3D Scanning & Printing Report
Group Assignment: Testing 3D Printer Design Rules
Visit our Week 5 group linkIndividual Assignment
3D Design & Printing
I am required to print 3D-print an artifact that cannot be done by any other method. I chose an fully assmbled chain because manufacturing a chain through the
normal processes requires several processes of bending, assembly of each link and then welding the each link to close it and the process repeats. With 3D printing
after modelling on the CAD software (solidworks for me) I set the printer to the required settings then it will print unil it completes.
I modeled the hat using SolidWorks using front and to plane to draw the chain link on the front and then the circular profile on the top plane.This was necessary to use the sweep profile.
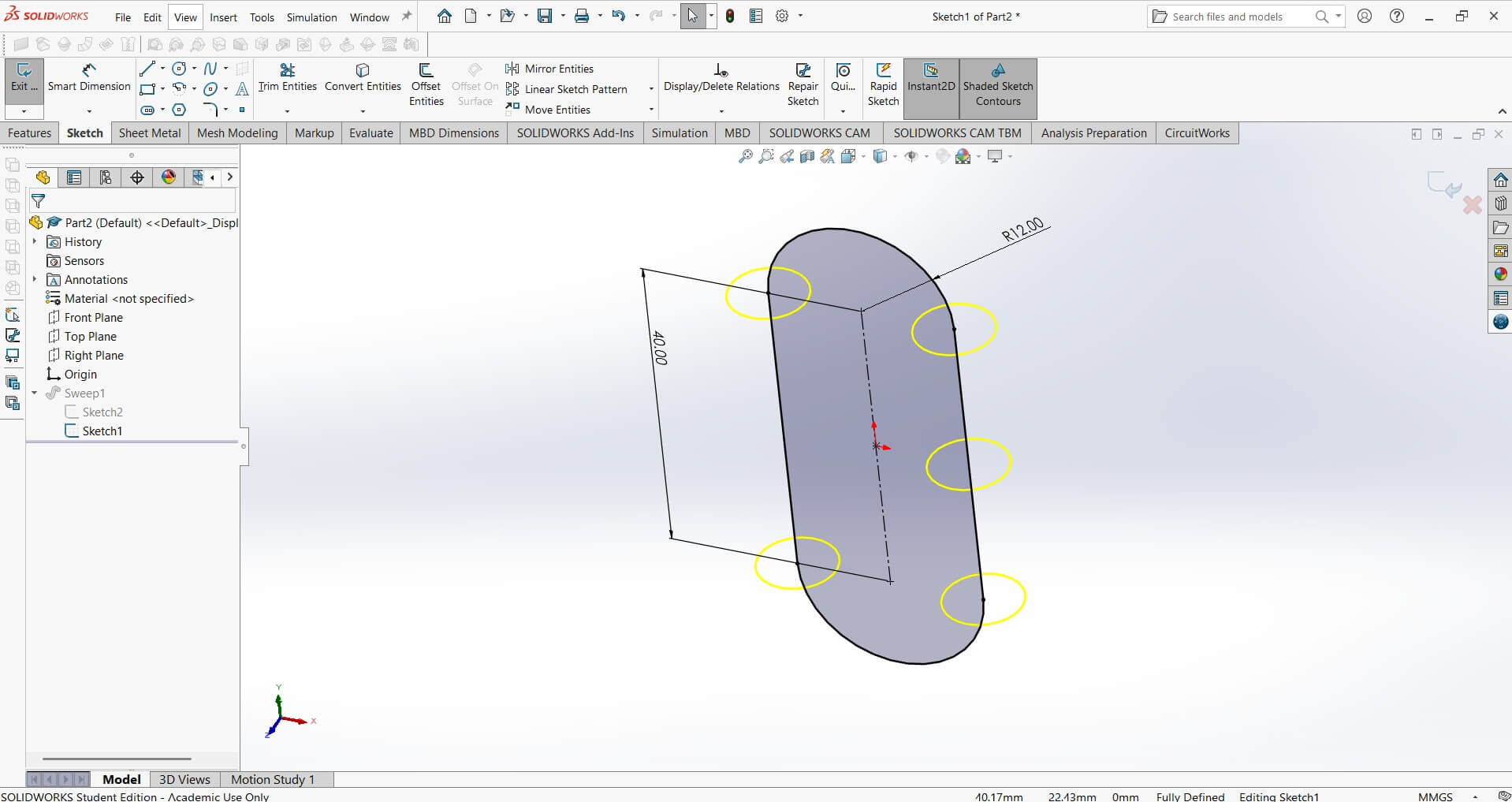
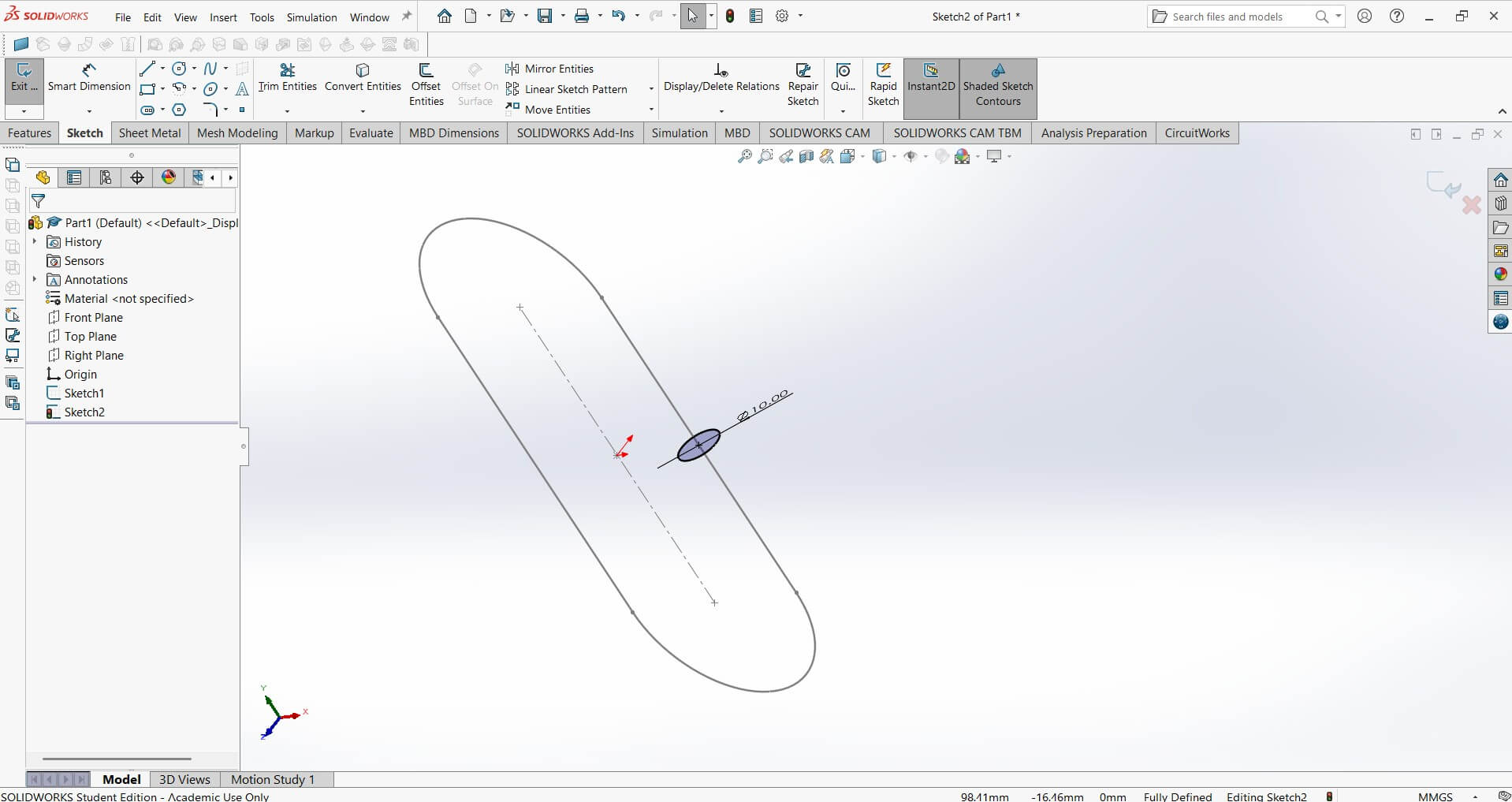
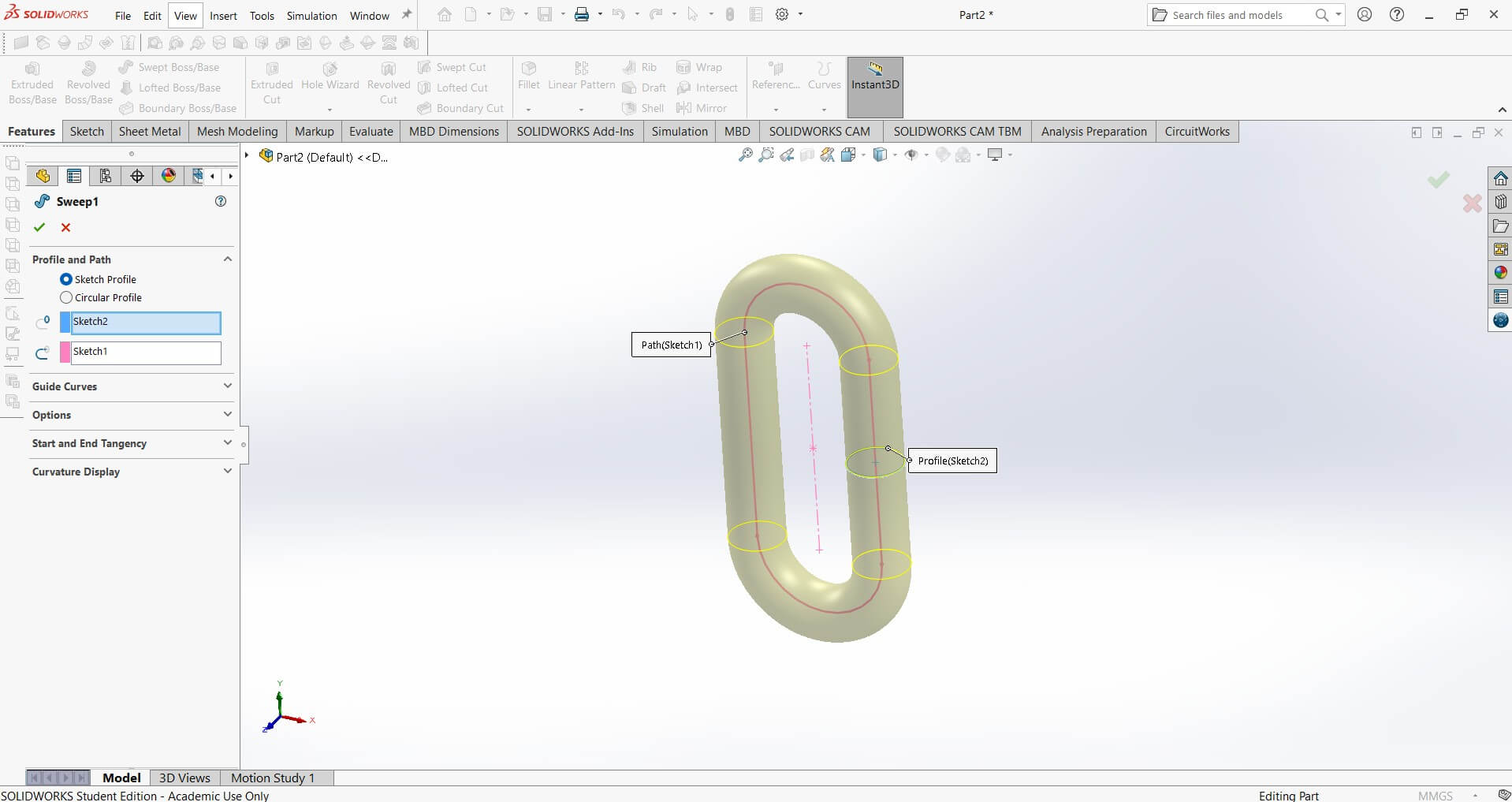
Sweep
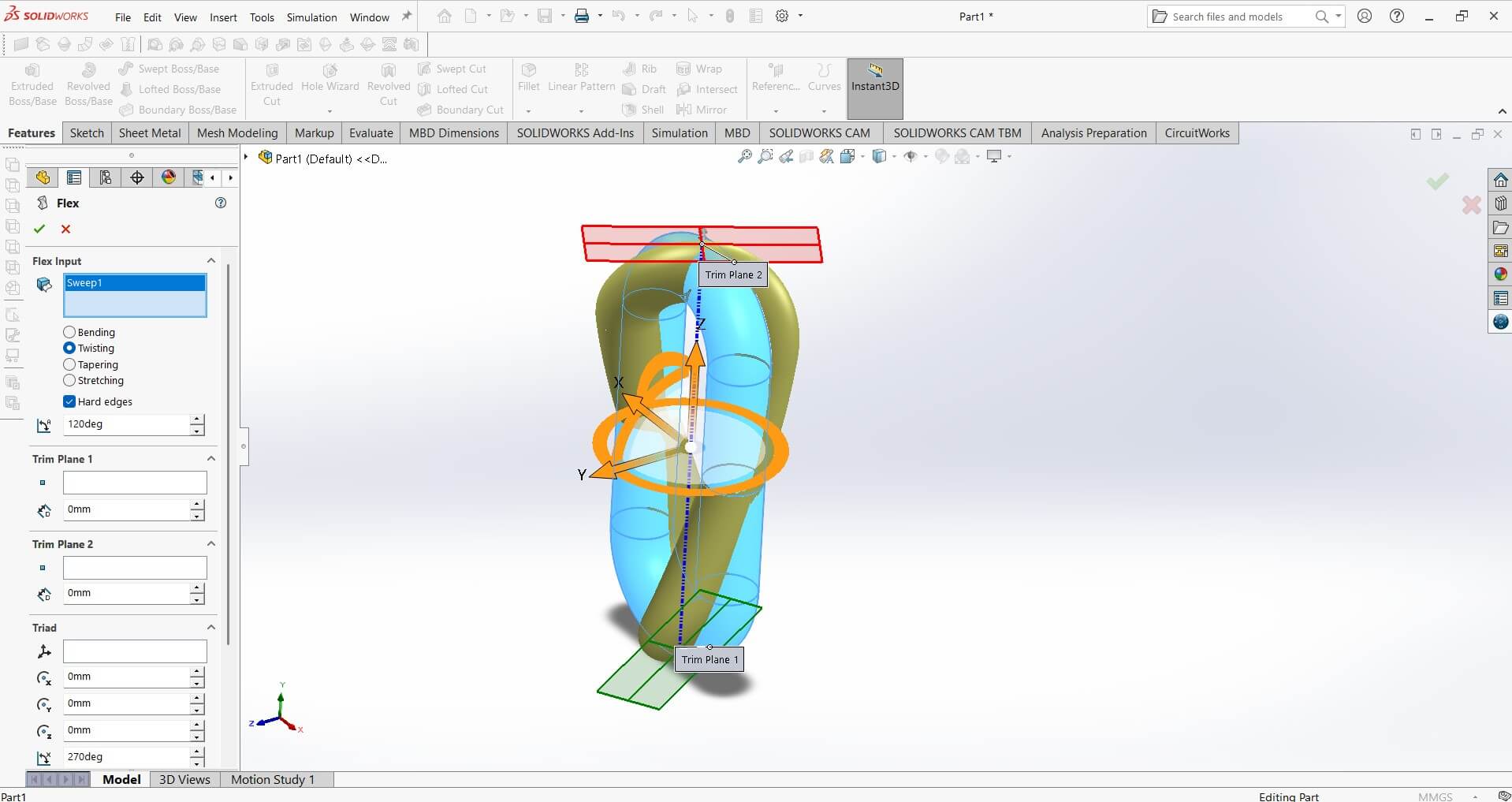
Twist
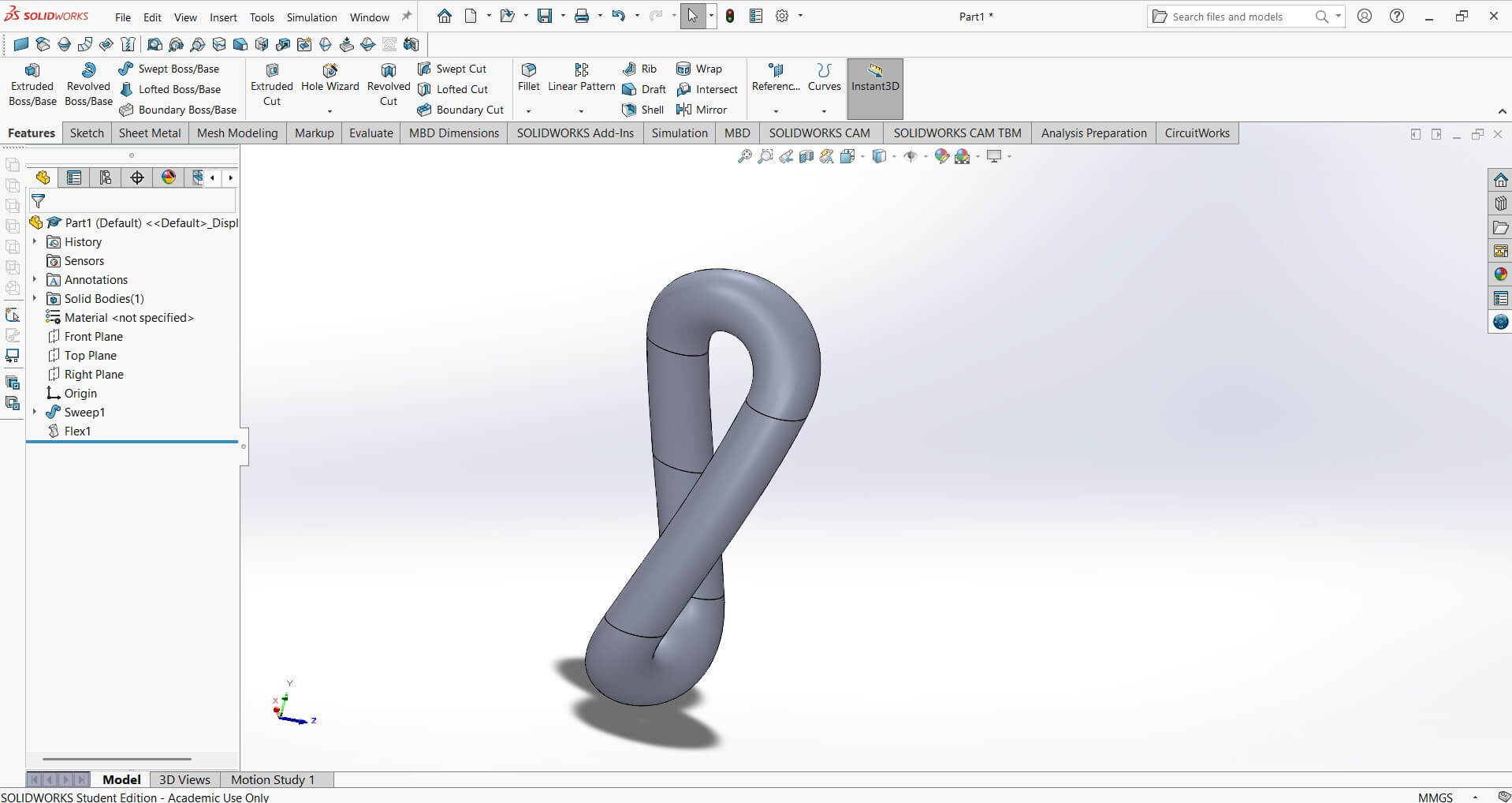
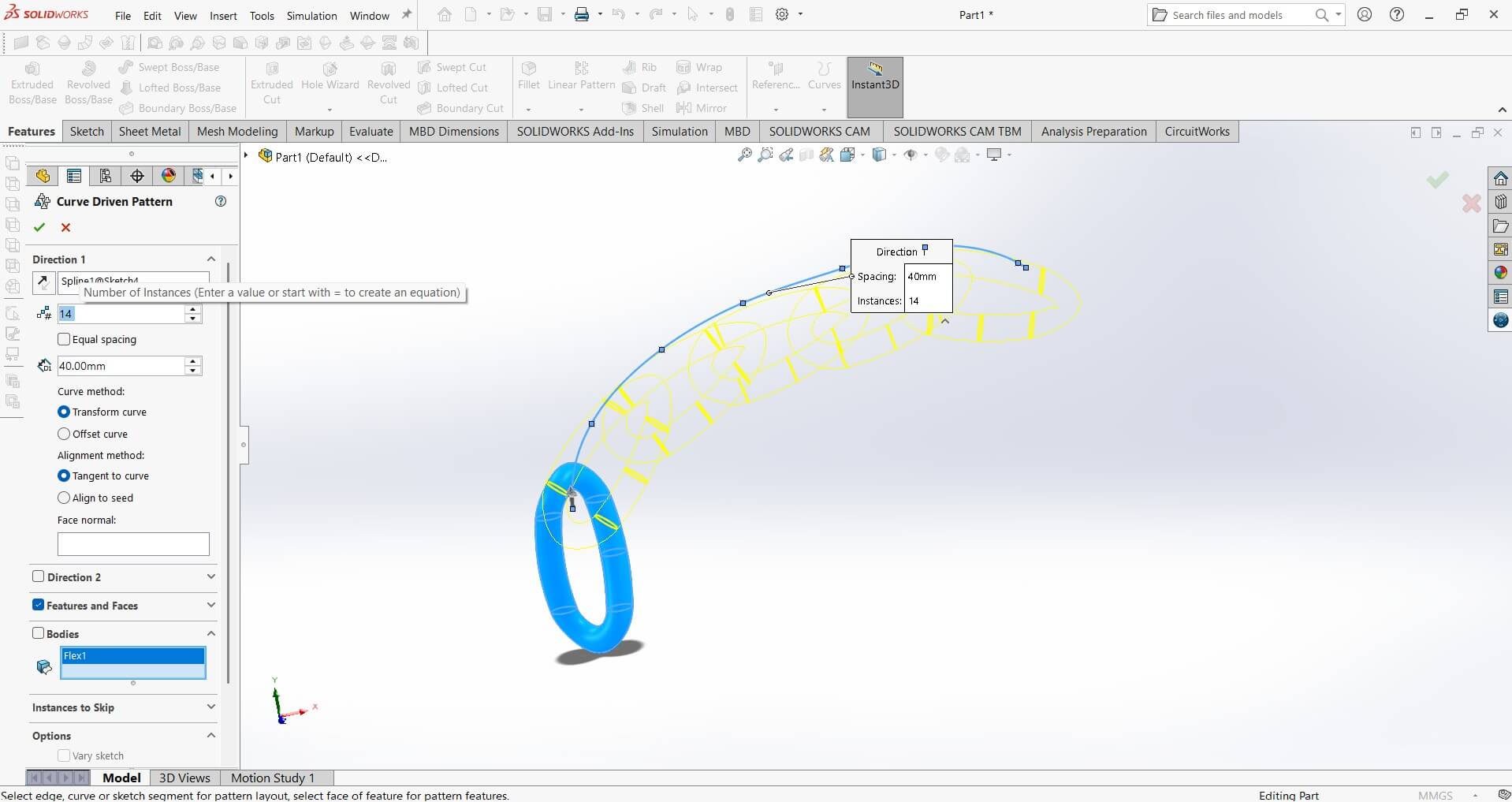
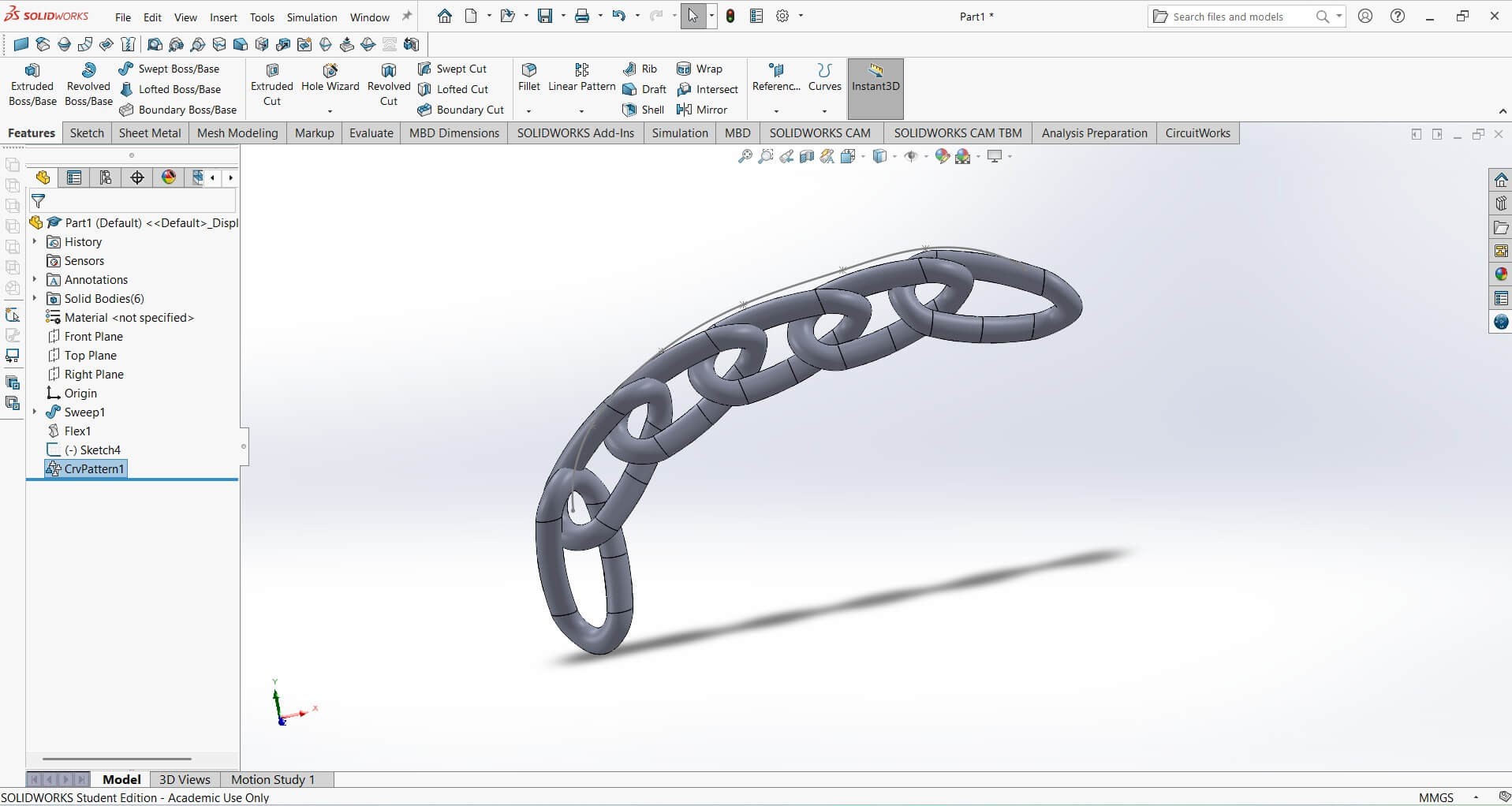
Curved Liner pattern
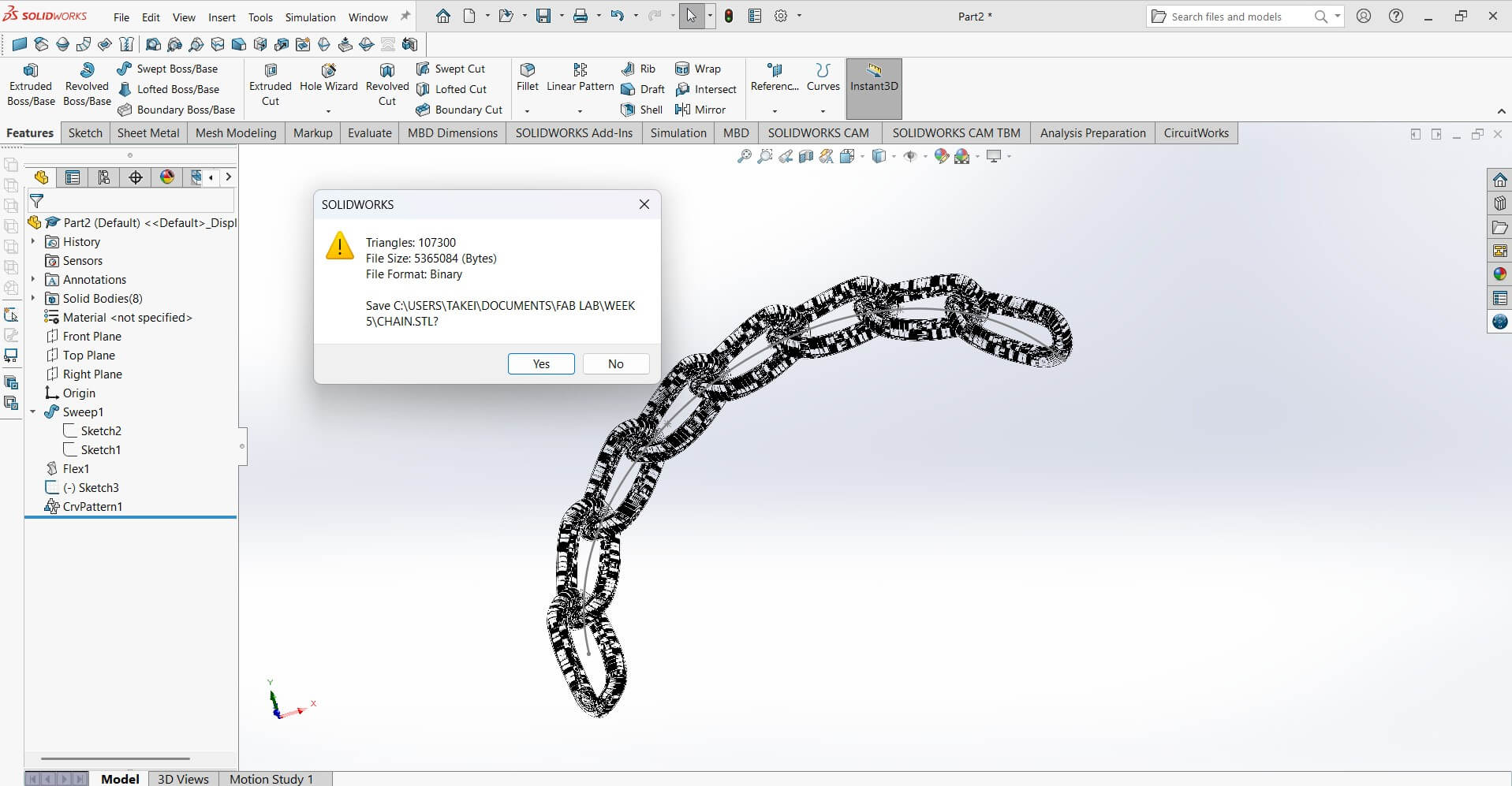
I converted the solid works file into an STL file type in order for the 3D Printer to recognise it
Ender-3 V3 SE 3D-Printer

Creality Slicer software preparing the twisted chain for print
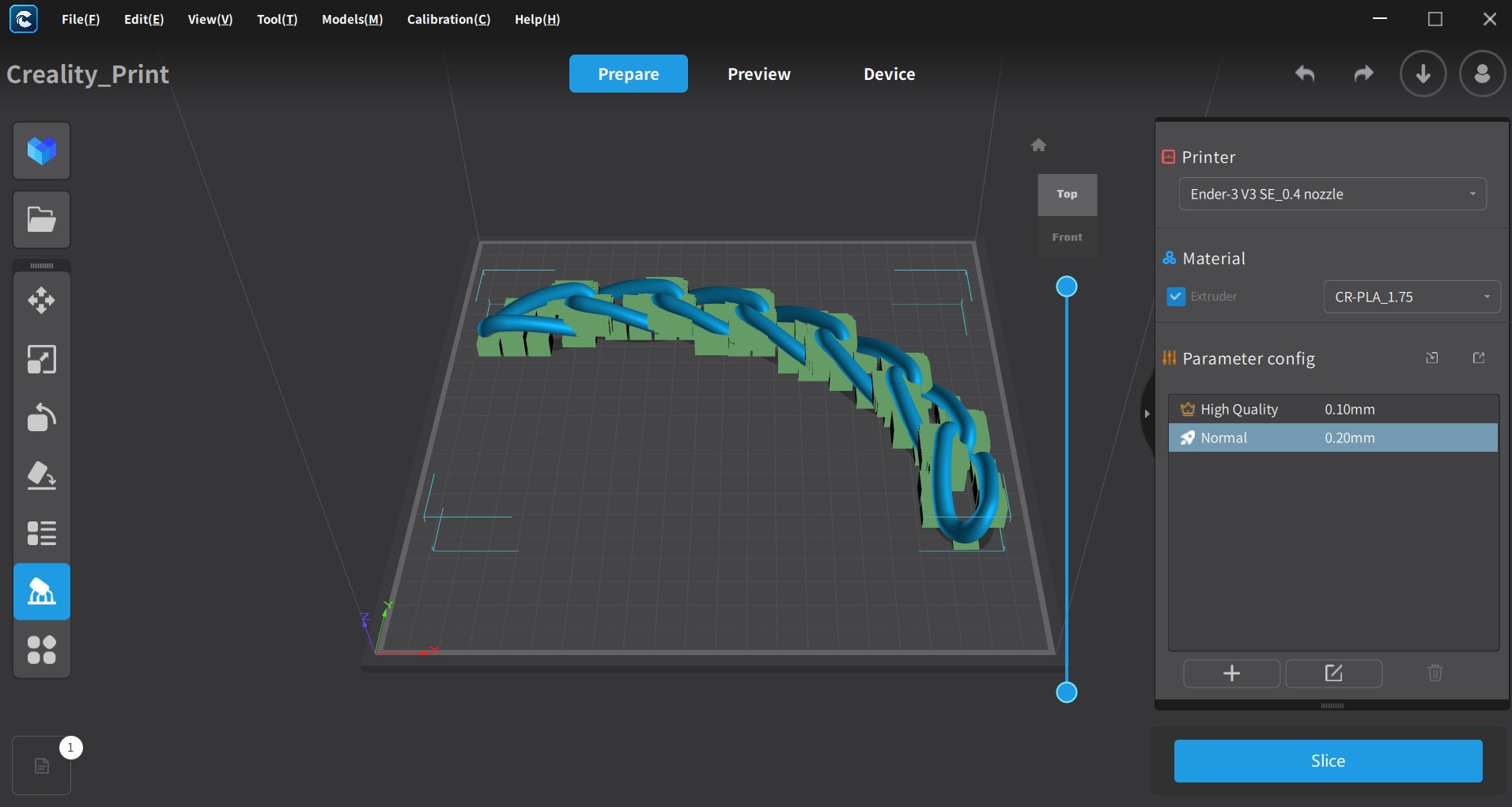
The picture below shows the Twisted Chain printed on the Creality Ender-3 V3 SE 3D-Printer
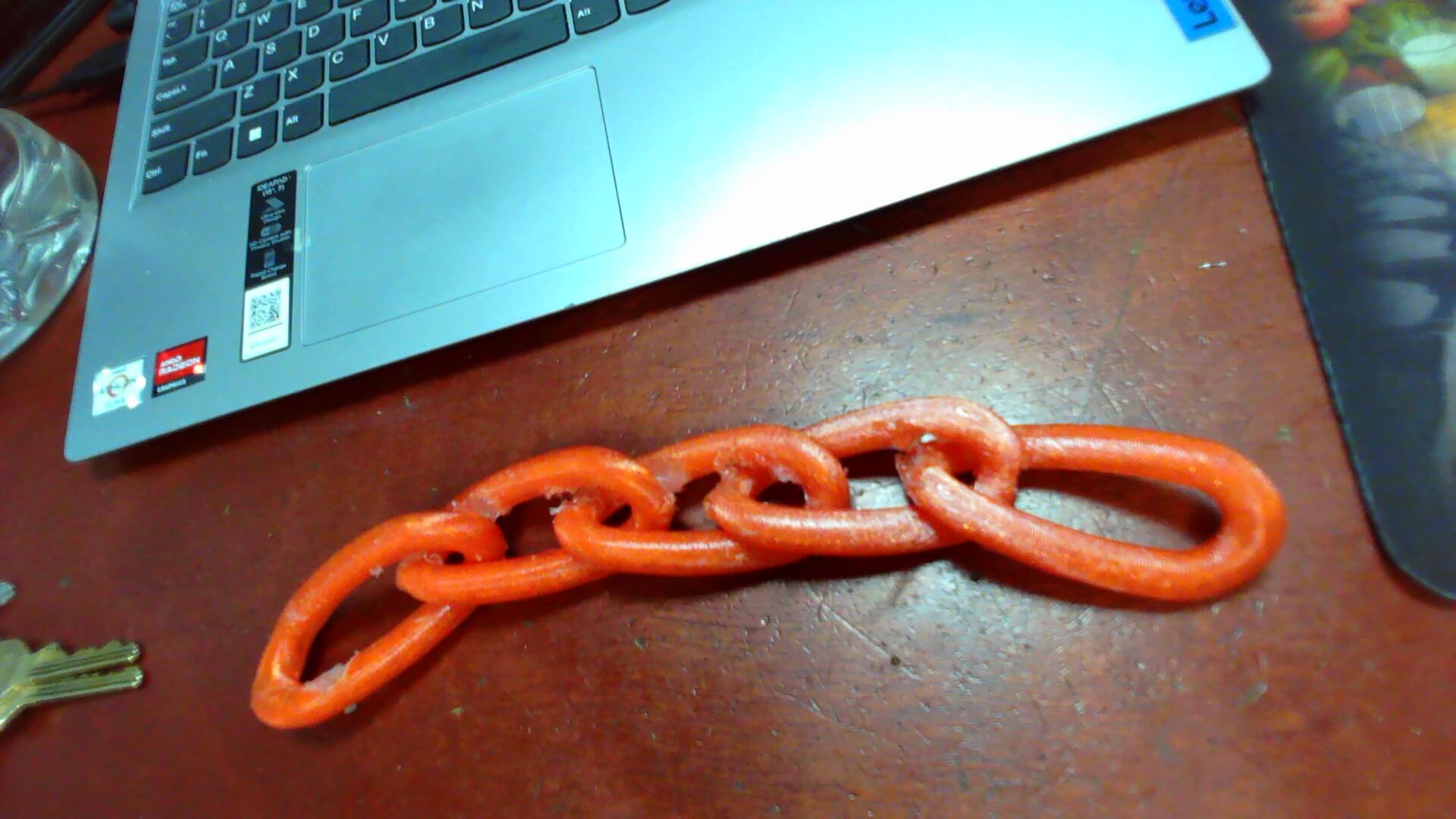

3D Scanning & Printing
Expalining the Einstar 3D Scanner
Einstar 3D Scanner: Overview and Features
The Einstar 3D scanner, developed by Shining 3D, is a handheld structured light scanner designed for affordability and ease of use while maintaining high-quality scans. It is suitable for makers, engineers, designers, and researchers who need a portable and efficient scanning solution.
- Structured Light Technology: Uses infrared structured light for precise scanning, reducing the impact of ambient light.
- High Accuracy: Achieves up to 0.1mm accuracy, making it suitable for capturing fine details.
- Full-Color Scanning: Supports texture capture, making it useful for digital modeling, art, and gaming applications.
- Large Scanning Area: Covers a wide field of view (200×100mm to 1000×1000mm), making it suitable for both small and large objects.
- High-Speed Capture: Scans at a speed of up to 14 frames per second, improving workflow efficiency.
- No Markers Needed: Unlike laser scanners, Einstar can capture objects without requiring reference markers.
- AI-Powered Processing: Built-in automatic alignment and noise reduction, improving scan quality.
- Connectivity: Uses a USB-C interface for fast data transfer to a computer.

Key Features
Applications
Explain the scanning process, tools used, and any modifications applied.
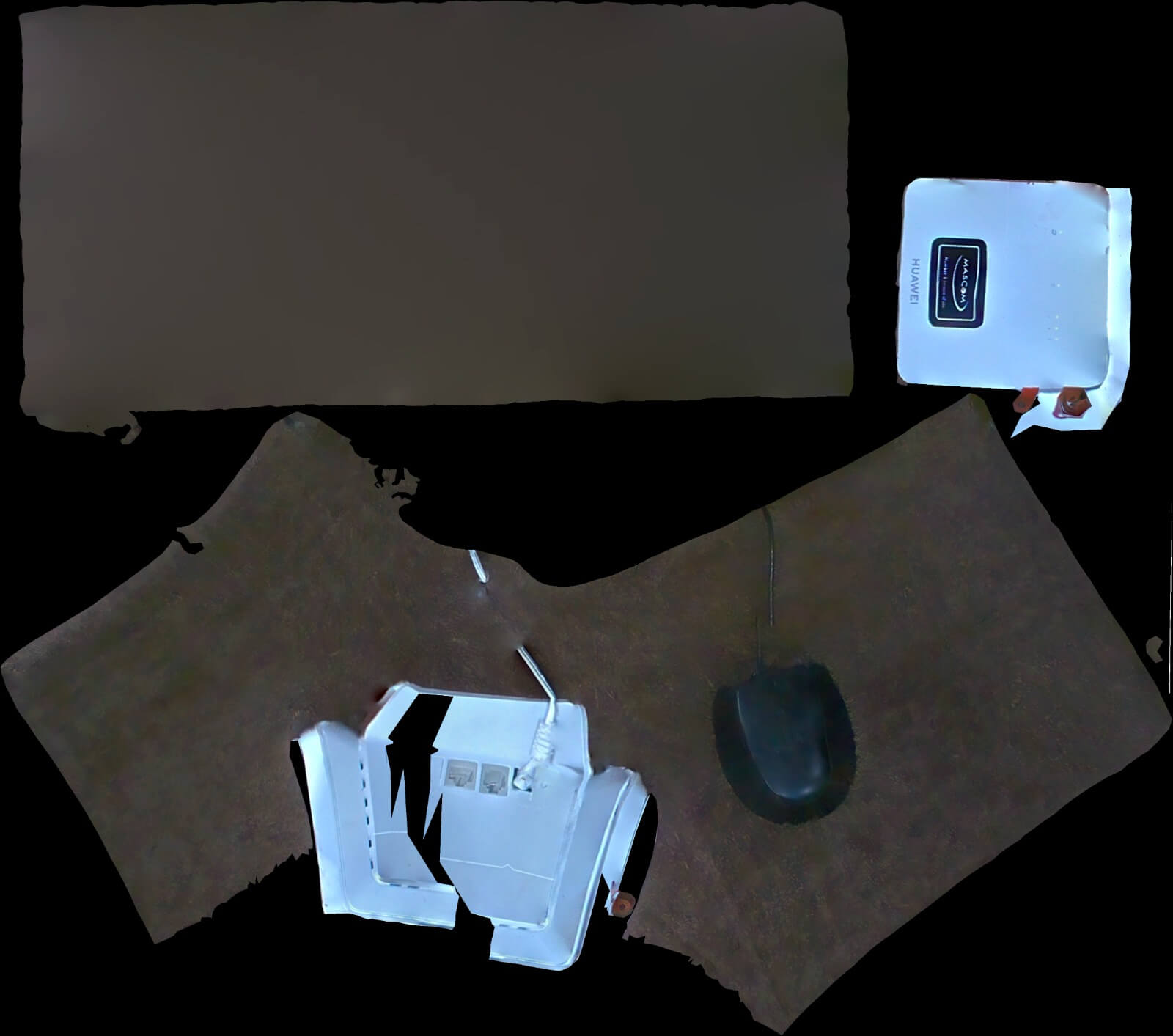
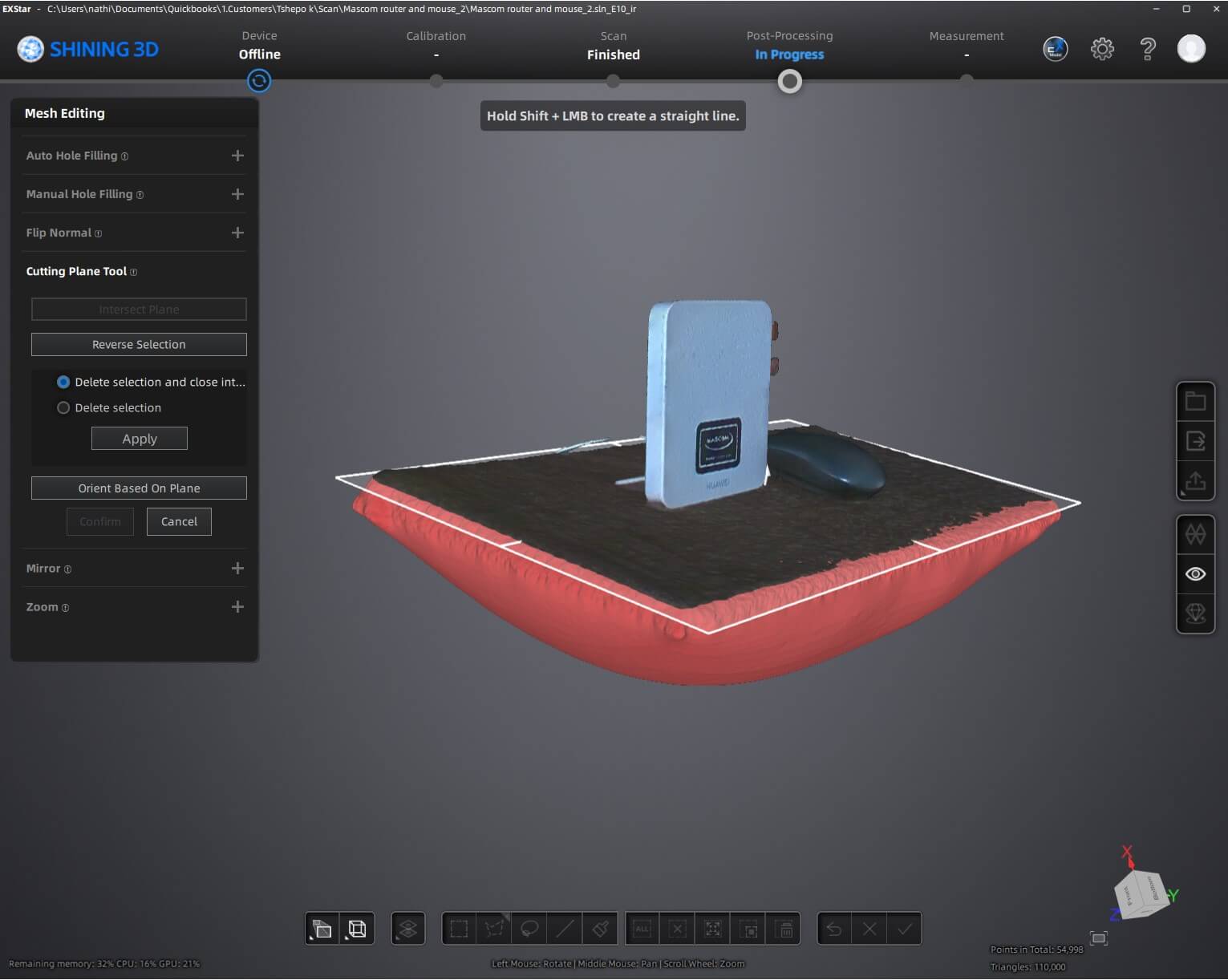
The scanning process was done on a Huewei and a computer mouse.It happened by scanning the object by moving the handheld scanner around it to capture its geometry.
.jpeg)
The scanning process on software
3D Scanning Process, Tools Used, and Modifications
Scanning Process
The 3D scanning process involves capturing the shape, texture, and dimensions of a physical object to create a digital 3D model. The Einstar 3D scanner follows these key steps:
- Ensure the object is well-lit and free from reflections or transparent surfaces that may interfere with scanning.
- Position the object on a stable surface or rotating turntable for even coverage. Scanning:
- The Einstar 3D scanner projects structured infrared light onto the object.
- The scanner’s sensors capture distortions in the light pattern to reconstruct the object's shape.
- The scanner collects multiple frames in real time, aligning them automatically.
- Alignment & Merging: If multiple scans are taken from different angles, the software aligns and stitches them together.
- Noise Reduction: The software removes unwanted data points or artifacts from the scan.
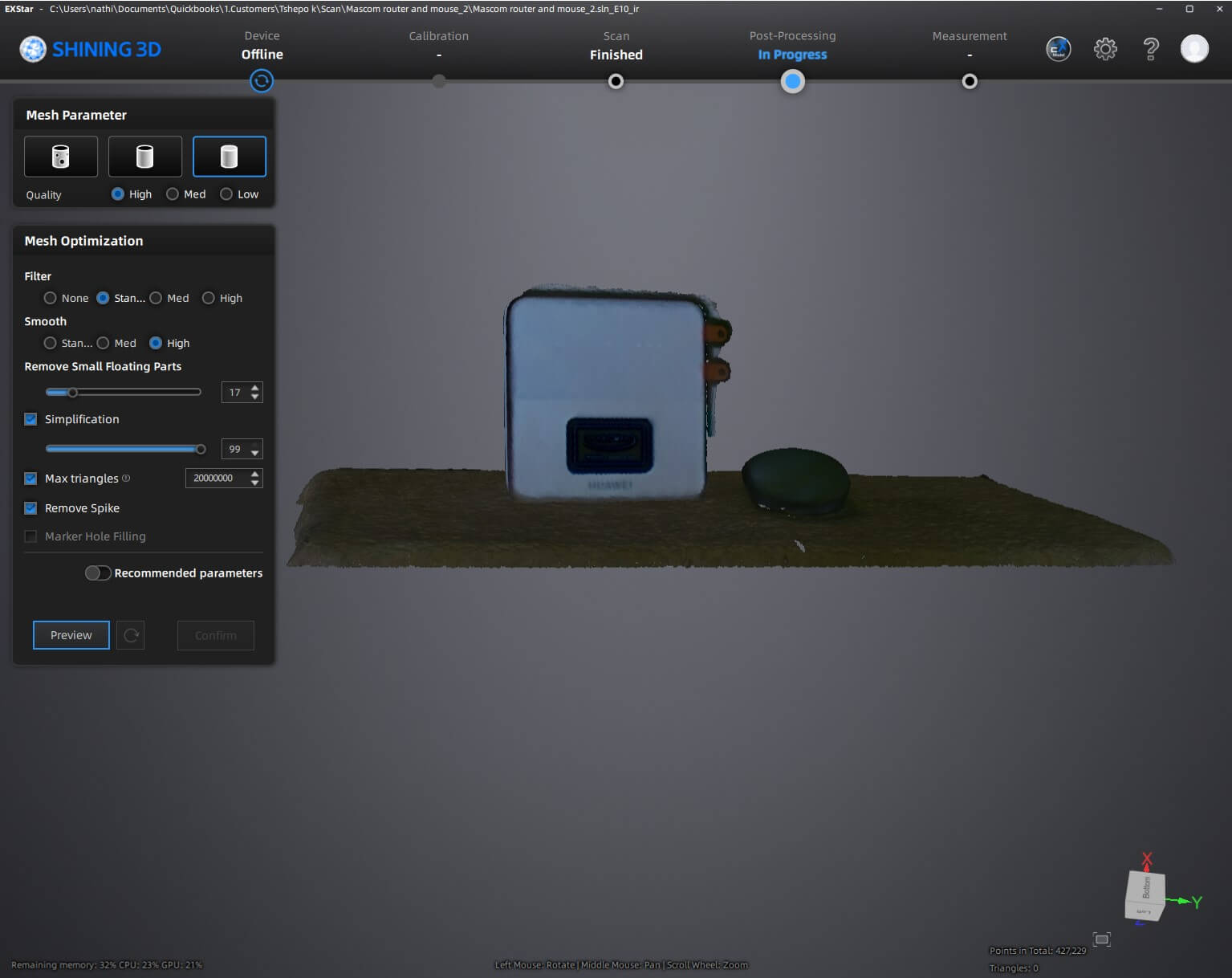
- Mesh Generation: A watertight 3D mesh is created, defining the surface geometry.
- Texture Mapping: If color capture is enabled, the scanned textures are applied to the model.
Processing & Refinement:

Tools Used
- Einstar 3D Scanner: Captures the object's shape and texture.
- Shining 3D Software (EXStar): Processes and refines the scan data.
- Computer: Runs the scanning software and handles data processing.
- Turntable (Optional): Helps with scanning smaller objects smoothly.
- Lighting Equipment: Ensures optimal scan quality by reducing shadows.
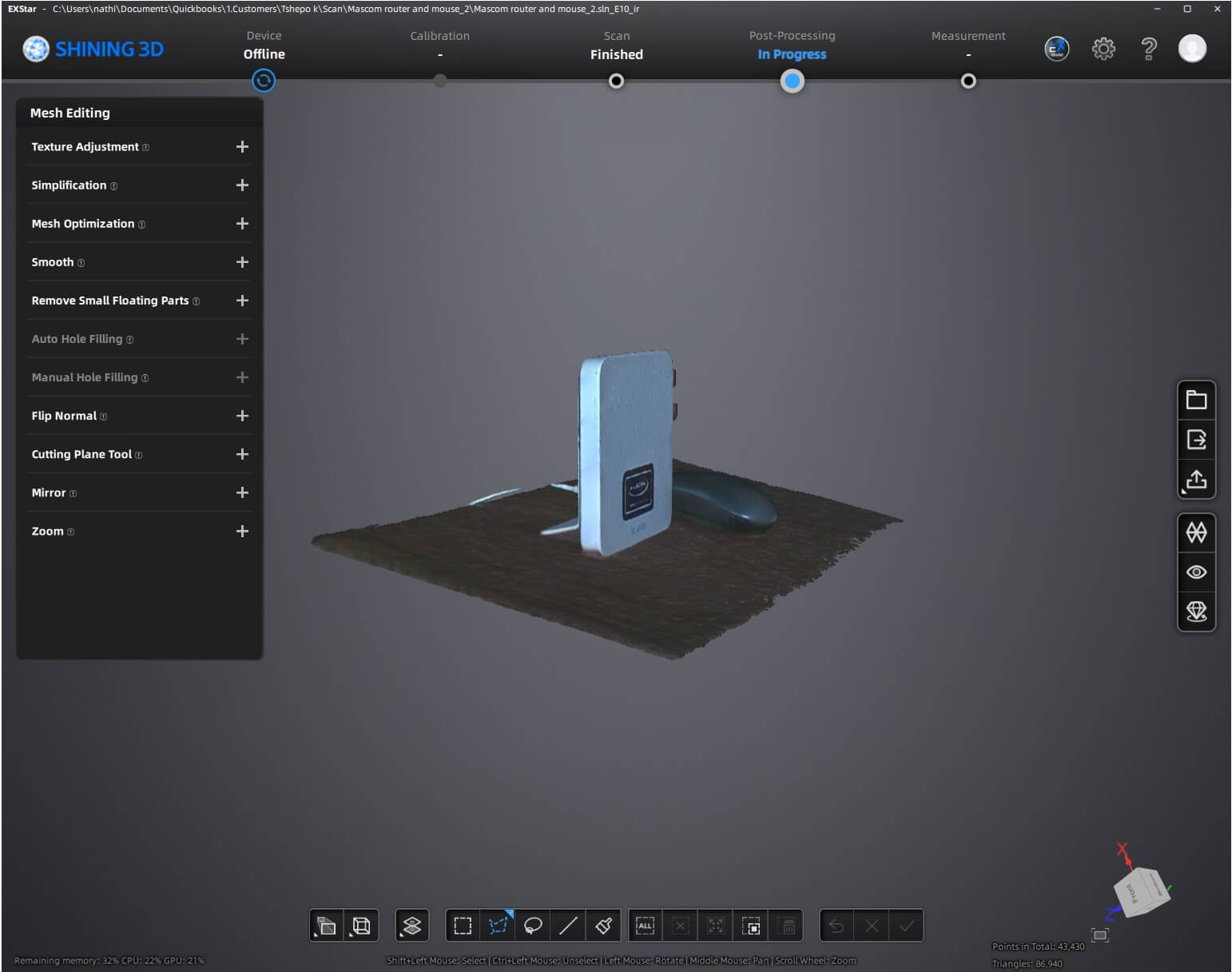
Modifications Applied
- Mesh Optimization: The model is simplified or smoothed to reduce file size while maintaining detail.
- Hole Filling: If any areas were missed during scanning, they are interpolated and reconstructed.
- Scaling Adjustments: The scan may be resized to match real-world dimensions.
- Texture Enhancement: Colors and surface details may be adjusted for better realism.
Zip Files for Downloads
Week 5 Design files for Download