Workflow of Assignment:
1. Inventions:
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition or process. The invention process is a process within an overall engineering and product development process.
2. Intellectual Properties:
To protect your idea so that someone else cannot steal your idea, you need to secure one or more of the four different types of intellectual property (IP).
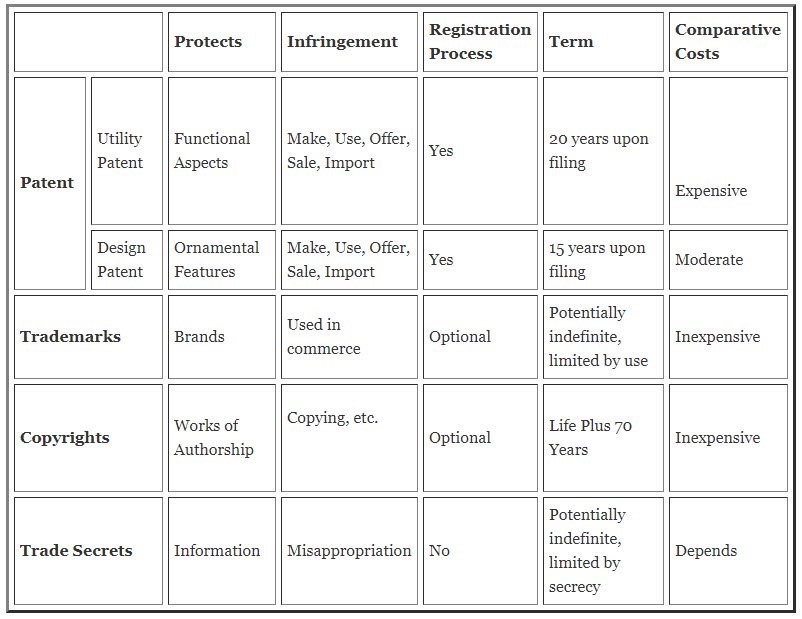
Protection by each Intellectual Property: The table below illustrates each of the four different types of intellectual properties and what they might be used to protect in a broader sense.
A. Trade Secrets:
Most inventions start off as trade secrets which provides short-term protection prior to the marketing of your invention. Inventors are often initially cautious about revealing their inventions to others, even their patent attorney, and this is a good instinct to have.
Trade secret protection is not appropriate for the long-term protection of any ideas which can be readily ascertained by reverse engineering or for inventions that can be independently created. If the information can be reverse engineered or independently created, then there is no nefarious act.
B. Trademarks:
When you sell a product or perform a service under a brand, trademark law gives you common law trademark rights that you can assert against others in your small geographical region where you used the mark. Hence, to obtain trademark rights, you do not need to register your trademark but there are significant advantages for doing so such as nationwide rights and the right to block others from securing a registered trademark.
C. Patents
Two types of patents may be obtained:
1. Utility (Function) and
2. Design (Aesthetic).
The criteria that need to be satisfied to obtain a patent are set out in national IP laws and may differ from one country to another. But generally, to obtain a patent an inventor needs to demonstrate that their technology is new (novel), useful and not obvious to someone working in the related field. To do this, they are required to describe how their technology works and what it can do.
D. Copyright
i. Open Source License:
Open source license is that allows the source code or design to be used, shared or modified under defined terms and conditions. Open-source licensed product is mostly free of cost. The most common open source licenses available are MIT license, Apache license and GNU GPLv3 license.
a. MIT license:
The MIT License is a permissive license that is short and to the point. Licensed works, modifications, and larger works may be distributed under different terms and without source code.
b. Apache license:
A permissive license whose main conditions require preservation of copyright and license notices. Contributors provide an express grant of patent rights. Licensed works, modifications, and larger works may be distributed under different terms and without source code.
c. GNU GPLv3:
Permissions of this strong copyleft license are conditioned on making available complete source code of licensed works and modifications, which include larger works using a licensed work, under the same license. Copyright and license notices must be preserved.
d. Creative Commons:
Is one of several public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted work. A CC license is used when an author wants to give people the right to share, use, and build upon a work that they have created. CC provides an author flexibility (for example, they might choose to allow only non-commercial uses of their own work) and protects the people who use or redistribute an author’s work from concerns of copyright infringement as long as they abide by the conditions that are specified in the license by which the author distributes the work.
ii. Comparison between the license:
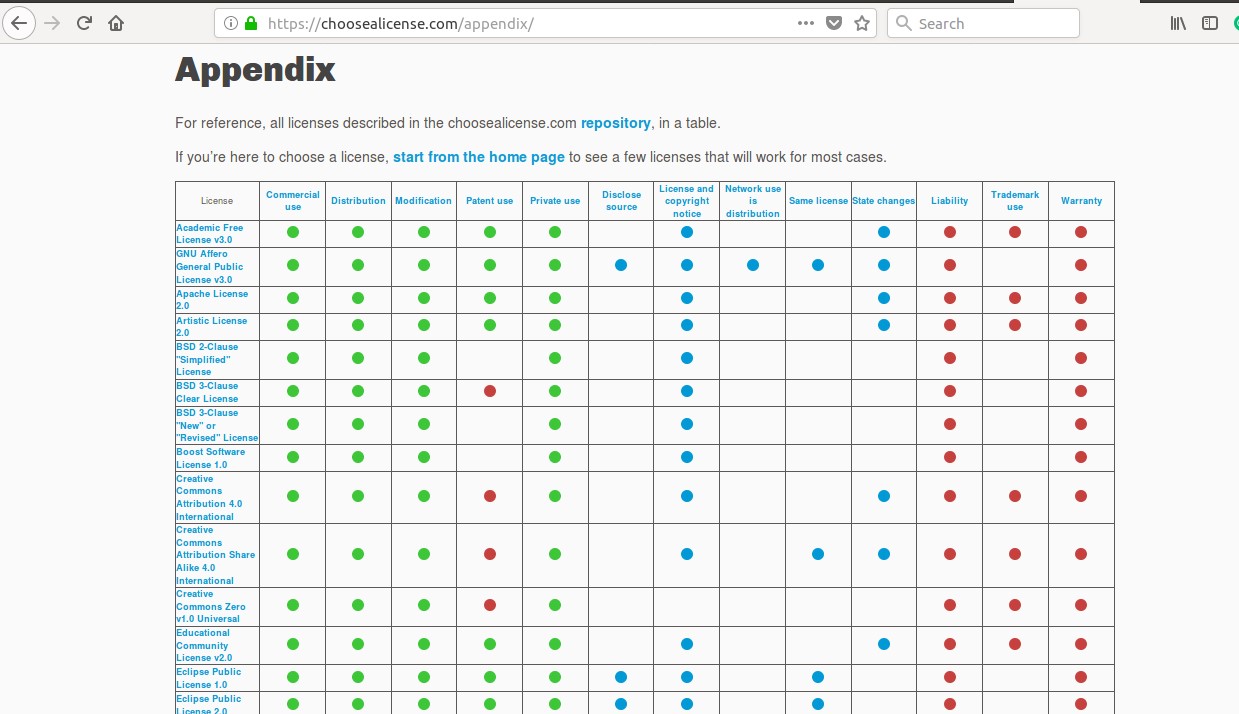
3. Creative Commons:
I compared and finalised to go with Creative Commons open source license for my project.
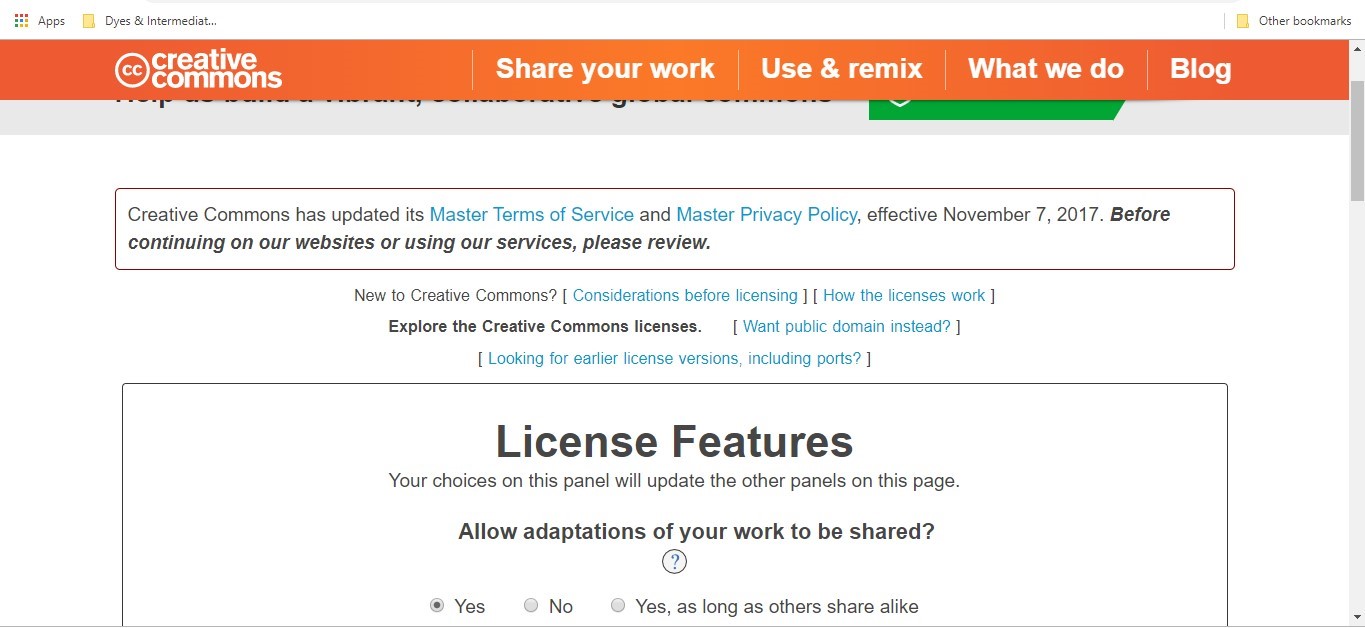
A. Website:
Opened the Creative Commons website for license and allowed adaptation for my work to be shared.
B.Commercial Use:
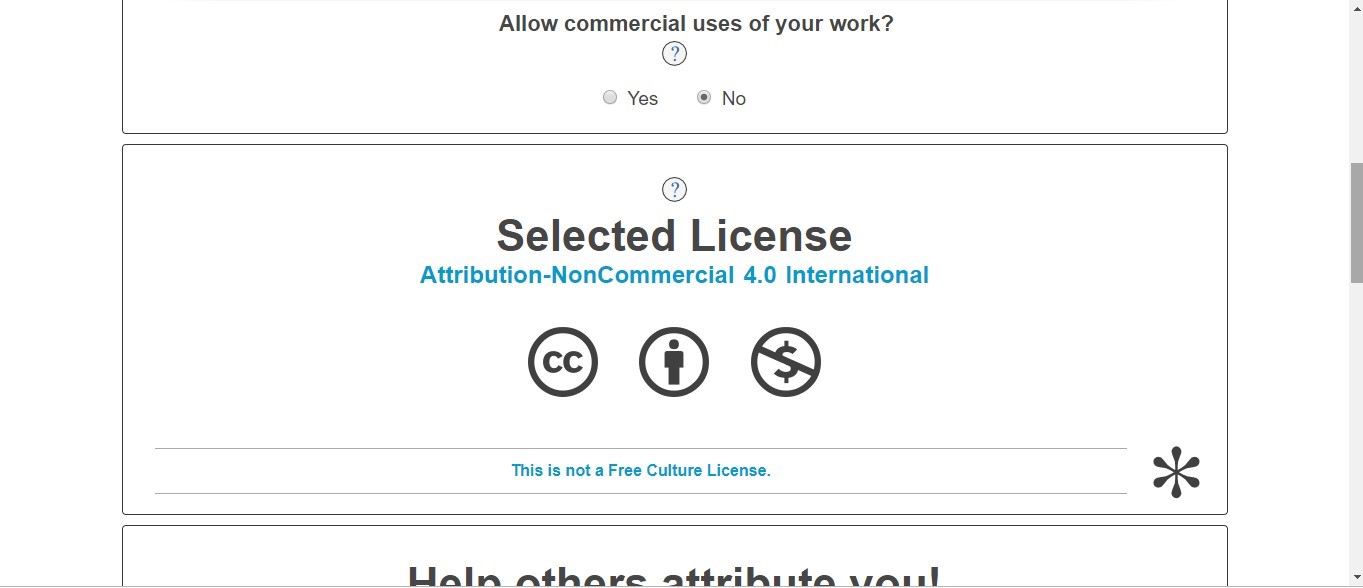
Didn’t allow the commercial use of my project work and it showed selected license- “Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International”.
C. Details:
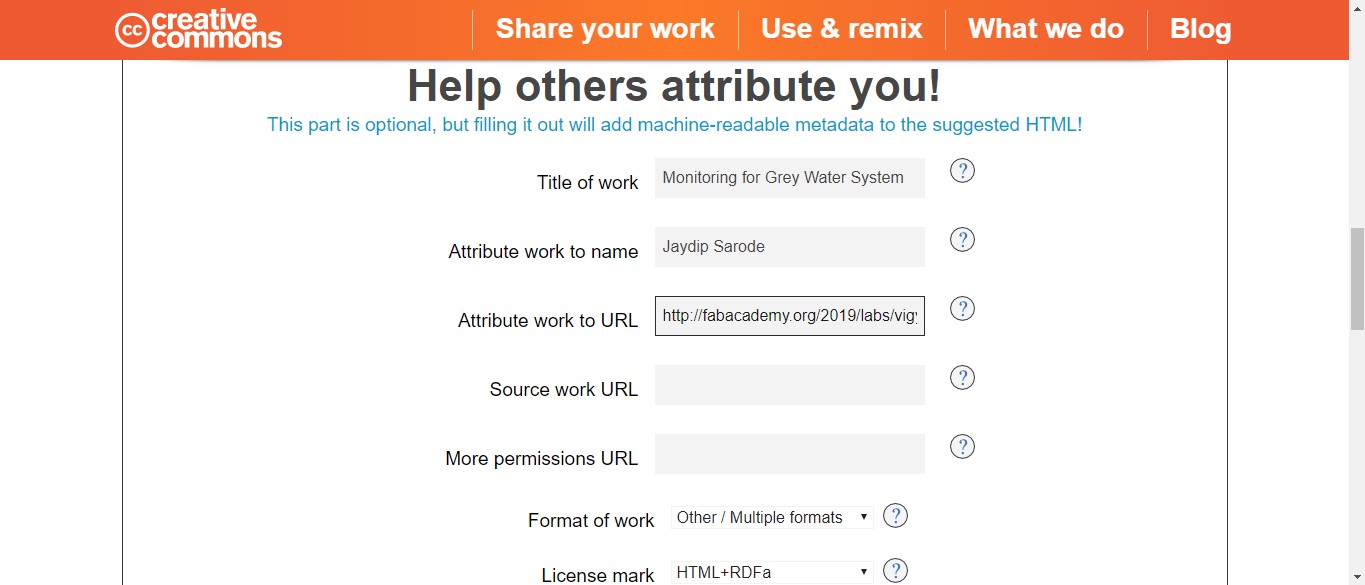
Filled the details with my name, project name and the website link for the license to be more specific.
D. Code:
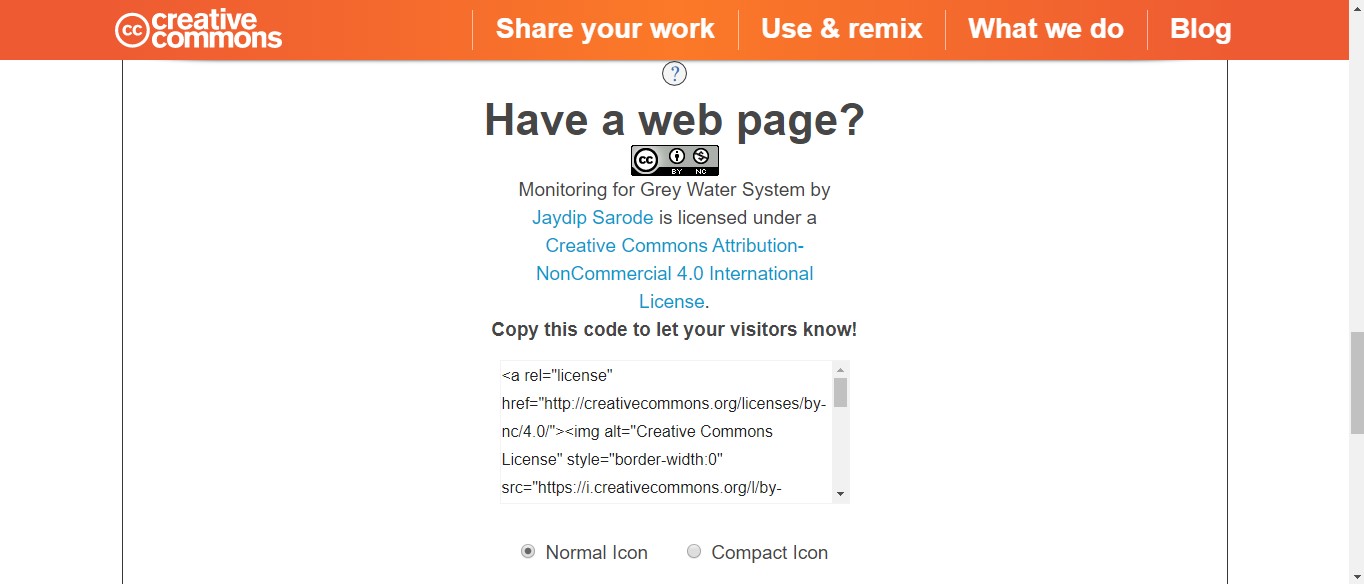
I got the code which I can paste in my website for the visitors to know. Chose normal icon on license which is bigger and more clear to me.
4. Future Plans and Business Model:
My project has been deployed at Chikhli, Pune City. This will give me the feedback of the functioning, accuracy and durability of the device. It is monitoring Grey Water Systems. Grey water technique is not very common in India so I don’t want to commercialize it for this particular application.
My future plan is to use the same application for Aquaphonics and Green House automation. I see great future and revenue source from this market.
Plan of dissemination:
I will make kits and sell to Aquaphonics units. A small training will teach them how to use my device.
I will not focus on making kits for school as the device has application only for aquaphonics.
Presentation:
Porject Slide Presentation:

Used the skills of Computer Aided Design Week to edit and make final slide in Photoshop. In movie maker software,compiled images and short videos/gifs of processes to make a minute video of entire project.
Learning Outcomes:
2. Understood the concept of Intellectual Properties.