INPUTS DEVICES
For this assignment, I decided to create a new PCB desing, in this assigment I wanted to work with a XIAO ESP32 and to try with a Cardiac sensor device.
Team Practice
Here its the link of our team practice.
COMPONENTS LIST
| Material | |
|---|---|
| Microcontroller | XIAO ESP32 |
| Pins | |
| Button | 1 |
| Resistor | 1002 k |
| LED | Orange color |
| Resistor | 1001 k |
| Ultrasonic sensor | 1 |
This components and the Xiao ESP32 are the components that I have used for this new PCB desing.
KiCad PCB Design
Step 1
For my schematic design, I used the KiCad program to create my circuit.
Step 2
To do this, I downloaded the KiCad program.

Step 3
Open a new project, assign a name to the project, and save it in the desired location.
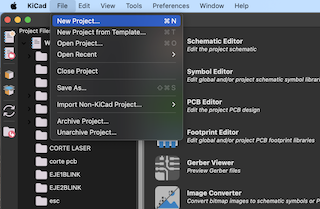
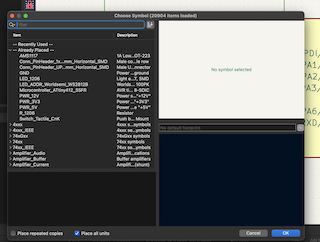
Step 4
With the components ready, I add them to the program by selecting the letter "A."
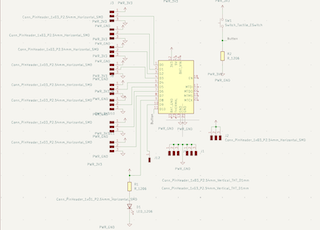
Step 5
I connect them with a "wire" by pressing the W key, grounding the necessary ones and connecting the required ones to 5V voltage.
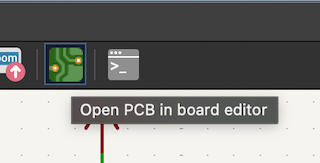
Step 6
Once the connections are ready, I save the schematic, and in the upper part, I select the PCB button, where I will generate my entire design for etching and cutting.
PCB Design
The PCB part helped me create the electronic desing before sending it for actual cutting, allowing me to identify any potential errors or issues.
Step 1
Within the new PCB tab, we go to "Tools" and select "Update PCB from Schematic," a box appears with the specifications where we check that there are no errors and click "Update PCB."
Step 2
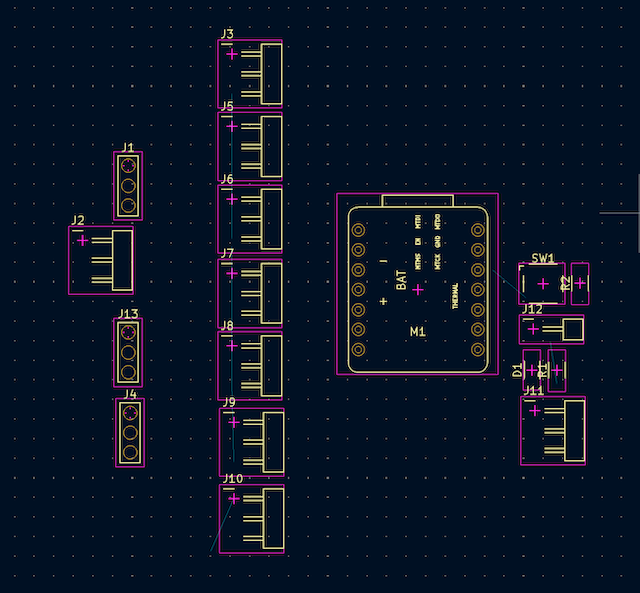
All our components will appear together, and with a click, we place them in the middle of our page.
Step 3
There we will begin to arrange them based on the lines that connect them to do it as best as possible and avoid connection errors or complications.
Step 4
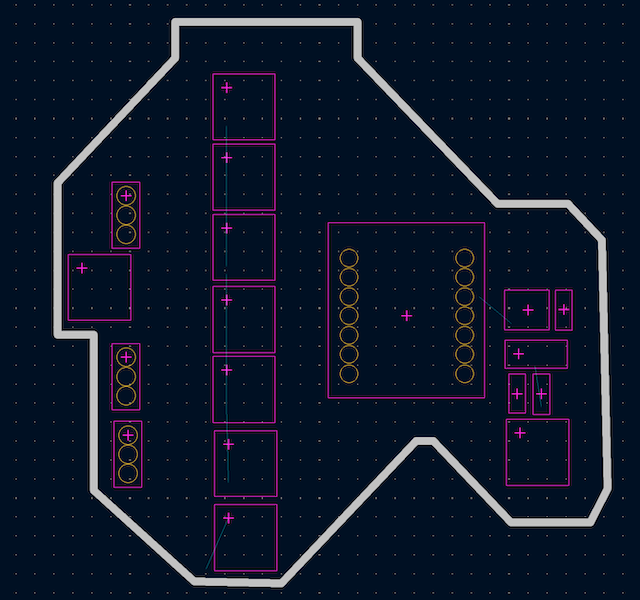
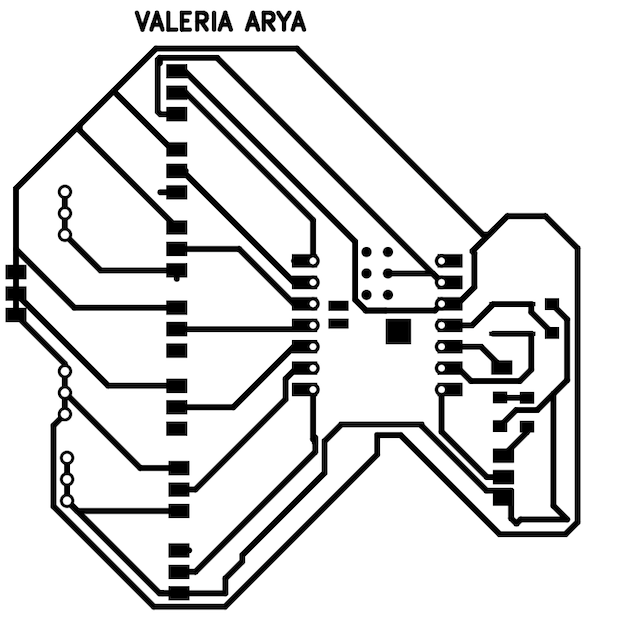
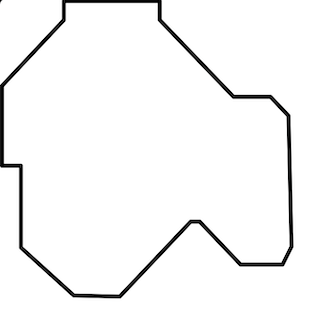
In this case, I decided to first put the outline of the shape of my heart that I previously drew in Procreate.
Step 5
I gave it the measure 8.7 x 7.3 mm since that space would fit perfectly on my cutting board.
Step 6
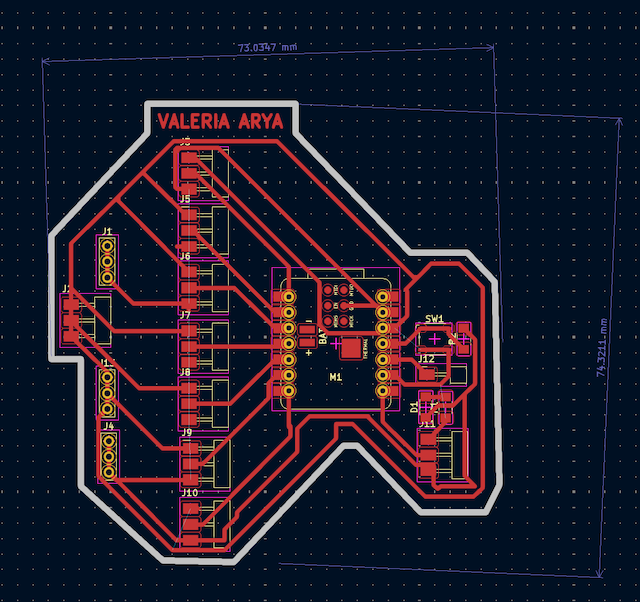
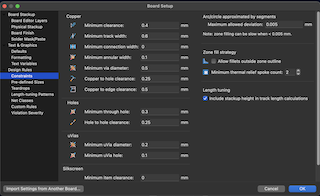
With the base shape, I arranged my components and gave a thickness to my track of 0.6mm and a separation between each of 0.4mm to maintain order and good track thickness.
Step 7
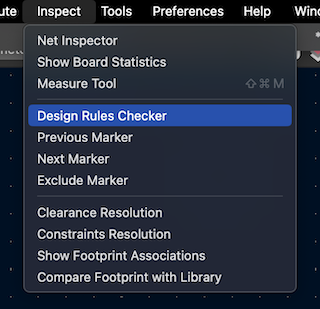
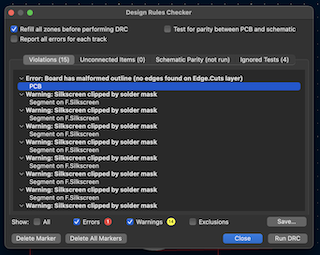
When my circuit was ready, I verified all the connections, went to "iINSPECT," and selected "Design rules checker," where it automatically presents possible connection errors and warnings.
Step 8
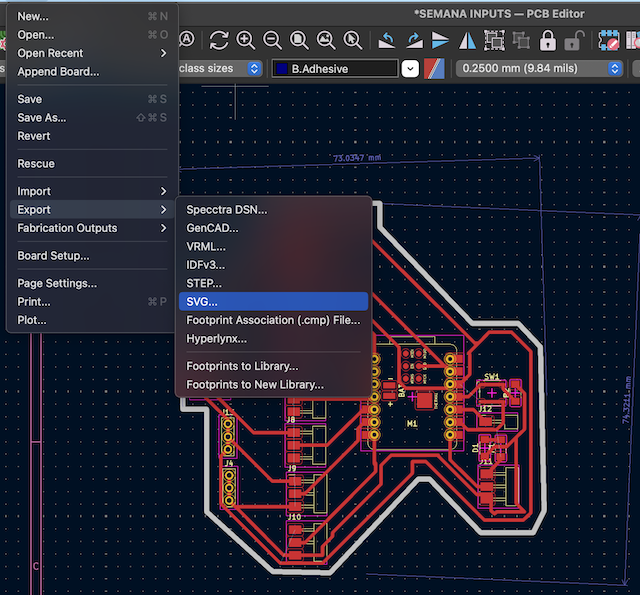
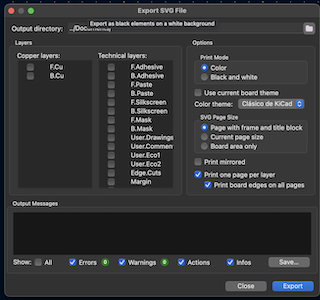
Once ready, I exported it in SVG format, from there, I select F.Cu as the layer where all the components are, this will be the etching of my board, and I export it.
Step 9
Then I do the same but in this case, I select the User drawing layer, which is the layer that has my plate cutting contour, and I export it as SVG.
ROLAND PCB
Step 1
First, open the "modsproject" page, where the interaction between the program and what we want to cut and engrave takes place to obtain the file we'll send to the SRM-20 cutter.
Step 2
Within the "Mods" program, right-click to access the menu, select "programs," then "open program," and choose the machine in this case, a "mill 2D PCB."

Step 3
Once in the program, navigate to the area where I would add my SVG file, in this case, the engraving of the PCB.
Step 4
With the file inside, I proceeded to adjust some parameters.
Step 5
The first parameter I checked was in the "set PCB default" section, ensuring that "mill traces" was set to 1/64.
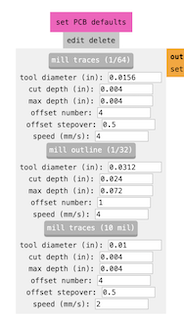
Step 6
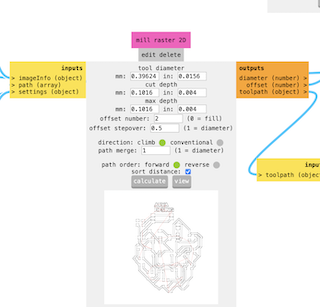
I then moved to the "mill raster 2D" section and changed the offset number to Select 2 offsets so that the part that engraves the plate can pass enough to engrave without any issues and without drilling it.
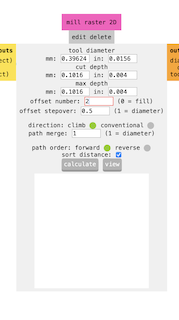
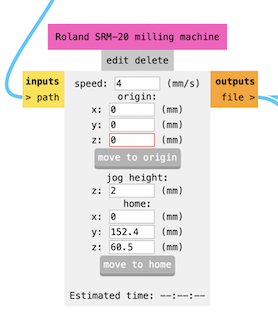
Step 7
Next, I went to "Roland SRM-20 milling machine" and set the X, Y, Z parameters to 0 to mark an origin point.
Step 8
I went to Inputs and Outputs, turning it on.
Step 9
Returning to the "mill raster 2D" section, I clicked the "calculate" button to generate the document for the machine and downloaded it in “.rml”format.
Step 10
I did the same but now with the cutting one and saved the format in ".rml".
Step 11
With both formats ready, I went to the Roland program.
Step 12
Once adjusted, I returned to the computer, opened the "VPanel for SMR-20" program, closed the machine door, and it calibrated automatically.
Step 13
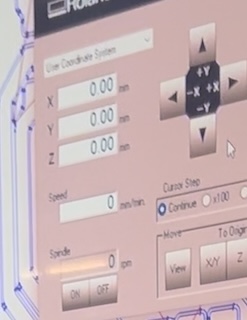
Using the program arrows, I positioned the engraving tip in the lower-left corner, marking X, Y parameters at 0 as the origin, and then set the Z point using a metric M2 key.

Step 14
I changed the cursor to "x100" in the program to lower the Z origin slowly, avoiding collision with the piece.
Step 15
To ensure the Z origin is well-defined, I started the program, waited for the necessary revolutions, and gradually lowered the Z point until it touched the material, marking Z as 0.
Step 16
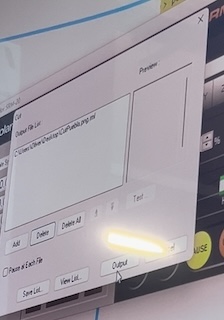
Moving to "Cut," I selected "add," added the previously saved file, and then selected "Output."

Step 17
The program automatically started engraving.
Step 18
After 18 minutes, the piece finished engraving.
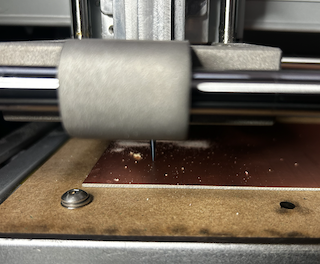
Step 19
I did the same process but now with the second contour document.


Step 20
I changed my drill to a cutting drill and recalibrated the Z position with the X, Y movement.
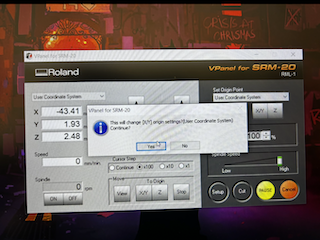
Step 21
Marked the Z origin again, went to "cut," deleted the previous file, added the new file, and clicked "output." The cutter started descending automatically and cut the board.
Step 22
Once finished, I opened the machine door and used a handheld vacuum to clean the dust, leaving the engraved and cut board free.

COMPONENT SOLDERING
To solder my components, I used a soldering iron and solder, although I also needed a heat gun from the soldering station.
Step 1
Based on my previously designed PCB, I positioned my components for soldering without errors.
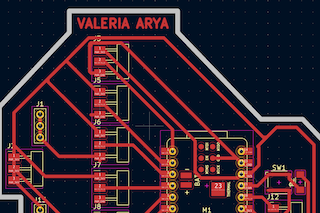
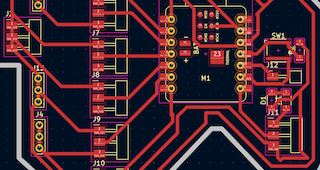
Step 2
I started with the microcontroller, working from the inside out.
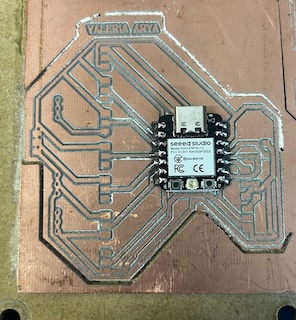
Step 3
And there, the soldering was completed.
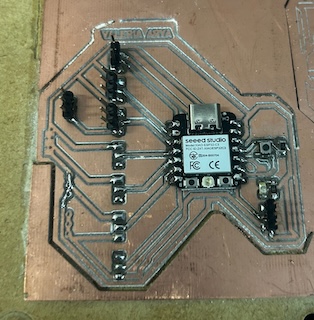
BOARD PROGRAMMING
To program my board with my XIAO ESP32 microcontroller, I have made the same process of my first electronic desing.
Step 1
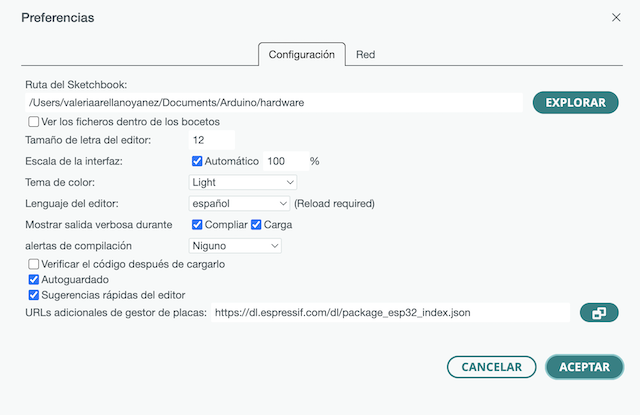
I have used ARDUINO IDE for programming,First, you need to download the ESP32 library. In the advanced configuration, you paste the link with the ESP32 library so that it can be searched and downloaded in the IDE library afterwards.
https://dl.espressif.com/dl/package_esp32_index.json
Step 2
For this assignment, I decided to use an ultrasonic distance sensor as input. I've always wanted to learn how to program one.

Step 3
This sensor needs to be connected to ground, voltage, and two digital inputs: one for TRIG and one for ECHO.

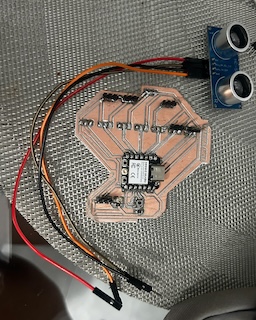
Step 4
When I made the connection, I went back to the Arduino interface, where I wrote a fairly simple code to test the sensor and its functionality in centimeters, and it worked fine.
#include <NewPing.h>
#define TRIGGER_PIN D0 // Pin de la Xiao ESP32 conectado al pin Trigger del sensor
#define ECHO_PIN D7 // Pin de la Xiao ESP32 conectado al pin Echo del sensor
#define MAX_DISTANCE 200 // Distancia máxima a medir (en centímetros)
NewPing sonar(TRIGGER_PIN, ECHO_PIN, MAX_DISTANCE); // Crear un objeto NewPing
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Inicializar la comunicación serial
}
void loop() {
delay(2000); // Esperar dos segundos entre cada medición
unsigned int distancia = sonar.ping_cm(); // Realizar una medición y obtener la distancia en centímetros
Serial.print("Distance: ");
Serial.print(distancia);
Serial.println(" cm");
}
