Fabacademy 2020
Intellectual property rights
Intellectual property rights include patents, copyright, industrial design rights, trademarks, plant variety rights, trade dress, geographical indications,[24] and in some jurisdictions trade secrets. There are also more specialized or derived varieties of sui generis exclusive rights, such as circuit design rights (called mask work rights in the US) and supplementary protection certificates for pharmaceutical products (after expiry of a patent protecting them) and database rights (in European law).
- Patents
- Copyright
- Industrial design rights
- Plant varieties
- Trademarks
- Trade dress
- Trade secrets A trade secret is a formula, practice, process, design, instrument, pattern, or compilation of information which is not generally known or reasonably ascertainable, by which a business can obtain an economic advantage over competitors and customers. There is no formal government protection granted; each business must take measures to guard its own trade secrets (e.g., Formula of its soft drinks is a trade secret for Coca-Cola.)
A patent is a form of right granted by the government to an inventor, giving the owner the right to exclude others from making, using, selling, offering to sell, and importing an invention for a limited period of time, in exchange for the public disclosure of the invention. An invention is a solution to a specific technological problem, which may be a product or a process and generally has to fulfill three main requirements: it has to be new, not obvious and there needs to be an industrial applicability.To enrich the body of knowledge and stimulate innovation, it is an obligation for patent owners to disclose valuable information about their inventions to the public.
A copyright gives the creator of an original work exclusive rights to it, usually for a limited time. Copyright may apply to a wide range of creative, intellectual, or artistic forms, or "works".Copyright does not cover ideas and information themselves, only the form or manner in which they are expressed
An industrial design right (sometimes called "design right" or design patent) protects the visual design of objects that are not purely utilitarian. An industrial design consists of the creation of a shape, configuration or composition of pattern or color, or combination of pattern and color in three-dimensional form containing aesthetic value. An industrial design can be a two- or three-dimensional pattern used to produce a product, industrial commodity or handicraft. Generally speaking, it is what makes a product look appealing, and as such, it increases the commercial value of goods.
Plant breeders' rights or plant variety rights are the rights to commercially use a new variety of a plant. The variety must amongst others be novel and distinct and for registration the evaluation of propagating material of the variety is considered.
A trademark is a recognizable sign, design or expression which distinguishes products or services of a particular trader from the similar products or services of other traders
Trade dress is a legal term of art that generally refers to characteristics of the visual and aesthetic appearance of a product or its packaging (or even the design of a building) that signify the source of the product to consumers.
Intellectual Property
Regarding licensing I want a license that makes sure that other can build onto my idea, improve it or create something else out of it. Because the documentation of other projects helped me a lot in the development of mine as well. As long as they will recognize me as the initial creator and refer to me when they use any of it.
Fab License
I think the Fab License would fit nice to my idea and the purpose I have with my project.
This work may be reproduced, modified, distributed, performed, and displayed for any purpose,
but must acknowledge “project name”.Copyright is retained and must be preserved. The work is provided as
is; no warranty is provided, and users accept all liability.
However, at this time I’m not sure what my future plans will be with my project. Therefore I looked further into other possibilities for licensing.
Creative commons
I also looked into the Creative Commons licensing and they have a nice tool that help you choose.
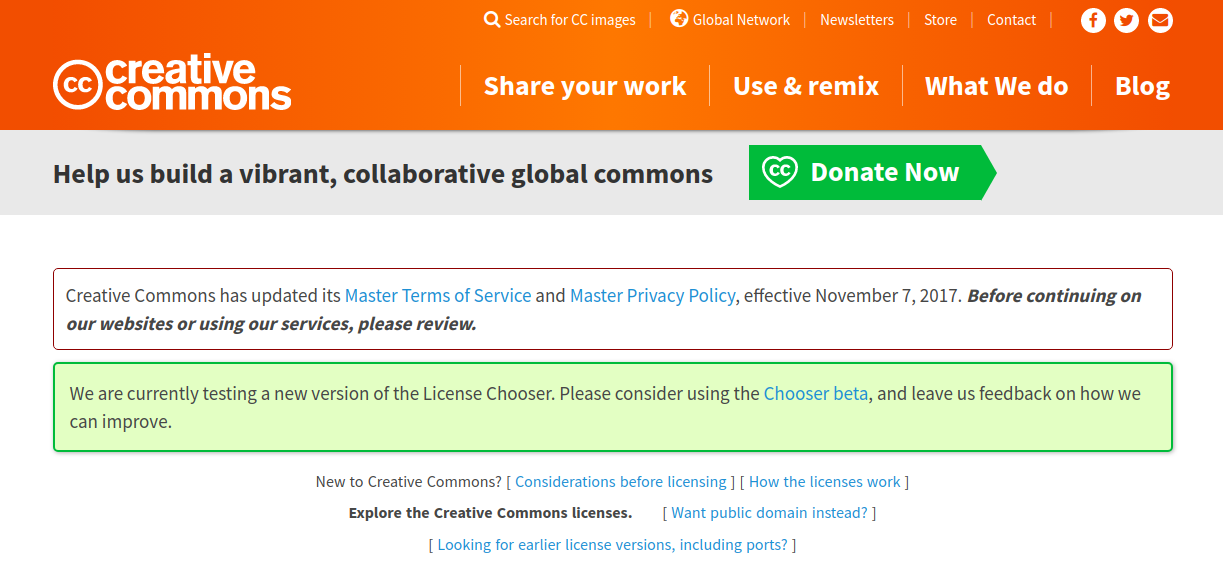
This feature helps you select the right license. So if we are not familier with licensing it helps us to find the right licence by asking us various questions as shown below.

Based on these choices Creative Commons selects the following license: Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0).This license requires that reusers give credit to the creator. It allows reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format, for noncommercial purposes only. More detailed information can be found on the creative commons license page and their wiki on the License Versions.

In the end I decided that I will use the creative commons license instead of the Fab License because this give me an option for further possibilities of the distributing and selling my own product. While it’s still possible for others to use and share parts of it. I will use the logo of the right license in the communication of my final project.
License Used

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Making Of slide and Video
At this stage since i havent finsihed much of the project I only have decided which software to use to make my slide and video. I have gained some experiance in using Gmp so prepared a draft file and Openshot.
I took a simple format with black background and i have to develop from here.
I have some experinace using openshot.I will continously add videos in the coming weeks and edit in to a single video.
The finally edited video and slide can be seen in the final project page.