Group Assignment
- Review the safety data sheets for each of your molding and casting materials, then make and compare test casts with each of them
- Compare mold making processes
Materials Introduction
RTV Silicone
RTV Silicone will be used for mold making in this assignment.
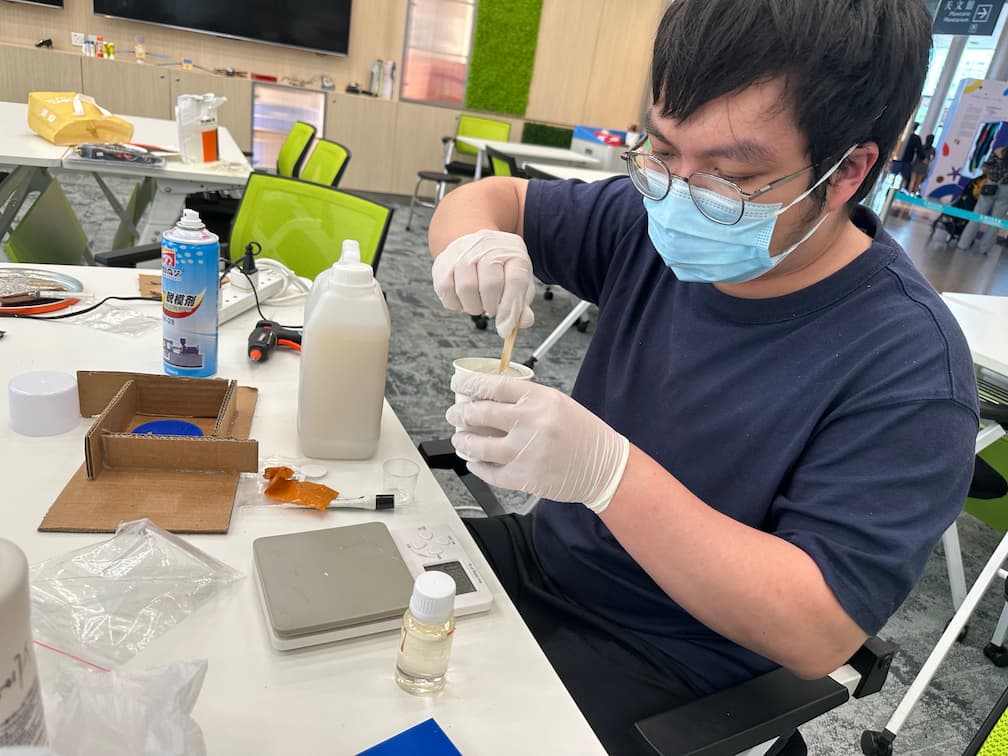
1. Mix the silicone with the curing agent at a 100:2 ratio and stir thoroughly. Operation time is about 5 minutes.
2. After pouring into the mold, remove once fully cured.
3. Before use, test with a small amount to understand its characteristics and avoid waste.
Bubble Reduction Methods:
1. Reduce the curing agent ratio to extend curing time. As curing time increases, bubbles will naturally escape, greatly reducing their presence.
2. Stir in one direction to reduce bubble formation.
3. When making molds, first brush a thin layer of silicone on the master mold and wait for bubbles to disappear before applying the remaining silicone. This reduces bubble formation at the contact surface.
4. Use a vacuum machine to extract bubbles after mixing.
(Dongguan Lixing Technology Co., Ltd.)
Address: Xiancun Industrial Zone, Dalang Town, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province
Shelf life: 6 months
Mould Release Spray
Efficient Mould Release Agent Spray will be used for spraying a layer on the surface of prototype. It case easier to remove the prototype from the mold (demolding).

1. Spray the prototype with the distance 25-35cm.
2. Flammable, keep away from fire.
3. Keep away from kids.
Resin
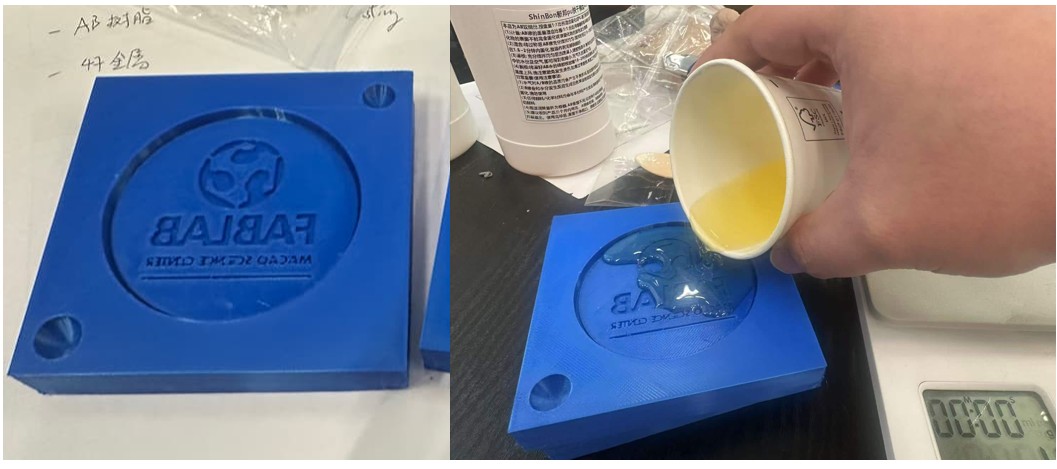
Resin the main casting materials. This resin consists of two components, A and B, mixed at a 1:1 weight ratio to form PU. It is easy to sand and has a short demolding time.
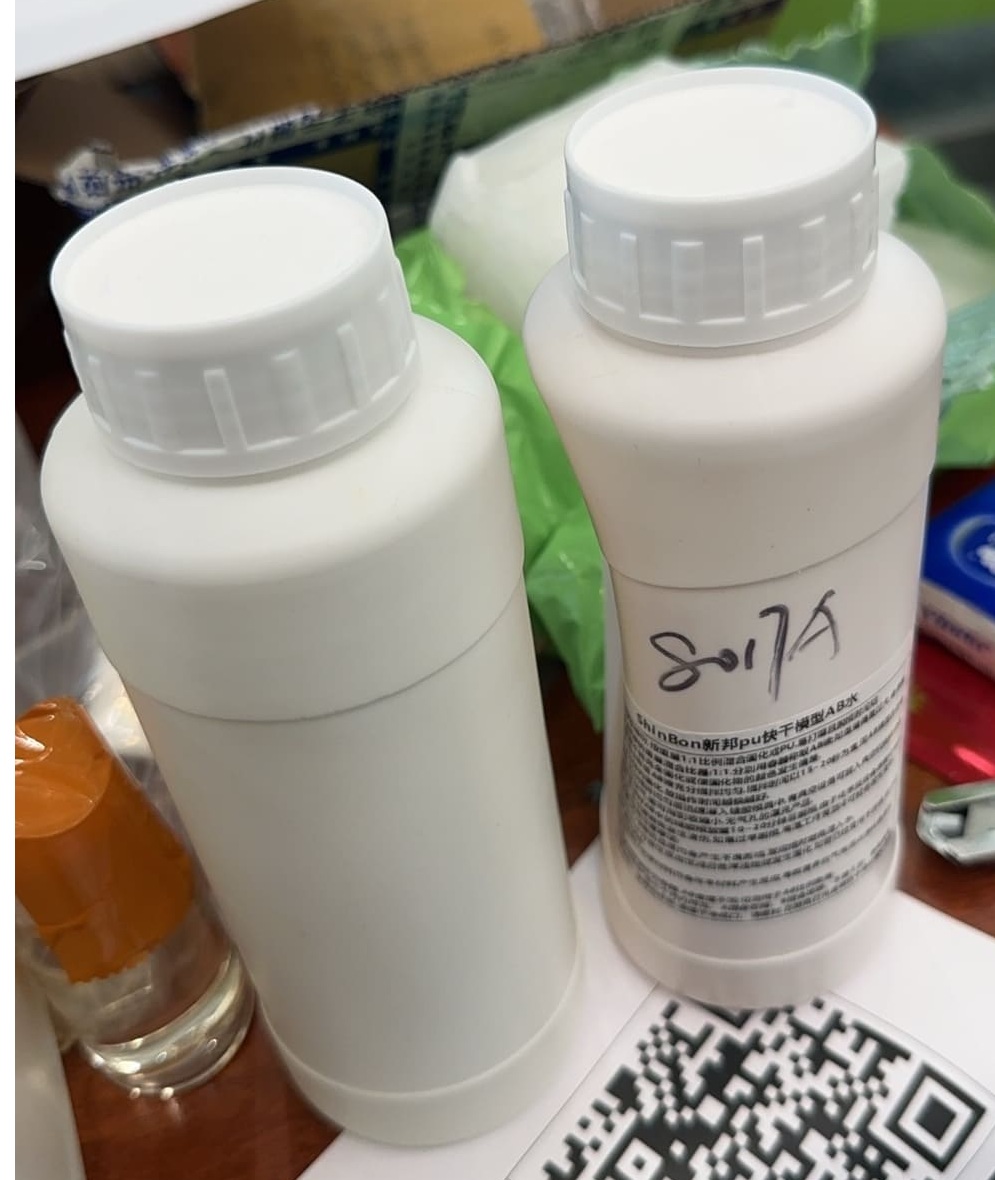

- Measurement: The weight mixing ratio of AB liquids is 1:1. Measure components A and B separately in containers. If the weight difference is too large, the cured surface may not fully solidify or the color of the cured material may deviate.
- Mixing: Thoroughly mix the pre-weighed AB liquids, stirring for 15-20 seconds. Since the AB liquid will solidify within 1.5-2 minutes after mixing, operation should be as quick as possible.
- Pouring: After thoroughly mixing, quickly pour into the silicone mold. If a vacuum machine is available, place it in the vacuum machine to remove moisture and air from the liquid, resulting in a beautiful product with minimal shrinkage and no air holes.
- Demolding: After vacuuming, place the silicone mold filled with AB resin on a flat work table. After 10-20 minutes, you can demold. Due to the heat of the curing reaction, the temperature of the cured material will rise - be careful to avoid burns. If demolded too early, the high-temperature cured material may deform due to sudden cooling.
Mold Making Process
Basically, the entire mold-making process can be divided into two parts:
- Creating the original parts
- Making the mold (using silicone)
Below, we will attempt to create the original parts using different processes.
3D Printing
Process
3D printing is a good idea for making a prototype quickly.
After exporting the .stl file, import the file to slicer and set the quiality as 0.08mm high with enable the grid support.
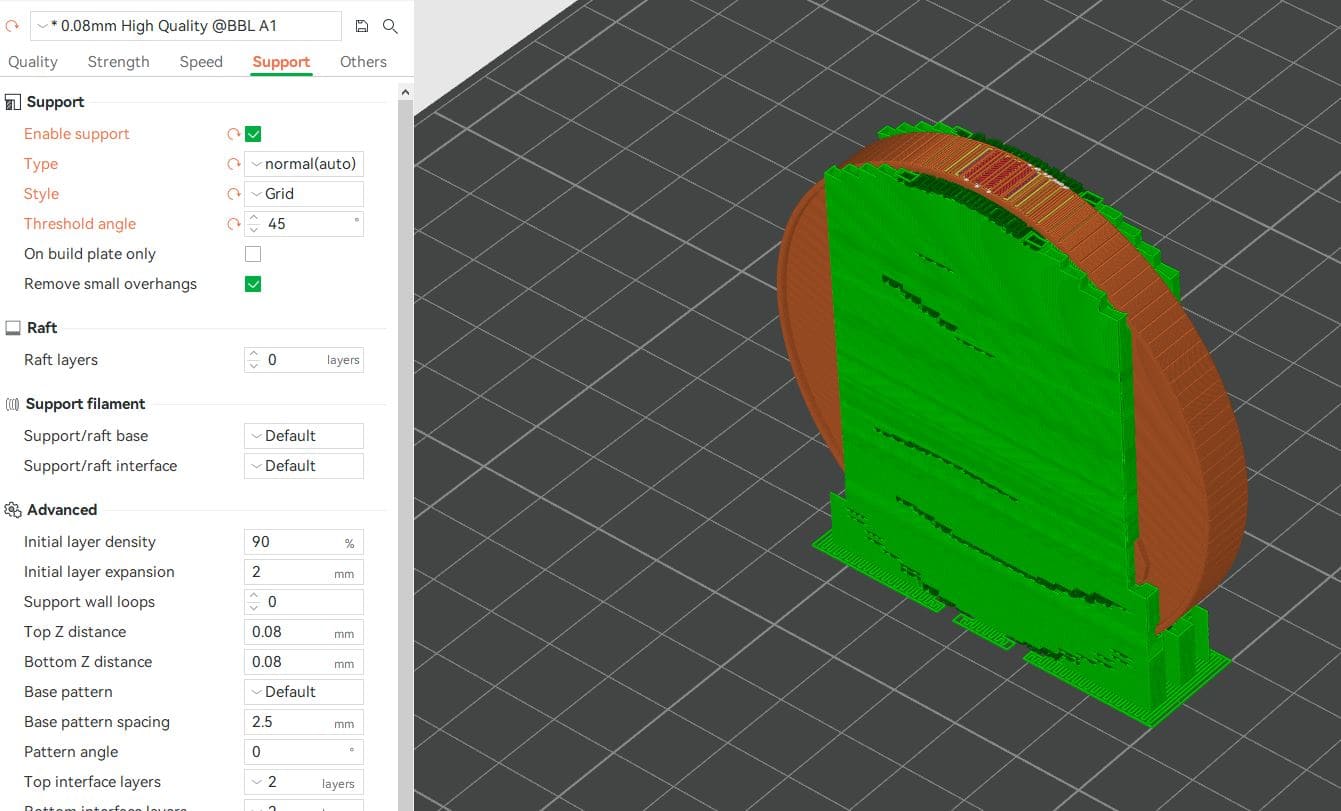
Then, print the prototype with PLA material.
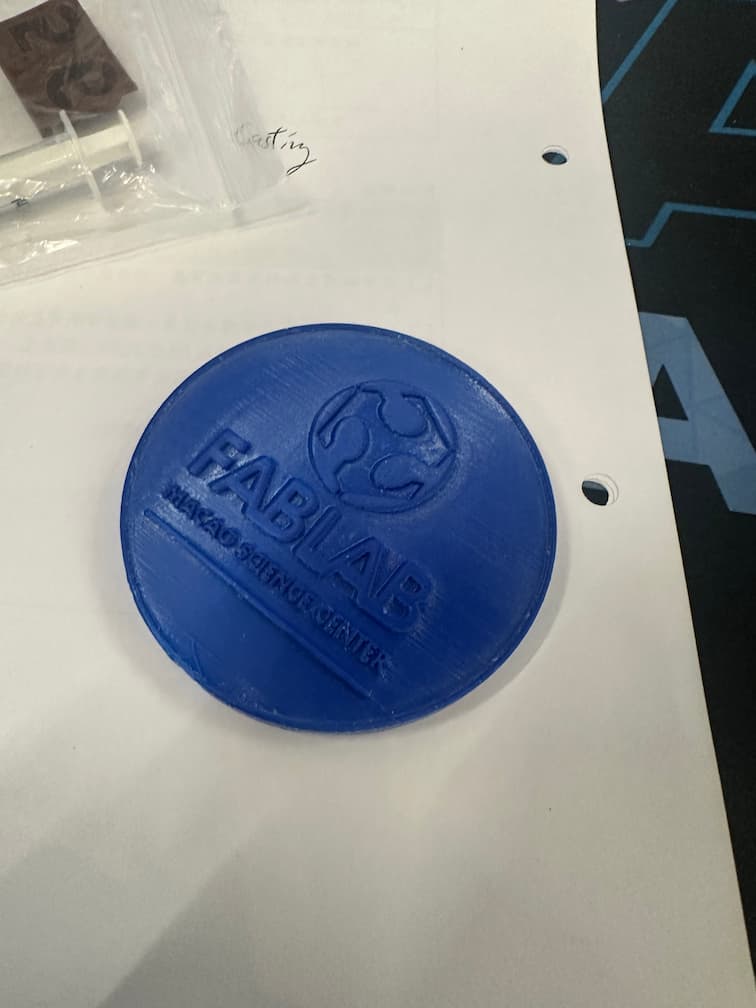
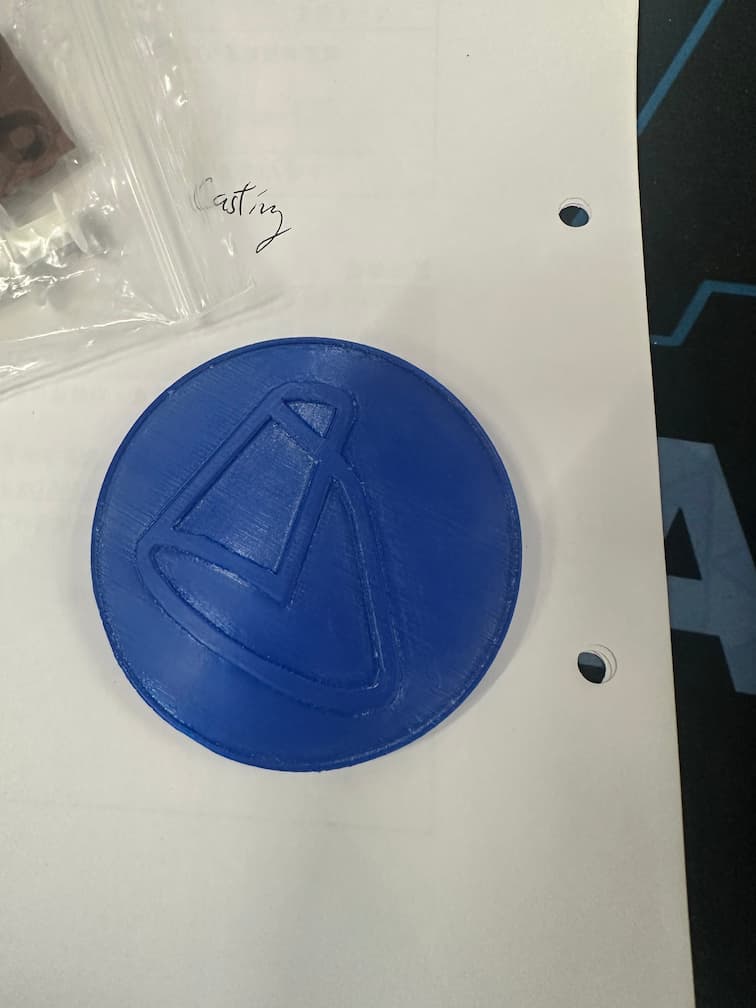


There's lots of tiny toolpath on the surface of the prototype, we need to sand the surface by sand paper to reduce the toolpath.
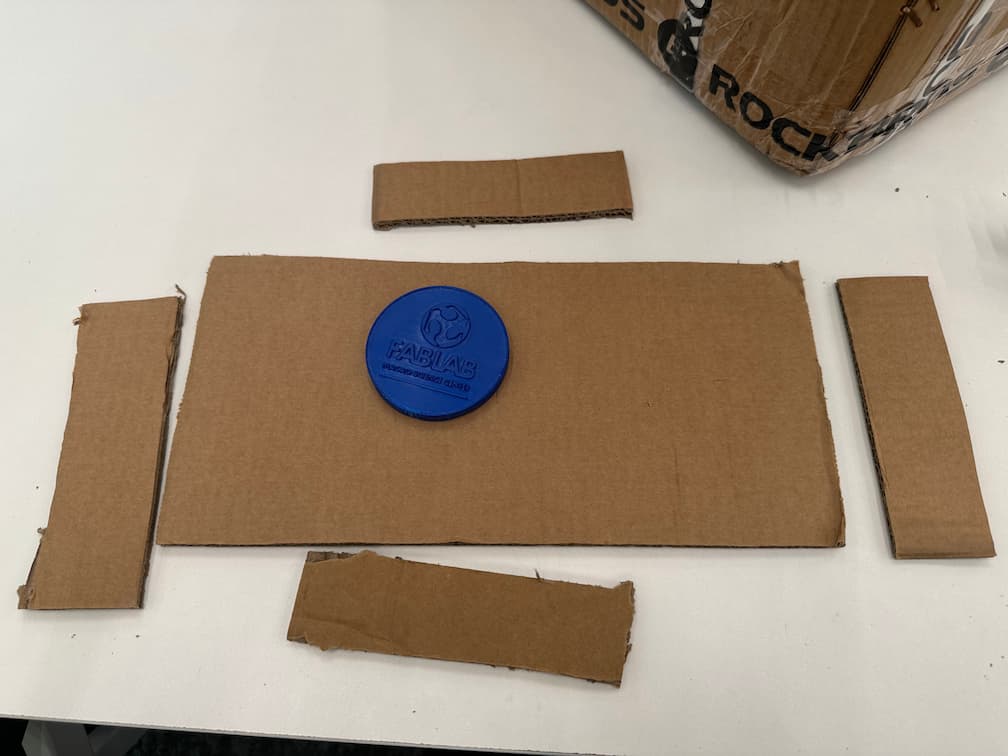

Assemble the cardboard as a box with glue gun.
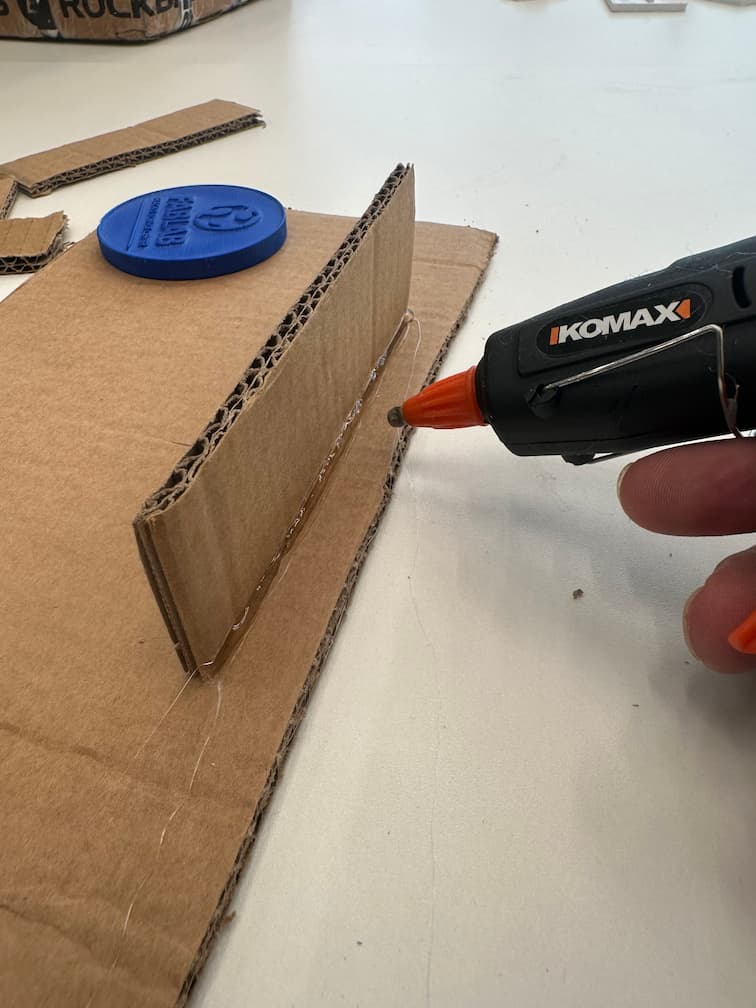
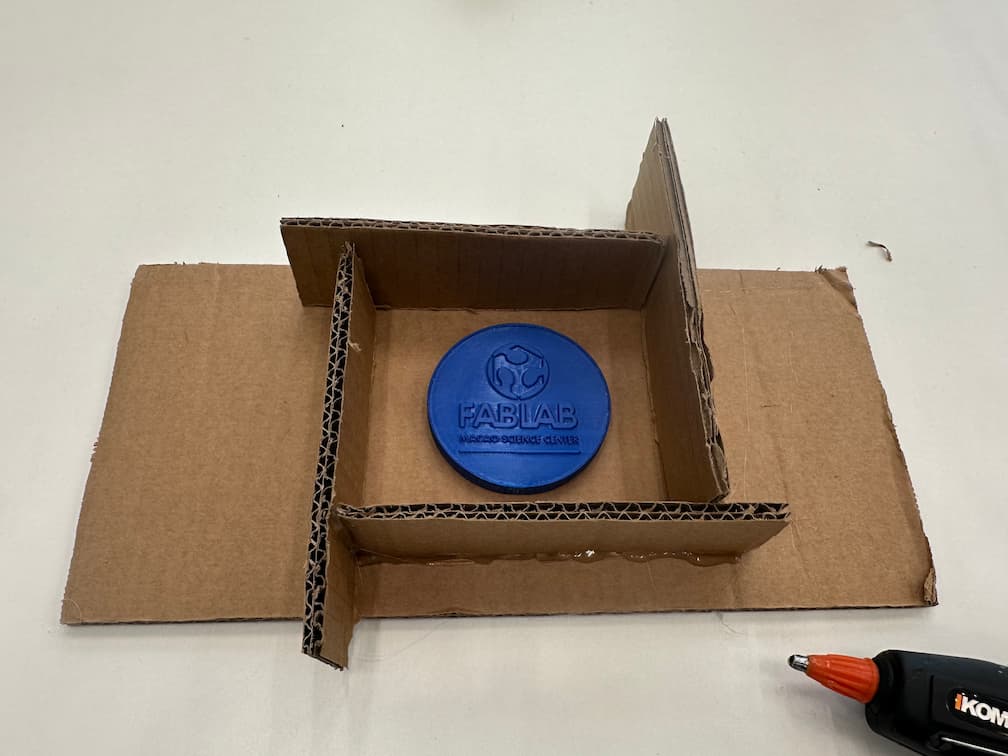


Turn the coin which's face you want to make as a mold and cast.
Then, spray the mold and prototype by Efficient Mould Release Agent Spray about 2-3 layers.
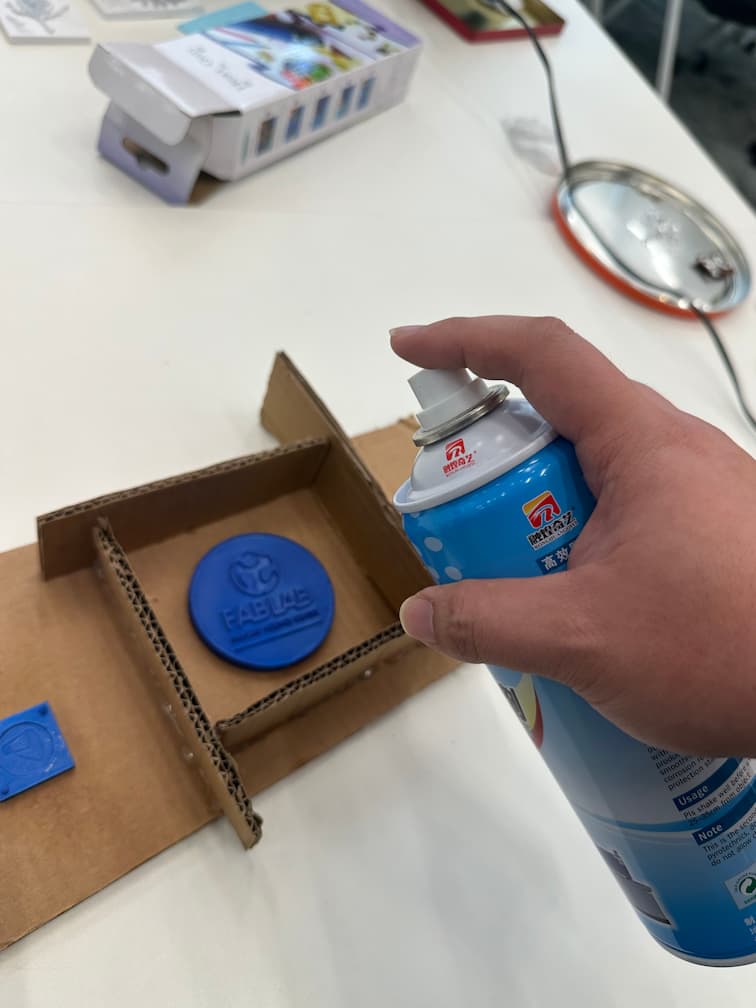

Mix the silicone with the curing agent at a 100:2 ratio and stir thoroughly. Operation time is about 5 minutes.

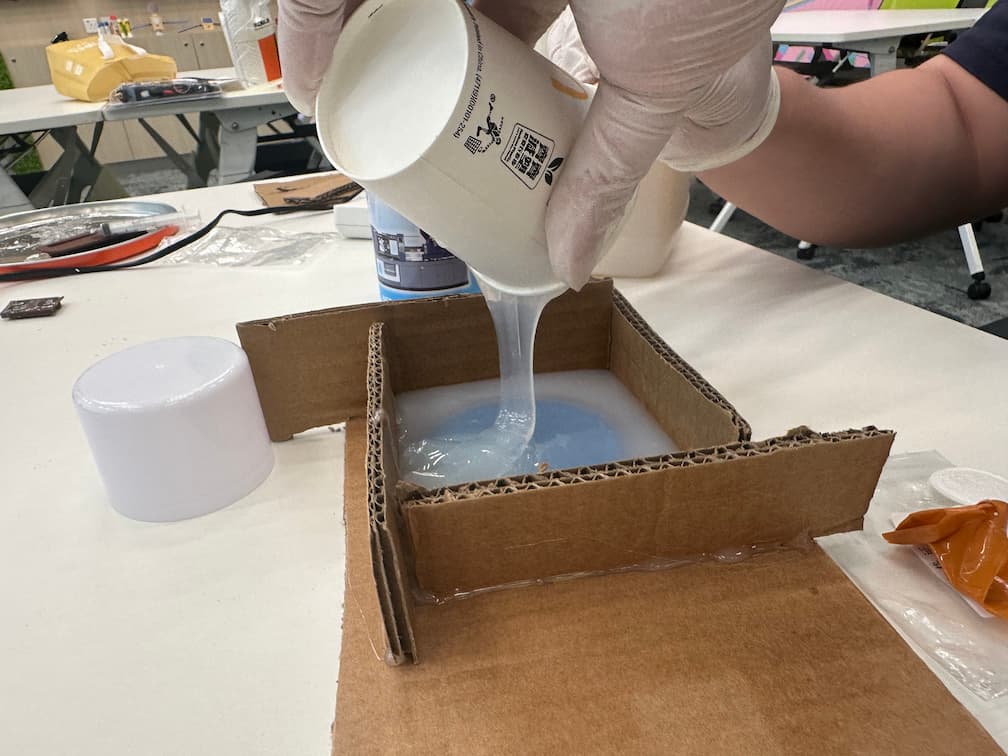
Pour away the silicone to the mold box.

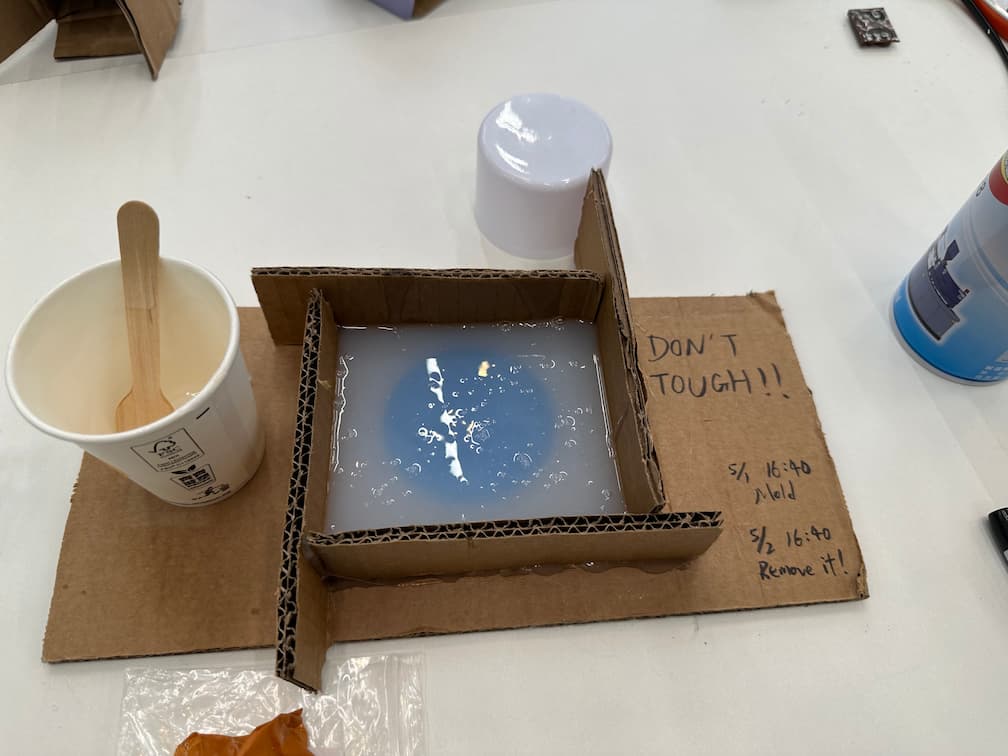
Place the mold for 24 hours.

Demold.
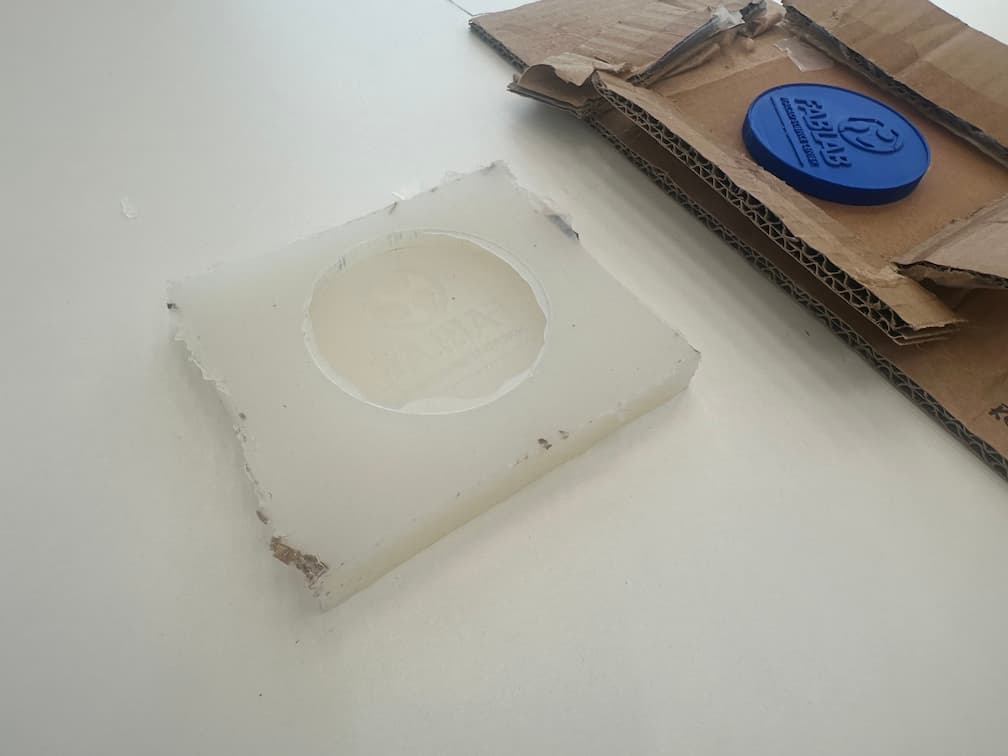

Then, cut the burrs with utility knife.
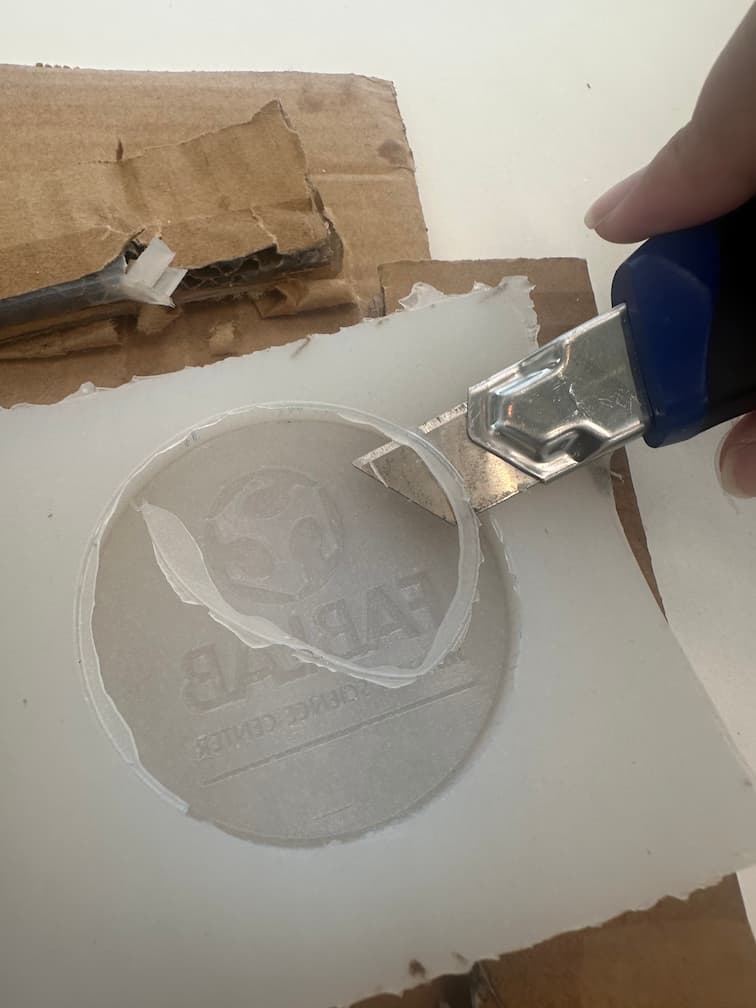

Here is our finish mold!!
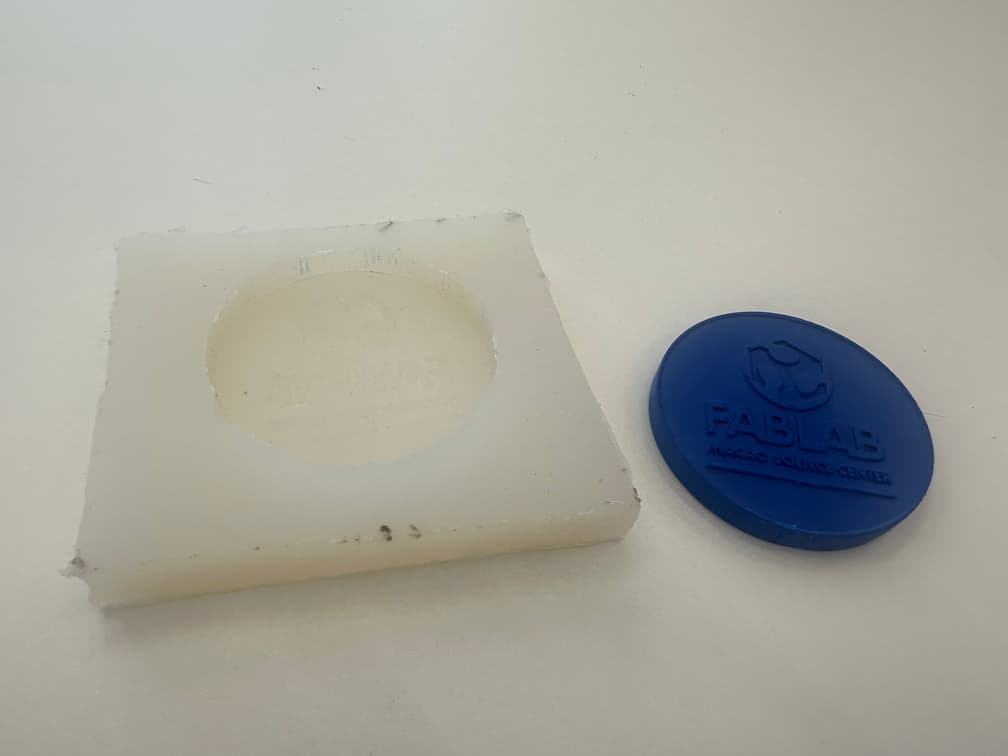

CNC Milling
Process
There's another way to make a prototype with high precision. We use Roland MDX-50 machine as CNC milling machine.

First, import the stl file to the CAM software for MDX-50 -- SRP Player.
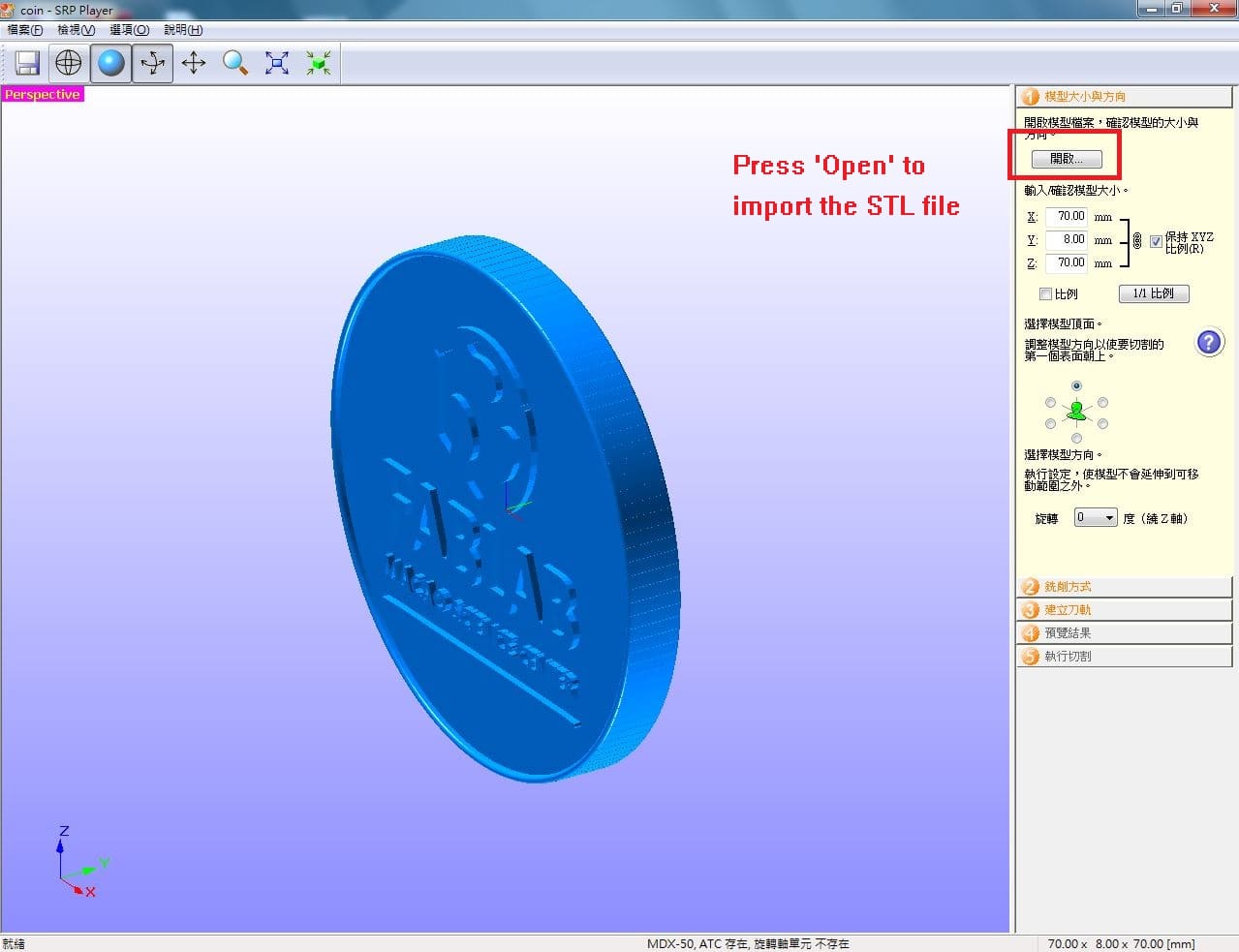
Set the direction of the stl file - Z-axis is normal to the face of coin.
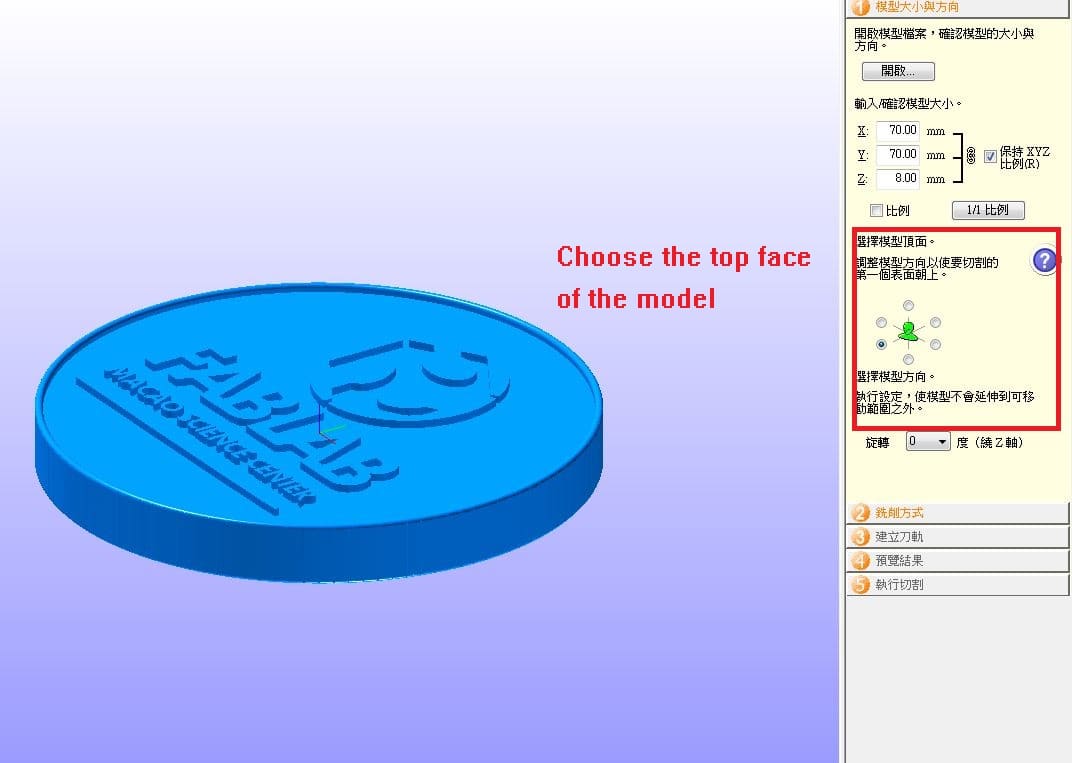
Then, setup the milling parameters as below.
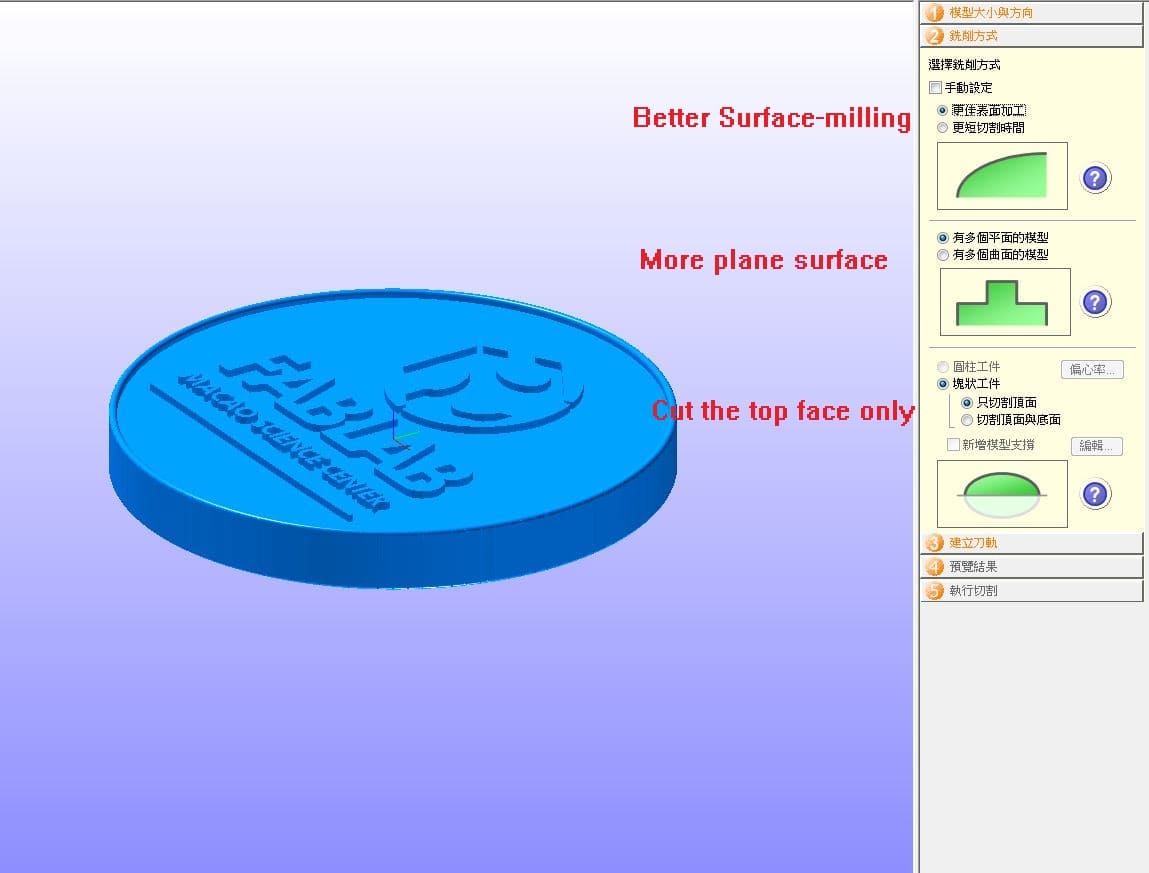
Setup the size of material and place the stl file on the top of the material.
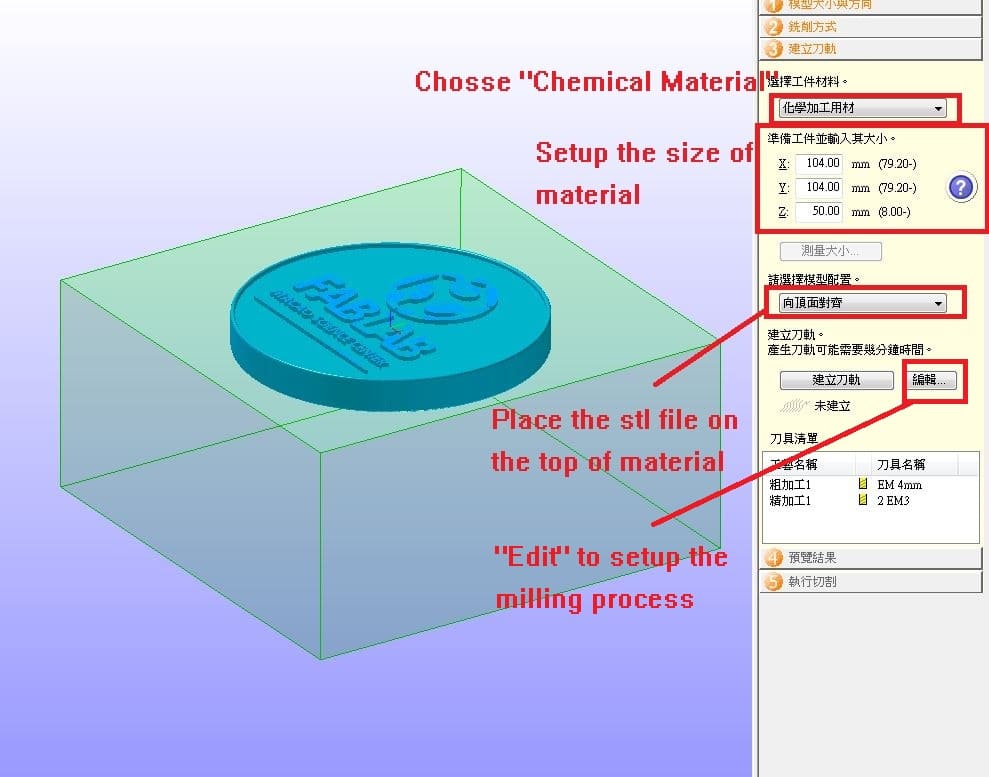
After setup, press "Edit" to edit the milling process.
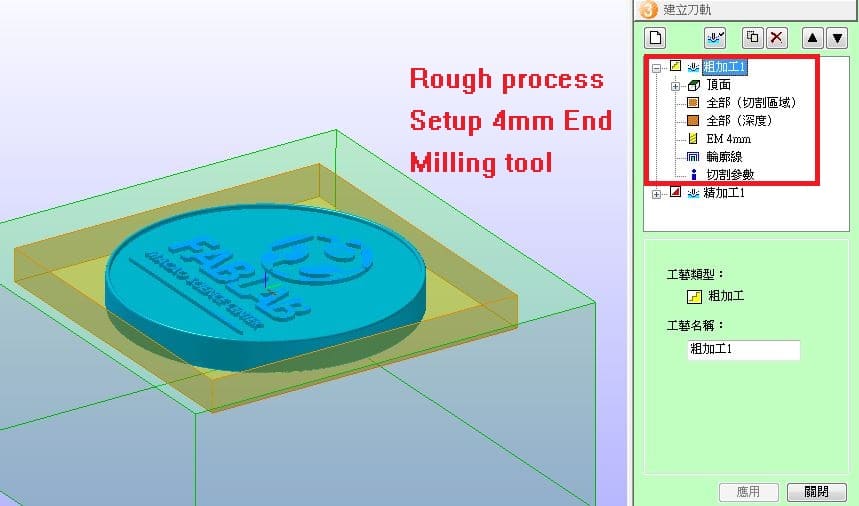
In rough process, setup 4mm End milling tool as milling tool.
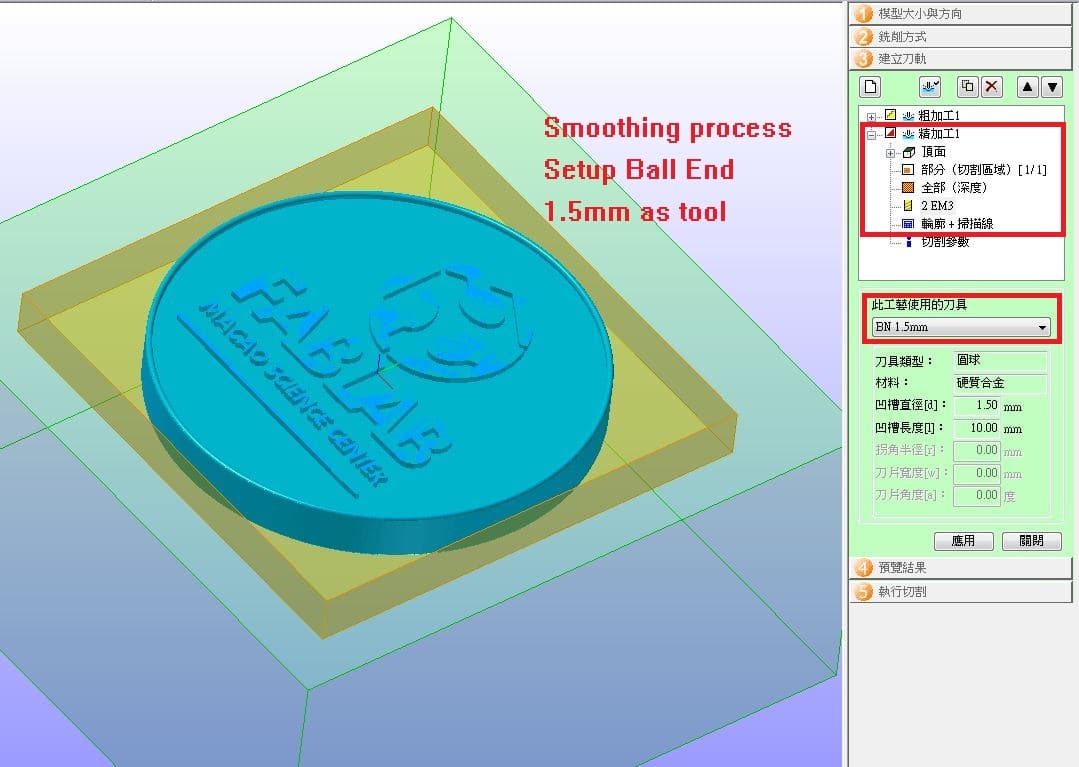
Then, setup 1.5 ball end tool in smoothing process.
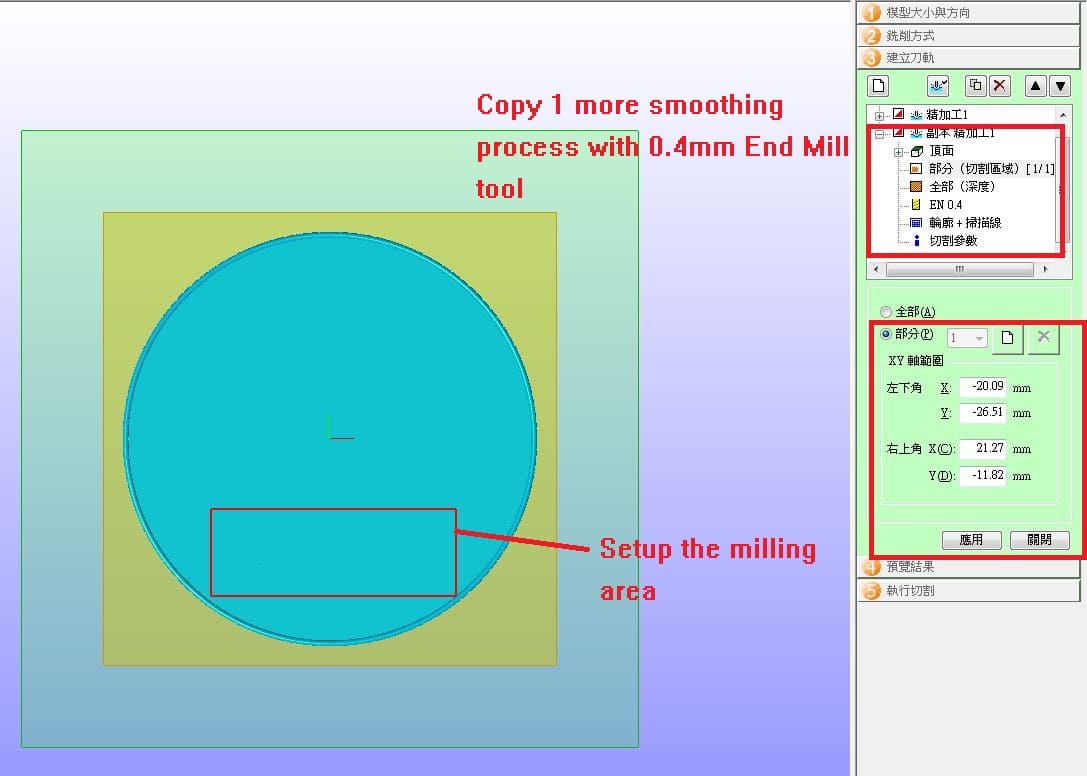
Copy 1 more smoothing process with 0.4mm End Mill tool.
Finally, generate the toolpath.
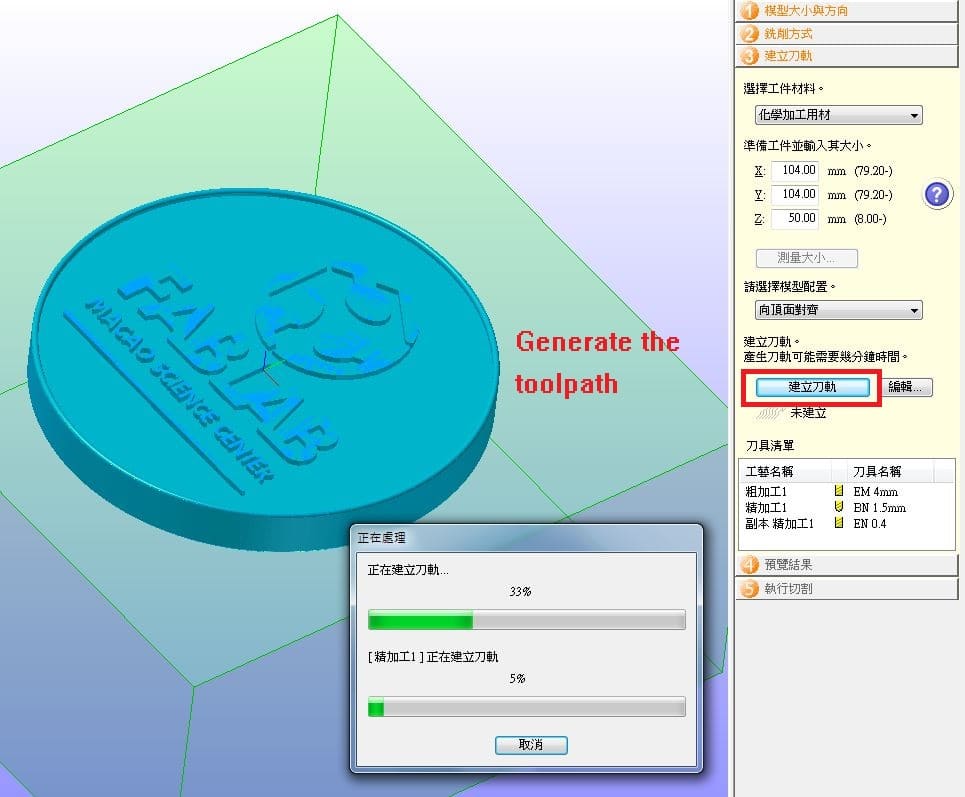
After checking the simulation, launch the milling!!

The milling process and the CNC mold.
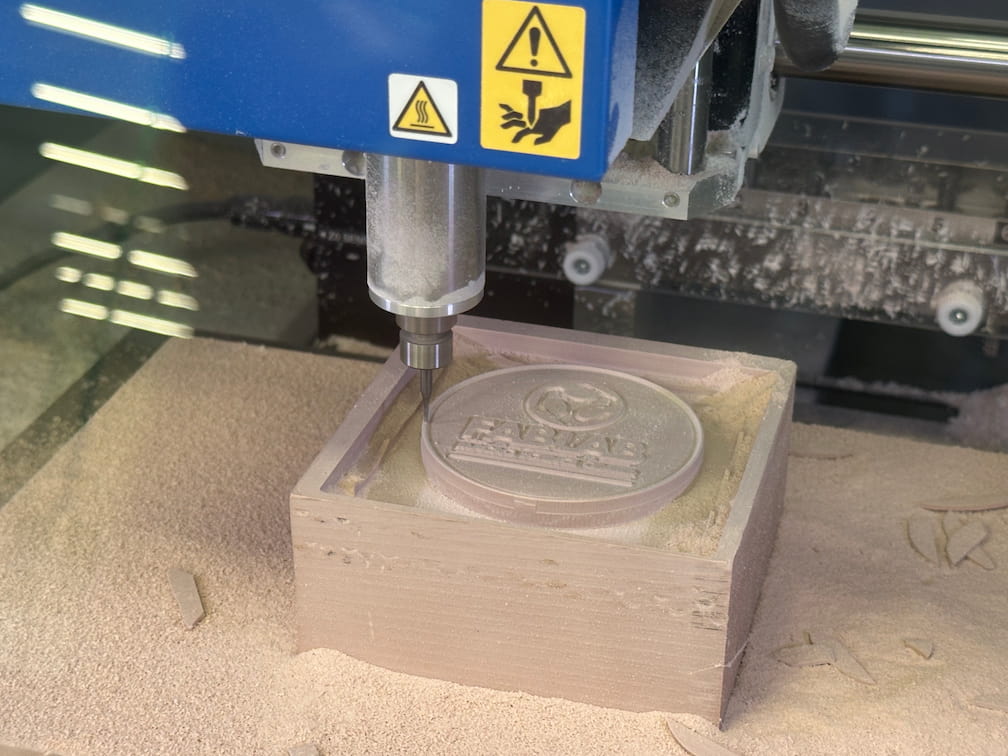


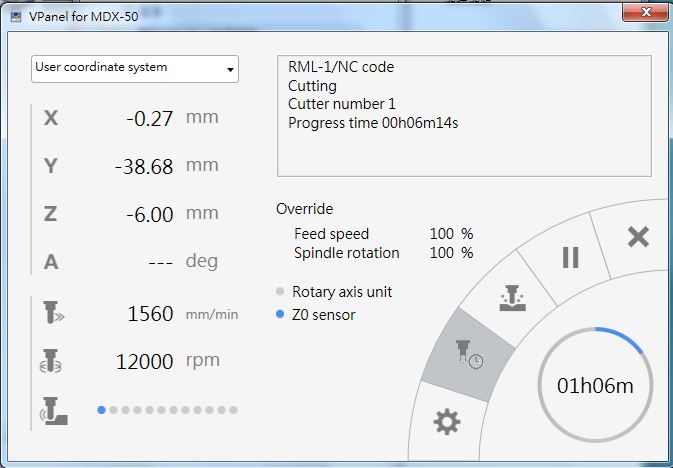
In rough process, feed rate is set as 100% with 1560mm/min. The spindle rotation speed is 12000rpm.
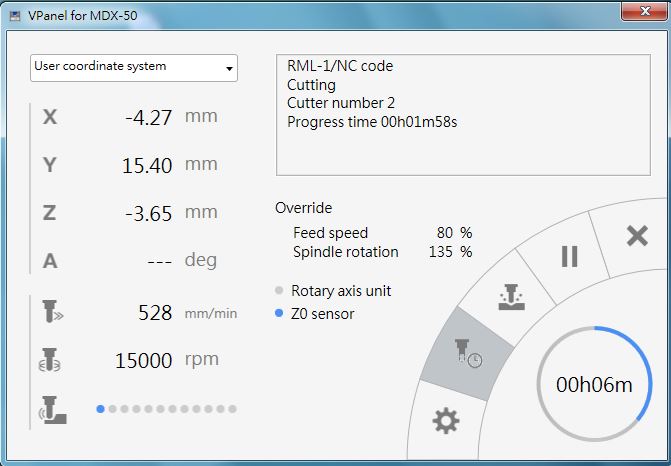
In smoothing process, feed rate is set as 80% with 528mm/min. The spindle roation speed is 15000rpm.
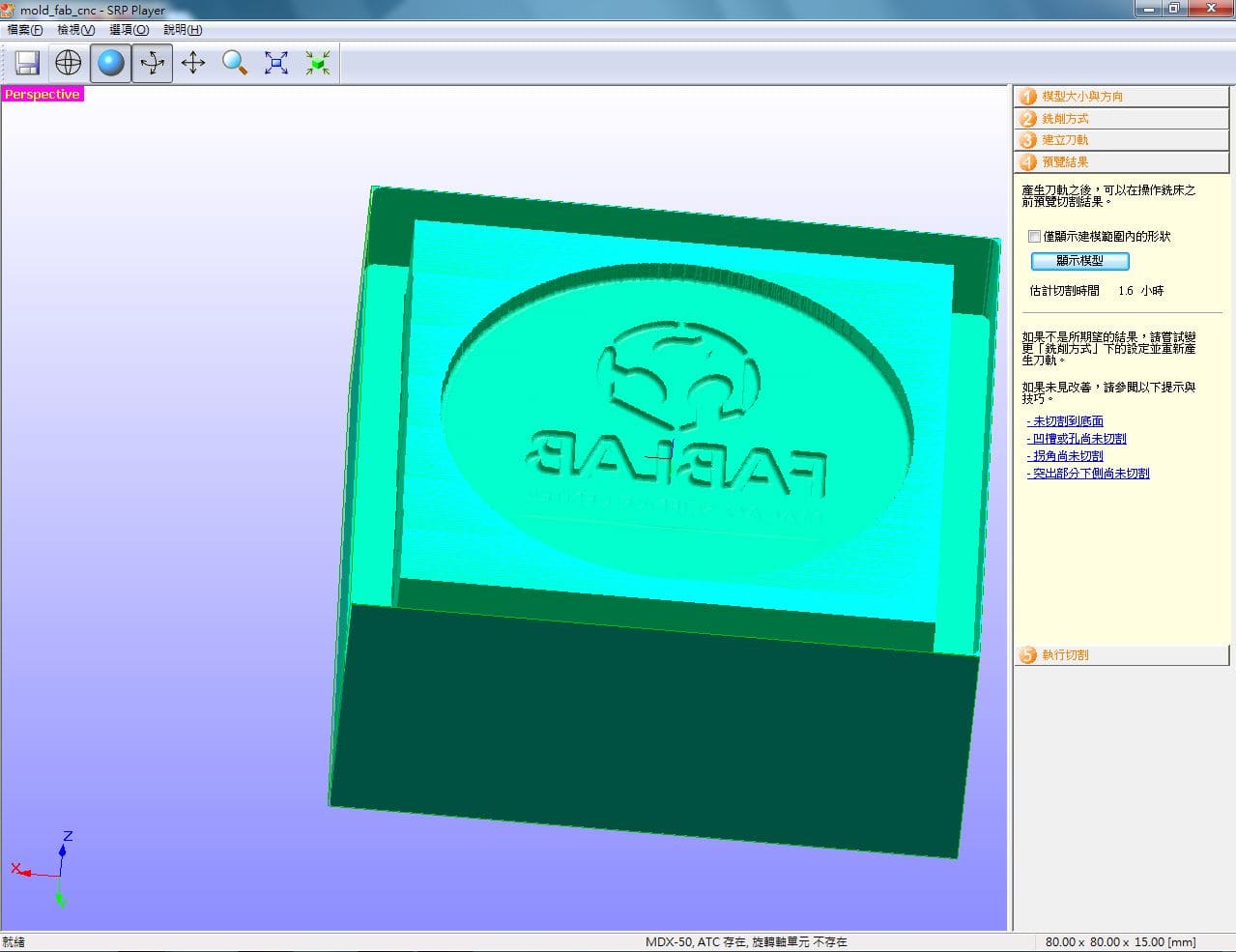
There's lots of toolpath on the 3D printed prototype without sanding the surface. The other prototype will be made for comparing each other. CNC milling prototype is more smooth than 3D printed.
Higher walls are needed for containing the silicone. Paste 4 cardboards around the CNC prototype.
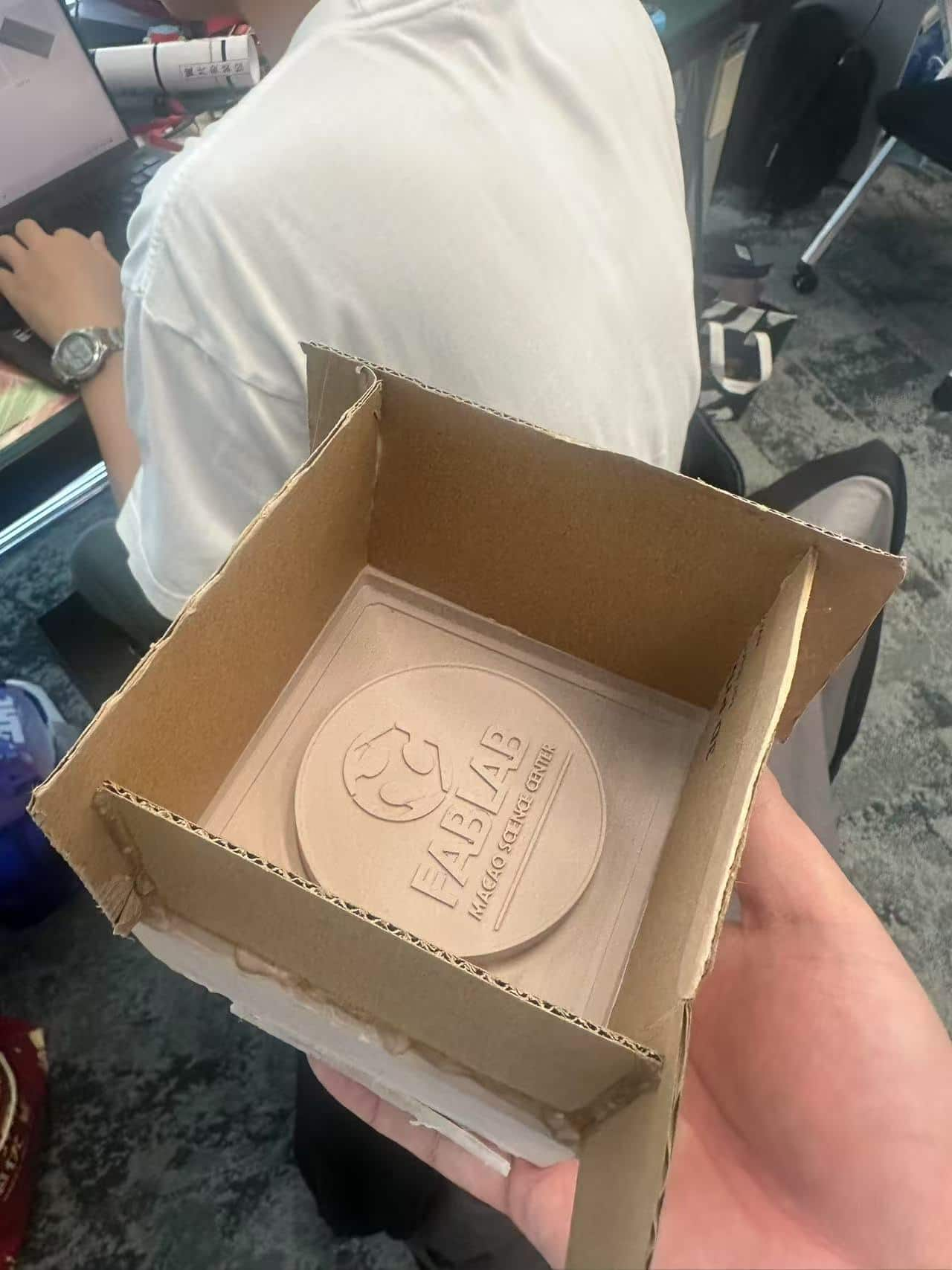

Pour away the silicone to the mold box and place it for 24 hours.

Separate the mold and silicone.

The new silicone mold contains more detail and less toolpath. There's something need to be improved. Bubbles problem cause some of detail lost is this mold.
The final mold:

3D print is a easier way and quickier way to form the orignal parts but usually with more process toolpath. To reduce the process toolpath, we can:
- reduce the layer height
- adjust the printing angle
- Doing additional processing like sanding, polishing
CNC need more time and material to form the orignal parts, but with a better outlook and less process toolpath. To save time and balance the less toolpath outlook, we can:
- use a large milling tool to mill the raw material first
- use a small diameter milling tool to mill the final surface

Mold Materials Comparison
In the last section, we use different processes to make the oringal parts for silicone molding. We also wonder whether if we can use these processes to form the mold directly.
In this section, we will tried to make the mold with different processes and materials :
- Silicone
- PLA (3D printing)
- Paraffin Wax (CNC)
- Chemical wood (CNC)
Silicone
Silicone one is descripted before and it's very useful for casting. It's easy to demold as Efficient Mould Release Agent and the silicone mold is soft.
PLA

It's the easiest way to make a mold by 3D printing, but same as the conclusion of the last section, there's lots of toolpath on the surface.
After we inject the resin into the mold, it stuck hard to the PLA mould. Even we spray 4 layers of mold release agent on the mold surface, we still cannot demold without breaking the 3D printed mold.
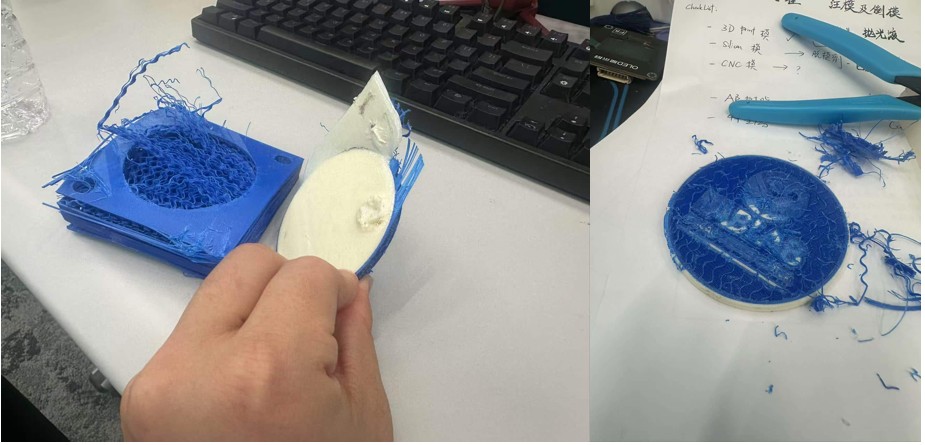 It's because while the resin is still in its liquid state, it flowed into the gaps in the PLA, and became stuck in the mold after solidification.
It's because while the resin is still in its liquid state, it flowed into the gaps in the PLA, and became stuck in the mold after solidification.
The rest of the following molds are produced by CNC milling process. We designed a mold and milling it.
Paraffin wax
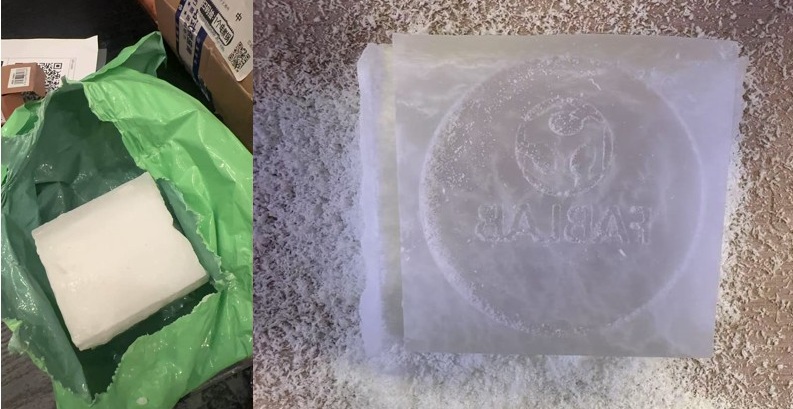

We made a wax mold by CNC milling as same as the steps we describled before, it's a soft material and easy to shape. Also the wax surface is relatively smooth, making it easy to demold.
But when we inject the resin and demold, we found that the result is worse than expected.

By the way, paraffin wax is still a general material for form the orginal parts, and use to forming the silicone mold.
Chemical Wood (Polyurethane Tooling Board)
The wood is a high density tooling board and easily shaped and machined. It can use as a prototype milling with good details.
We also make a mold by this material and pour away the AB resin onto it. Same as PLA mold, we cannot demold without breaking the milled mold (It's hard). Resin is stick on the chemical wood mold. AB resin may not usable in this material.

It's a good material for making as a prototype and helpful for vacuum forming, scale model, casting, etc.
Conclusion
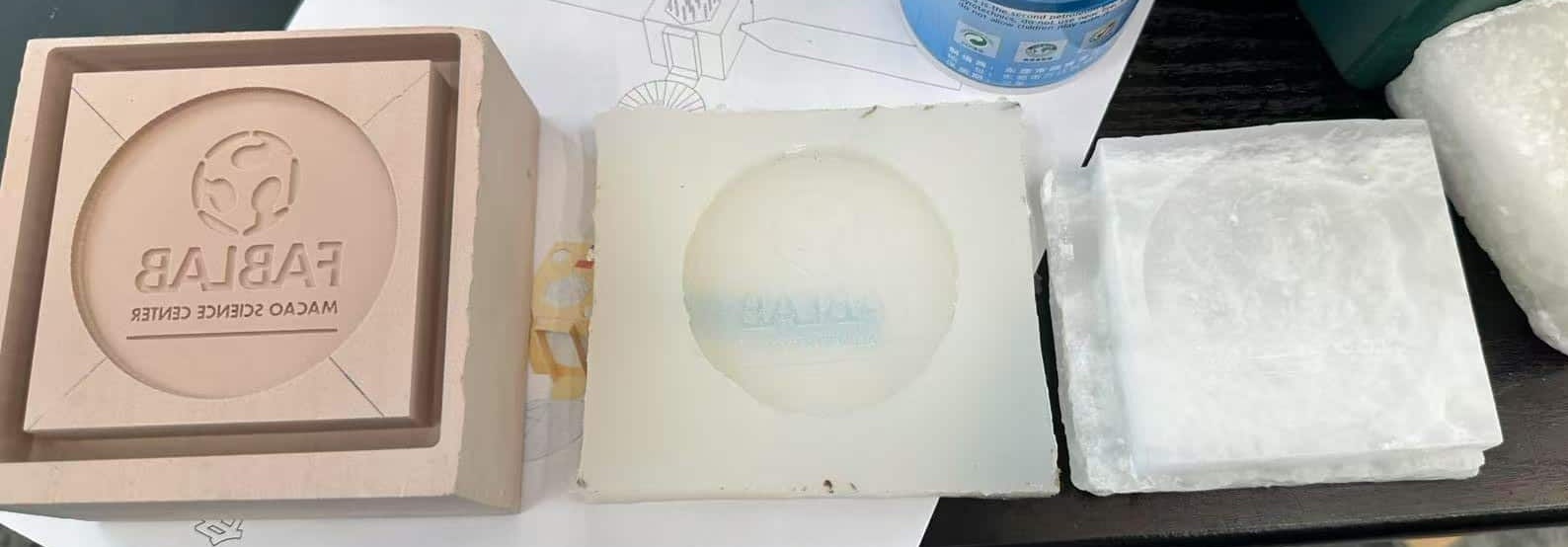 In our FABLAB, casting process is successful by using soft mold, such as silicone mold.
In our FABLAB, casting process is successful by using soft mold, such as silicone mold.
PLA, Paraffic wax or chemical wood as hard enough and it's not easy to demold and break the cast model. It's important that doing research for the material properties.