

1.Group Assignment.
characterize your lasercutter's focus, power, speed, rate, kerf, joint clearance and types
In this week of Computer-Controlled-Cutting,We have seen many things regarding substractive processes by using Laser cutter machine
Firstly we have been reminded by our Instructor the general working principle of Laser cutter machine,from the physics as theory of reflection of beams.
A laser cutter machine uses a high-powered laser beam to cut or engrave various materials. The laser beam is generated in a laser resonator and then directed through a series of mirrors and lenses to focus the beam onto the material being cut or engraved.
The laser beam is typically generated by exciting a gas, such as carbon dioxide, in the resonator using a high-voltage electrical discharge. The excited gas molecules emit photons, which create a coherent beam of light that is directed through the laser cutter's optics.
The laser beam is directed by mirrors and focused by lenses to a very small spot size. This intense concentration of energy is used to vaporize or melt the material being cut or engraved, creating a precise cut or engraving. The laser beam is controlled by computer software that directs the beam along the desired path, allowing for complex and intricate designs.
We have discussed different types of Laser according to wavelength(carbon dioxide and fiber),Applications(carbon dioxide(Non-Mettalic)and fiber(metallic)) and according to tubes (Glass tube and Mettalic tubes).
We discussed also on the focal point as the core reason for laser to cut because of the concentration of beams.
Our Laser is Epilog laser Mini , A laser cutting machine has settings known as the computer numerical control (CNC), as well as laser optics, which control and direct the laser beam’s intensity for the desired design effect, or the specific cuts required in a manufacturing or design project. The laser beam is generated by a process whereby electrical discharges or a lamp trigger a lasing material within a confined container causing a chemical reaction, resulting in a high powered beam being released. The beam is then reflected using a mirror in a stream of monochromatic light. From the mirror, the light is then directed by fibre optics or mirrors to the work area, with the narrowest point of the beam cutting or making the design etch on the material, For our laser its primary element is Carbon dioxide to be used in creating the beam of light. here
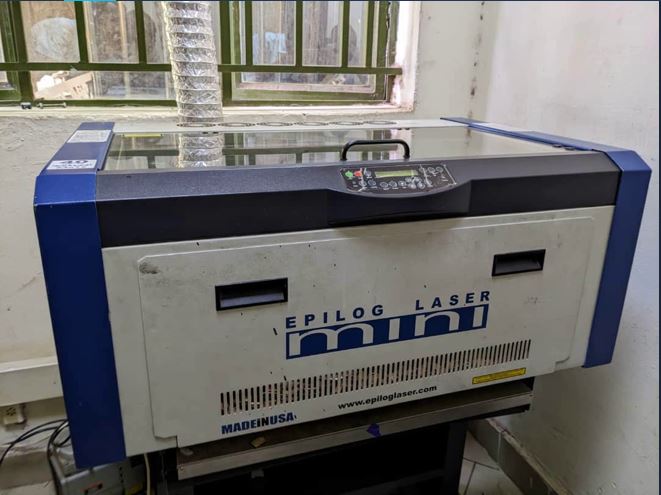

Names:Epilog Laser Mini
Wave length: Carbon dioxide Laser
Working Power: 40 watts
Bed-size:(306-609)mm
We have spent time in setting the parameters and their effect on the job, below are some experiments we did on Laser cutter to check the effect of the parameters.
Laser Cut Focus means the extremely concentrated point where all rays converges on the same point,It ensures that the maximum amount of available energy produced by the tube reaches the work piece.
Place the material/work piece that you want to cut or engrave on the cutting bed of the laser cutter. Make sure it is securely fastened in place.
Use a Vernier caliper to measure the thickness of the material. This information is needed to determine the correct focus distance.
By using the focus checker ,Adjust bed on Z-axis in order to create material-focus checker contact, once there's contact
Turn on the laser cutter and run a test cut or engrave on a small portion of the material. If the cut is too shallow or too deep, adjust the focus lens accordingly and repeat the test until the focus is correct.
Once the focus has been set correctly,and It is repeatitive work or using same material, you can remain with the focus until material is changed.
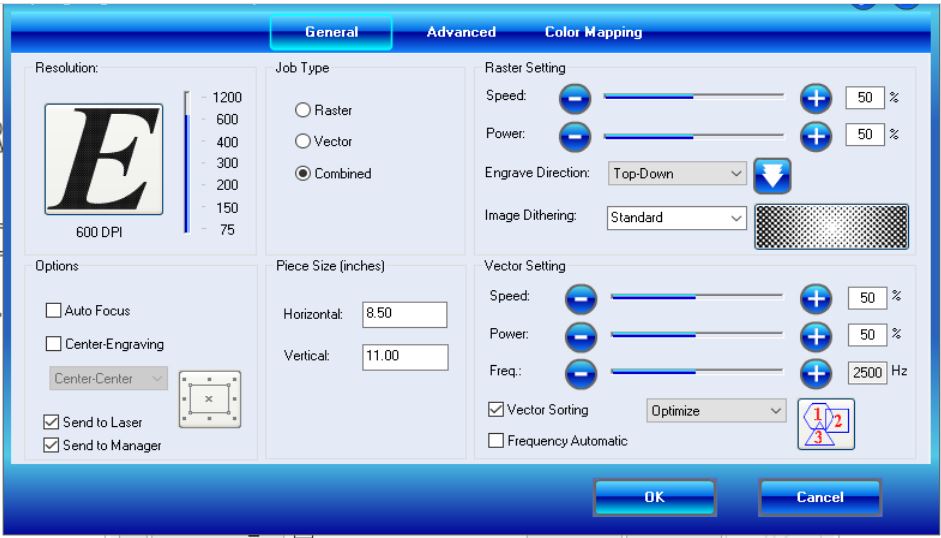
Laser Power:Refers to the amount of energy absorbed into the work sheet, And as you increase the temperature of beam increases in order to penetrate and also produce smokes which are consumed by filters,and also
It's critical to know the parameters to be used while using laser cutter machine, without knowing the variation of parameters and their effect to the outout it will be difficult to get the desired ,and they told us that requires some experience as someone get used in it he will get to know the parameters that fits to each type of material.
Laser Power:Refers to the amount of energy absorbed into the work sheet, And as you increase the temperature of beam increases in order to penetrate and also produce smokes which are consumed by filters.
As The higher the laser power, the faster the material will be cut. However, high laser power can also cause thermal damage to the material being cut and can lead to warping or melting mostly for plastic materials like Acrylic.
Laser Speed:The cutting speed refers to the speed at which the laser moves across the material being cut. Increasing the cutting speed can reduce the time it takes to complete a cut, but it can also lead to reduced cut quality and increased chance of burning. For example, large-scale engravings of TroLase materials are engraved at high speeds between 80 and 100%, but for photo engravings with lots of detail on wood, the speed should not exceed 10%.
Laser Rate:It basically refer to how many cycles per period time, it is interconnected to the speed of the head in way that one depend on the other,and also it means The pulse frequency which refers to the number of laser pulses per second. Higher pulse frequencies can increase the cutting speed, but they can also increase the chance of thermal damage to the material

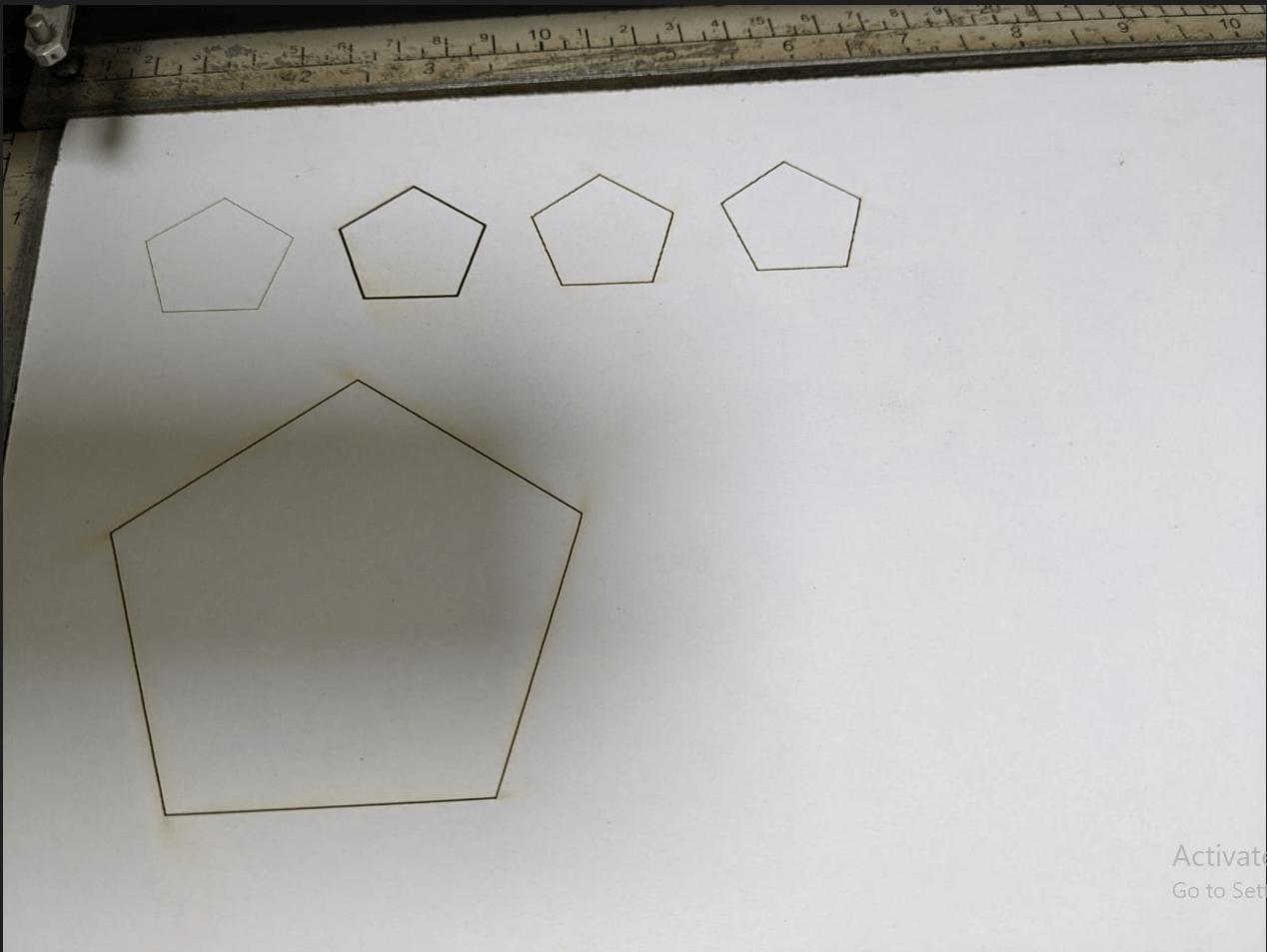
By using different parameters power,rate,speed it cuts same part but it results different outputs
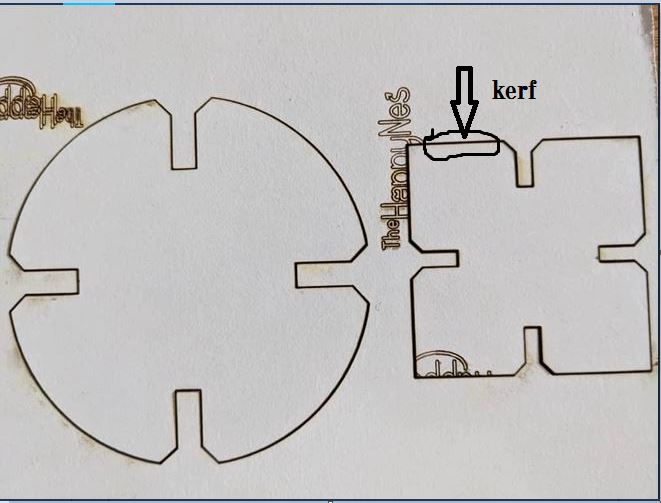
Laser Kerf:Kerf refers to the width of the cut made by a laser, saw, or other cutting tool. In laser cutting, the kerf is determined by the width of the laser beam, which is typically very small. However, the kerf can still have an effect on the materials being cut.
One effect of kerf is material loss. The width of the kerf can result in a small amount of material being lost during the cutting process, which can be a concern when cutting expensive materials or when cutting to tight tolerances.
Another effect of kerf is the potential for material distortion. Depending on the thickness and type of material being cut, the heat generated by the laser can cause the material to warp or bend slightly along the edges of the cut. This can affect the dimensional accuracy of the cut and may require additional finishing or correction steps.
Additionally, the kerf can affect the precision of the cut. If the kerf is wider than desired, the cut may not be as precise as intended, which can be a concern when cutting intricate or detailed designs.
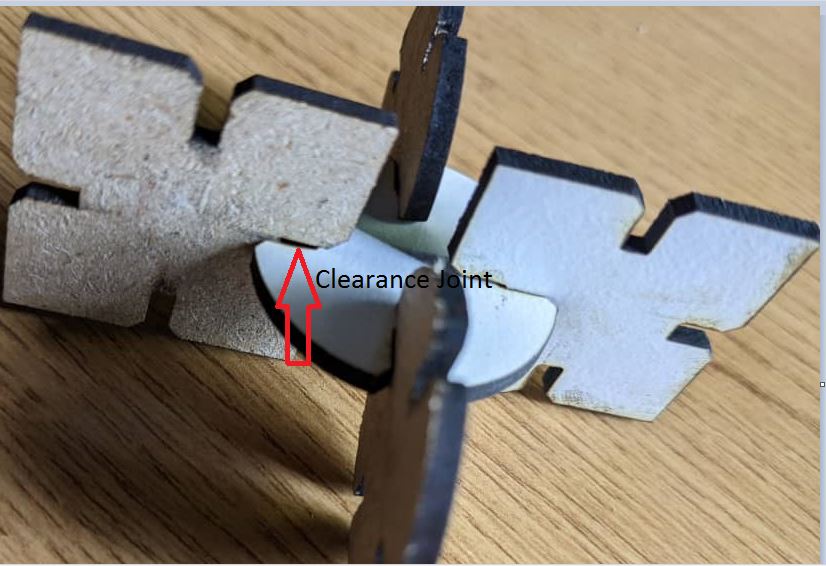
Laser Joint clearance:Laser joint clearance refers to the gap between the two parts being joined together by a laser welding process,The size of the joint clearance can have an effect on the material being welded.
If the joint clearance is too small, it can lead to insufficient penetration of the laser beam into the material. This can result in an incomplete weld, reduced joint strength, and potential failure of the joint under stress.
On the other hand, if the joint clearance is too large, it can result in excess weld material that may cause deformation, warping, or cracking of the material being welded. This can also lead to reduced joint strength and potential failure under stress.
Proper selection of the joint clearance is important for achieving a strong and reliable weld. The ideal joint clearance will depend on factors such as the material being welded, the thickness of the material, and the desired strength and durability of the joint. In general, a joint clearance of around 10-15% of the material thickness is often recommended.
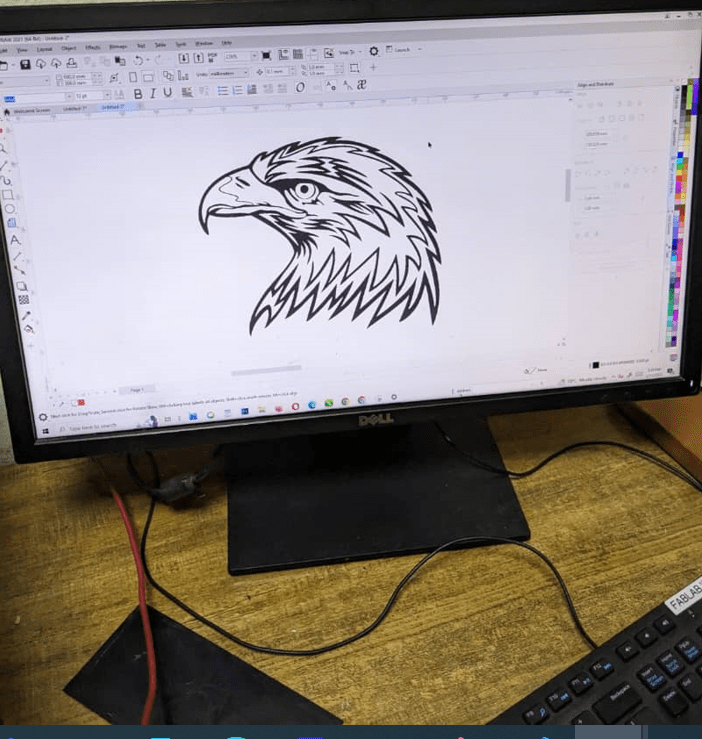
From the Corel draw we changed eagle Image into it's vectors,
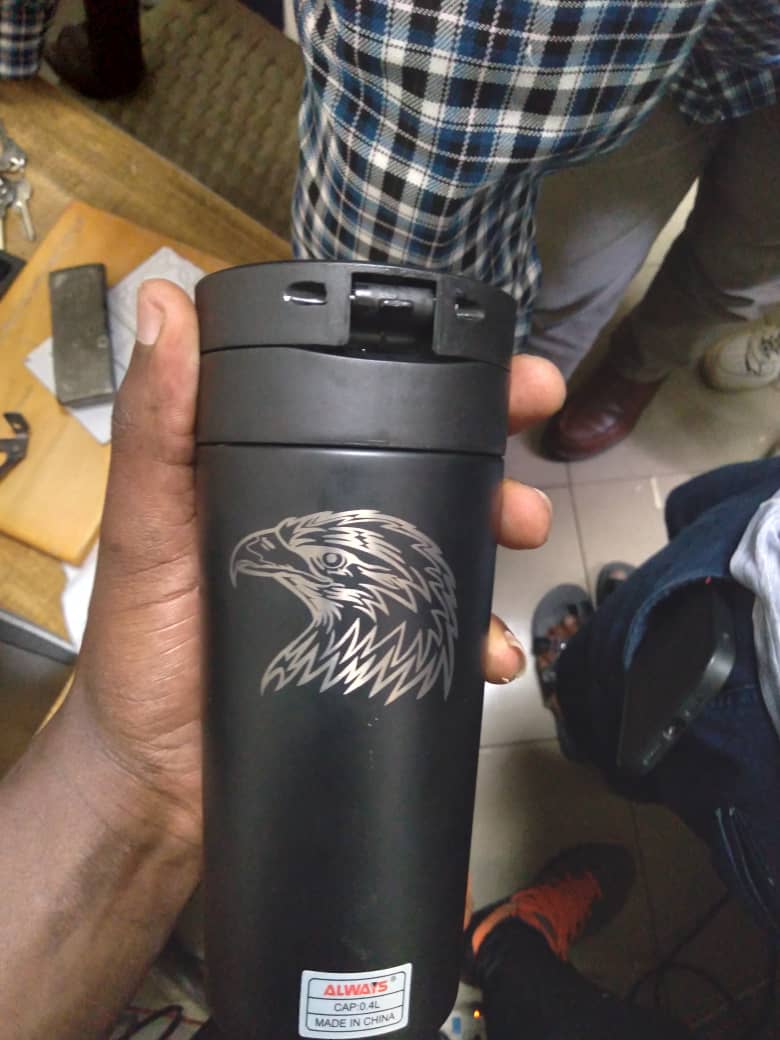
And final output from the Laser cutter machine was this below;

In order to have successful progress in our Manufacturing Laboratory will always require the protocol and the essential ones are the safety measures because we are using Machines that can harm our lives.
NEVER leave the laser machine unattended when in operation.
Carry out the advised routine maintenance to schedule.
Make sure your materials are laser-friendly. Check with your supplier if you are using a new material and unsure if it is safe to laser process.
Exhaust systems must be installed properly and meet all manufacturer specifications.
Exposure to laser beam can cause severe eye damage or skin burns
