Invention, IPR and Business Models:
In this Seventeenth week of Fab Academy, we had to explore about Invention, IPR and Business Models.

Objective:
Individual Assignment:
Learning Outcomes:
Checklist:
Opening Quotes:
- Necessity is the mother of invention
Inventions:
Generally speaking, an invention is a new product or process that solves a technical problem. This is different from a discovery, which is something that already existed but had not been found.
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition or process. The invention process is a process within an overall engineering and product development process. It may be an improvement upon a machine or product or a new process for creating an object or a result. An invention that achieves a completely unique function or result may be a radical breakthrough. Such works are novel and not obvious to others skilled in the same field. An inventor may be taking a big step toward success or failure.Some inventions can be patented. The system of patents was established to encourage inventors by granting limited-term, limited monopoly on inventions determined to be sufficiently novel, non-obvious, and useful. A patent legally protects the intellectual property rights of the inventor and legally recognizes that a claimed invention is actually an invention. The rules and requirements for patenting an invention vary by country and the process of obtaining a patent is often expensive.(Wikipedia)
Types of Invention:
Inventions are of three kinds: scientific-technological (including medicine), sociopolitical (including economics and law), and humanistic, or cultural.
Scientific-technological inventions include railroads, aviation, vaccination, hybridization, antibiotics, astronautics, holography, the atomic bomb, computing, the Internet, and the smartphone.
Sociopolitical inventions comprise new laws, institutions, and procedures that change modes of social behavior and establish new forms of human interaction and organization. Examples include the British Parliament, the US Constitution, the Manchester (UK) General Union of Trades, the Boy Scouts, the Red Cross, the Olympic Games, the United Nations, the European Union, and the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, as well as movements such as socialism, Zionism, suffragism, feminism, and animal-rights veganism.
Humanistic inventions encompass culture in its entirety and are as transformative and important as any in the sciences, although people tend to take them for granted. In the domain of linguistics, for example, many alphabets have been inventions, as are all neologisms (Shakespeare invented about 1,700 words).(Source-Wikipedia)
Intellectual Property:
Intellectual property (IP) is a term referring to a brand, invention, design or other kind of creation, which a person or business has legal rights over. Almost all businesses own some form of IP, which could be a business asset.
Patent, copyright and trademark are all types of intellectual property rights that provide the creator an exclusive right over the use of his/her creation of mind for a limited amount of time. Entrepreneurs who are seeking to register intellectual property must know the differences between the three and obtain the right registrations to protect his/her intellectual property.
What is Patent?
Patent is an exclusive right for an invention provided by the law for a limited time to the Patentee. By patenting an invention, the patentee is able to control the making, using, selling or importing of the patented product or process for producing that product without his/her consent. An invention relating either to a product or process that is new, involving inventive step and capable of industrial application can be patented in India.
What is Copyright?
Copyright is a right given by the law to creators of literary, dramatic, musical and artistic works and producers of cinematograph films and sound recordings. Copyright does not protect brands or names, short word combinations, slogans, short phrases, methods, plots or factual information. Copyright also does not protect ideas or concepts. Therefore, copyright is mainly used to protect the creativity of writers, artists, designers, dramatists, musicians, architects and producers of sound recordings, cinematograph films and computer software.
What is Trademark?
Trademark is a visual symbol which may be a word signature, name, device, label, numerals or combination of colours used by one Enterprise on goods or services or other articles of commerce to distinguish it from other similar goods or services originating from a different undertaking. Hence, trademarks are mostly used to protect brand names, business names, slogans and more.
Trade secrets:
Trade secrets are a type of intellectual property that comprise formulas, practices, processes, designs, instruments, patterns, or compilations of information that have inherent economic value because they are not generally known or readily ascertainable by others, and which the owner takes reasonable measures to keep secret. In some jurisdictions, such secrets are referred to as confidential information.
Right of publicity:
The right of publicity , sometimes referred to as personality rights, is the right of an individual to control the commercial use of one's identity, such as name, image, likeness, or other unequivocal identifiers. It is generally considered a property right as opposed to a personal right, and as such, the validity of the right of publicity can survive the death of the individual (to varying degrees depending on the jurisdiction).
DIFFRENT COPYRIGHT LICENSES:
- Creative Commons (CC) license
- GNU General Public License
- BSD license
- MIT - Open Source license
- Apache License
Creative Commons (CC) license:
 A Creative Commons (CC) license is one of several public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted "work". A CC license is used when an author wants to give other people the right to share, use, and build upon a work that the author has created. CC provides an author flexibility (for example, they might choose to allow only non-commercial uses of a given work) and protects the people who use or redistribute an author's work from concerns of copyright infringement as long as they abide by the conditions that are specified in the license by which the author distributes the work.
A Creative Commons (CC) license is one of several public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted "work". A CC license is used when an author wants to give other people the right to share, use, and build upon a work that the author has created. CC provides an author flexibility (for example, they might choose to allow only non-commercial uses of a given work) and protects the people who use or redistribute an author's work from concerns of copyright infringement as long as they abide by the conditions that are specified in the license by which the author distributes the work.
GNU General Public License:
 The GNU General Public License (GNU GPL or simply GPL) is a series of widely used free software licenses that guarantee end users the freedom to run, study, share, and modify the software. The licenses were originally written by Richard Stallman, founder of the Free Software Foundation (FSF), for the GNU Project, and grant the recipients of a computer program the rights of the Free Software Definition. The GPL series are all copyleft licenses, which means that any derivative work must be distributed under the same or equivalent license terms. This is in distinction to permissive software licenses, of which the BSD licenses and the MIT License are widely used, less restrictive examples. GPL was the first copyleft license for general use.
The GNU General Public License (GNU GPL or simply GPL) is a series of widely used free software licenses that guarantee end users the freedom to run, study, share, and modify the software. The licenses were originally written by Richard Stallman, founder of the Free Software Foundation (FSF), for the GNU Project, and grant the recipients of a computer program the rights of the Free Software Definition. The GPL series are all copyleft licenses, which means that any derivative work must be distributed under the same or equivalent license terms. This is in distinction to permissive software licenses, of which the BSD licenses and the MIT License are widely used, less restrictive examples. GPL was the first copyleft license for general use.
BSD license:
 BSD licenses are a family of permissive free software licenses, imposing minimal restrictions on the use and distribution of covered software. This is in contrast to copyleft licenses, which have share-alike requirements. The original BSD license was used for its namesake, the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), a Unix-like operating system. The original version has since been revised, and its descendants are referred to as modified BSD licenses.BSD is both a license and a class of license (generally referred to as BSD-like). The modified BSD license (in wide use today) is very similar to the license originally used for the BSD version of Unix. The BSD license is a simple license that merely requires that all code retain the BSD license notice if redistributed in source code format, or reproduce the notice if redistributed in binary format. The BSD license (unlike some other licenses e.g. GPL) does not require that source code be distributed at all.
BSD licenses are a family of permissive free software licenses, imposing minimal restrictions on the use and distribution of covered software. This is in contrast to copyleft licenses, which have share-alike requirements. The original BSD license was used for its namesake, the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), a Unix-like operating system. The original version has since been revised, and its descendants are referred to as modified BSD licenses.BSD is both a license and a class of license (generally referred to as BSD-like). The modified BSD license (in wide use today) is very similar to the license originally used for the BSD version of Unix. The BSD license is a simple license that merely requires that all code retain the BSD license notice if redistributed in source code format, or reproduce the notice if redistributed in binary format. The BSD license (unlike some other licenses e.g. GPL) does not require that source code be distributed at all.
MIT license:
 The MIT license gives users express permission to reuse code for any purpose, sometimes even if code is part of proprietary software. As long as users include the original copy of the MIT license in their distribution, they can make any changes or modifications to the code to suit their own needs. It is one of the most simple open source license agreements. The intent was for the text to be understandable by average users and to avoid extensive litigation, which may arise from other similar Free and Open Source Software (FOSS) licenses.
The MIT license gives users express permission to reuse code for any purpose, sometimes even if code is part of proprietary software. As long as users include the original copy of the MIT license in their distribution, they can make any changes or modifications to the code to suit their own needs. It is one of the most simple open source license agreements. The intent was for the text to be understandable by average users and to avoid extensive litigation, which may arise from other similar Free and Open Source Software (FOSS) licenses.
Apache License:
 The Apache License is a permissive free software license written by the Apache Software Foundation (ASF).] It allows users to use the software for any purpose, to distribute it, to modify it, and to distribute modified versions of the software under the terms of the license, without concern for royalties. The ASF and its projects release their software products under the Apache License. The license is also used by many non-ASF projects.
The Apache License is a permissive free software license written by the Apache Software Foundation (ASF).] It allows users to use the software for any purpose, to distribute it, to modify it, and to distribute modified versions of the software under the terms of the license, without concern for royalties. The ASF and its projects release their software products under the Apache License. The license is also used by many non-ASF projects.
Creating the Cretaive Commons License for my FAB Academy Project:
I decided to create the Creative Commons License for my FAB Academy Work and Project for the year 2021.
After reading about different types of Licenses, I noticed that the Creative Commons license is the most appropriate type of License for me and the type of the work that I am doing because it organizes the open-source copyrights with many options. Finally, i decided to go with creative commons open-source license. I wanted that my work should be refrred by anyone just by giving me the credit if they want to use it.
Steps for creating license.
On web browser goto "Creativecommons.org".
 and select "share your work". A window will pop up. Then select - "Get Started"
and select "share your work". A window will pop up. Then select - "Get Started"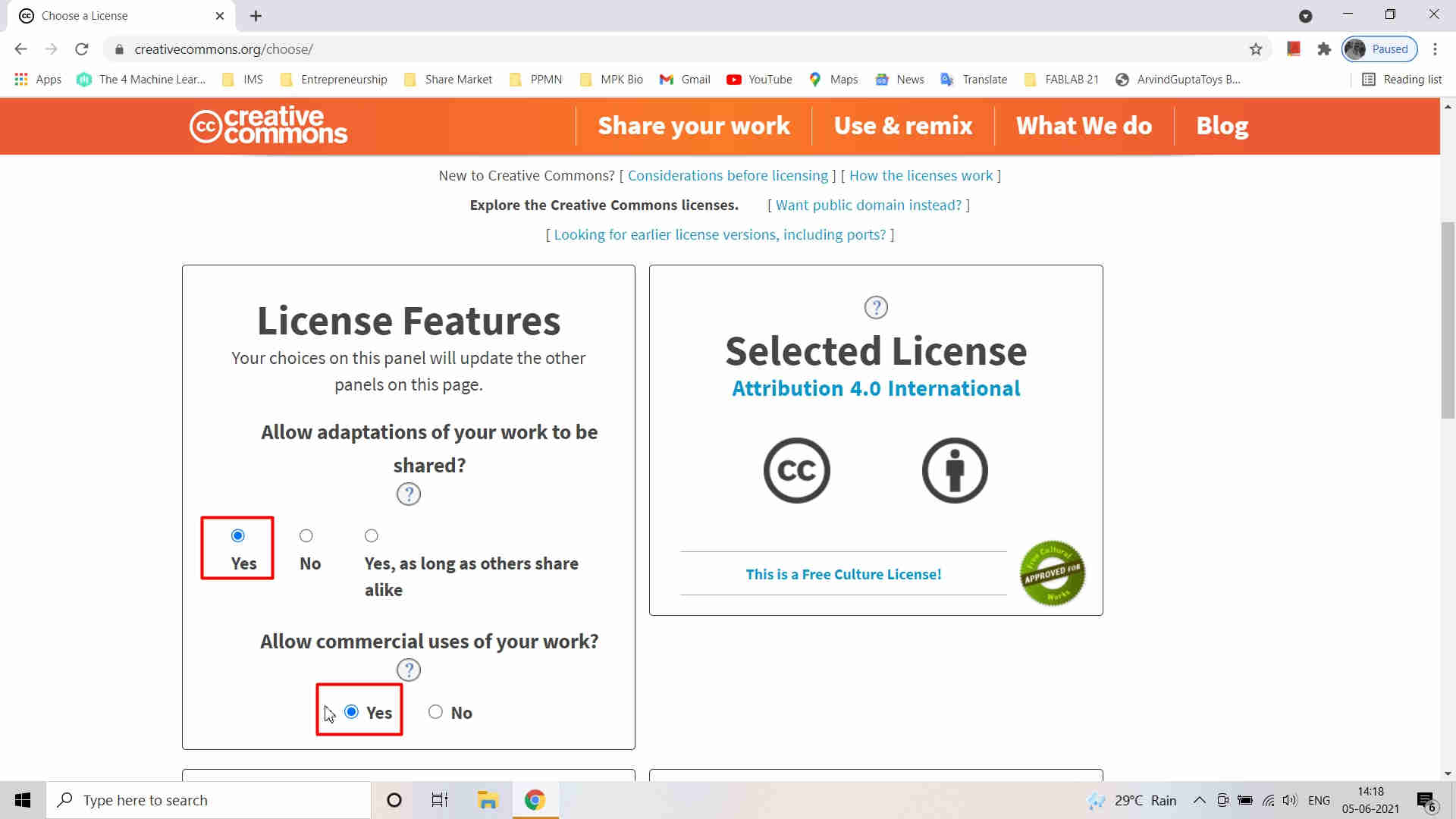 Select the appropriate actions from the dialogue box and tick mark them. I have selected the highlighted options.
Select the appropriate actions from the dialogue box and tick mark them. I have selected the highlighted options. Then, I selected the "Chooser Beta" for completion of License creating process
Then, I selected the "Chooser Beta" for completion of License creating process Tick Mark the appropriate actions from the dialogue box. My selection is highlighted in the image. Iknew the License that I wanted to create.
Tick Mark the appropriate actions from the dialogue box. My selection is highlighted in the image. Iknew the License that I wanted to create.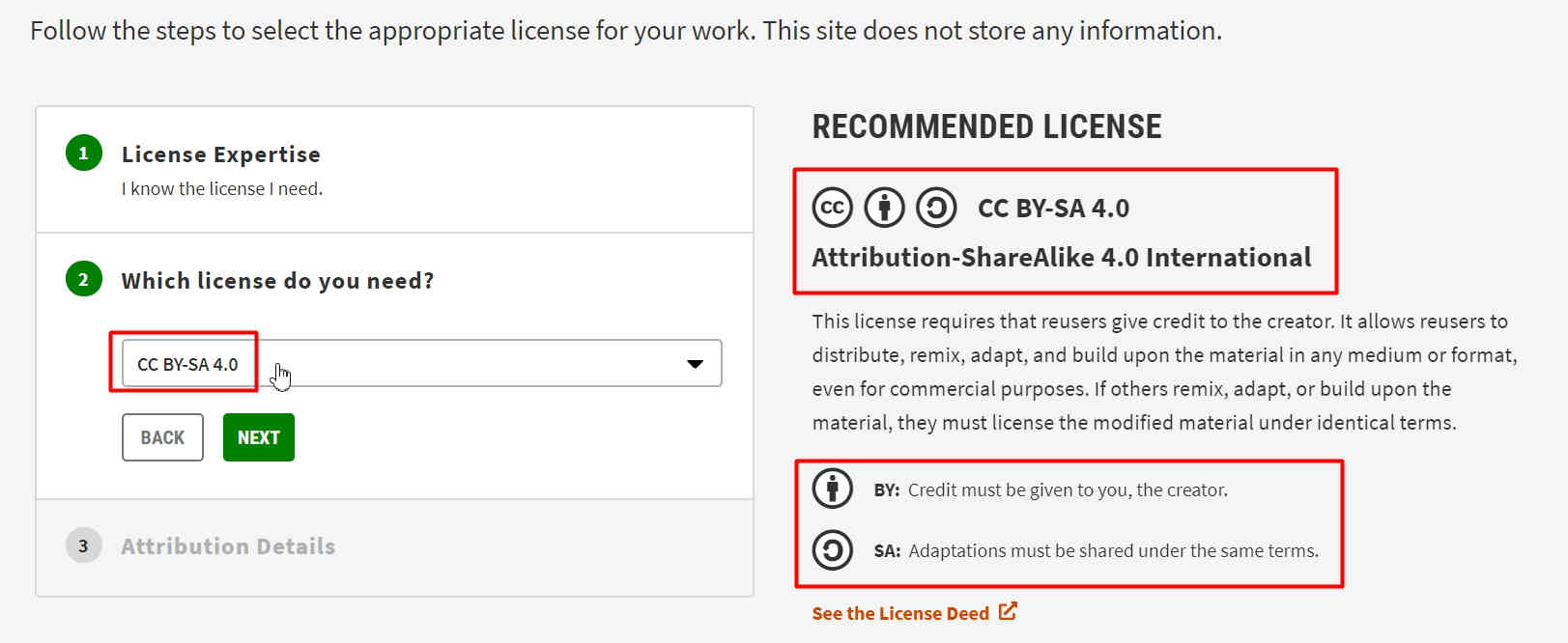 I selected the CC by SA 4.0 License. This license requires that reusers give credit to the creator. It allows reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format, even for commercial purposes. If others remix, adapt, or build upon the material, they must license the modified material under identical terms.
I selected the CC by SA 4.0 License. This license requires that reusers give credit to the creator. It allows reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format, even for commercial purposes. If others remix, adapt, or build upon the material, they must license the modified material under identical terms.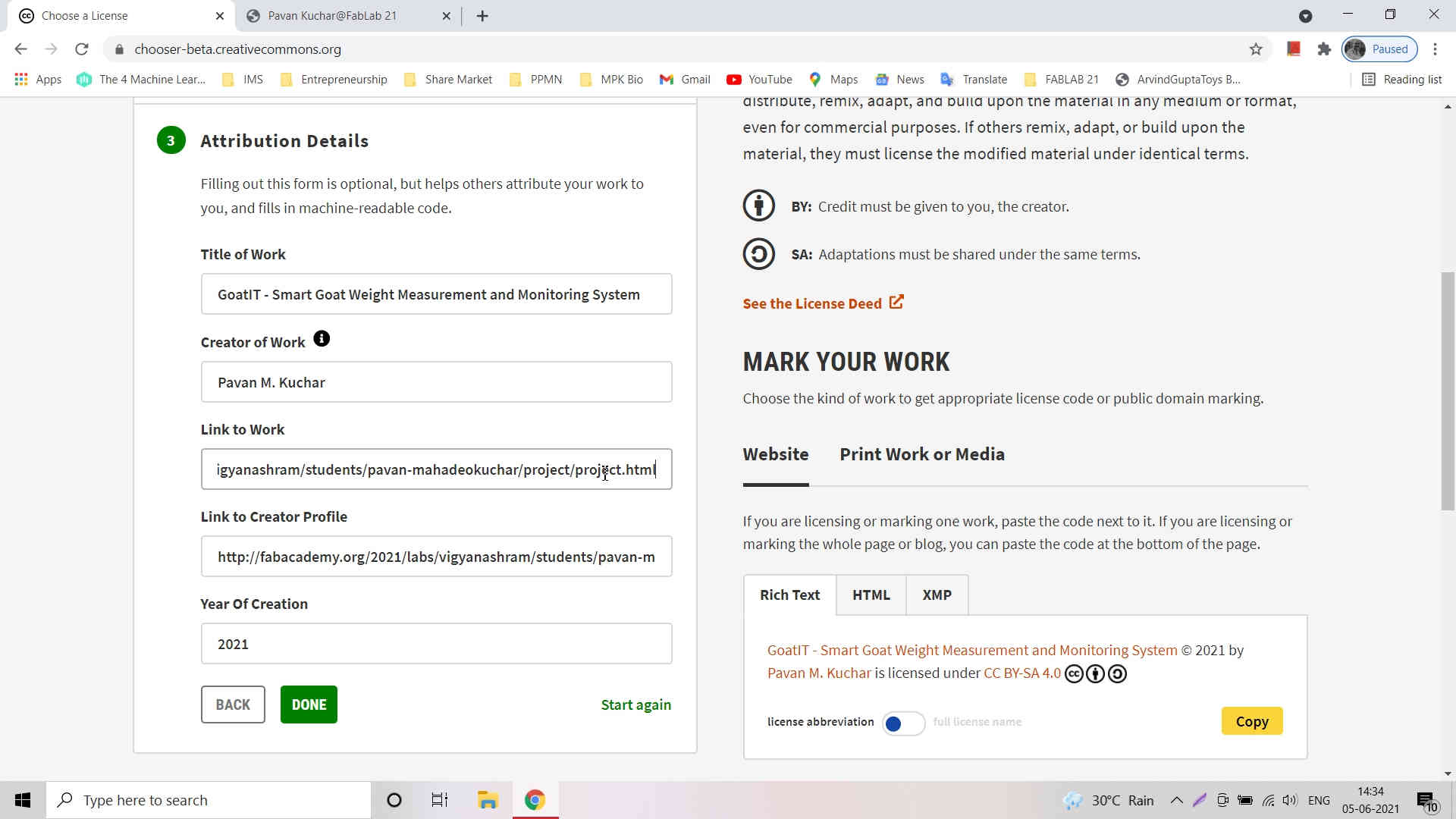 I filled the Attribution details for my Project and Work. I also pasted the link for my Final Project of FAB Academy.
I filled the Attribution details for my Project and Work. I also pasted the link for my Final Project of FAB Academy.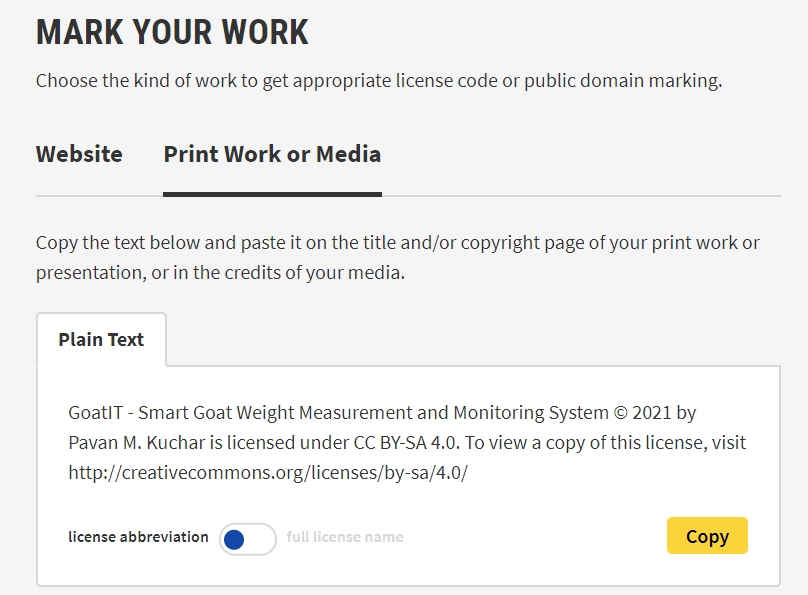 Once Done, License is created. This could be copied and pasted in the Work that is published in Media.
Once Done, License is created. This could be copied and pasted in the Work that is published in Media.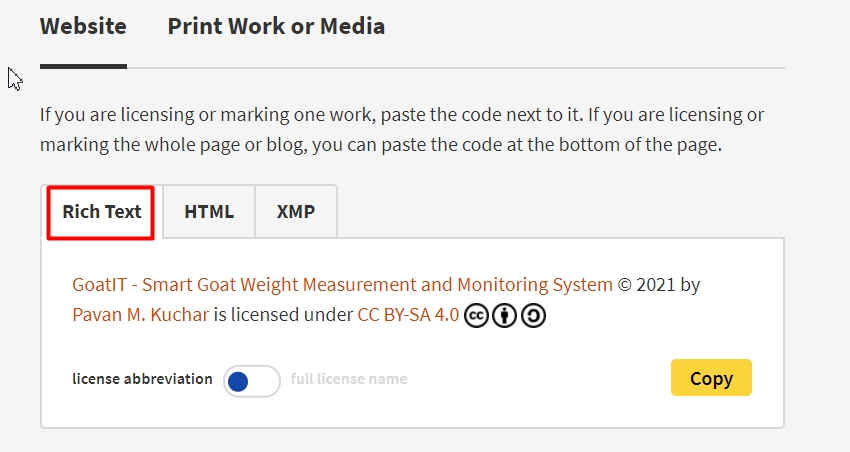 I copied the Embed code and pasted at the bottom of my every page.
I copied the Embed code and pasted at the bottom of my every page. .png file of Presentation
Video of Final Presentation
.png file of Presentation
Video of Final Presentation
Planning and Possibilities for future Development of Project:
My Design and Final Product is not an invention. I have designed this Weighing Scale keeping in mind the Goats and thats why it is rectangular in shape. It gives a Cantilever effect to it. I will have to resolve the issue related to the dimensions and shape.
I am Planning to make changes to the design by reducing its height and properly placing the Load cell on the Base. I will have to make changes to the Code as well which will display the weight for a longer time.
As far as the Commercialization is concerned, I will deploy this model in the Vigyan Ashram for the Weight Measurement of Goats and Monitor their health. It could then be shared through various platforms like Instructables and Iot Projects for making DIY projects by others. I may also contact few Goat Farmers and make customized Balance for them in low cost.
Where you would Fabricate and Assemble your devices?
For my Final Project, I will be using the Infrastructure and amenities of the Vigyan Ashram for Fabricating and Assembling the Device.
I may then contact other Welding Workshops and Fabricators for making it available to them and the needy.
How you would distribute the devices? (you directly, resellers, through internet, under the shape of a kit, etc)
As the design is not new and Load cells have been used since long for various purposes, my USP (Unoque Selling Proposition) remains its Low Cost and Customization. Also, it is equipped with RFID Tag reader for unique Identification and Differentiation. The ESP32 board can send the data to the user through Bluetooth and WiFi for easy access anytime, anywhere. This gives a competitve advantage to the Goat Farmers.
I will try to promote my device in Farm Equipment Fairs and Exibitions in collaboration with Fabricators and Agri Equipment Manufacturers.
NGO's like Vigyan Ashram which are focusing on Rural Technology could be better for percolation of this Device.
Even Rural Haats, ITC eChoupal, APMC's (Agricultural Produce Marketing Corporation) are better for marketing the device.
A Integrated Model of Business could be used for reaching all types of customers. Internet e-Commerce giants like amazon, India Mart and others could be contacted for listing the product, Videos could be promoted on the YouTube of the making of Device, Traditional CHannel like the Intermediaries could be used for distribution and demostration of the device. I would not restrict myself to one medium in this age of information.
Summary:
In this week,
- I learned about the various types of Licences available and the Procedure for taking Licences.
- I created the Creative Common License for my work in Fab Academy 2021
- I created the draft .png image for my presentation and .mp4 file for its video.
- I also drafted and outlined the future possibilities and opportunities for my finished project
- I also detailed about the methodology of my Business model (Not for Profit).

