Introduction.
In this I met and explore information related to laser cutters, I find it very interesting
things that can be done or rather cut with such precision. The vinyl cutter is a machine
that is mainly used to trim vinyl and other materials in many shapes or letters, depending
on the needs of use.
The vinyl cutter is not a very large device; You can connect to a computer with a cable to
give cutting instructions.
To make the cut in both vinyl and laser it is necessary to use software to model the cut,
there is something very interesting called parametric design, which allows you to design and
assign values to your dimensions through the use of variables, which is nothing more than
a kind of excel sheet that allows changing values. Among the software that allows this is
freecad, autocad, fusion, rhino and others.
Laser cutter characterization.
One that is used is the CAMFive
CFL-CMA1080K laser cutting recorder, which has a work area of 1.00 x 0.80m, the
table can automatically raise and lower, in addition to having a rotating accessory with
which it is possible to cylindrically engrave objects.
Laser cutting is a type of thermal separation process. The laser beam impacts the
surface of the material and heats it with such force that it melts or vaporizes by
full. Once the laser beam has completely penetrated the material at one point,
The actual cutting process begins. The laser system follows the selected geometry and
separates the material in the process depending on the application the use of process gases
It can positively influence the results.

Soft material |
Cut |
Graven |
|---|---|---|
| Paper | yes | yes |
| Paperboard | yes | yes |
| Foaming | yes | yes |
| Felt | yes | yes |
| Cotton fiber and mixed fabrics | yes | yes |
| Thick synthetic fibers fabrics | yes | yes |
| Synthetic fabric Lycra and thin | yes | no |
| Leather (Natural leather) | yes | yes |
| Leather (Synthetic leather) | yes | yes |
| Rubber (rubber or rubber) | yes | yes |
| Cork | yes | yes |
Hard materials |
Cut |
Graven |
|---|---|---|
| MDF | yes | yes |
| Wood | yes | yes |
| Foaming | yes | yes |
| Triplay | yes | yes |
| Plastic | yes | yes |
| Acrylic | yes | yes |
| Glasses and crystals | no | yes |
| Ceramics | no | yes |
| Marble, Onyx and other rocks | no | yes |
| Tile | no | yes |
| Metal (apply special resin) | no | yes |
Technical specifications
WEIGHT: 185 Kg (407.85 pounds) DIMENSIONS: Width: 1.35 meters (53.15 ") Height: 1.17 meters (46.06") Depth: 0.99 meters (38.97 ") To make use of the laser cutter there must be a hygiene and safety plan and must always be respected, to avoid accidents and to ensure the proper functioning of the equipment. The first step is to verify that it is connected to the power, then activate the voltage regulator's power switch, set to 216V input voltage and 220V output voltage. Then, turn on the machine, releasing the emergency stop button and insert the key. Turn the intensity knob and press the laser button, which will turn on white, indicating that the laser is active. From here you must be very careful, because the laser is not visible. To make a cut or engrave, there are two options: upload the file directly to the machine through the USB port or through software that controls the machine. Files must be in .DXF format.
Before making a cut, take into account the following data, as you can see both the
speed and the power range depend on the type of material and its thickness.
Remember that these are suggestions of standard measures to program cutting or engraving
jobs, but depending on the type of edge you want in the design. These parameters will
also vary, as the ray burns or sublimates, leaving a more intense color in the contours
of certain materials such as wood.
|
CUT |
RECORDED |
||||
|
Material |
Thickness in mm |
Speed in mm / min |
Power range |
Speed in mm / min |
Power range |
|
MDF |
3 |
15-20 |
50-60 |
200-400 |
30-50 |
|
6 |
10-15 |
60-70 |
|||
|
9 |
5-8 |
80-85 |
|||
|
12 |
3-8 |
85-90 |
|||
|
Acrylic |
3 |
10-20 |
60-65 |
200-400 |
20-35 |
|
6 |
6-10 |
60-70 |
|||
|
9 |
5-7 |
80-85 |
|||
|
12 |
2-5 |
92-93 |
|||
|
18 |
1-2 |
85-90 |
|||
|
Bond paper |
NA |
100 |
15-20 |
600 |
15-20 |
|
Cardboard |
NA |
50 |
30-35 |
600 |
40-45 |
The process of laser cutting
Laser cutting is based on the interaction between a focused laser beam and the workpiece. In
order for this process to be carried out safely and precisely, a multitude of components and
auxiliary means come into play in the laser beam and in its environment, which are clarified
in the following graphic.
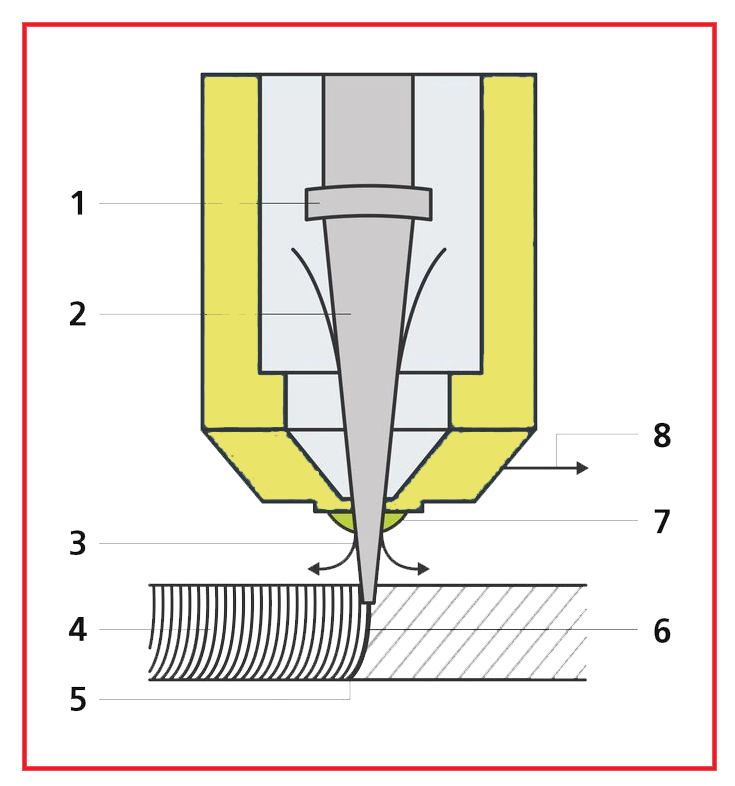
- Focusing optics: mirror and lens optics focus the laser beam on the machining point.
- Laser beam: the laser beam strikes the part and heats it until it melts or evaporates.
- Cutting gas: with the help of cutting gas, the generated melt is blown out of the cutting groove. The cutting gas exits the nozzle coaxially at the same time as the laser beam.
- Cut grooves - In laser cutting, the cut edge receives a characteristic groove pattern. With a low cutting speed, these grooves run practically parallel to the laser beam.
- Casting: the laser beam (concentrated laser light) is guided along the contour and melts the material locally.
- Cutting face: On the cut piece, the width of the cut groove just barely exceeds that of the focused laser beam.
- Nozzle: the laser beam and cutting gas strike the workpiece through the cutting nozzle.
- Cutting direction: by moving the cutting head or the workpiece in a certain direction, the cutting groove is produced.