that they were not very resistant.



In the case of the vegetable glirecerin, only one test was done, the product was heated until it became liquid. This process is quite fast (1 minute). it was placed in a container and after 30 minutes it solidified.
Individual Assignment¶
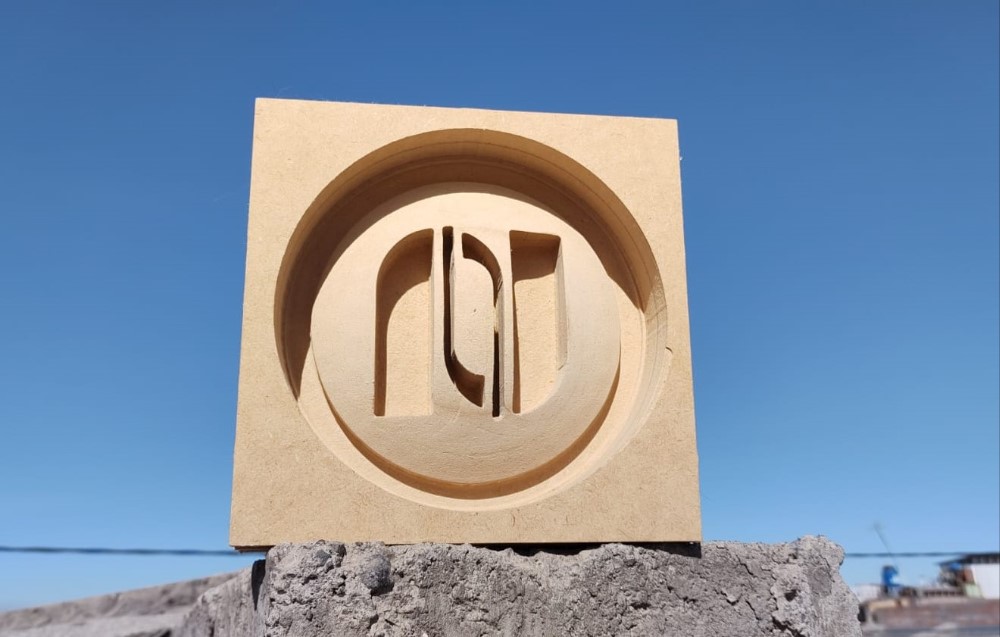
For the individual work I decided to model the logo of my faculty using Autocad software. This model has a diameter of 15 cm.
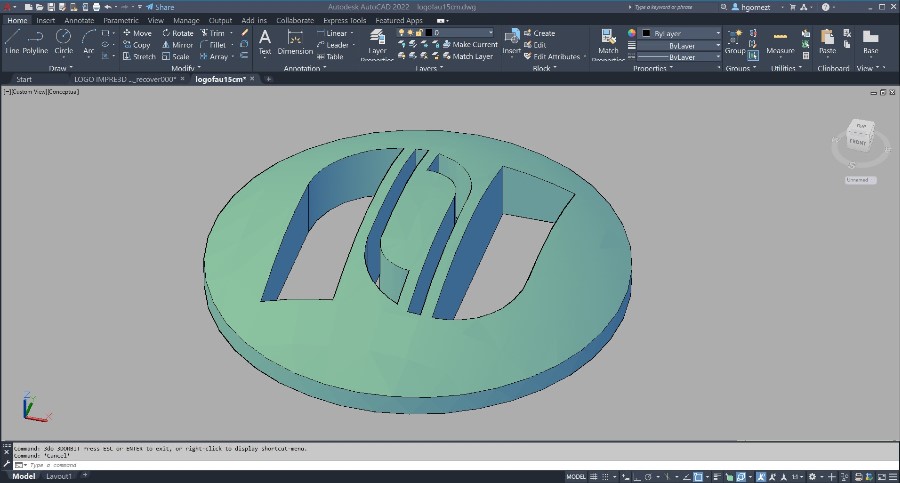
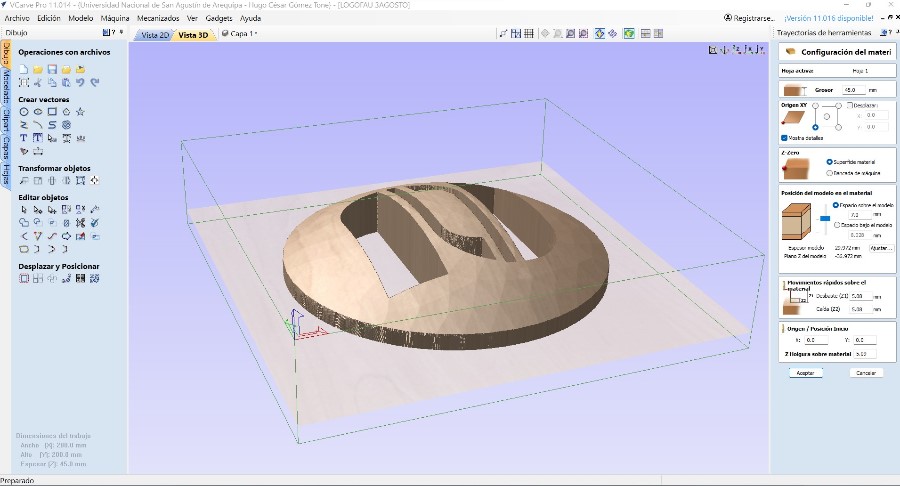
For the production I decided to use MDF. Three 1.5 cm thick pieces were glued together with synthetic carpenter’s glue to make a total of 4.5 cm.
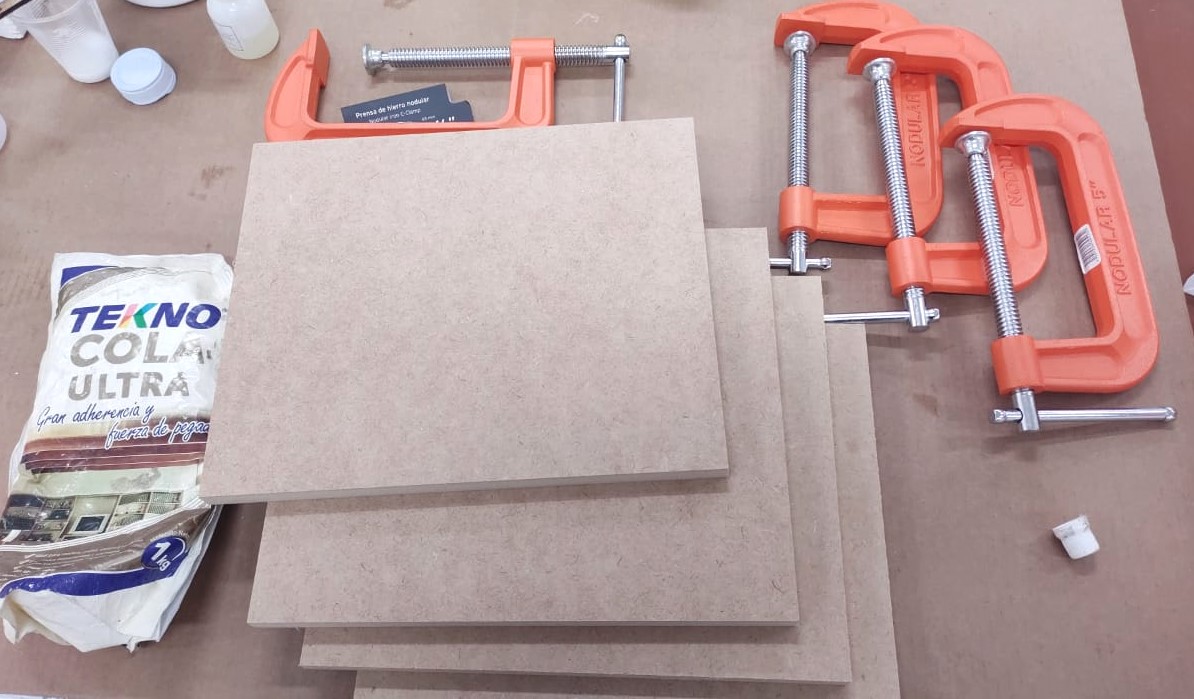
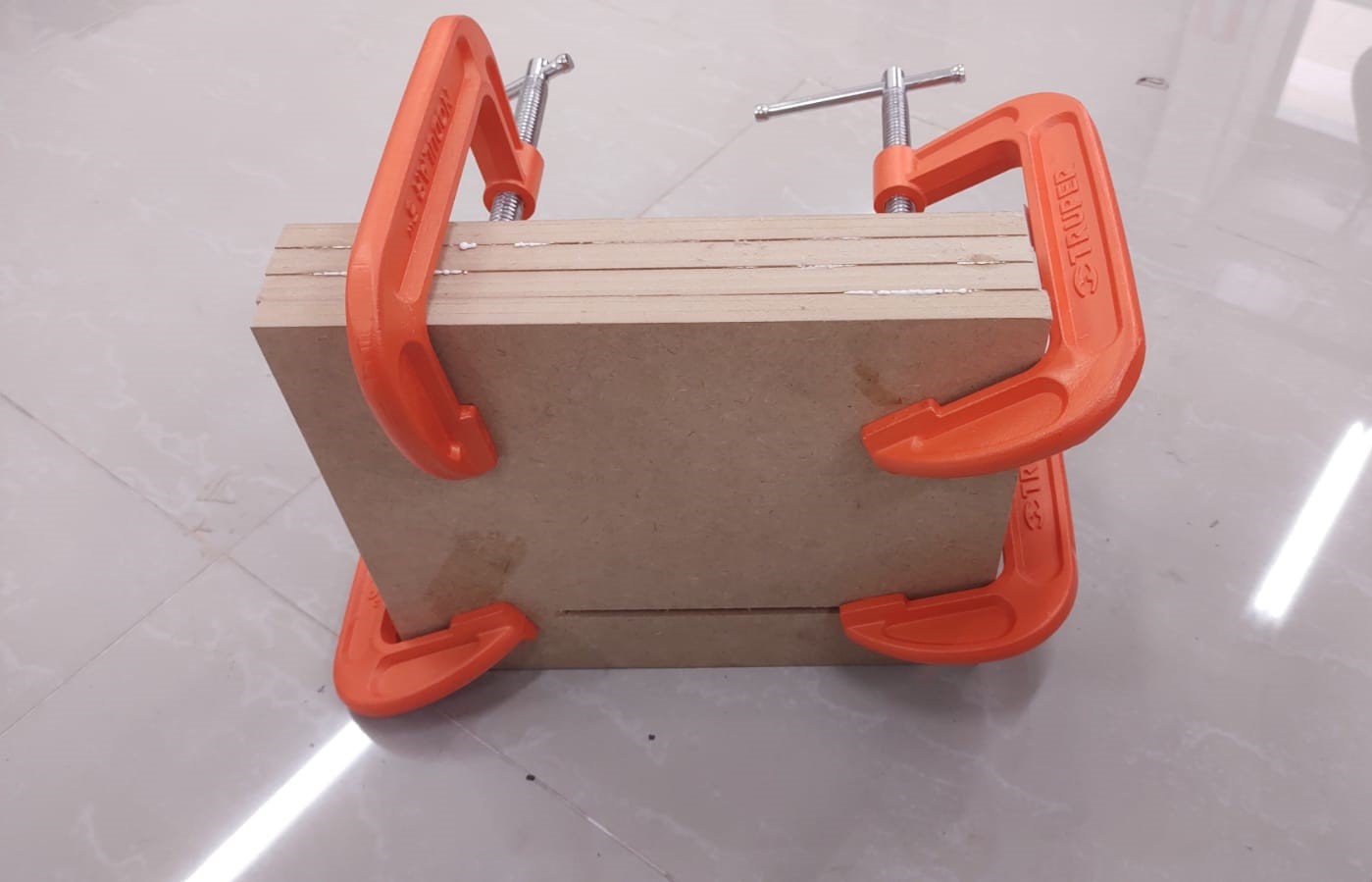


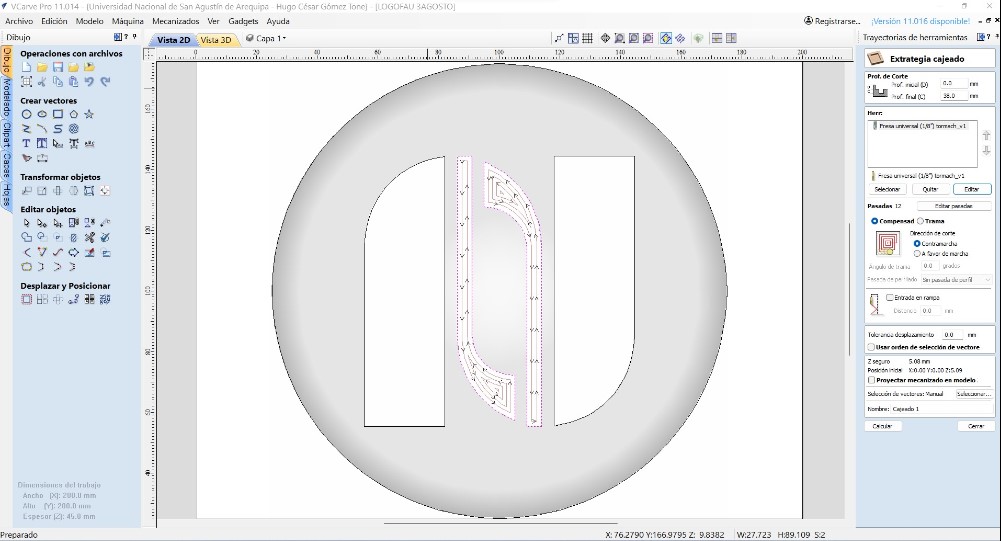
In the software Vcarve Pro version 11.014 the 3D model in STL exported from Autocad was imported. The first settings are to determine the material thickness 45 mm and the thickness on the model 7 mm.
For the first roughing process the 1/4” universal milling cutter was used with the following parameters:
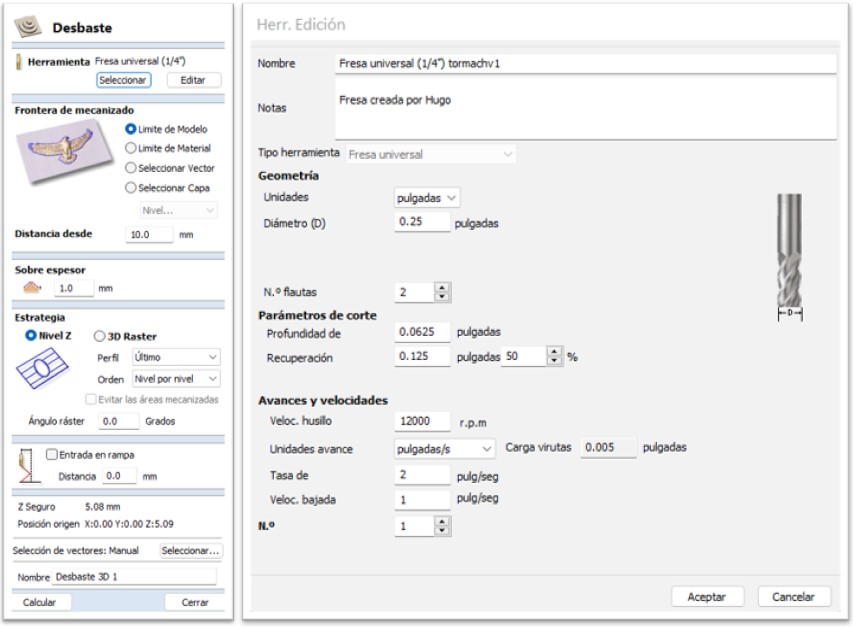
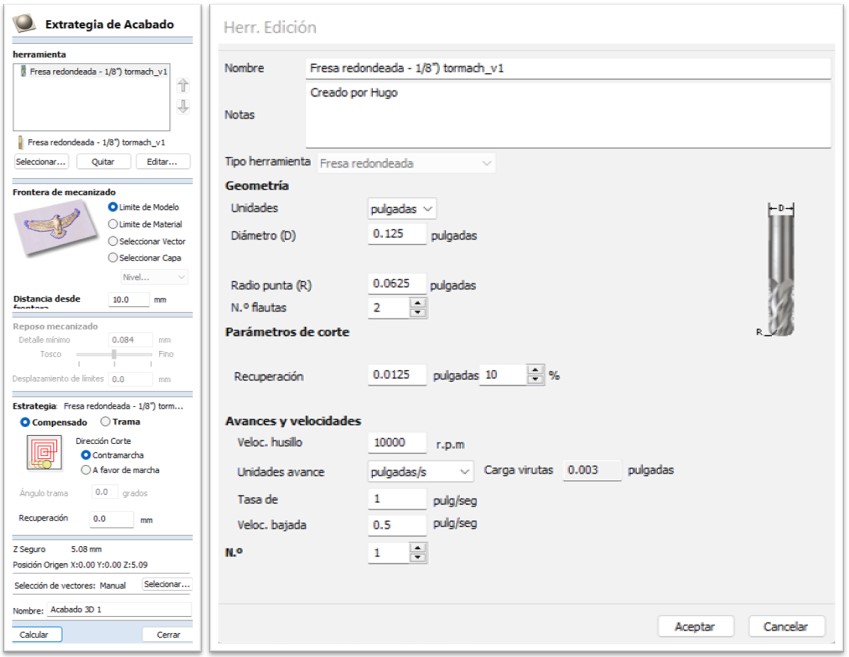
For the finishing process the 1/8” rounded milling cutter was used with the following parameters:
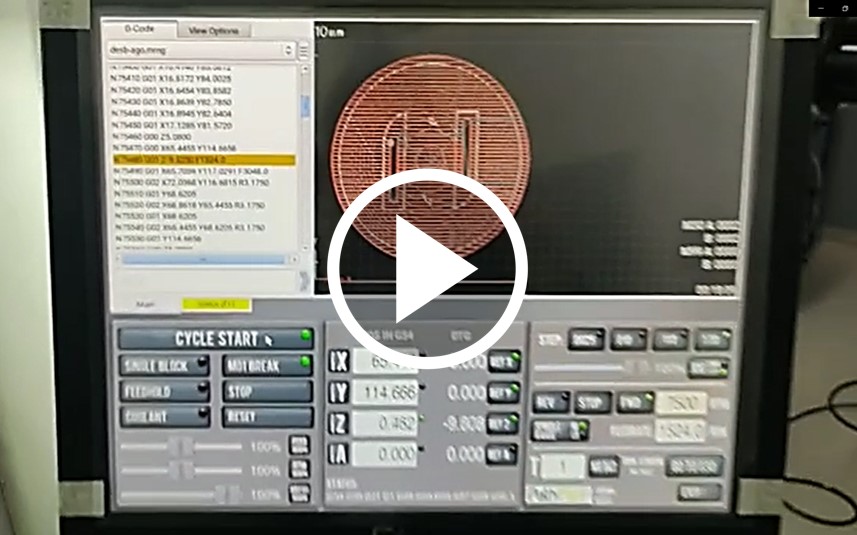
G-codes for both processes were recorded in *.mmg format to be taken to the Tormach CNC. In the Tormach CNC, after defining the origin point for the X, Y and Z coordinates, the G-code was executed.
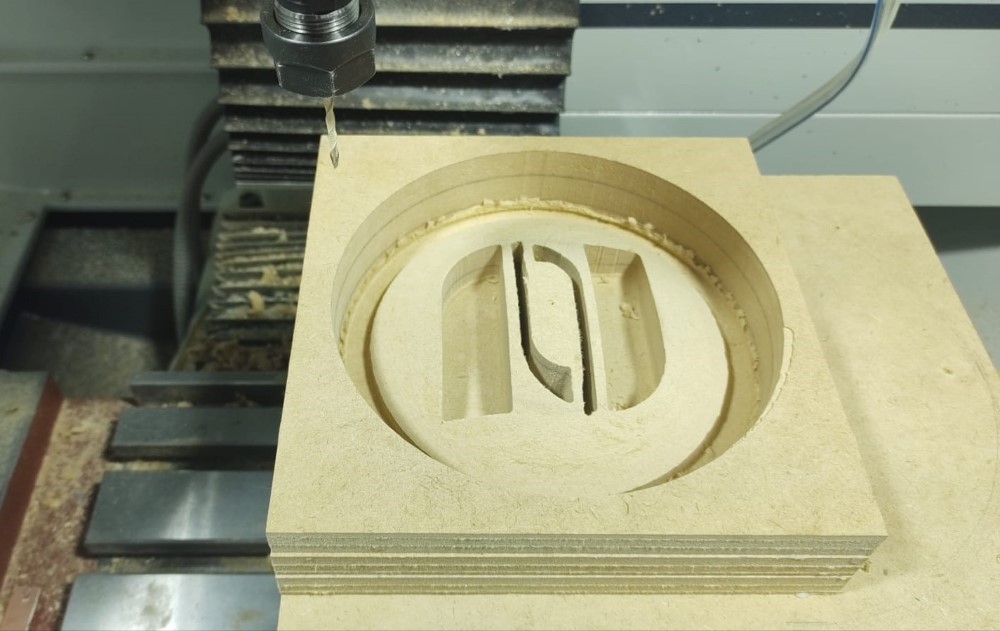
It happened that when the finishing procedure was executed the 1/8” end mill broke. The end mill used was of the down-cut type which caused the chip and dust evacuation to be very bad and ended up breaking the milling end mill in the thinnest channel of the design. Care must be taken to remove all the pieces of the broken end mill, otherwise, when the process is resumed with another end mill, it will break.
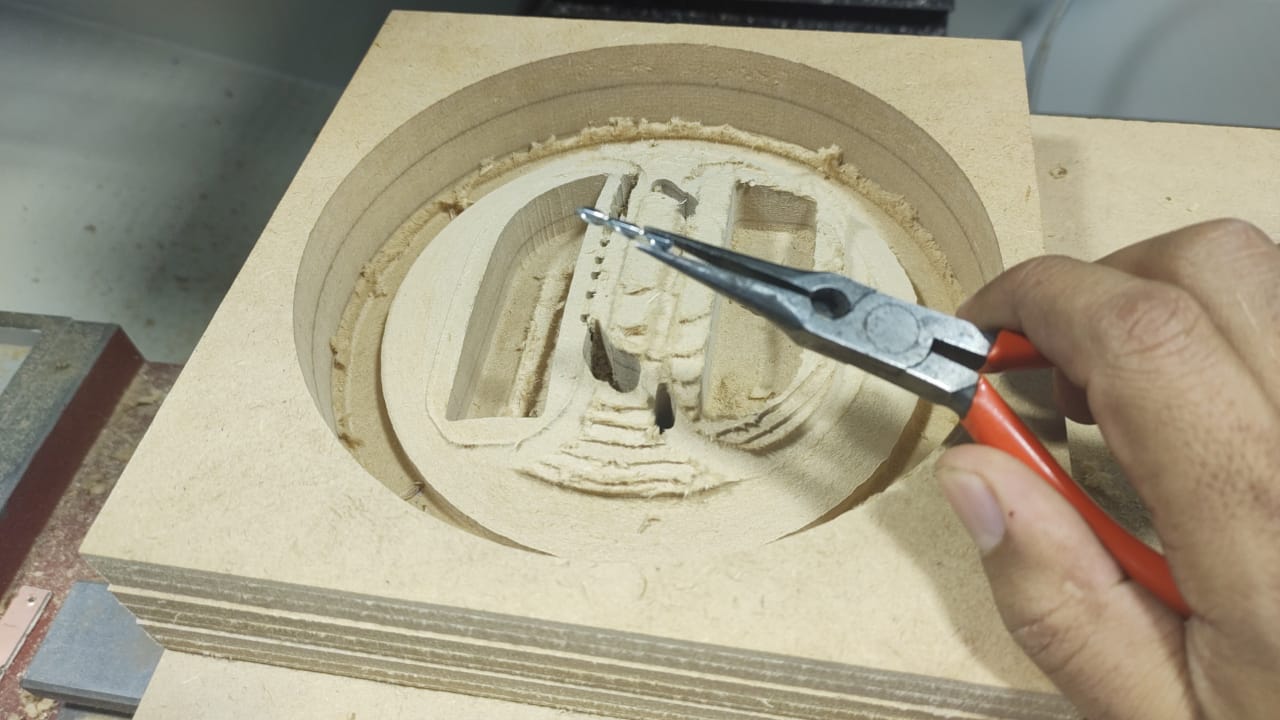

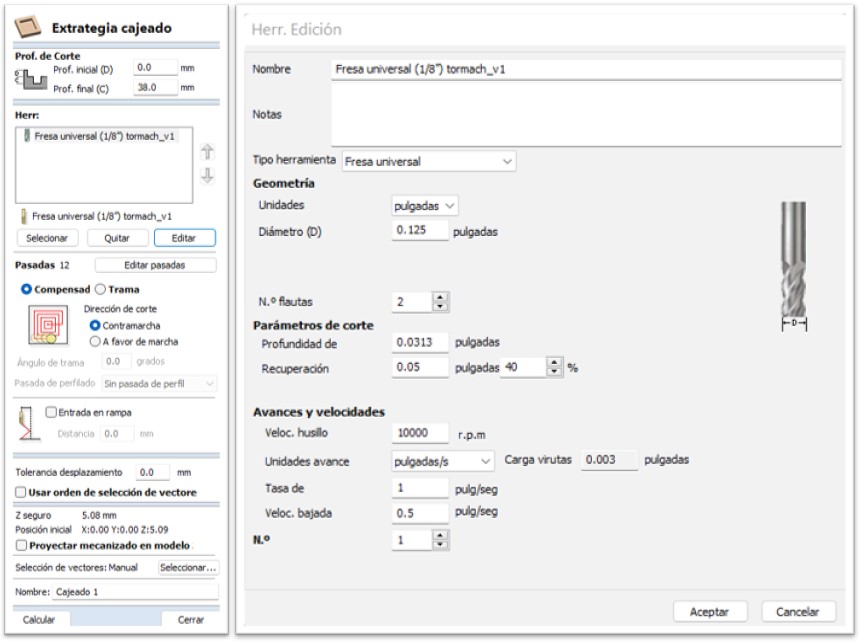
To avoid the risk of breaking the end mill again, it was decided to create a new milling process for the two thin spaces in the design, and care was also taken to vacuum the chips and dust permanently. For this process a 1/8” universal end mill was used with the following parameters:
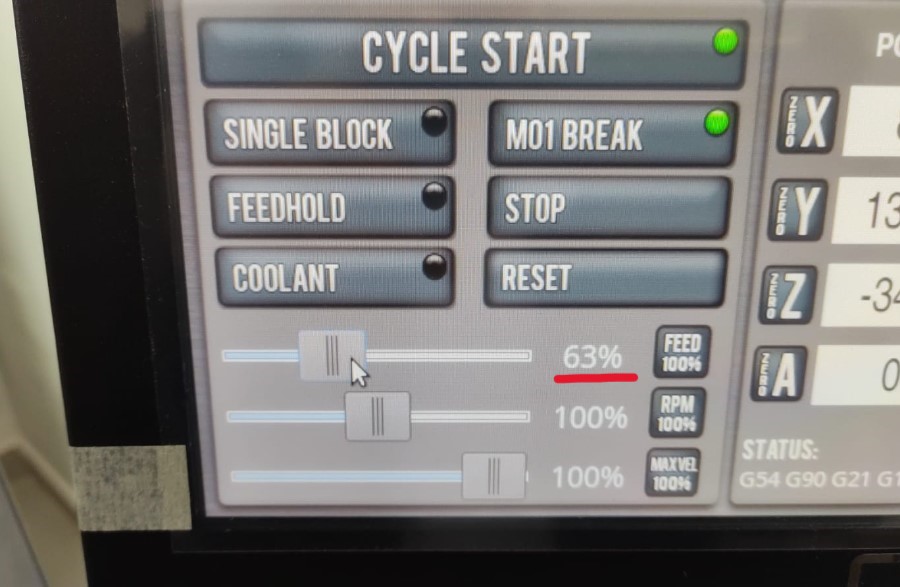
In addition, during the milling process, it was decided to lower the speed to avoid the risk of breakage.
The finished piece is already a work of art!

Silicone F-20 Plus was used to create the mould.
![]()
We proceeded to mix 200 gr. of silicone and 5 gr of catalyst in a container. The mixing process must be rigorous. A disadvantage of the catalyst being colourless is that it was not possible to visually recognise how well it was mixed.
![]()
800 gr. of silicone were consumed to fill the entire MDF mould. After 24 hours of drying, the silicone was removed from the MDF.
![]()
In the thinnest part of the mould, the silicone came off, leaving a gap. The repair was made with the same silicone.
![]()
The first prototype that was made was using the fast drying Stone Plaster Type 3. We used 40 ml per 100 gr. in order to have a more liquid mixture and to be able to get into the narrow grooves.
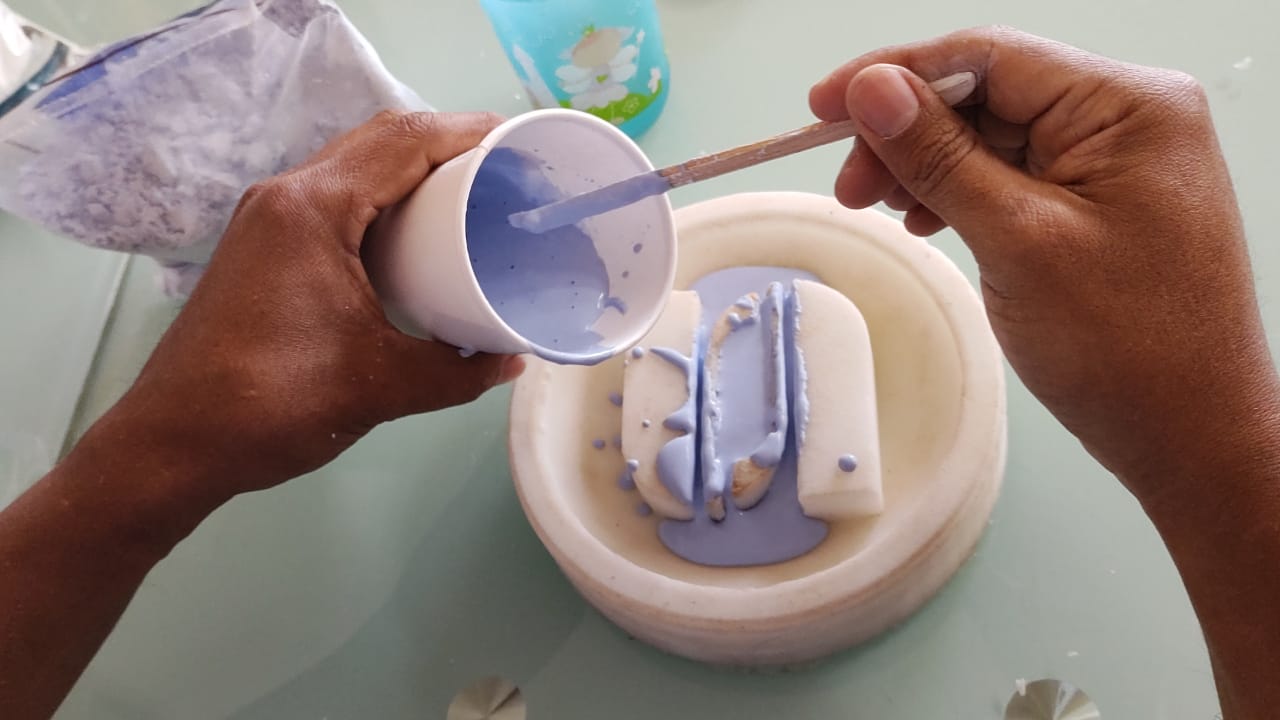
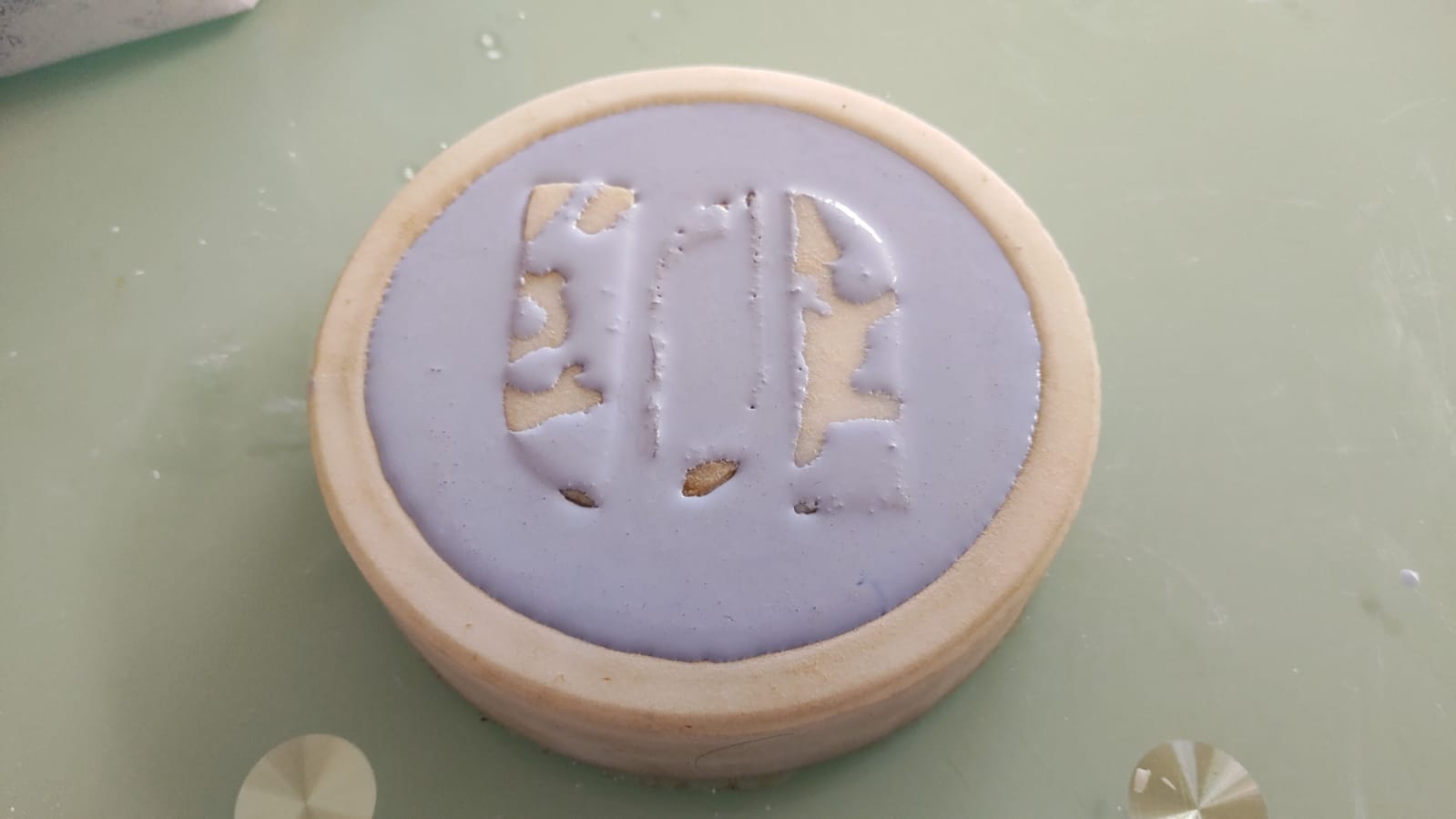


The final prototype turned out very well. The flexibility of the silicone helped in the demoulding.

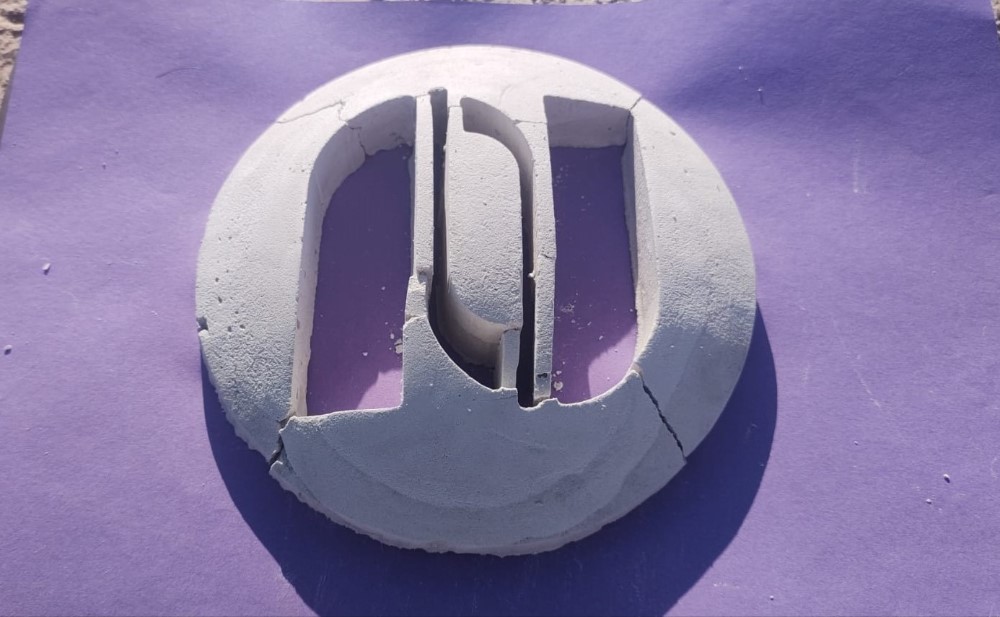
The second prototype was made with ceramic plaster. We also used more water for the thin groove effects.
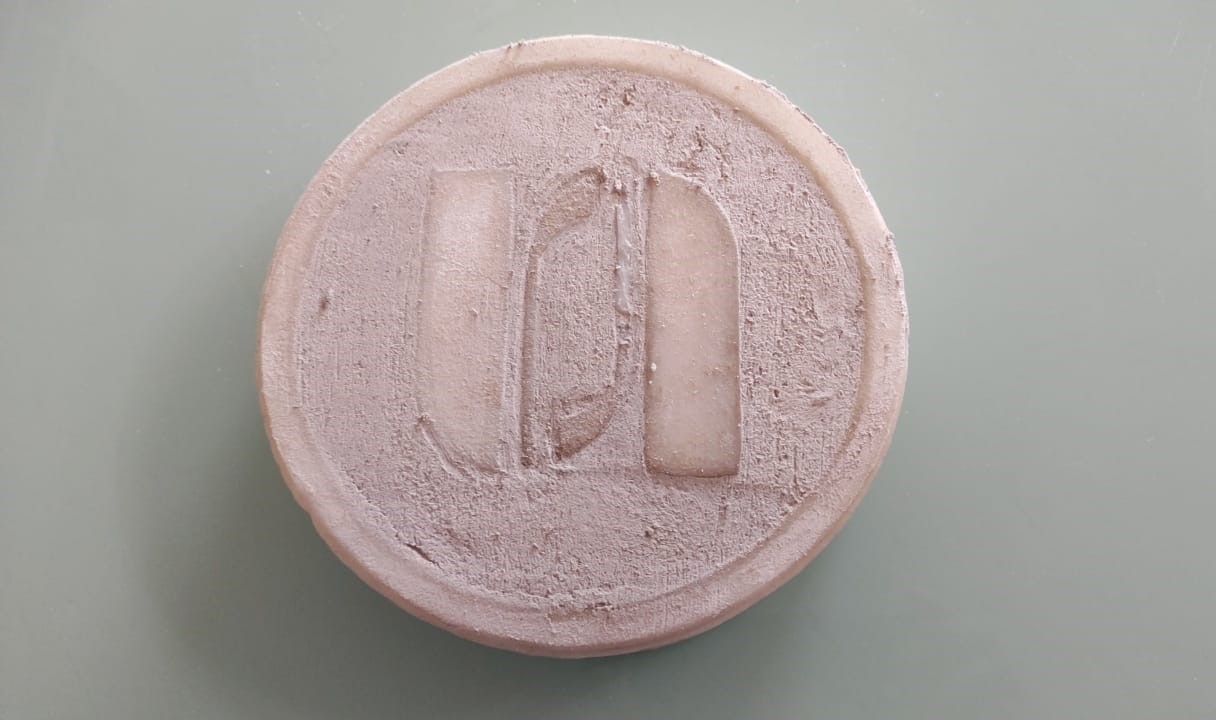

Unfortunately this plaster is not fast drying. After 24 hours it demoulded, but ended up fracturing. It is not recommended to work with this material.