I2C
Two Arduino boards Communication

ref.Arduino同士でI2C通信する方法
I2CではMasterとSlaveの組み合わせが大原則になっています。
通信の主導権は常にMasterが持ち、Masterからの要求に応じてSlaveが応える仕様になっています。
したがって、Slave同士での通信やSlaveからMasterにリクエストを送ることはできません。
In I2C, the combination of Master and Slave is a major principle.
Master always takes the initiative in communication, and Slave responds to requests from Master.
Therefore, it is not possible to communicate between Slave or send a request from Slave to Master.
Master(write), Secondary(read)
Master(write)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 | #include <Wire.h>
void setup() {
Wire.begin();
}
void loop() {
Wire.beginTransmission(8) ; //Secondary address #8
Wire.write("1", strlen("1")); //Send 1 to Secondary
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(1000);
Wire.beginTransmission(8) ;
Wire.write("0", strlen("1"));
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(1000);
}
|
Secondary(read)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 | #include <Wire.h>
int x = 0;
void setup() {
Wire.begin(8); //Secondary address is 8
pinMode (13, OUTPUT); //Built in LED
Wire.onReceive(receiveEvent);
}
void receiveEvent(int bytes) { //INTERRUPTION 割り込み
x = Wire.read(); //read 1 from Master
}
void loop() {
if (x == '1') {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH);//LED
}
if (x == '0') {
digitalWrite(13, LOW);//LED
}
}
|
Master(request), Secondary(write)
Master(request)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 | #include <Wire.h>
int int_x = 0; // char
void setup() {
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
Wire.requestFrom(8, 1); // request 1 bytes to Secondary #8
while (Wire.available()) {
int_x = Wire.read(); // receive from Secondary
Serial.print("x = "); Serial.println(int_x);
}
}
|
Secondary(write)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 | #include <Wire.h>
int int_y = 0; // char
void setup() {
Wire.begin(8); //Secondary address is 8
pinMode(5, INPUT);
Wire.onRequest(requestEvent);
}
void requestEvent() { //INTERRUPTION 割り込み
int_y = digitalRead(5);
Wire.write(int_y); //write to Master
}
void loop() {
}
|
Master(write and request), Secondary(read and write)
| Master |
Secondary |
| Write “1” to Secondary …(1) |
|
|
ISR onReceive run receiveEvent …(2) |
|
input “1” from Master into x …(3) |
|
“1” run ISR within if(x == `1`){ } …(4) |
| request 1 byte to Secondary …(5) |
|
| loof forever and wait from Secandary …(6) |
|
|
ISR onRequest run requestEvent …(7) |
|
read value from sensor and send to Master …(8) |
| Read value from secondary …(9) |
|
| Exit from forever loop by the value from Secondary …(10) |
|
Master(write and request)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28 | #include <Wire.h>
int int_x = 0;
void setup() {
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
Wire.beginTransmission(8) ; // Secondary address is 8
Wire.write("1", strlen("1")); // Send 1 to secondary ...(1)
Wire.endTransmission();
while (1) {// loop forever ...(6)
Wire.requestFrom(8, 1); // request 1 bytes to Secondary #8 ...(5)
while (Wire.available()) {
int_x = Wire.read(); // receive from Secondary ...(9)
Serial.print("int_x = "); Serial.println(int_x);
}
if (int_x == 1) { //...(10)
break; //exit from forever loop
}
delay(1000);
}
}
|
Secondary(read and write)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36 | #include <Wire.h>
int x = 0;
int int_y = 0;
void setup() {
Wire.begin(8); //Secondary address is 8
pinMode (5, INPUT); //Sensor pin
pinMode (13, OUTPUT); //Built in LED
Wire.onReceive(receiveEvent); // ...(2)
Wire.onRequest(requestEvent); // ...(7)
}
void receiveEvent(int bytes) { //Interrupt Service Routine 割り込み
x = Wire.read(); //read 1 from Master ...(3)
}
void requestEvent() { //ISR 割り込み
int_y = digitalRead(5); // ...(8)
Wire.write(int_y); //write to Master
}
void loop() {
if (x == '1') { // ...(4)
//digitalWrite(13, HIGH);//LED
while (int_y == 0) {
int_y = digitalRead(5);
digitalWrite(13, HIGH);
}
//rest
digitalWrite(13, LOW);//LED
x = '0';
}
}
|
Example
Master
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163 | #include <Servo.h>
//#include <Servo_megaTinyCore.h>
#include <Wire.h>
int weight1 = 0;
int masu = 85; //weight of masu
int sake = 30; //weight of sake
int pour = 0;
//int x = 1;
int ledPin = 12; // LED connected to digital pin 12
//int switchPin = 7; // Switch to behave scale weight
int switchPin = A3; // Switch to behave scale weight(pro micro)
Servo myservo1; // create servo1 object to control a servo
Servo myservo2; // create servo2 object to control a servo
int pos = 0; // change the servo degrees
int pos_now = 1;
int Liquid_level = 0; // received liquid_level from Secondary
//int int_x = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
myservo1.attach(6); // attaches the servo1 on pin 8 (PWM) to the servo object
myservo2.attach(9); // attaches the servo2 on pin 9 (PWM) to the servo object
//Set the servos to initial positions
myservo1.write(90);
myservo2.write(135);
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
//Wire.swap(1);
Wire.begin();
}
void loop() {
Serial.println("Loop");
int sensorValue = analogRead(switchPin);
float weight1 = sensorValue * ((masu + sake) / 1023.0);
Serial.println(weight1);
if (weight1 < 75) {
// do nothing
Serial.println("do nothing under 75g");
} else if (weight1 > 90) {
// do nothing
Serial.println("do nothing over 90g");
} else {
// Servo1
if ((weight1 >= 75) && (weight1 <= 90)) { //If the weight1 is 75-90g
Serial.println("masu is ON");
for (pos = 90; pos >= 0; pos -= 1) {
myservo1.write(pos); // tell servo1 to go to position in variable 'pos'
delay(30); // waits 30ms for the servo to reach the position
}
//mp3
Wire.beginTransmission(8) ; // Secondary address is 8
Wire.write("2", strlen("2")); // Send 1 to secondary
Wire.endTransmission();
Serial.print("sent "); Serial.println("2");
delay(500);
//OLED
Wire.beginTransmission(9) ; // Secondary address is 9
Wire.write("3", strlen("3")); // Send 1 to secondary
Wire.endTransmission();
Serial.print("sent "); Serial.println("3");
delay(500);
// Servo2
for (pos = 135; pos >= 55; pos -= 1) { // goes from 135 degrees to 55 degrees
myservo2.write(pos);
sensorValue = analogRead(switchPin);
weight1 = sensorValue * ((masu + sake) / 1023.0);
Serial.println(weight1);
Serial.println("pouring quickly");
pos_now = pos;
if (weight1 >= (masu + sake / 3) ) { //85 + 30/3=95g
break;
}
delay(50);
}
//in here, weight1 >= masu + sake / 3
// Servo2
for (pos = pos_now; pos >= 45; pos -= 1) { // goes from 55 degrees to 45 degrees
myservo2.write(pos);
sensorValue = analogRead(switchPin);
weight1 = sensorValue * ((masu + sake) / 1023.0);
Serial.println(weight1);
Serial.println("pouring slowly");
pos_now = pos;
if (weight1 >= (masu + sake)) { //85 + 30=115g
break;
}
delay(300);
}
// in here, weight1 > masu + sake
// Servo2
for (pos = pos_now; pos <= 135; pos += 1) { // goes from 45 degrees to 135 degrees
myservo2.write(pos);
delay(50);
}
// Servo1
for (pos = 0; pos <= 90; pos += 1) { // goes from 0 degrees to 90 degrees
// in steps of 1 degree
myservo1.write(pos);
delay(30);
//
}
pour = pour + 1;
Serial.print("pour= "); Serial.print(pour); Serial.println(" not_empty");
delay(500);
if (pour >= 3) {
Serial.println("empty now request to Refill");
delay(3000);
Wire.beginTransmission(8) ; // Secondary address is 8
Wire.write("1", strlen("1")); // Send 1 to secondary
Wire.endTransmission();
Serial.print("sent "); Serial.println("1");
delay(3000);
while (1) { // loop forever
Wire.requestFrom(8, 1); // request 1 bytes from secondary device #8
Serial.println("request Liquid_level");
while (Wire.available()) {
Liquid_level = Wire.read(); // receive from secondary
Serial.print("Liquid_level="); Serial.println(char(Liquid_level));// "1" is ASCII code 49
}
if (Liquid_level == '1') {//Liquid is full
break;
}
delay(5000);
}//while(1)
Serial.println("break");
pour = 0;
}//if (pour >= 3)
}//if
}//else
delay(500);
} //loop
|
Secondary
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77 | #include <Wire.h>
int x = 0;
int Liquid_level = 0;
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
SoftwareSerial Serial1(2, 3);//(Rx_UNO_to_Tx_mp3,Tx_UNO with 1k ohm)
void setup() {
Wire.begin(8);
pinMode (14, OUTPUT); // A0 MOTOR
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial1.begin(9600);
volume(0x1E);//Volume settings 0x00-0x1E
Wire.onReceive(receiveEvent);
Wire.onRequest(requestEvent);
}
void receiveEvent(int bytes) { // Interrupt Service Routine 割り込み
x = Wire.read(); // read e from Master
Serial.print("received -------------" ); Serial.println((char)x);// "1" is ASCII code 49
Liquid_level = 0;//empty
}
void requestEvent() { //ISR 割り込み
Serial.println("REQUESTEvent");
if (Liquid_level == 1) {
Wire.write("1", strlen("1"));
Serial.print("sent Liquid_level = "); Serial.println(Liquid_level);
} else
Wire.write("0", strlen("0"));
}
void loop() {
Serial.println("Loop");
//mp3
if (x == '2') {
Serial.println("play music");
play(0x01);//Play the specified audio:0x01-file0001//au
delay(2000);
x = '0';
}
//Motor
if (x != '1') {
// do nothing
Serial.println("do nothing");
}
else if (x == '1') {
Serial.println("MOTOR ON");
digitalWrite(14, HIGH); //MOTOR
delay(5000);
digitalWrite(14, LOW);//MOTOR
delay(500);
Liquid_level = 1;//full
Serial.print("Motor OFF: Liquid_level ="); Serial.println(Liquid_level);
x = '0';
}
delay(500);
}//loop
void play(unsigned char Track) {
unsigned char play[6] = {0xAA, 0x07, 0x02, 0x00, Track, Track + 0xB3};
Serial1.write(play, 6);//(buf, len)
}
void volume( unsigned char vol) {
unsigned char volume[5] = {0xAA, 0x13, 0x01, vol, vol + 0xBE};
Serial1.write(volume, 5);
}
|
Open 2 Serial Monitors
mac in Terminal
| % ls /dev | grep usb
tty.usbmodem14301
tty.usbserial-D307RG9V
% screen /dev/tty.usbmodem14301 9600
// command + n // open new Terminal
% screen /dev/tty.usbserial-D307RG9V 9600
|
Windows in PuTTY
Setup
- Download PuTTY from site or here
- Run Installer (putty-64bit-0.76-installer)
Open Serial Monitor
- Start “PuTTY” from Start menu and set COM port
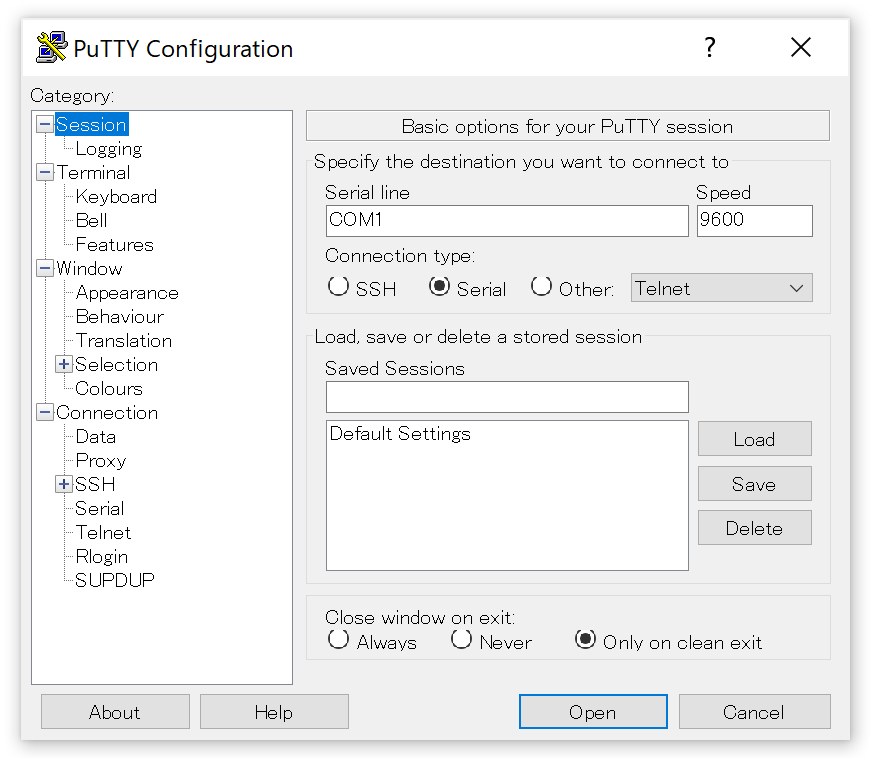
- To open 2nd Serial Monitor, re-start “PuTTy” and set other COM port
You may see here to send Japanese character in strings.
- type
cmd to open Command Prompt
- type
mode
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40 | C:\Users\name>mode
デバイス状態 COM6:
------------
ボー レート: 9600
パリティ: None
データ ビット: 8
ストップ ビット: 1
タイムアウト: OFF
XON/XOFF: ON
CTS ハンドシェイク: OFF
DSR ハンドシェイク: OFF
DSR の検知: OFF
DTR サーキット: ON
RTS サーキット: ON
デバイス状態 COM4:
------------
ボー レート: 0
パリティ: None
データ ビット: 0
ストップ ビット: 1
タイムアウト: OFF
XON/XOFF: OFF
CTS ハンドシェイク: OFF
DSR ハンドシェイク: OFF
DSR の検知: OFF
DTR サーキット: OFF
RTS サーキット: ON
デバイス状態 CON:
-----------
行数: 9001
桁数: 120
キーボード速度: 31
キーボード ディレイ: 1
コード ページ: 932
コード ページ: 932
|
I2C address
| #define SCREEN_ADDRESS 0x3C //0b0111100 //7bits
#define SCREEN_ADDRESS 0x78 //0b01111000 //8bits
#define SCREEN_ADDRESS 0x78>>1 //0b0111100 //
|
| 7bits (device) address |
Decimals |
Hexadecimal |
8 bits address(7bit +0) |
Hex |
| 0b0000 000_ |
0d000 Reserved |
0x00 |
0b0000 0000 |
0x00 |
| 0b0000 001_ |
0d001 Reserved |
0x01 |
0b0000 0010 |
0x02 |
| 0b0000 010_ |
0d002 Reserved |
0x02 |
0b0000 0100 |
0x04 |
| 0b0000 011_ |
0d003 Reserved |
0x03 |
0b0000 0110 |
0x06 |
| 0b0000 100_ |
0d004 Reserved |
0x04 |
0b0000 1000 |
0x08 |
| 0b0000 101_ |
0d005 Reserved |
0x05 |
0b0000 1010 |
0x0A |
| 0b0000 110_ |
0d006 Reserved |
0x06 |
0b0000 1100 |
0x0C |
| 0b0000 111_ |
0d007 Reserved |
0x07 |
0b0000 1110 |
0x0E |
| 0b0001 000_ |
0d008 min |
0x08 |
0b0001 0000 |
0x10 |
| … |
|
|
|
|
| 0b0111 100_ |
0d060 OLED |
0x3C |
0b0111 1000 |
0x78 |
| … |
|
|
|
|
| 0b1111 111_ |
0d127 max |
0x7F |
0b1111 1110 |
0xFE |
ref. Convert decimal to binary, octal and hexadecimal
There are both 7- and 8-bit versions of I2C addresses. 7 bits identify the device, and the eighth bit determines if it’s being written to or read from. The Wire library uses 7 bit addresses throughout. If you have a datasheet or sample code that uses 8 bit address, you’ll want to drop the low bit (i.e. shift the value one bit to the right), yielding an address between 0 and 127. However the addresses from 0 to 7 are not used because are reserved so the first address that can be used is 8. Please note that a pull-up resistor is needed when connecting SDA/SCL pins. Please refer to the examples for more informations. MEGA 2560 board has pull-up resistors on pins 20 - 21 onboard.
ref. Wire Library
Last update: October 6, 2021

