Get to know me

Hey, I'm Alejandro Alvarez, a 24-year-old Biomedical Engineer who's all about diving into the world of biomedical informatics, data sciences, and disability studies. I thrive on teamwork and hands-on experience, always ready to tackle whatever challenges come my way.
When I'm not knee-deep in engineering, you'll catch me leveling up in video games, strategizing over board games, or hitting the trails on my mountain bike (still getting the hang of it, but loving the adrenaline rush!). And let's not forget my childhood passion: Legos! They kickstarted my journey into building and creating, and I've been hooked ever since.
I'm passionate about mentoring aspiring engineers, especially when it comes to planning and executing cool projects. Prosthetics are a huge interest of mine, and I'm stoked to soak up knowledge like a sponge at the FAB Academy 2024. My journey will be fueled mostly with worrying amounts of coffee so bring on the learning and the maker vibes!
Academic PROJECT: USE OF BACTERIAL CELLULOSE BASED WOUND DRESSING FOR DELIVERY OF AMOXICILLIN-CLAVULANIC ACID IN PEDIATRIC BURN INJURIES
The project has a theoretical and methodological basis for the development of in vitro tests of the dressing for the release of Amoxicillin-Clavulanic Acid. In the Fall 2022 we will start researching the relationship between the concentration of the drug Amoxicillin- Clavulanic Acid and the inhibition of Staphylococcus spp and Staphylococcus aureus bacteria over a 24-hour period. For this, we aim to develop a program using MATLAB software to perform image-processing and to be able to observe the interaction of the antibiotic released by the cellulose over a period of 24 hours. With this code, we aim to obtain a mathematical model to stablish the optimum antibiotic concentration for the bacterial cellulose-based dressing.
The project has been developed in the facilities of the Institute for Technological Development and Innovation (IDIT) of the Universidad Iberoamericana Puebla, where the microbiology and chemistry laboratories where the research labs for the project are located. Bacterial cellulose is an easily obtained biocompatible material, using low-cost elements such as tea, sugar, acetic acid and the inoculum of our bacteria Acetobacter Xylinum. Once the culture medium has been made under sterile conditions and has an adequate maintenance, bacterial cellulose can be produced continuously and in wide extensions according to the research needs, which could benefit us in the future for the implementation of dressings according to the dimensions required by the patient.
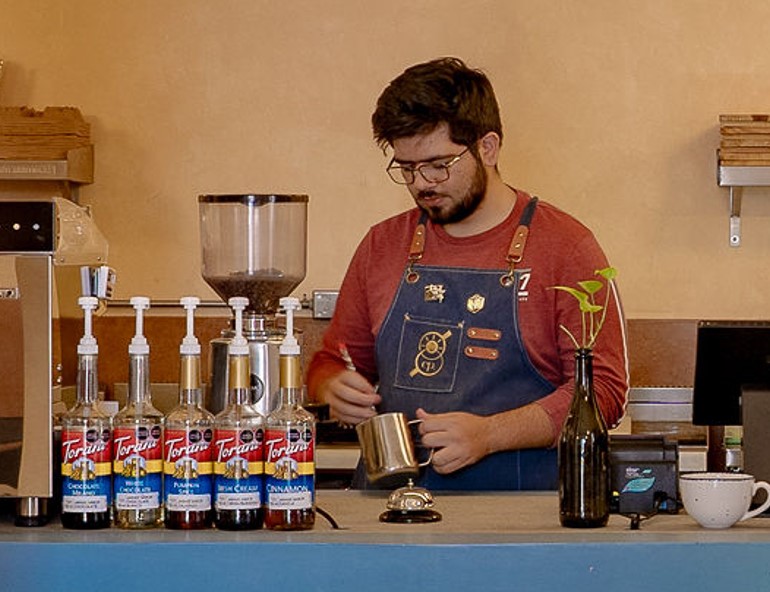
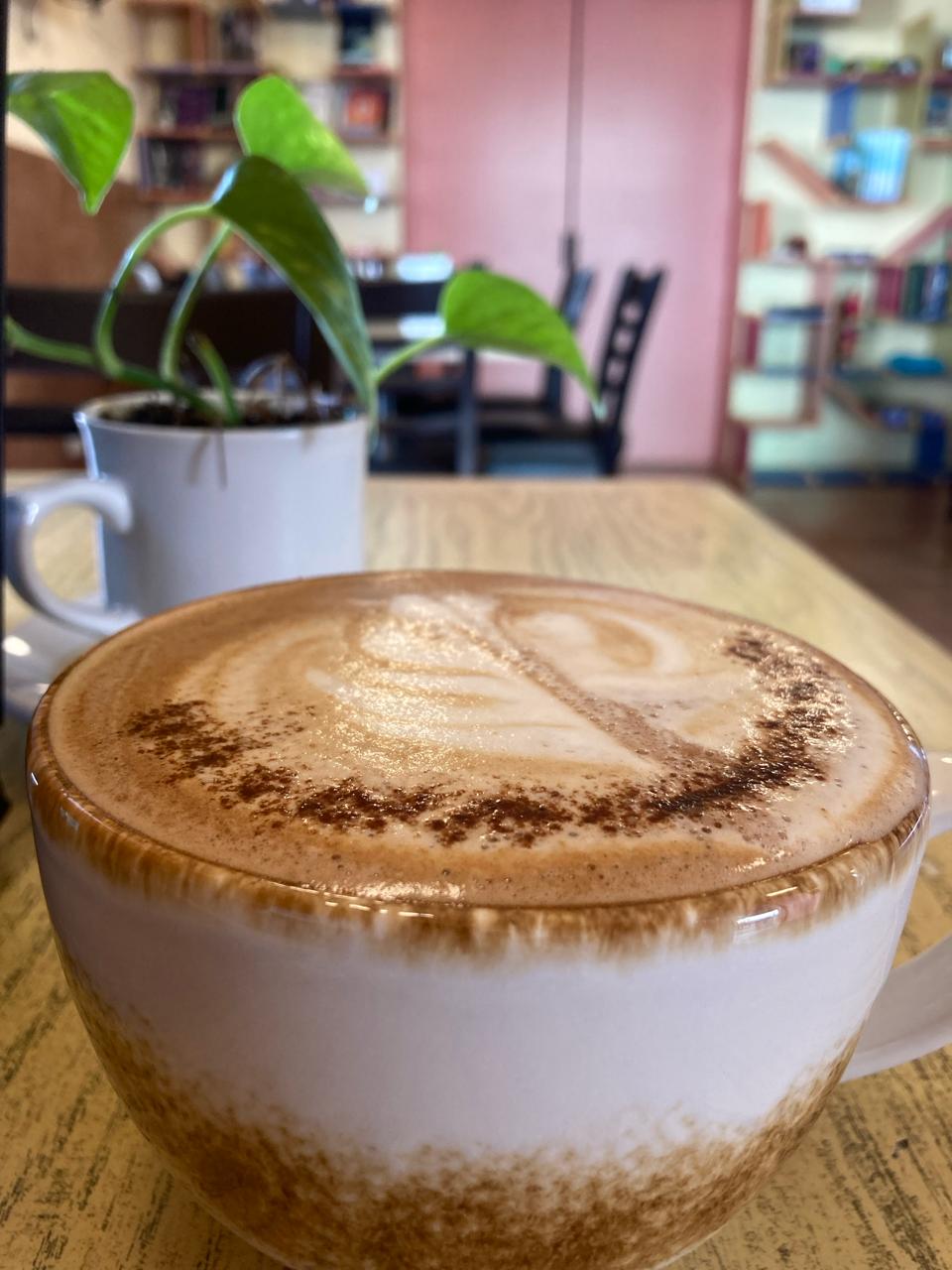
personal PROJECT: Epigrafe Cafeteria
At beginings of 2023 I started my own cafetria "Epigrafe" with a friend, I learned a lot of Management, providers and of course, coffee.




Alejandro Alvarez Flores - FAB Academy
Navigation
Contact Info
Location
 Universidad Iberoamericana Puebla
Universidad Iberoamericana Puebla