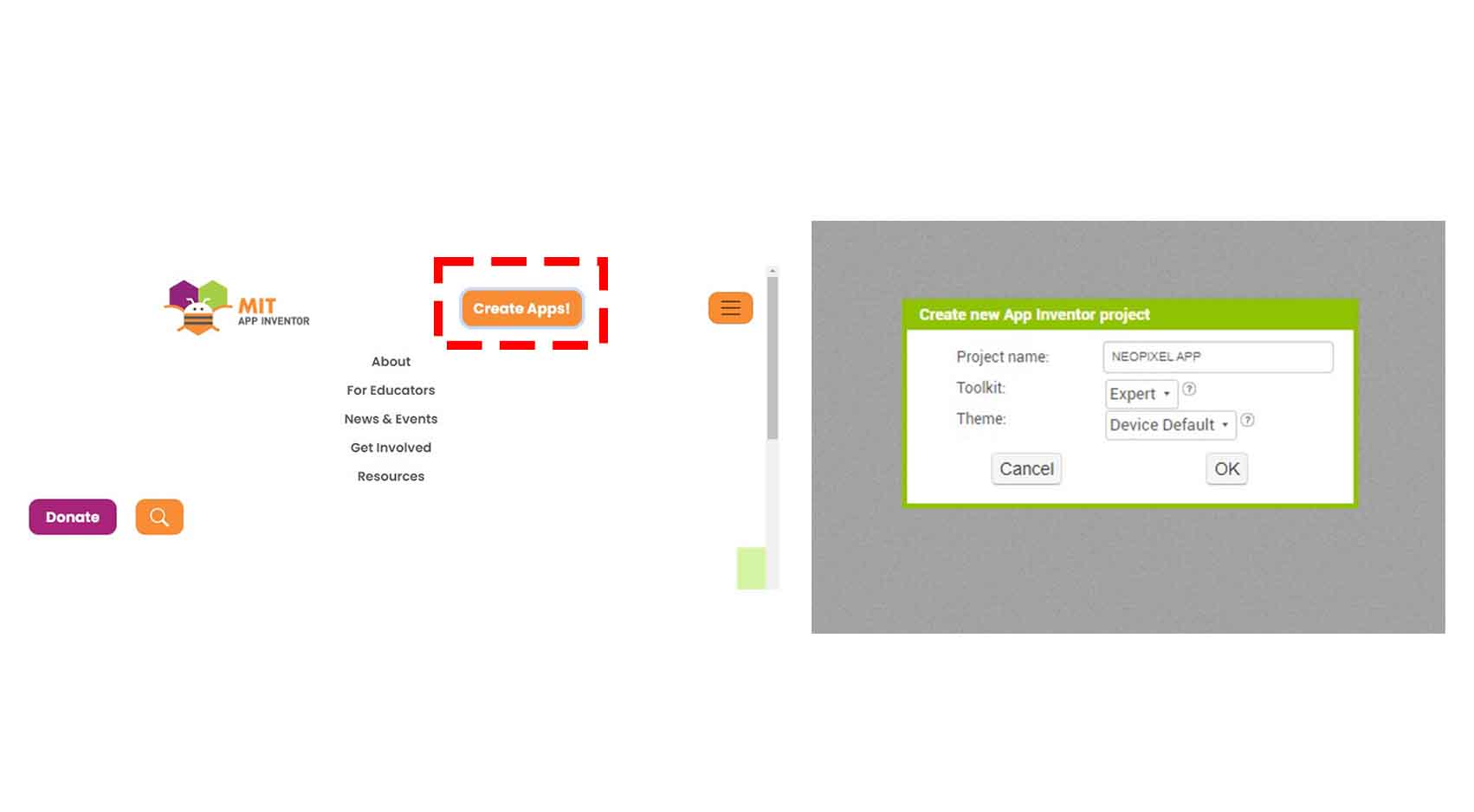
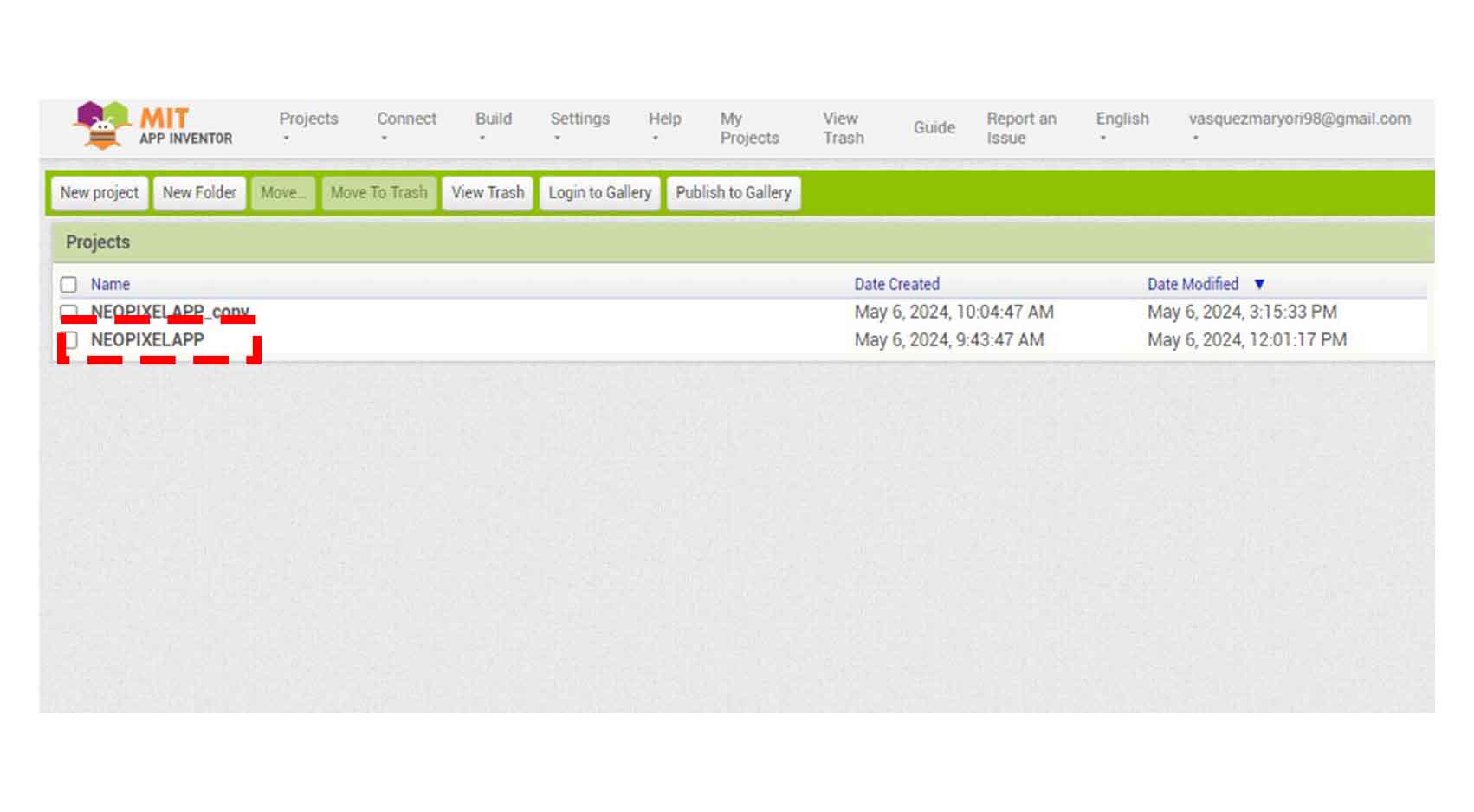
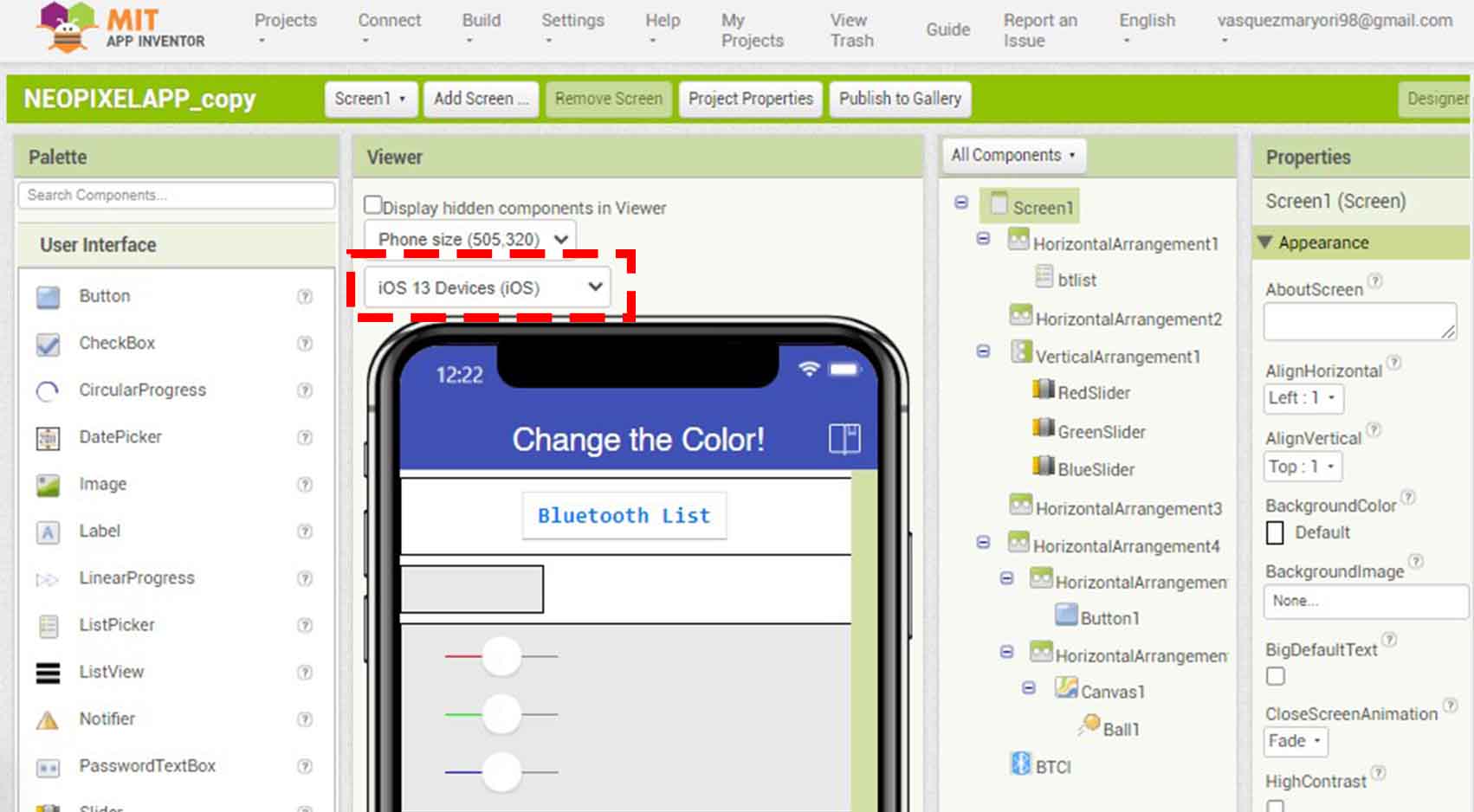
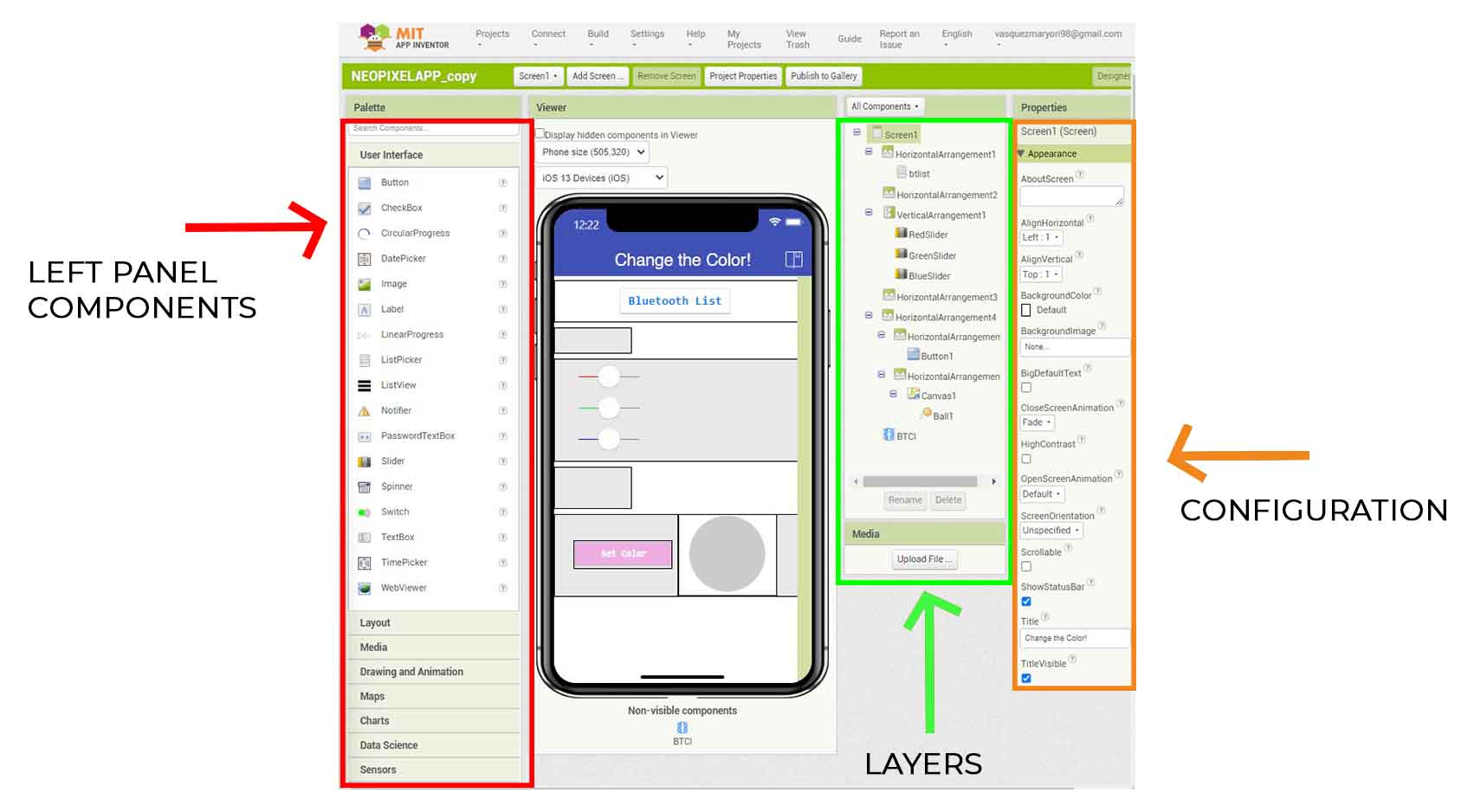
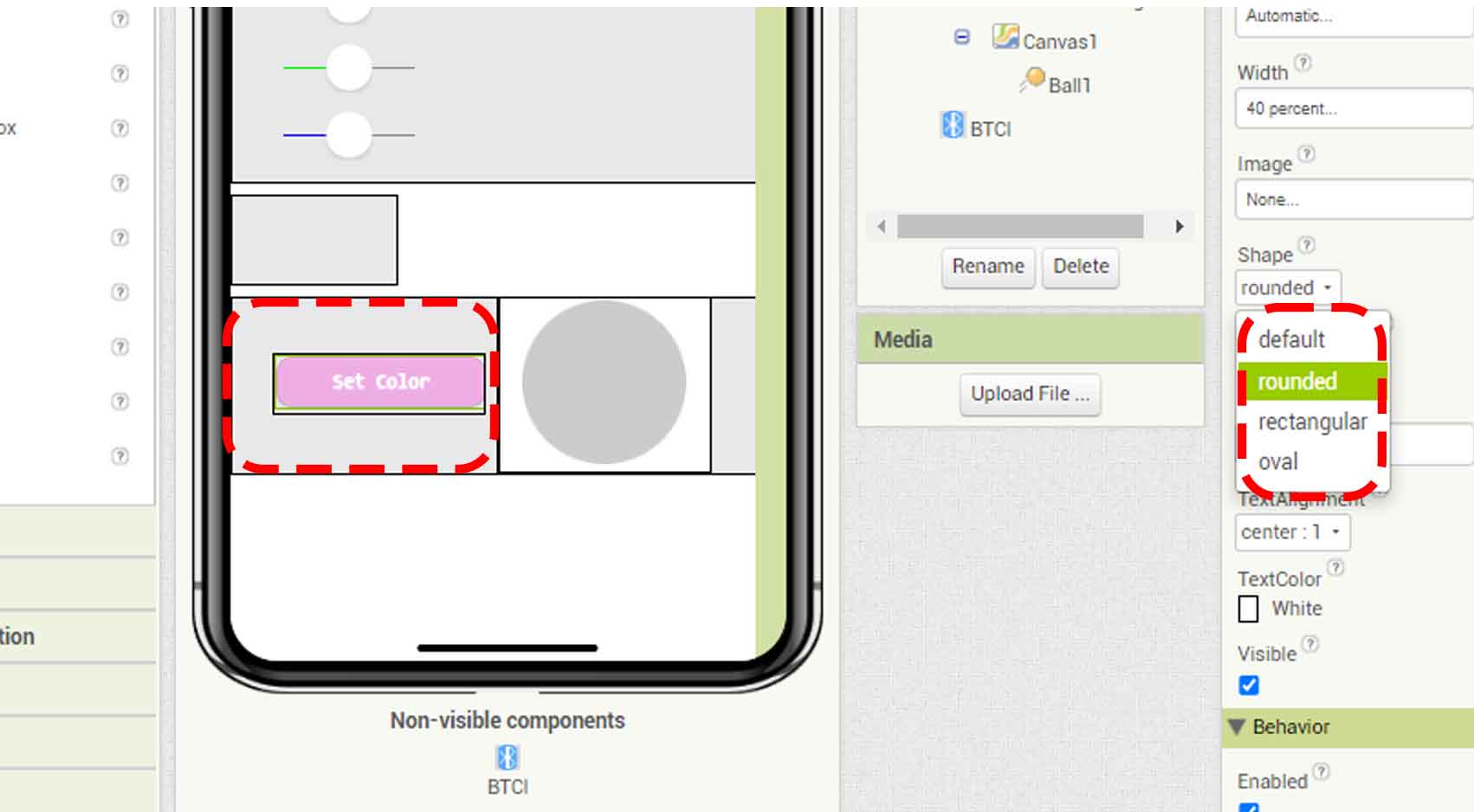
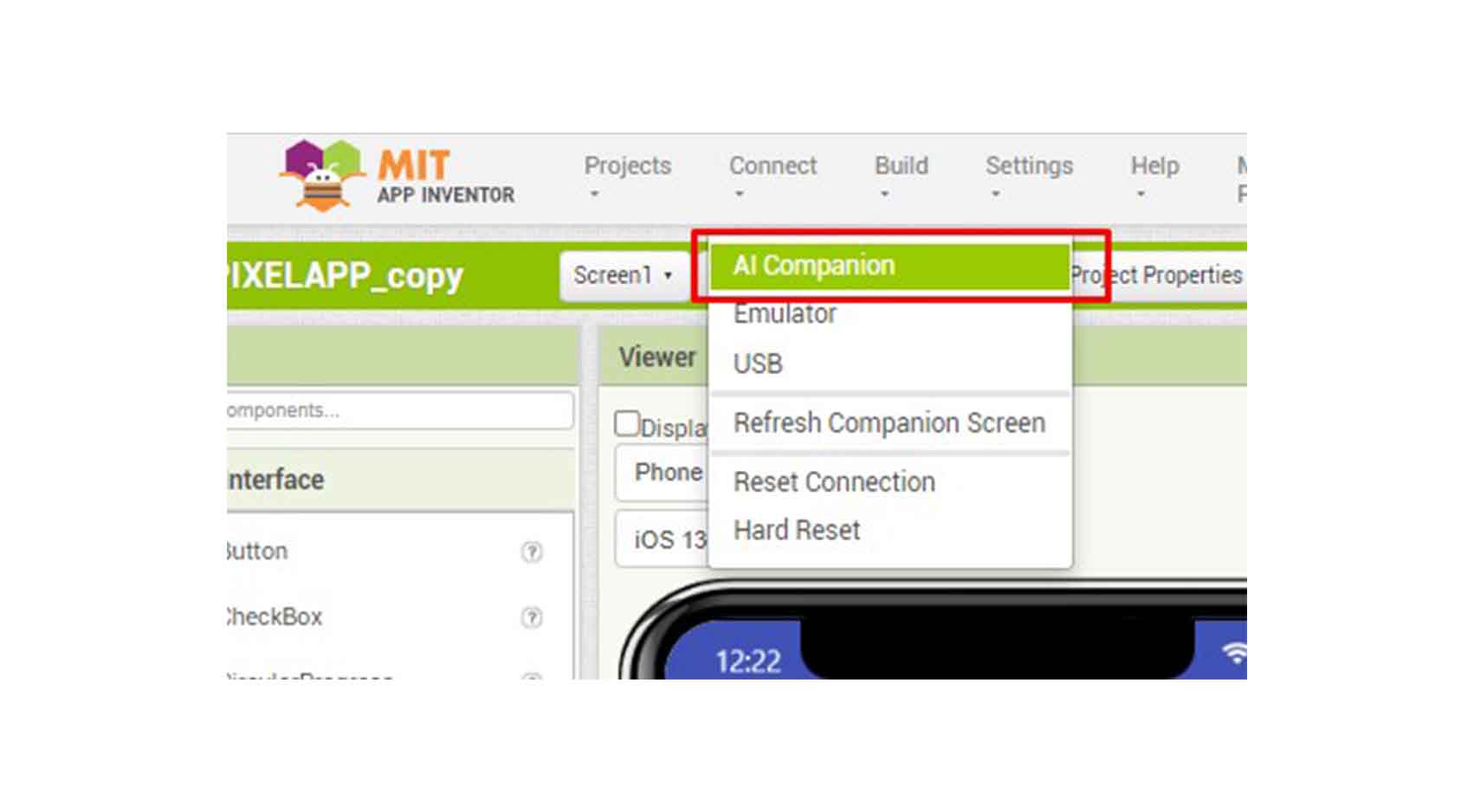
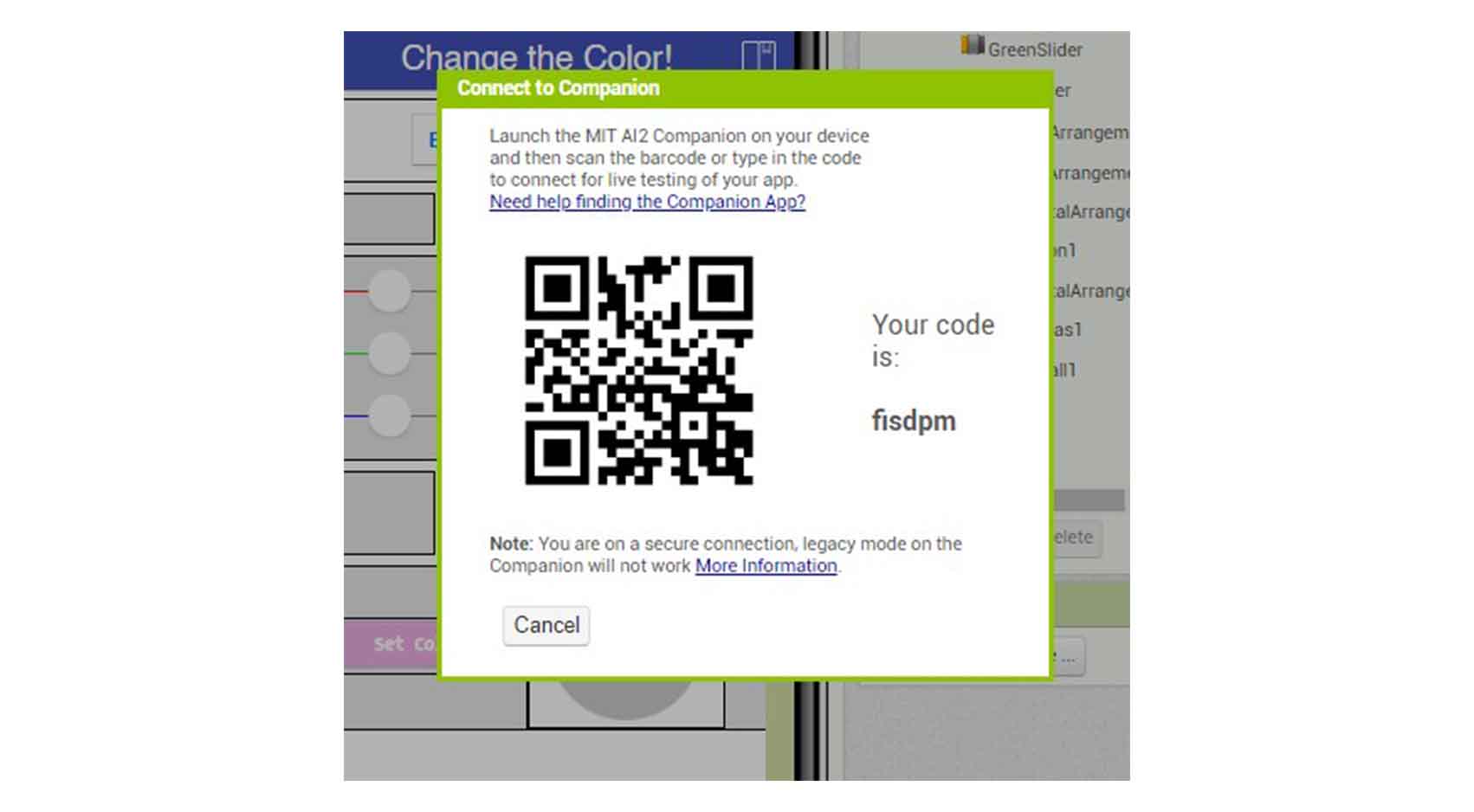
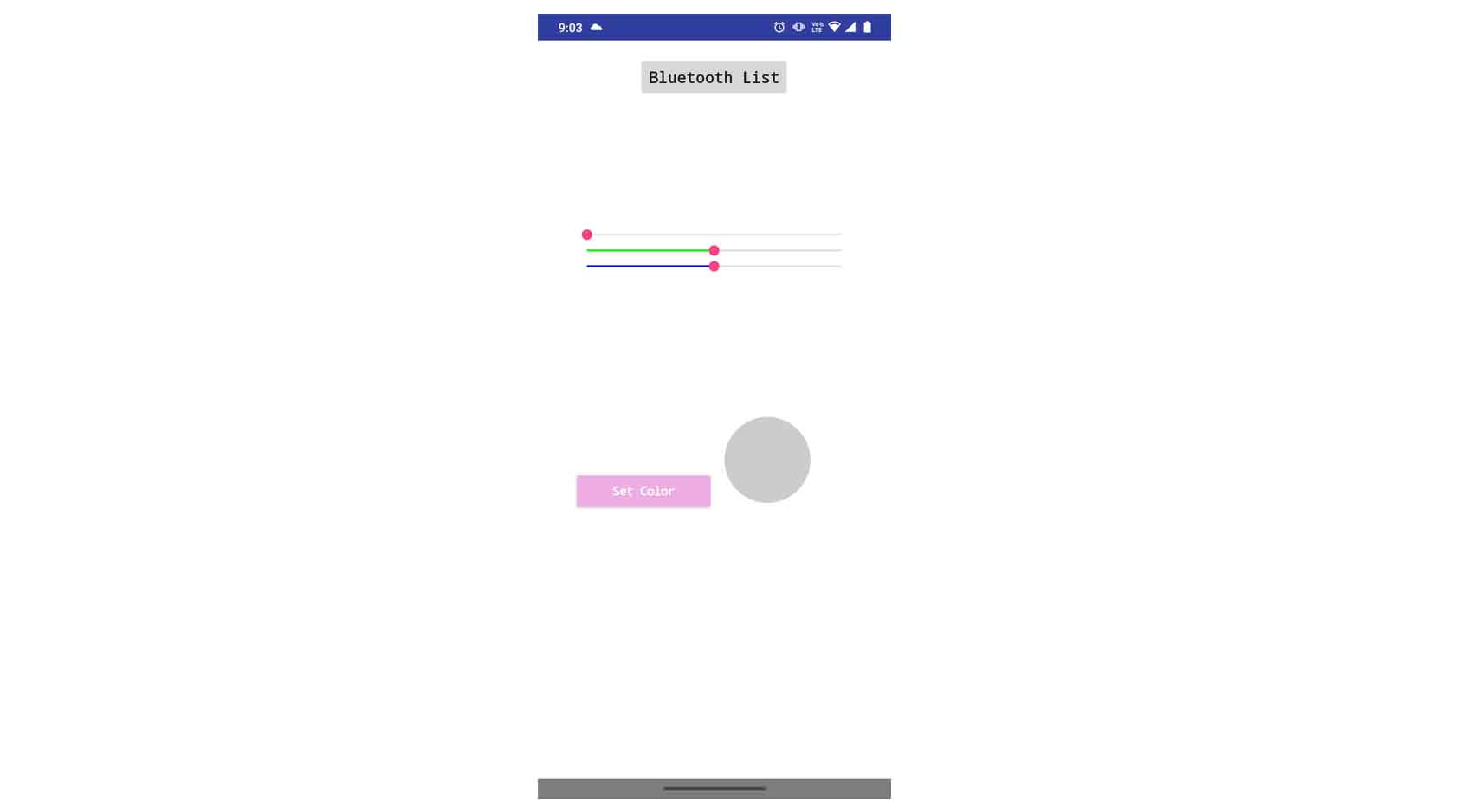
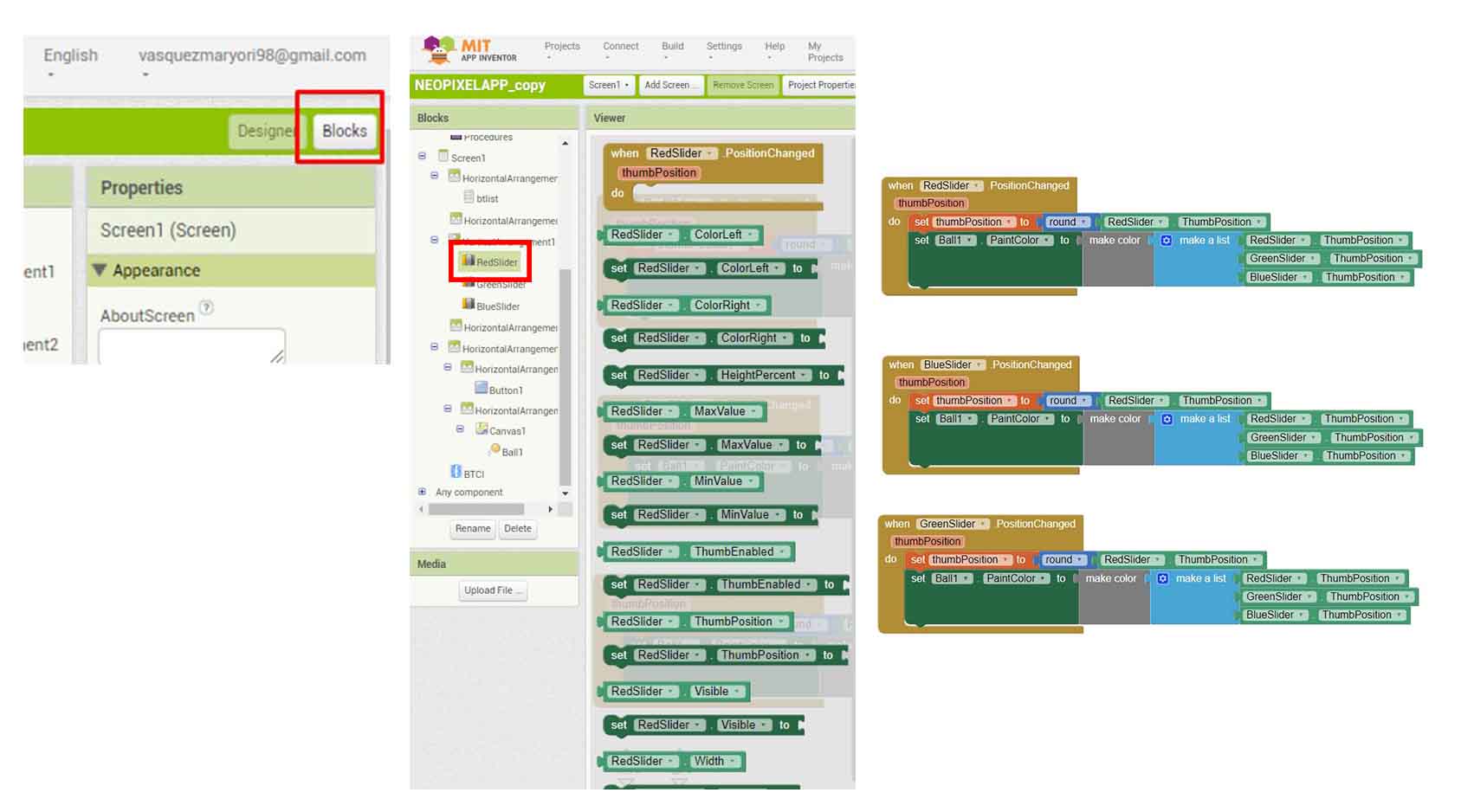
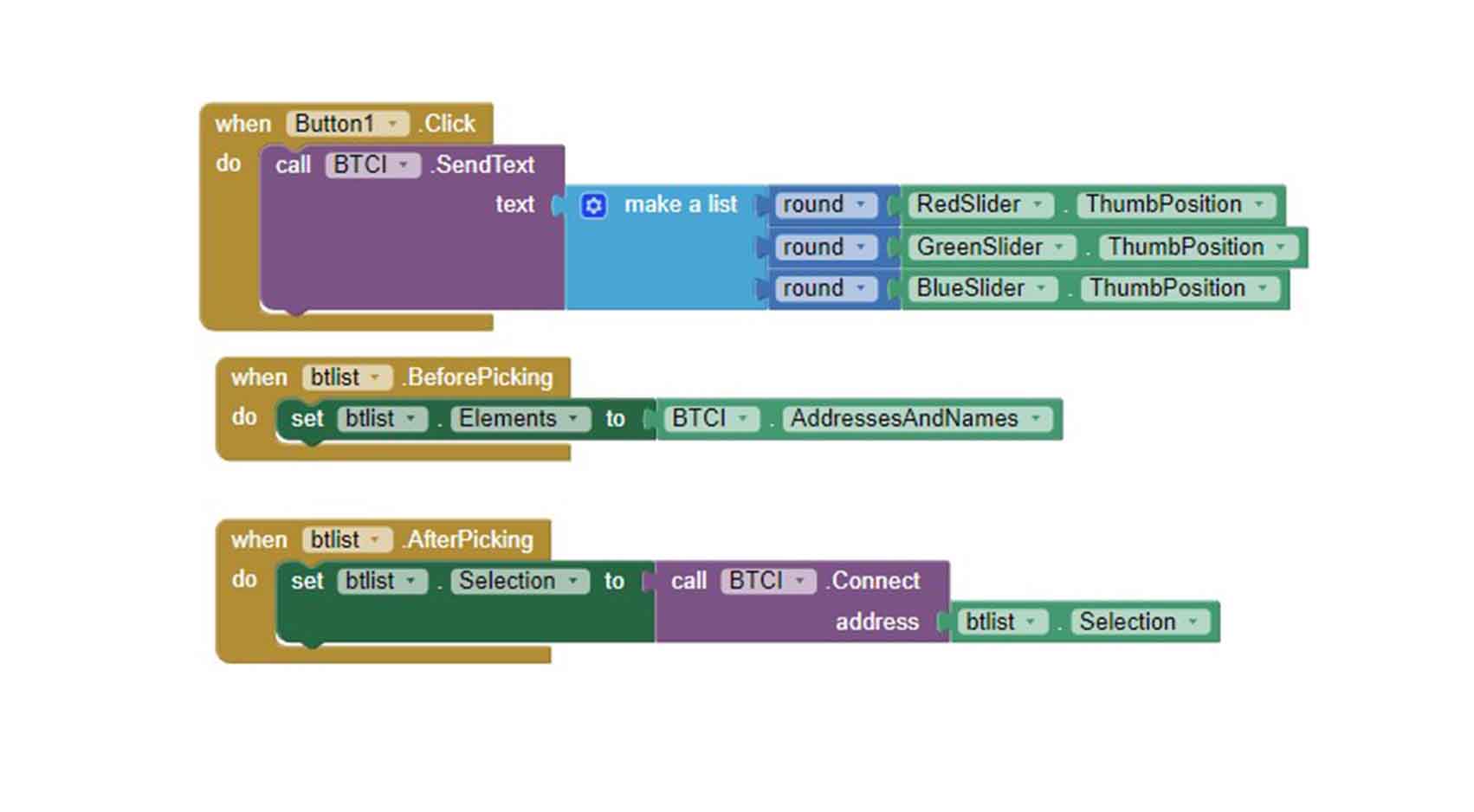
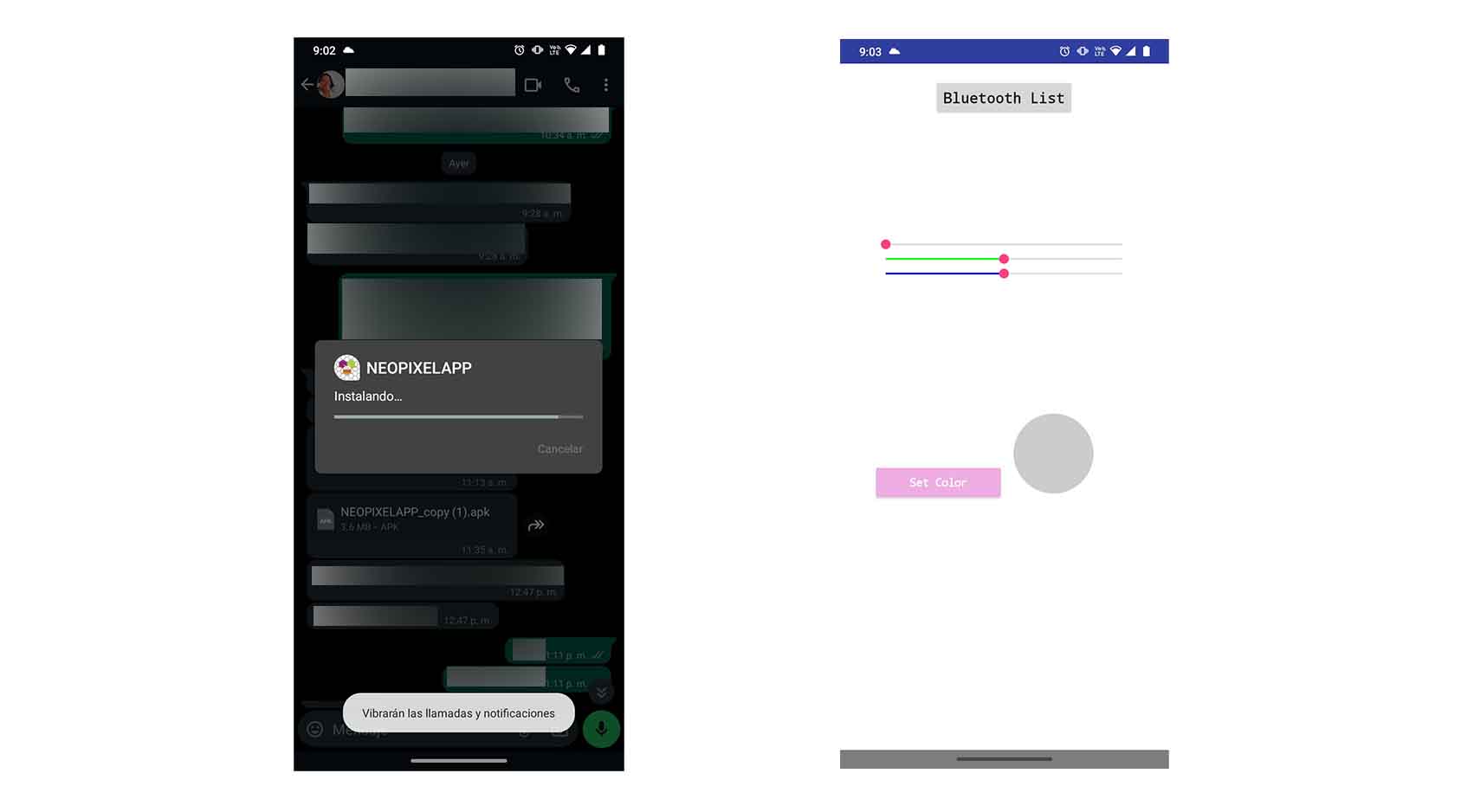
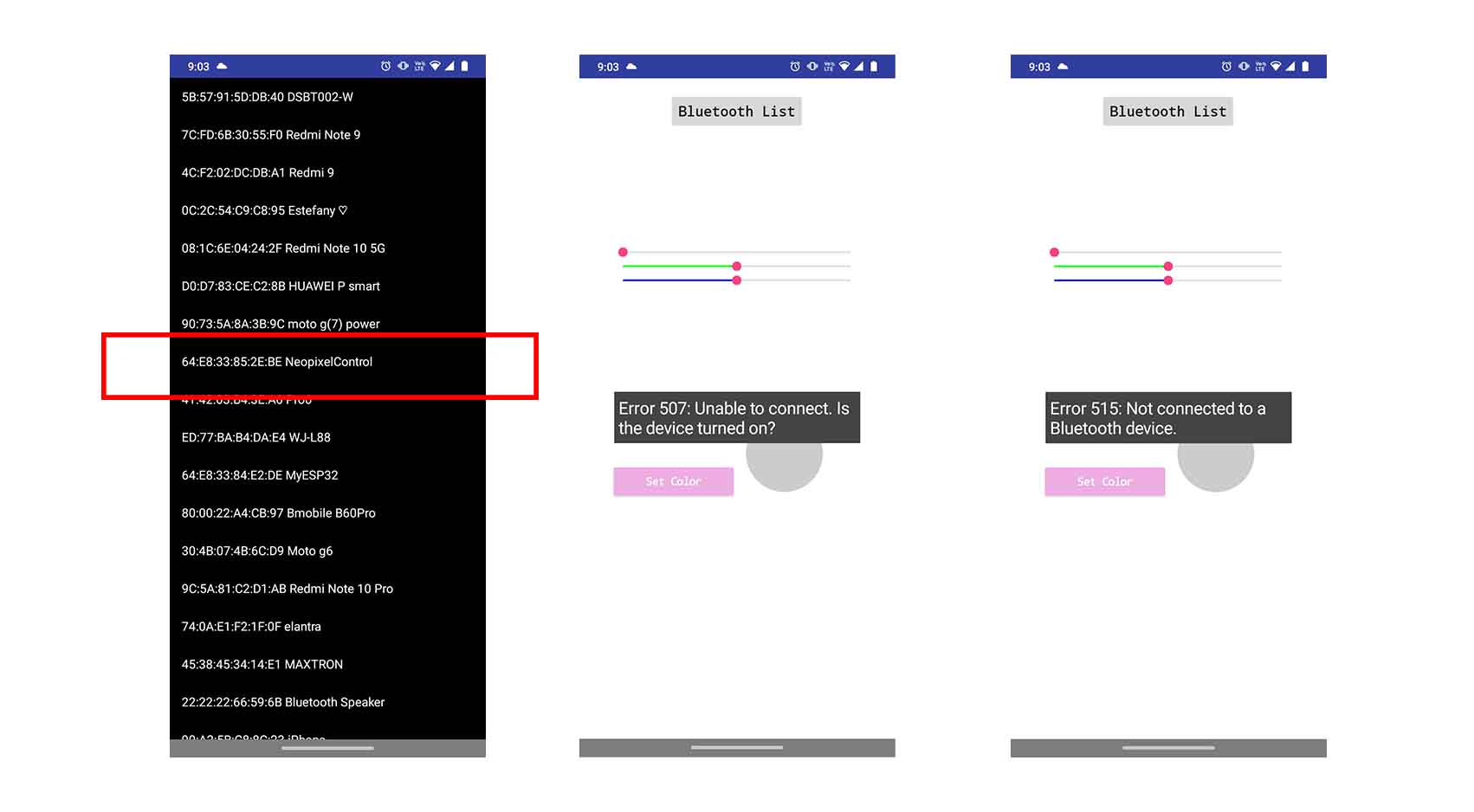
COMPARING MANY TOOL OPTIONS
HTML CODE
The purpose of using this language is to light an LED on my Xiao ESP32-C3 board using HTML and Visual Studio Code, for this I need to write a program in C/C++ language using the ESP-IDF development environment, which is compatible with Visual Studio Code. Here I guide you step by step:
Prerequisites
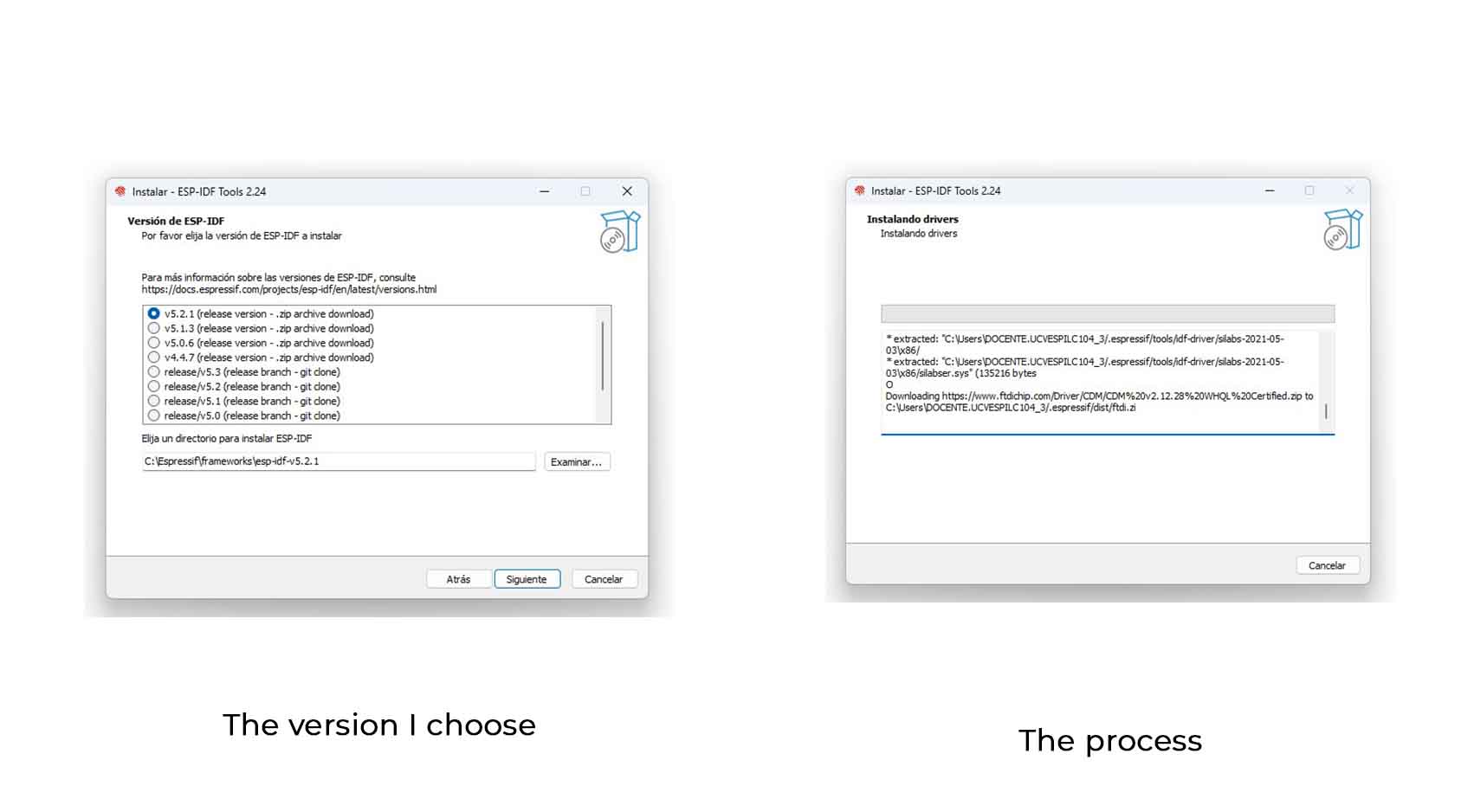
1. ESP-IDF Installation and Tools
Make sure you have installed ESP-IDF and the necessary development tools by following the official instructions.
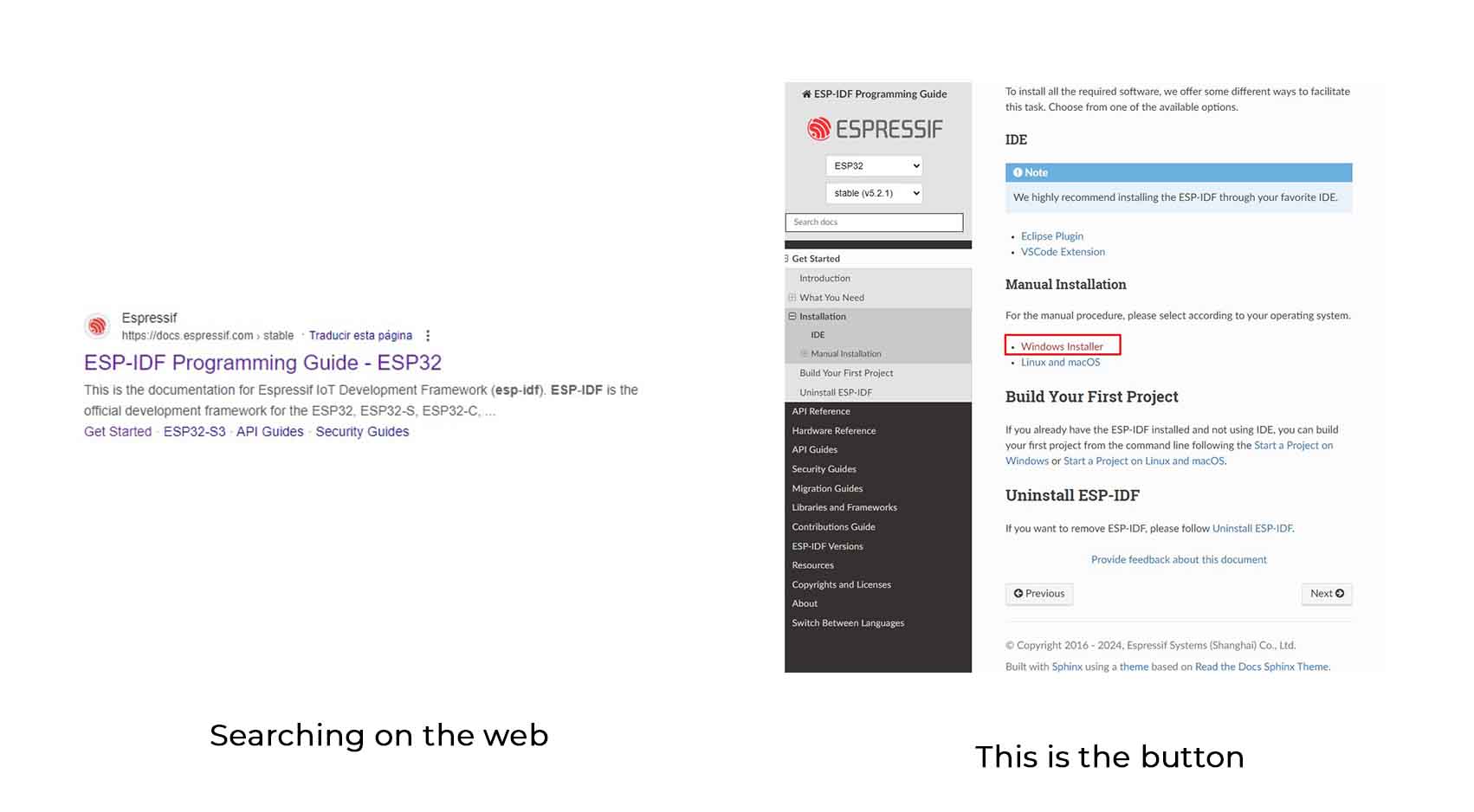
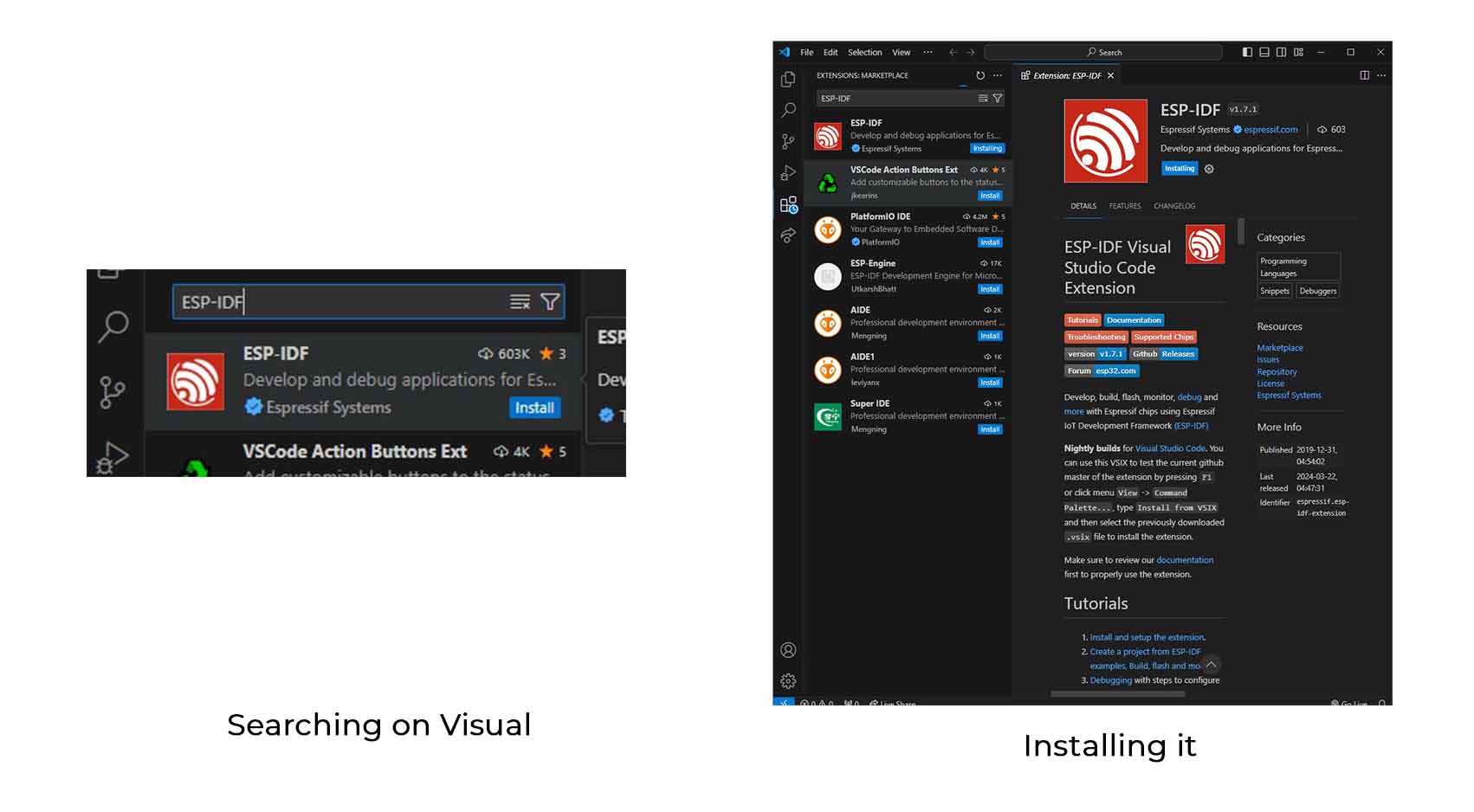
2. Visual Studio Code Configuration
Install the ESP-IDF extension in Visual Studio Code to configure your development environment.
Project Creation
1. Initialising the Project
Open a terminal in Visual Studio Code and start a new ESP-IDF project with the command:
idf.py create-project esp32c3-led
Next, navigate to the project directory
cd esp32c3-led
2. Code Configuration
Open the main/main.cpp file in your project and write the following code:
#include "freertos/FreeRTOS.h"
#include "freertos/task.h"
#include "driver/gpio.h"
// Definir el número de pin del LED
#define LED_PIN GPIO_NUM_3
void app_main() {
// Configurar el pin GPIO para el LED como salida
gpio_pad_select_gpio(LED_PIN);
gpio_set_direction(LED_PIN, GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT);
while (1) {
// Encender el LED
gpio_set_level(LED_PIN, 1);
vTaskDelay(1000 / portTICK_PERIOD_MS); // Esperar 1 segundo
// Apagar el LED
gpio_set_level(LED_PIN, 0);
vTaskDelay(1000 / portTICK_PERIOD_MS); // Esperar 1 segundo
}
}
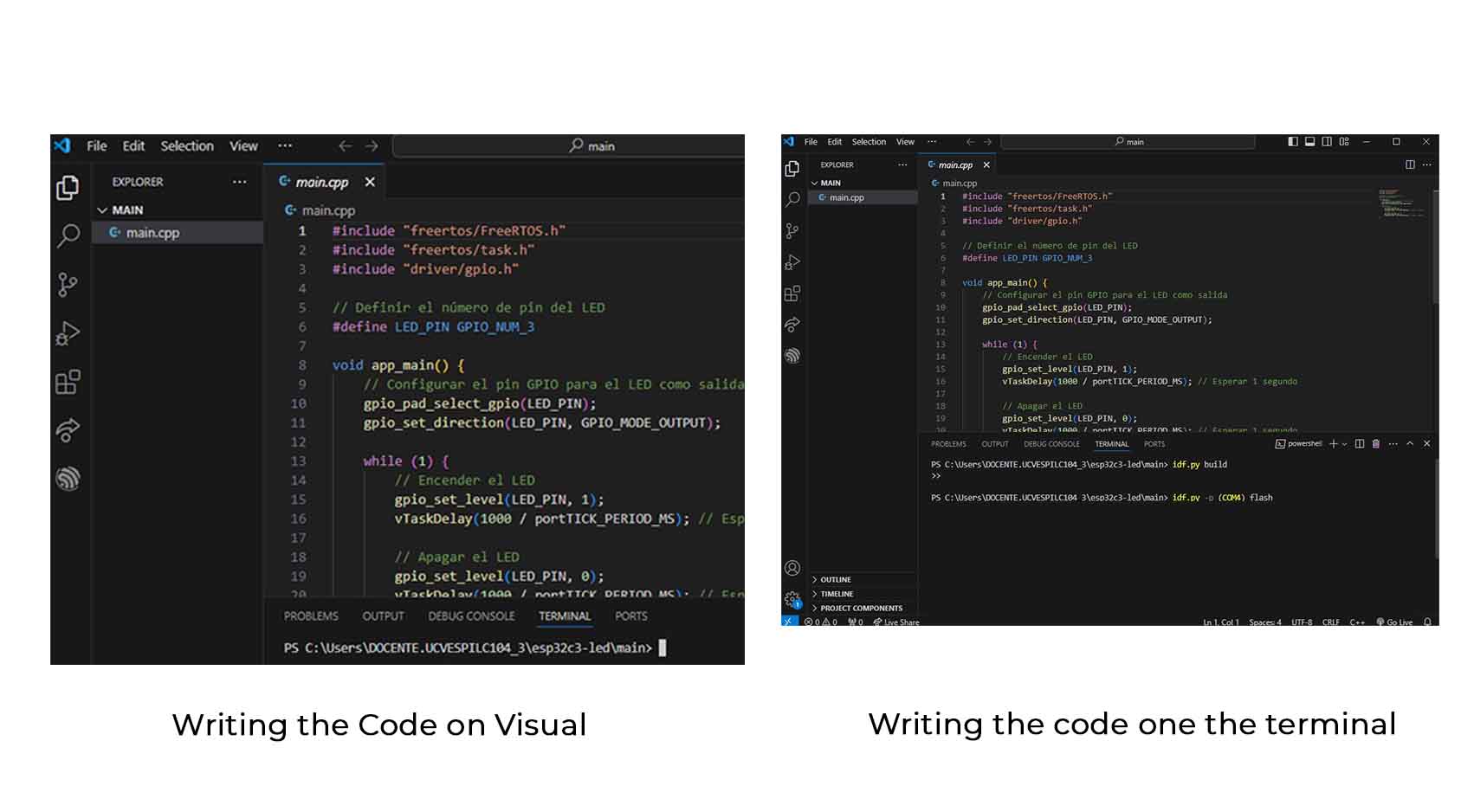
Compiling and Loading the Program
1. Compilation
In the Visual Studio Code terminal, run the command to compile the project:
idf.py build
I searched for the error with AI tools, but they told me that it might be an ESP-IDF installation error, so I uninstalled it and I still got the error.
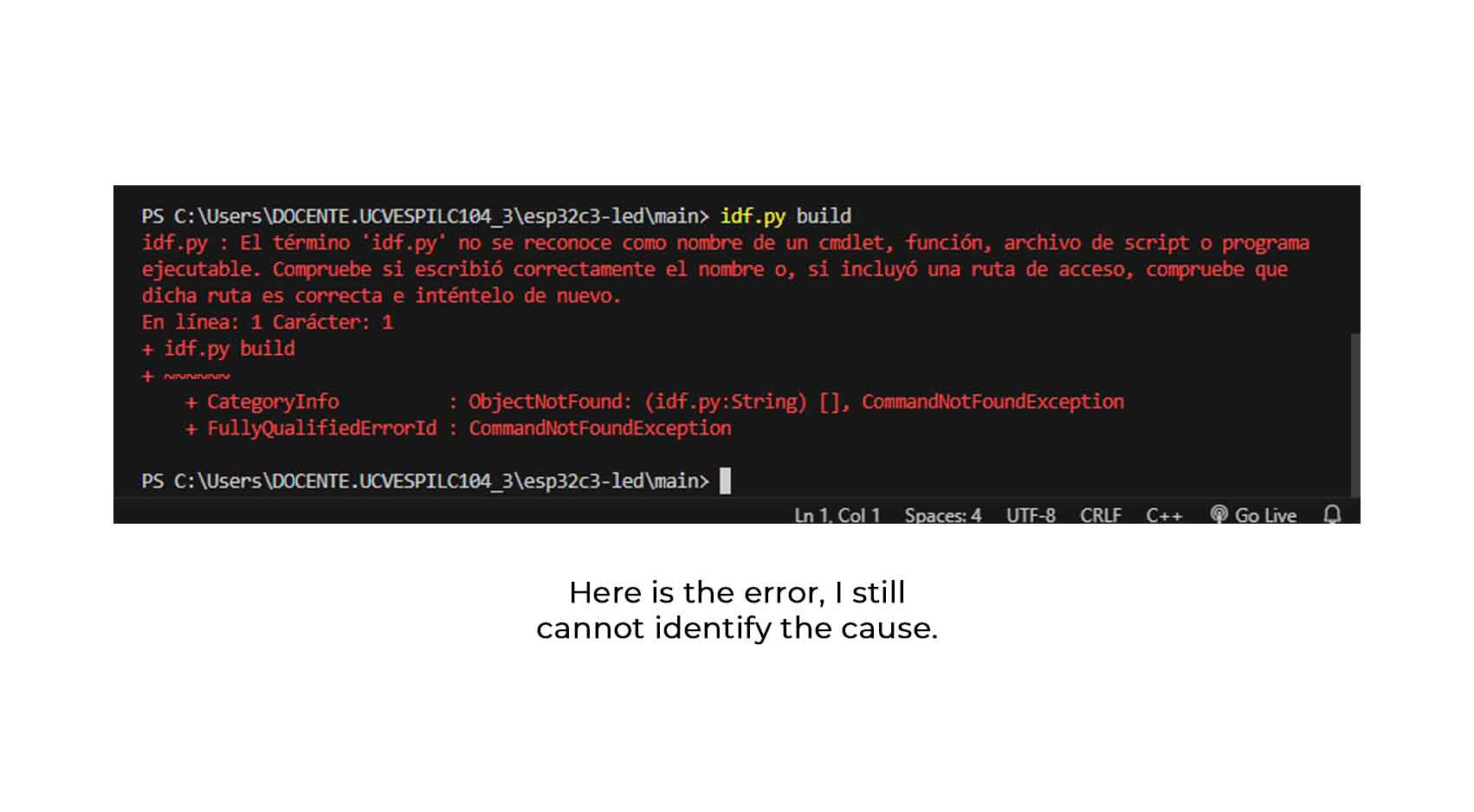
From here I leave you the next steps, I tried to verify that maybe the error was because I didn't have Python installed, I leave you my screenshots of the installation.
2. Loading the Programme
Connect your Xiao ESP32-C3 board to your computer via USB.
Upload the program to the board with the command:
idf.py -p (puerto_USB) flash
Replace (USB_port) with the serial port where your board is connected (for example, /dev/ttyUSB0 on Linux or COM1 on Windows).
Verification
Once the program has been successfully loaded, the LED connected to pin D3 on your board should start flashing, turning on and off every second.
I didn't get any results! but I will continue my search to identify the error from here, I won't give up!