Week 12 : Assignment
- add an output device to a microcontroller board you've designed, and program it to do something
In week 12 assignment was to add an output device in microcontroller and I have to program it to do something ! I thought it will be a good idea to use the input devices I used in week 11.
All Details of 328p board is uploaded in week 11.
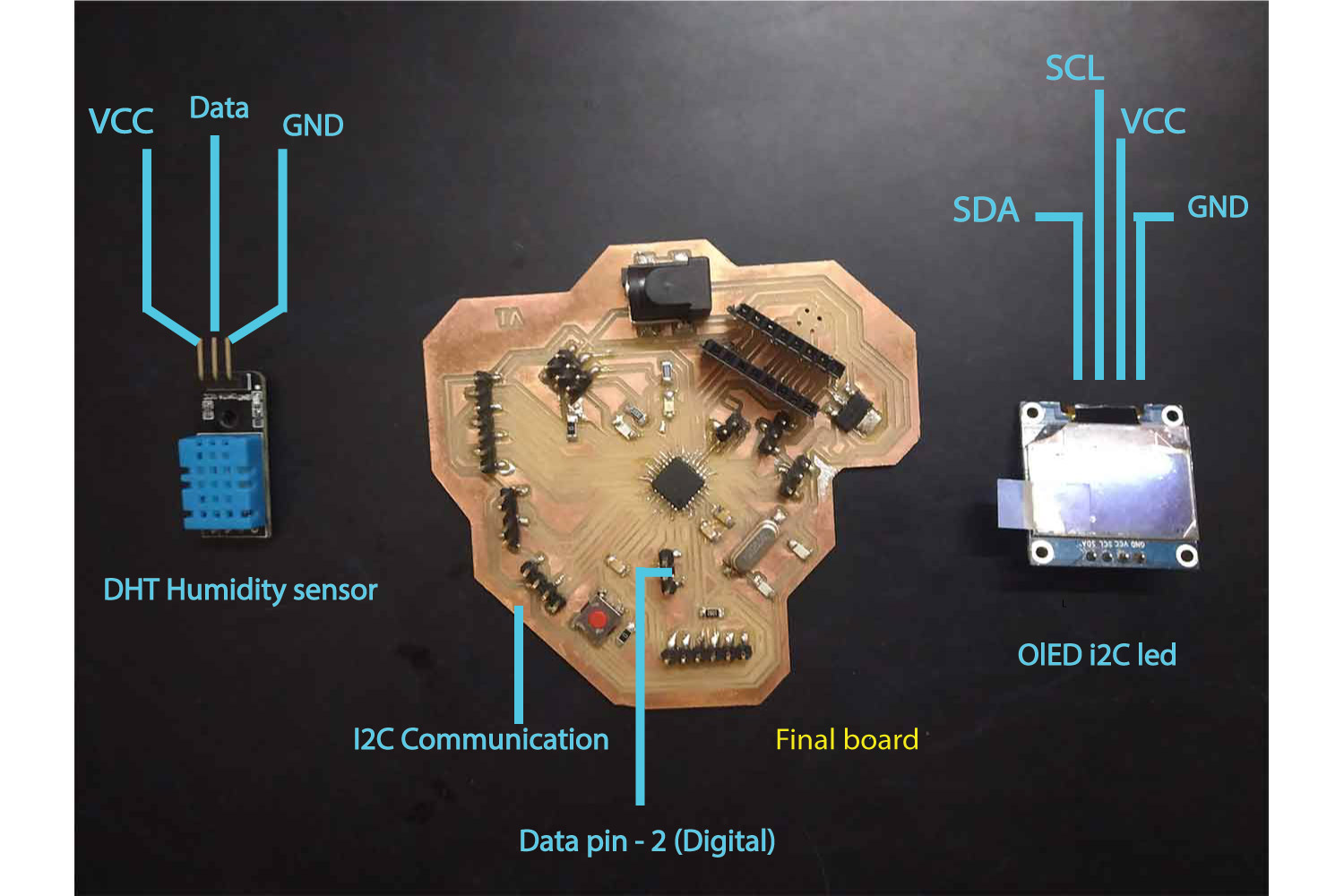
Humidity sensor with OLED
I already used the humidity sensor and print details on serial Monitor, I wanted to print them on my OLED now.
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) is a self light-emitting technology composed of a thin, multi-layered organic film placed between an anode and cathode. In contrast to LCD technology, OLED does not require a backlight. OLED
possesses high application potential for virtually all types of displays and is regarded as the ultimate technology for the next generation of flat-panel displays. my
reference for this code.
Click here to know more.
setup
in setup, I connected
Code
I got these codes from Random Tutorials and About OLED and DHT sensor. I still needed to understand this code, I wrote in every comment what each line is doing, the way
I understand...The below code will show Humidity and temperature.
Don’t forget to include
/*
* Random Nerd Tutorials - Rui Santos
* Complete Project Details https://randomnerdtutorials.com
*/
// require libraries one will need to run the code
#include <Wire.h> // wire library for I2C communication
// Adafruit library for the OLED printing
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h>
#include <Adafruit_SSD1306.h>
#include <DHT.h>// library for Dht sensor
#define DHTPIN 2 // digital pin is defined to humidity sensor
#define DHTTYPE DHT11 // defined reading
#define OLED_RESET 4 // OLED HAS TO DEFINE RESET IN EVEN IT IS NOT IN PINOUT
Adafruit_SSD1306 display(OLED_RESET); //FOR DISPLAY
// Initialize DHT sensor
DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE);
void setup() {
Wire.begin();
dht.begin();
display.begin(SSD1306_SWITCHCAPVCC, 0x3C);// initialize with the I2C addr 0x3C
}
void displayTempHumid(){
delay(2000);
// Reading temperature or humidity takes about 250 milliseconds!
// Sensor readings may also be up to 2 seconds 'old' (its a very slow sensor)
float h = dht.readHumidity();
// Read temperature as Celsius
float t = dht.readTemperature();
// Read temperature as Fahrenheit
float f = dht.readTemperature(true);
// Check if any reads failed and exit early (to try again).
if (isnan(h) || isnan(t) || isnan(f)) {
// if sensor failed to received any of three data it will fullfill this condition, if readings are available it will skip this loop
display.clearDisplay(); // clearing the display
display.setTextColor(WHITE); //setting the color
display.setTextSize(1); //set the font size
display.setCursor(5,0); //set the cursor coordinates
display.print("Failed to read from DHT sensor!");
return; // it will return to start if condition fulfilled
}
display.clearDisplay();
display.setTextColor(WHITE);
display.setTextSize(1);
display.setCursor(0,10);
// prints on display from below
display.print("Humidity: ");
display.print(h);
display.print(" %\t");
display.setCursor(0,20);
display.print("Temperature: ");
display.print(t);
display.print(" C");
// you can get tempreture values from below in fahrenheit
// display.setCursor(0,20);
// display.print("Temperature: ");
// display.print(f);
// display.print(" F");
}
void loop() {
displayTempHumid();
display.display();
}
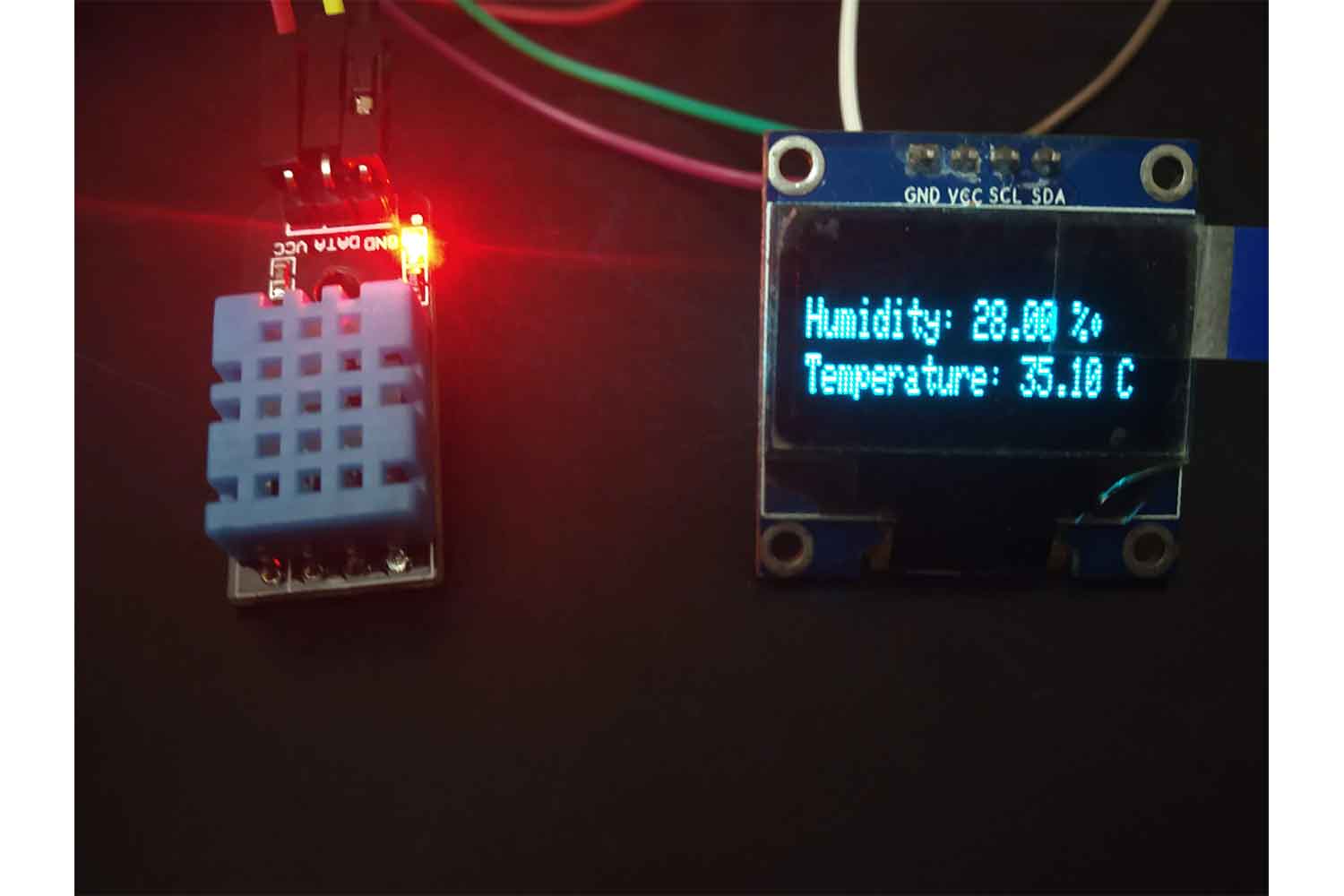
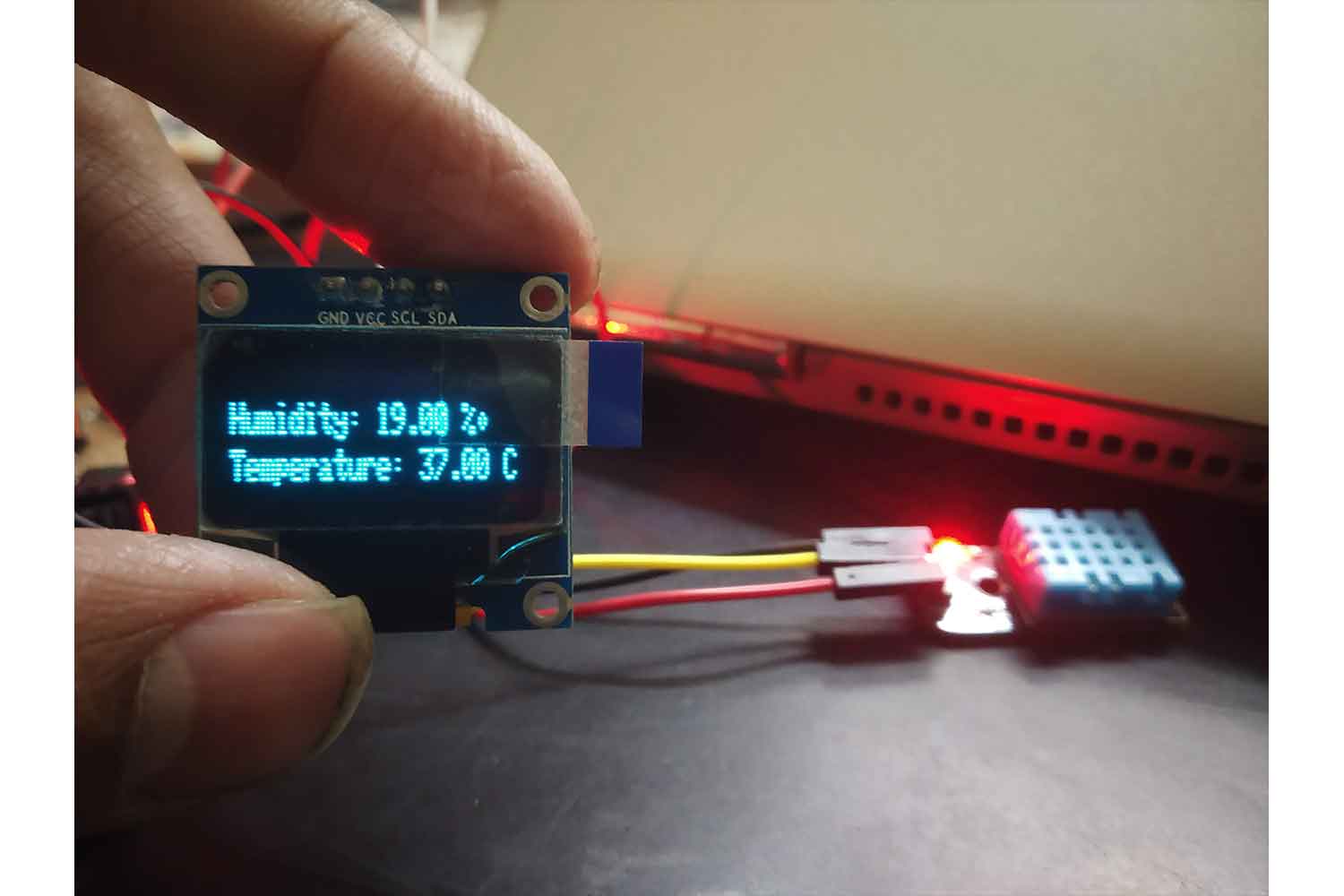
Output
Below I am trying to increase the humidity with a wet Handkerchief, see Below in video!
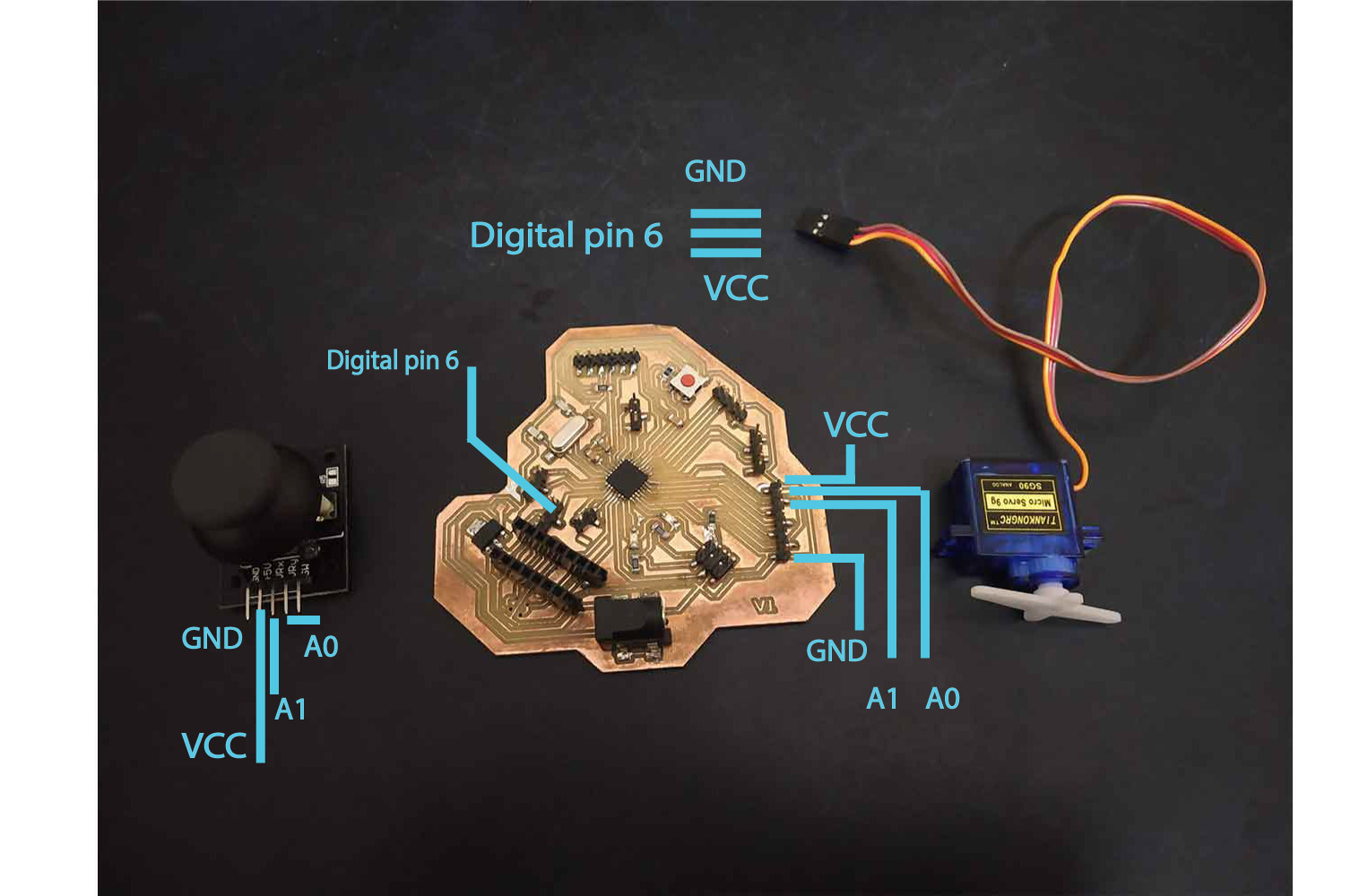
Servo motor with the Joystick
Then I tried to run Micro-servo with joystick module!Setup
Joystick connected to (A1,A0) // Vrx, Vry
servo pin 6
Code
II explained code in the comments, I thought it would be a more efficient way, for simplicity copy code in Arduino and read, it will be more clear there.
Don’t forget to add a library of servo below.
#include <Servo.h>
// including servo library
Servo servo1;
// define servo name
// initialize variables and define pins
int x_pos;
int y_pos;
// Define pin for servo, define PWM pins
int servo1_pin = 6;
int initial_position = 90; // defined initial position, wanted to rotate both side
// set initial numbers
int xPosition = 0;
int yPosition = 0;
int SW_state = 0;
int mapX = 0;
int mapY = 0;
int VRx = A1;
int VRy = A0;
int SW = 8;
void setup ( ) {
Serial.begin (9600); // defining the input and output pins
servo1.attach (servo1_pin );
servo1.write (initial_position);;
pinMode(VRx, INPUT);
pinMode(VRy, INPUT);
pinMode(SW, INPUT_PULLUP);
}
void loop ( ) {
// cod is reading joystick x and y axis readings
xPosition = analogRead(VRx);
yPosition = analogRead(VRy);
SW_state = digitalRead(SW);
// printing on serial monitor
Serial.print("X: ");
Serial.print(mapX);
Serial.print(" | Y: ");
Serial.print(mapY);
Serial.print(" | Button: ");
Serial.println(SW_state);
delay(100);
x_pos = analogRead (xPosition); // reading position for servo control
// below code dividing the values in two segments, (0,300) and (700,1023).
// first part, lets say it is for rotation servo anti-clockwise code
/* Below if position comes below 300 */
if (x_pos < 300){
if (initial_position < 10) {
} // first it will check it is below 10 or what, if it is it will do nothing and forward the loop
else{
/* else it will decrease the data by 10, and new servo position will be available, this position values
will be added or decrease depends on the readings
*/
initial_position = initial_position - 10;
servo1.write ( initial_position );
delay (120); }
}
// second segment if values are greater then the 700, it will run servo to rotate oposite side
if (x_pos > 700){
if (initial_position > 980)
{
}
else{
initial_position = initial_position + 10; // it will just increase the values
servo1.write ( initial_position );
delay (120);
}
}
// same things for y
if (y_pos < 300){
if (initial_position < 10) {
}
else{ initial_position = initial_position - 10;
servo1.write ( initial_position );
delay (120); }
}
if (y_pos > 700){
if (initial_position > 180)
{
}
else{
initial_position = initial_position + 10;
servo1.write ( initial_position );
delay (120);
}
}
}
video
Group work
in group work, we have to measure the power consumption of any output component possible. we measured Power Consumption for a BLDC motor. In this group work, we don’t need to divide specific tasks! we did it together so.
Check group website for more information.
- For lower speed around 12, power consumption was 2.54 w (0.212 A on 12 v )
- For highest speed around 140, power consumption was 8.412 w (0.701 A on 12v)
Conclusion
This week made input week complete, learned I could use an input device to get different types of outputs.