4.- Embedded Programming
Currently, there are many microcontrollers on the market and each one with different characteristics, the question is which one should we use? To answer this question we must consider the following:
- Memory type (how much memory does it have and what type of memory is needed (FLASH, RAM or EEPROM))
- Speed
- Power consumption
- Connectivity (WiFi, Bluetooth, etc.)
- Number of pins (digital, analog, PWM, etc.)
- Dimensiones
- Interface (SPI, UART, I2C, EDP, etc. )
- Cost
Datasheet
As mentioned previously, data sheets are essential elements when connecting a microcontroller since
they not only tell us the characteristics of the device, but also give us the pinout to be able to
make any connection. Below is a comparison table between different microcontrollers.
| Microcontroller\ Features | CPU | Interface | Bit depth | Storage | I/O pins | Power/ Downloading |
Dimensions | Connectivity | How to program | Special Functions | Programming language |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XIAO-RP2040 | Dual-core ARM Cortex M0+ processor up to 133MH | I2C SPI UART |
32-bit | 264KB of SRAM, and 2MB of on-board Flash memory | Digital - 11 Analog - 4 PWM - 11 |
3.3V - 5V Type - C |
20x17.5x3.5 mm | No | USB mass-storage boot mode, drag-and-drop programming | USB 1.1 Host/Device, 8 Programmable I/O (PIO) state machines | Arduino MicroPython CircuitPython |
| ESP32-C3 | RISC-V single-core processor up to 160 MHz | I2C SPI UART |
32-bit | Up to 4MB SPI flash memory, 400KB SRAM | Digital - 11 Analog - 4 PWM - 11 |
3.0V – 3.6V | 20x17.5x3.5 mm | WiFi y Bluetooth 5 (BLE) | Serial/UART programming, OTA (Over-The-Air) | Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n), Bluetooth 5.0 LE, Rich set of peripherals | Arduino MicroPython |
| PIC 16F84A | PIC 16 - 20 MHz | - | 8-Bit | 68 bytes of data RAM 64 bytes of data EEPROM |
Digital - 13 | 4V - 5.5V | 22.86 x 6.35 mm | No | PICkit, MPLAB X | 1000 erase/write cycles Enhanced Flash program memory 1,000,000 typical erase/write cycles EEPROM data memory |
Assembler C |
The following links show the different data sheets of the microcontrollers presented in the table.
The link shown below presents a comparison between microcontrollers of the "XIAO" family.
Simulation
When we speak, the opening of the mouth and the position of the lips depend on the word we want to say, for this reason, in the following simulations we intend to represent the movement of the mouth when saying vowels, which is one of the objectives of the final project.
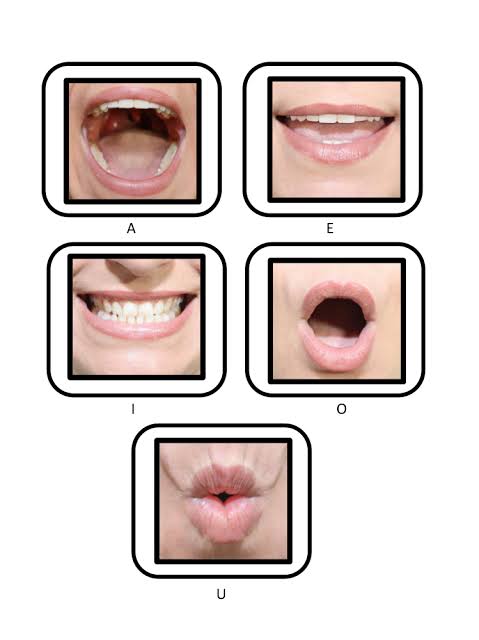
It should be noted that to carry out the simulations in this section, two simulators will be used.
At the same time, two simulation languages will be used.
Programs
The programs seek to move 3 pairs of servomotors, which will be grouped into three specific parts:
- Opening/closing of mouth
- Lip movement
- Cheek movement
When the movement has already been carried out, a button must be pressed for the servos to return to their original position. Likewise, to select the movement you want to execute, from the terminal you must enter the desired vowel.
C
When programming in C, the first lines are usually used to introduce the libraries, in our case it is essential to use
" #include < Servo.h> ", which will allow us to use the servomotors. We continue by
declaring all the servomotors " Servo name;", it is important to know that the instructions
end with " ;"
In the " voit setup()", which is a function that is executed only once at the beginning of
the program, the input and output pins that will be used must be entered, as well as the initial state of the servos.
After this, the " voit loop()", follows, in which the code is executed cyclically; We start by
placing a " while(Serial.available() > 0)" , which asks if the serial port is available, if so
it enters the "loop", it should be noted that every time we open a loop, it must be accompanied by
" { }", which delimit the loop. Within the loop, the serial port is read, and the information
is saved in "msg", if "msg" matches some of the conditions ("if"), it enters the condition and continues to the next;
Within all the "if", there are "for" conditions which indicate the degrees by which the servos want to move. It is
worth mentioning that a sweep is made, so that the movements of the face are not so abrupt; Once the servos reach
their initial position, they wait for the button to be activated to return to their initial position..
Below is the code used.
The following video shows the operation of the servomotors.
Note. Tinkercad was used and the "Pi pico" controller was replaced with an arduino, because the time taken by the simulation in "Wolki" was excessive. The following links lead to the simulation and the simulation file.
Python
Python is an open source, interpreted, high-level programming language. It is one of the most popular.
As in "C", the first lines are intended for libraries, however, in this case they were used to
import a specific part of some module with the instruction " from machine import Pin, PWM ".
On the other hand, " import time", adds time-related functions.
In the same way as in "C", the program begins by declaring the input pins that the servos will occupy and only
the frequency with which they will work must be added. The working frequency is between the values of 40Hz to
66Hz, since that is the frequency range in which the servos work.
Instead of starting the program with the " voit loop()" that is used in "C", here you start with a " while True:,
although the logic is the same as that used in "C", there are some subtle differences such as the lack of ";" or "{ }"
between each loop. In python, tabs are very important.
The following video shows the operation of the servomotors.
The following links lead to the simulation and the simulation file.
Comparative Table: C vs Python
Using "Copilot", a comparative table was made between "C" and "Python" using the following promt "Create a comparative table between C and Python, highlighting key differences in terms of language type, syntax, speed, primary use, memory management, libraries, learning curve, portability, and paradigm".
| Feature | C | Python |
|---|---|---|
| Language Type | Compiled | Interpreted |
| Syntax | Strict and detailed | Simple and readable |
| Speed | Very fast | Fast, but slower than C |
| Primary Use | Operating systems, drivers | Web development, data science, AI |
| Memory Management | Manual | Automatic (garbage collection) |
| Libraries | Less extensive | Very extensive |
| Learning Curve | Steep | Gentle |
| Portability | High, but depends on compiler | Very high |
| Paradigm | Procedural | Multi-paradigm (procedural, object-oriented, functional) |
Learning outcome
In this week, we learned the characteristics that should be considered when selecting a microcontroller, as well as the differences between two of the most used languages today "C" and "Python".
