Juan Ranera
Fab Academy 2013 Participant
Output devices
The assignment in the last week was add an output device to a microcontroller board and program it to do something.
This week I've decided to control a motor with an Arduino board using
"PWM" signal, because my final project have four motors and
is very important to me to Know more about how to control a motor through Arduino board. There are a lot of samples and tutorials about control
motor with Arduino and my colleague and me decided to test a simple circuit with a Mosfet.
This tutorial explain very well a similar circuit.
Also I've used a "Processing" as interface to change the motor speed with the mouse
movement because I really liked the experience of last week and I wanted to learn more about it.
Circuit scheme:

MotorPWM is connected to digital output pin 9 and the ground is connected to the ground of Arduino board. Vbat is connected to a power supply with 12V, because is the voltage of the motor.
The motor I've used is the same model that I will use to move the platform of my final project. It can rotate at 120 rpm and has a power of 40 Watts. You can find more features "here".
Image of the motor:

I've started to design the board that will move the motors in my final project. I will use more powerful mosfet and gate drivers to ensure correct switching. In a few days I'll upload the new design, in the section of the final project.
Image of the prototype board with mosfet:
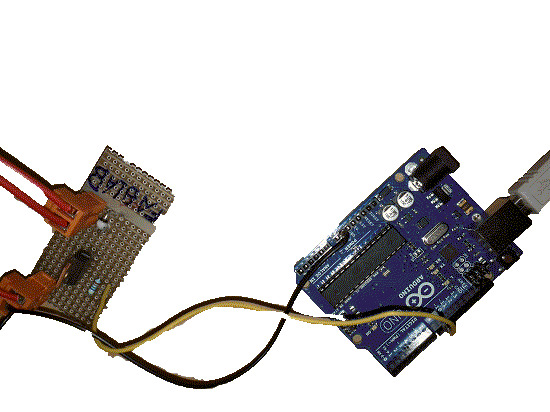
Processing code:
/* April 2013 By Joan Ranera Fablab 2013 */ import processing.serial.*; import cc.arduino.*; Arduino arduino; PImage img; PFont font; int zero_zone = 20; void setup() { size(512, 512); arduino = new Arduino(this, Arduino.list()[0], 57600); font = createFont("SansSerif",1); textFont(font,20); } void draw() { background(constrain(mouseX, 0, 255)); //Neutral zone: the engine is stopped in this area (protects motor sharp changes) if ((mouseX < 255 + zero_zone) & (mouseX > 255 - zero_zone)){ arduino.analogWrite(9, 0); arduino.analogWrite(11, 0); } //Half of the screen to the right, you can move an engine through output pin 9 Arduino UNO if (mouseX >= 255 + zero_zone){ arduino.analogWrite(9, constrain(mouseX, 255, 512)); arduino.analogWrite(11, 0); } //Half of the screen to the left, you can move another engine through output pin 11 Arduino UNO if (mouseX < 255 - zero_zone){ arduino.analogWrite(11, constrain(255 - mouseX , 0, 255)); arduino.analogWrite(9, 0); } //Print my name textFont(font,20); text("Juan Ranera",330,438); textFont(font,20); text("FabLab 2013",330,458); }
In the video you can see the voltage and current in each momente through the power supply and the PWM pulses through the oscilloscope.
