1.16 Applications and Implications
1. IDEAS: Heart of the Universe: or What have in common an ECG, a radio telescope and a robotic ant?
Heart of the Universe is a three-act storytelling, a playful way to mix bits and atoms.
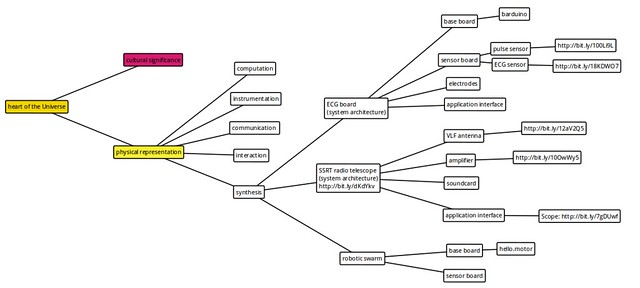
Figure 1. Final project proposal: components interaction and integration.
1.1 Components
- QUORE
- FRACTALSTORM
- PROTOBOTS
1.2 Questions
2. QUORE
2.1 Overview
A portable low-cost EKG device based on the FabECG.
Will be required to make a circuit board and a (plastic, cardboard or wood) box. This requires the use of computer aided design, computer controlled cutting (laser cutting), electronics design, electronics production (board milling)
The estimated cost will be about 40 USD dollars in materials, plus the cost of the process (machine time in laser cutting, CNC milling, etc) and the cost of the design (in man-hour). It is necesary to make iterations focusing on the minimum viable product which in this case is
2.2 Conceptual Design: Structure
It is really necesary to design one piece structures in order to make this project or any object?. I think that it is not necesary, because if in the end everything are comprised of atoms, we can resemble this using interchangeable parts, similar as in architecture is the use of space frames to achieve complex structures. The main benefit is error correction, because in case of an error we can simply change one small bad piece instead of discard a complete work. Thats how nature work, and it seems to work well.
This idea is similar to what I have intended to make in Computer Controlled Cutting, which was to generate a 3D structure from a 2D design grammar. In this case the grammar has to be thinked natively in 3D



2.2 Conceptual Design: Instrumentation
I am using the FabECG v6m design of Charles Fracchia and Adam Marblestone
There is several concepts to understand the data, there is an interesting essay written by Abdallah Ishbeata describing the physiology fundamentals and the concepts behind the circuit design.
2.3 Conceptual Design: Computation
At this version it will only show the signal
3. NOISESTORM
3.1 Overview
A solar storm amateur mini radio telescope. Everybody can be a radio astronomer
3.2 Conceptual Design: Structure
There is a system architecture defined on this document: How to build your own Radio Telescope (page 11 of the .pdf file). But it only defines in a basic high level:
- VLF Antenna
- Amplifier
- Digitalizer (soundcard)
- Application interface (software)

These is the structure of the components needed to create, and it is also the way we can make a work breakdown. In the end we only need to integrate the components to obtain the result. Our work then is to make independently a VLF antenna, an amplifier, a soundcard (we can reuse the one that is usually integrated on laptops), and a application interface.
3.2.A - VLF Antenna: Because of the basic architecture, the VLF antenna can be replaced with a simple antenna but it will only receive and amplify the electrical noise in the environment
3.2.B - Amplifier: There is a basic circuit schematic of John Brooks but there is only a image of the schematic not the circuit design so it was necesary to translate the schematic into an eagle design.
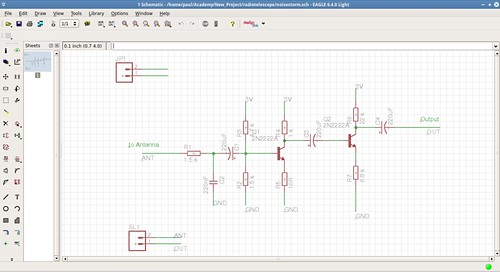
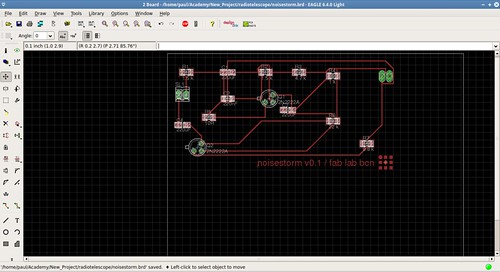

3.2.C - Digitalizer: reuse the soundcard audio input port
3.2.D - Application interface: a software to process the data received
