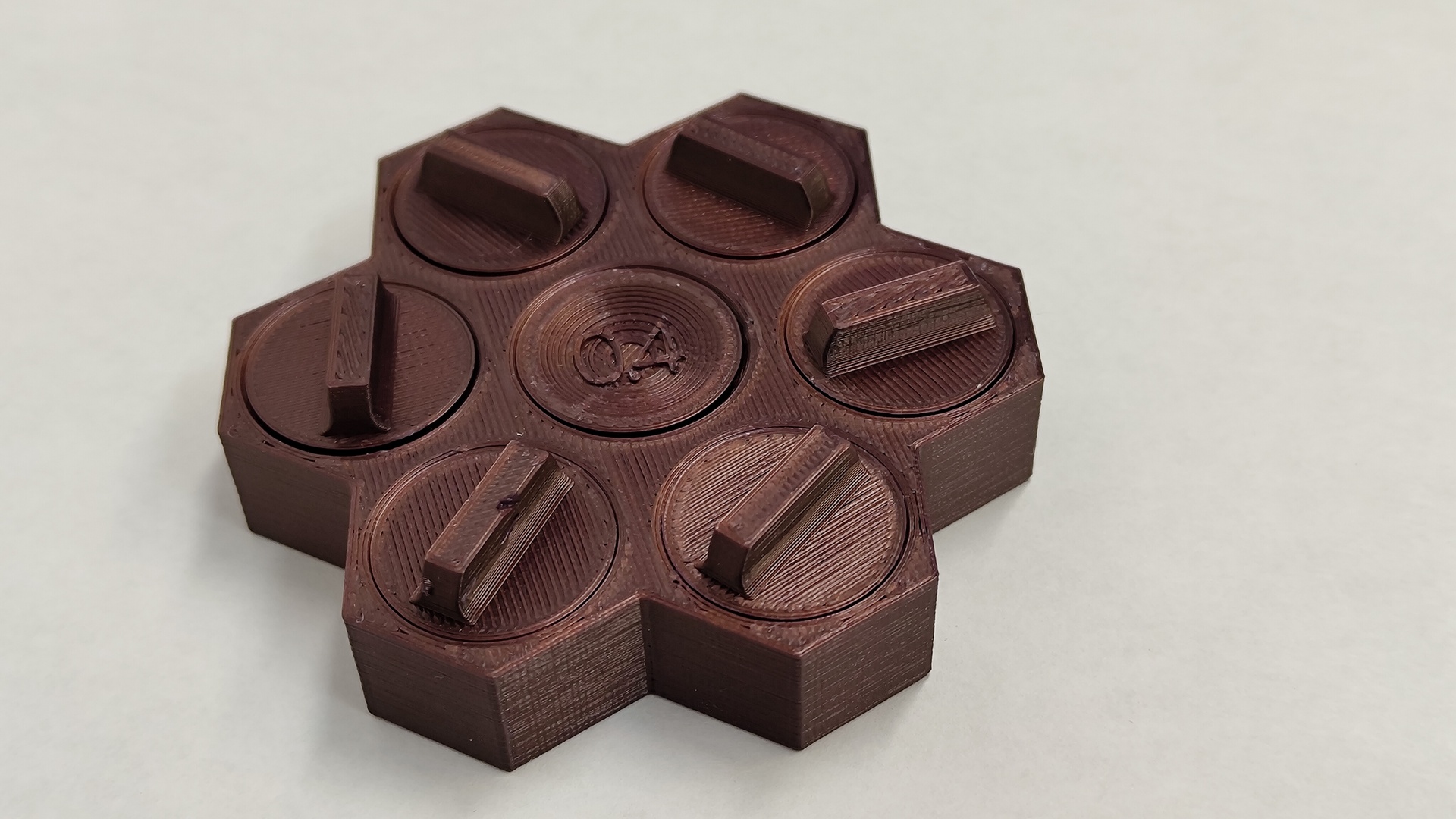
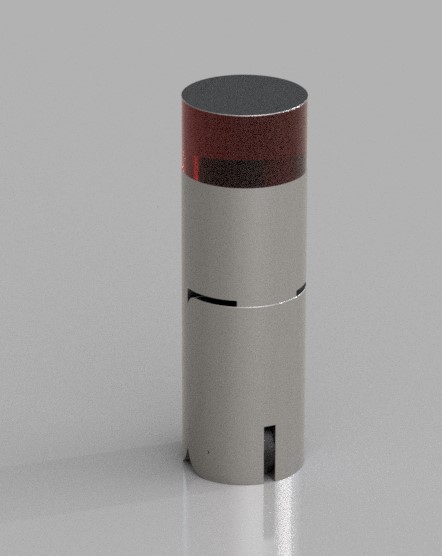
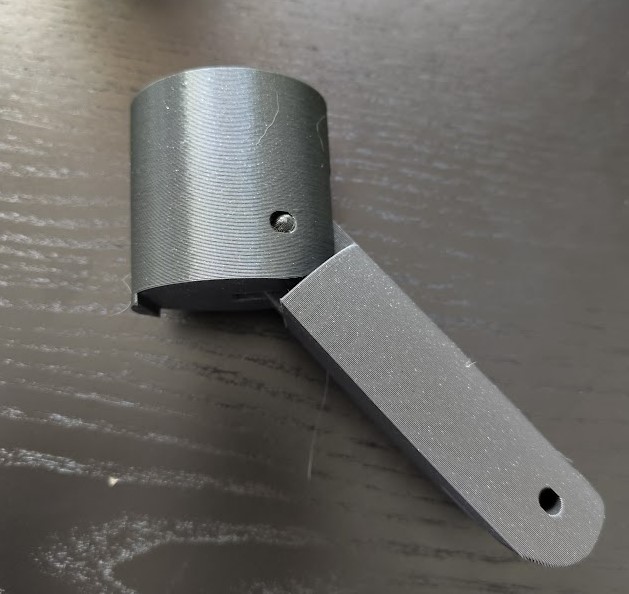
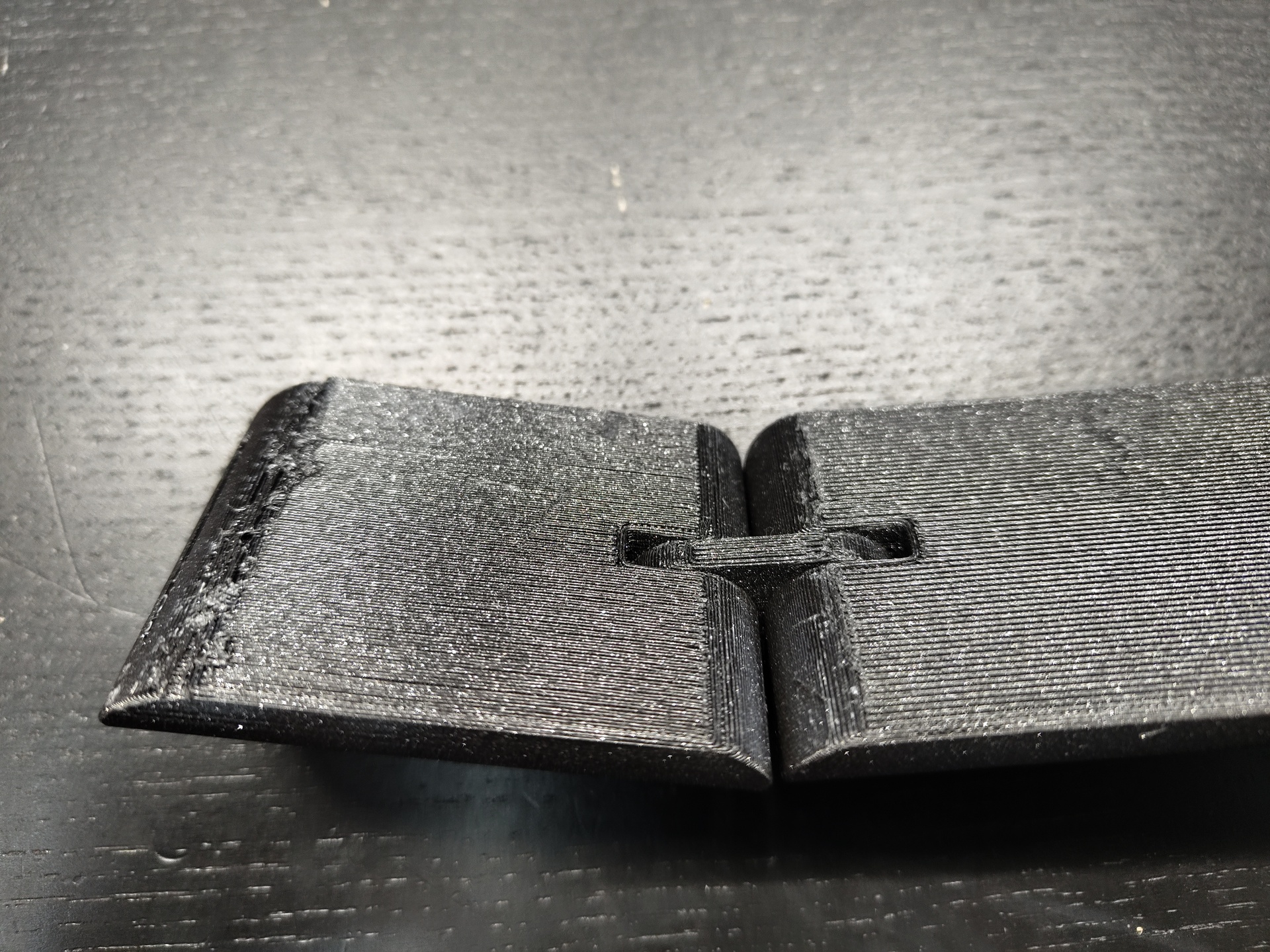
Groupe Assignment
Comparer les performances

Original Prusa i3 MK3S+ 3D printer
- Build Volume : 25×21×21 cm (9.84"×8.3"×8.3")
- Layer height : 0.05 - 0.35 mm
- Nozzle : 0.4mm default, wide range of other diameters/nozzles supported
- Filament diameter : 1.75 mm
- Supported materials : Wide range of thermoplastics, including PLA, PETG, ASA, ABS, PC (Polycarbonate), CPE, PVA/BVOH, PVB, HIPS, PP (Polypropylene), Flex, nGen, Nylon, Carbon filled, Woodfill and other filled materials.
- Max travel speed : 200+ mm/s
- Max nozzle temperature : 300 °C / 572 °F
- Max heatbed temperature : 120 °C / 248 °F
- ExtruderDirect Drive, Bondtech gears, E3D V6 hotend
- Print surface : Removable magnetic steel sheets(*) with different surface finishes, heatbed with cold corners compensation
- Printer dimensions (without spool) : 7 kg, 500×550×400 mm; 19.6×21.6×15.7 in (X×Y×Z)
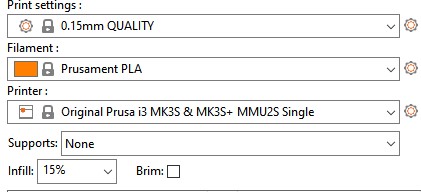
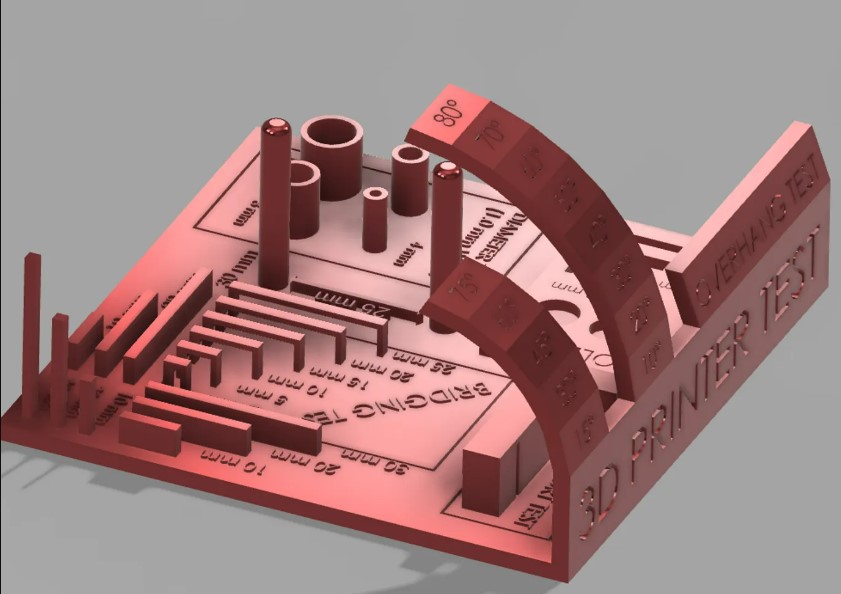
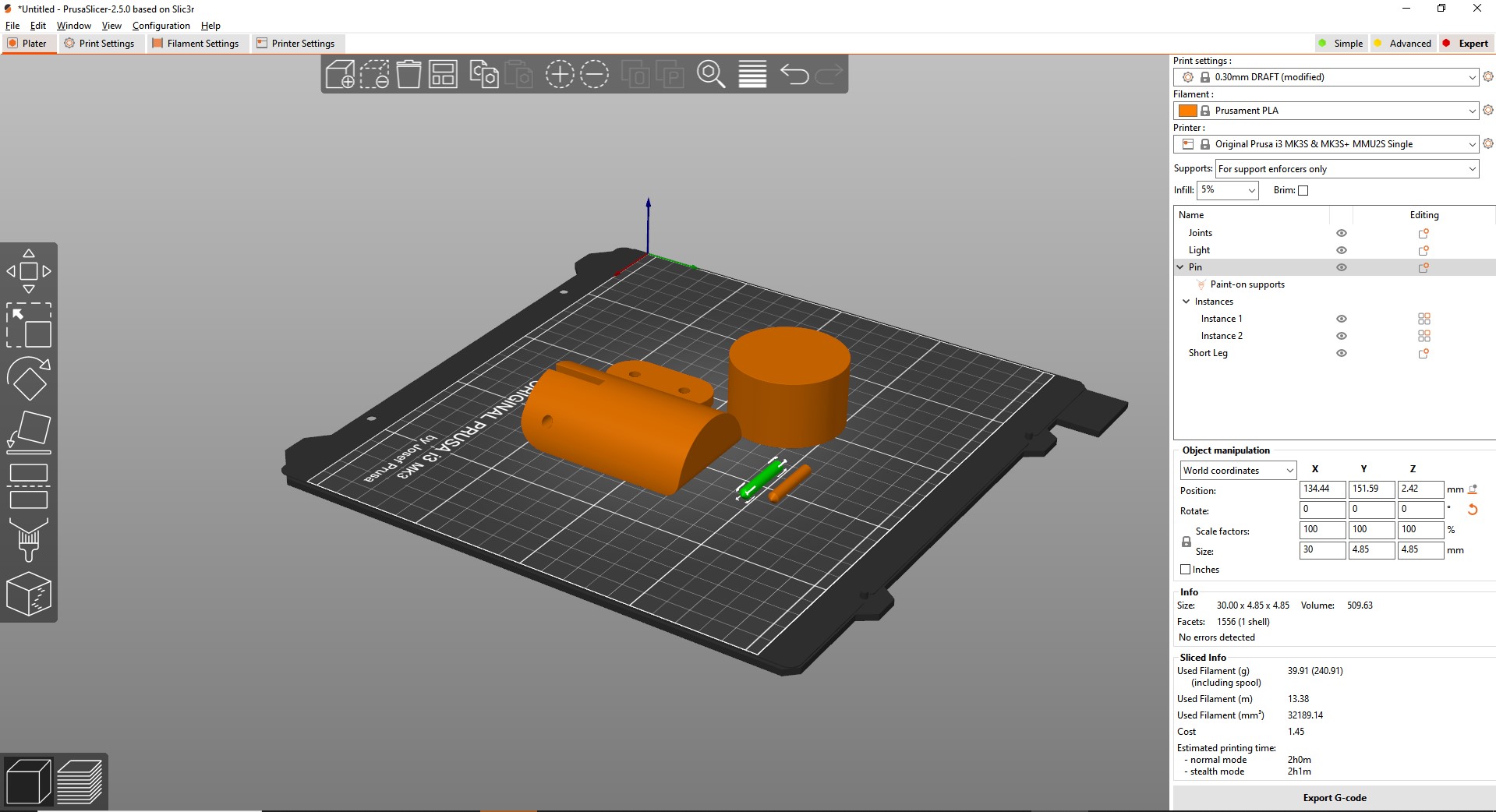
I will use the Prusa MK3 to make some test on it, to find the limit of it. To do that i will use two different files.