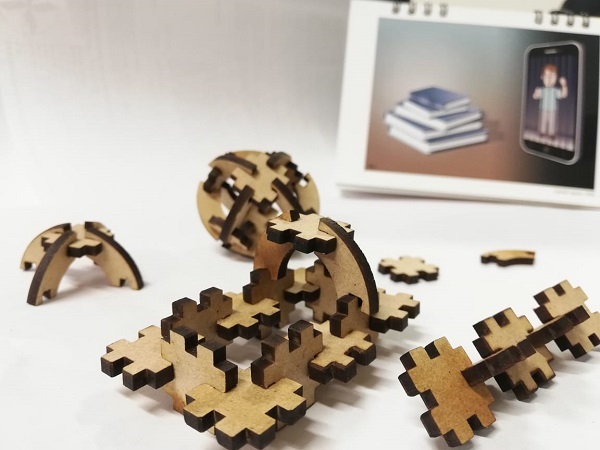
For this week, I learned about the laser cutter and vinyl cutter.
There are many parameters that affect cut quality, such as the material properties, thickness, focal length of the lens, pressure of compressed air and also “the laser kerf”.
The high power of the laser vaporizes the material. So, the laser literally disappears a portion of material when is cut. This measure is known as the laser kerf.
Group assignment: Get the kerf dimension and test different cutting and engraving settings
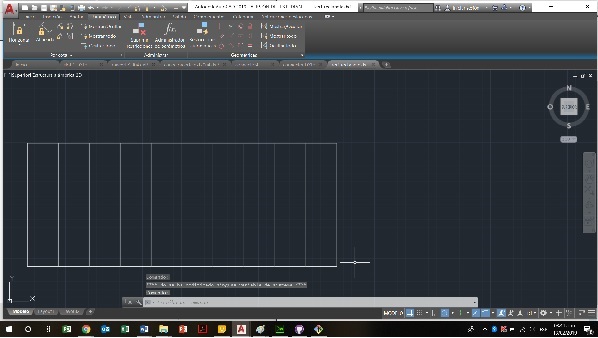
To calculate the kerf, our team designed in Autocad a rectangle with 11 cuts, creating 10 small rectangles, then, the kerf was calculated in the following way: The length of the rectangle, minus the length of the pieces that were cut, divided by the number of cuts and then divided by two
((100mm-98.24)/11)/2=0.08 mm.
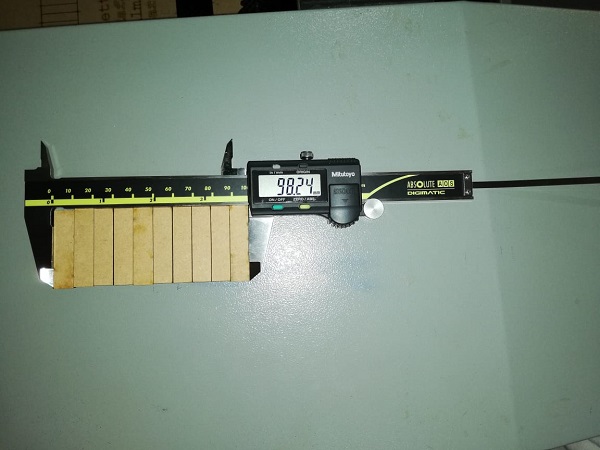

For cut 3mm MDM

Final result.
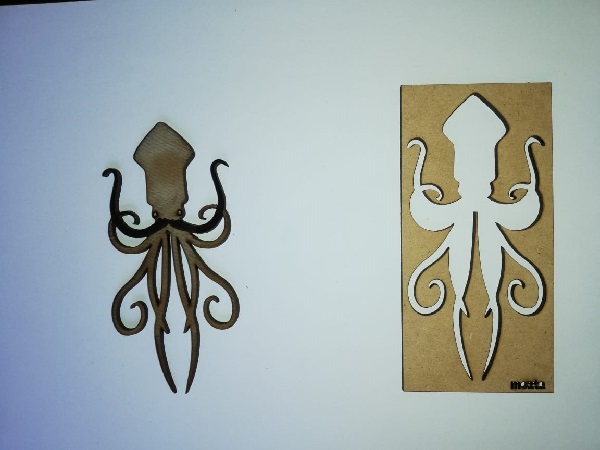

Individual assignment: Vinyl cut test
For the vinyl cut test I used Illustrator for doing the vectors of the image that I wanted to cut.
I got a shape of a world for vinyl cutting
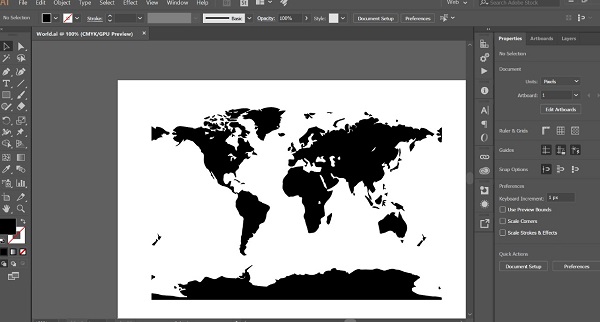
Then I used the software vinyl to make the cut.
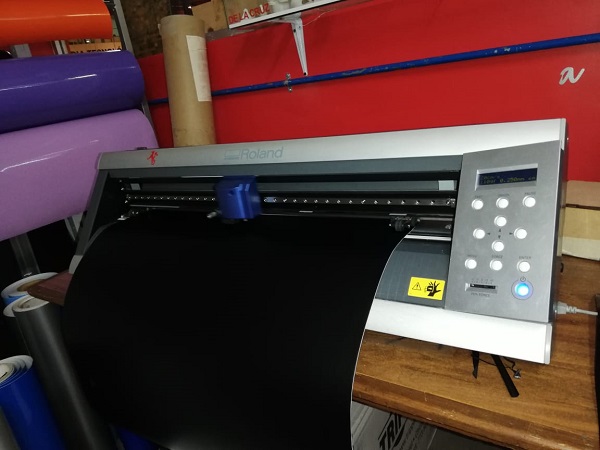

After letting the machine do its job, I removed the remaining material and pasted the transfer paper

Press fit
For a well assembly it is very important to know the kerf of your laser cut, and you must design your piece with aprox .2 mm smaller than the width of the material.
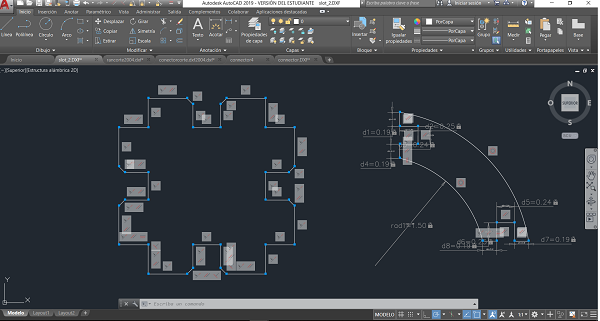
I decided to use Autocad to make my parametric assembly, but without previous experience, I did not succeed in my initial model, so I resigned myself and made a very simple model

So, there are two types of constraints; Geometric constraints that contols the relationships of objects with respect to each other, and Dimensional constraints that controls the distance, length, angle, and radial values of objects
