10. Molding and casting¶
Due date 2024/04/23
chess pieces for a travel set
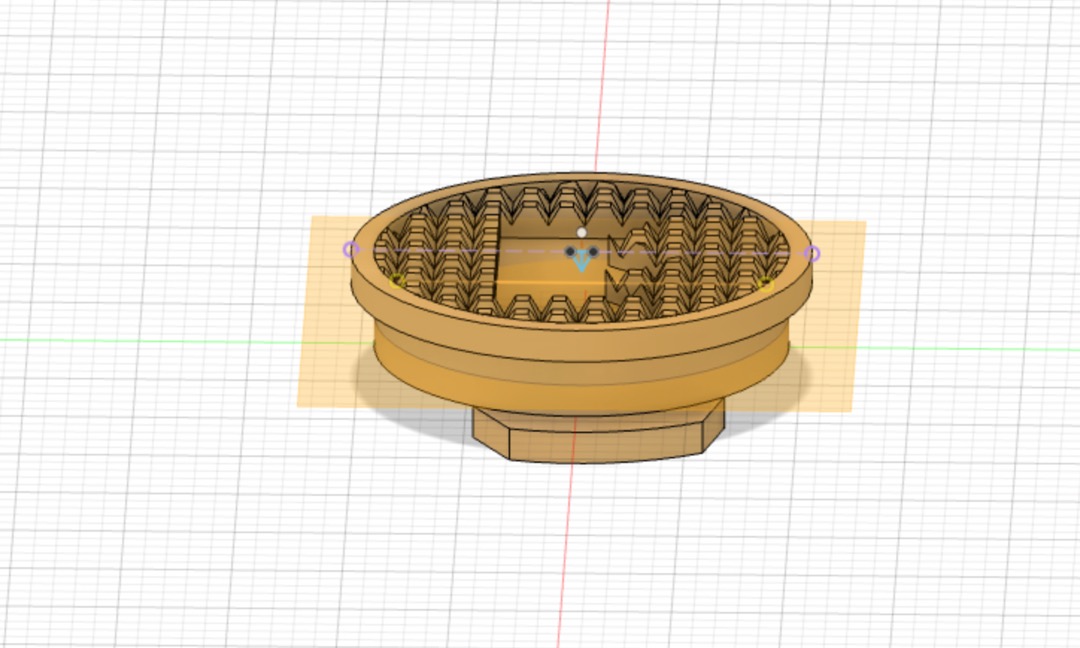
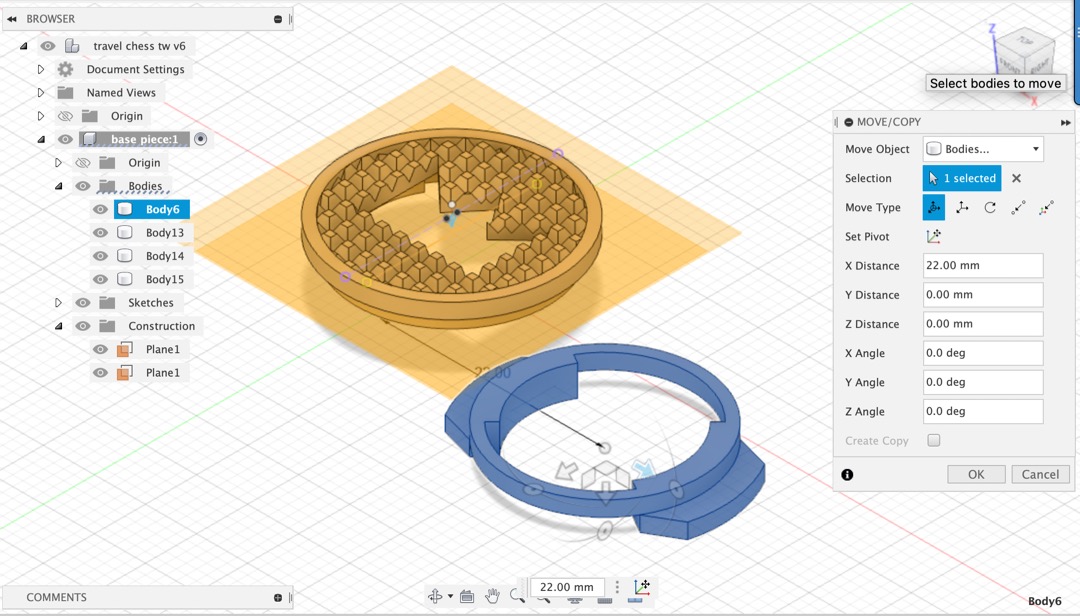
Conceive¶
- This week we focused on learning how to create 3-dimensional objects using forms, composites, casts and machined molds.
How to use this document
Please refer to instructions in the week02 weblog entry
- Create this box using the Admonition extension
Assignment¶
| Have you? | Done |
|---|---|
| Group assignment | ⬇ |
| Review the safety data sheets for each of your molding and casting materials | No |
| Make and compare test casts with each of them | No |
| Compare printing vs milling molds | No |
| Individual assignment: | ⬇ |
| Design a mold around the process you’ll be using, produce it with a smooth surface finish, and use it to cast parts. | No |
| No |
Learning outcomes¶
| Have you? | Done |
|---|---|
| Design appropriate objects within the limitations of 3 axis machinin | No |
| Demonstrate workflows used in mould design, construction and casting | No |
Checklist questions¶
| Have you? | Done |
|---|---|
| Linked to the group assignment page and reflected on your individual page what you have learned? | Yes |
| Reviewed the safety data sheets for each of your molding and casting materials, then made and compared test casts with each of them? | No |
| Documented how you designed and created your 3D mold, including machine settings? | No |
| Shown how you safely made your mold and cast the parts? | No |
| Described problems and how you fixed them? | No |
| Included your design files? | No |
| ‘hero shot’ of the mold and the final object? | No |
Context¶
- Syllabus Molding
- Assessment Molding
- Tutorial Molding
- Video Molding
- Review Molding
- FabAcademy 2021 Documents
- FabAcademy Mattermost Chat Page
- FabAcademy Evaluation Page This site requires a fablab.io account to login
- FabAcademy Home Page
- FabLabs Home Page
Comprehend¶
- Forming and molding
- Unlike subtractive manufacturing when machines remove chips to create objects or additive fabrication when machines create objects by fusing together layers of material, manufacturing by forming and molding happen when machines make complete objects at once using pressure or vacuum to force material into predefined shapes. (callister, p. 417 & p.612; TMEH vol.2 ch.16)
- Casting
- Casting happens when machines produce complete objects from molten material using molds and allowed to solidify.
- Materials
- Metals
- Plastics
- Composites
- Material constraints
- Wear properties
- Heat resistance
- Tensile strength
- When done properly, finished objects retain their structure, complexity and strength.
- In general, one can form or cast a part much faster than make it from subtractive or additive properties.
Take caution¶
- Human
- Machine
- Environment
Calibrate¶
Control¶
- Design the object to meet all constraints-FAW03
- Determine part constraints including the following
- Availability
- Material requirements
- Cost
- Available processes
- Choose the material to meet the constraints
- Choose the process to use
- Fabricate the object
- Group assignment (learn the skills that implement the concept)
- Review the safety data sheets for each of your molding and casting materials
- Make and compare test casts with each of them
Create¶
- Abundance of material
- News paper
- Scrap metal
- Plastic bottles (type 1)
- wood
- Identify Renewable materials
- Reduce Energy requirements
- Lower melting points of material
- Improve part removal from molds
- Improve material flow into molds
- Individual assignment
- ReadDesign a 3D mould around the stock and tooling that you’ll be using, mill it (rough cut + (at least) three-axis finish cut), and use it to cast parts.