Materials
- Acrylic sheets (thicknesses: 5 mm and 8 mm)
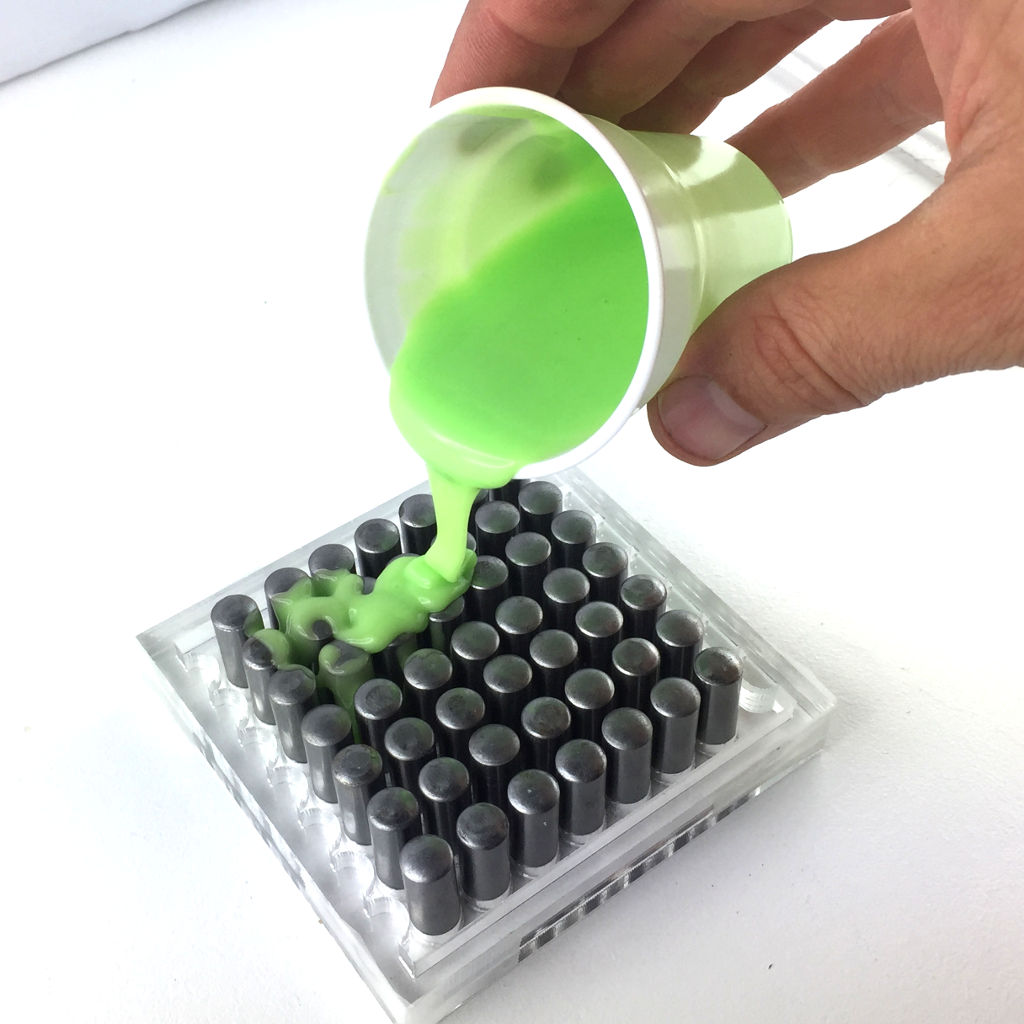
- >50 dowel pins (6, 8 or 10 mm of diameter)
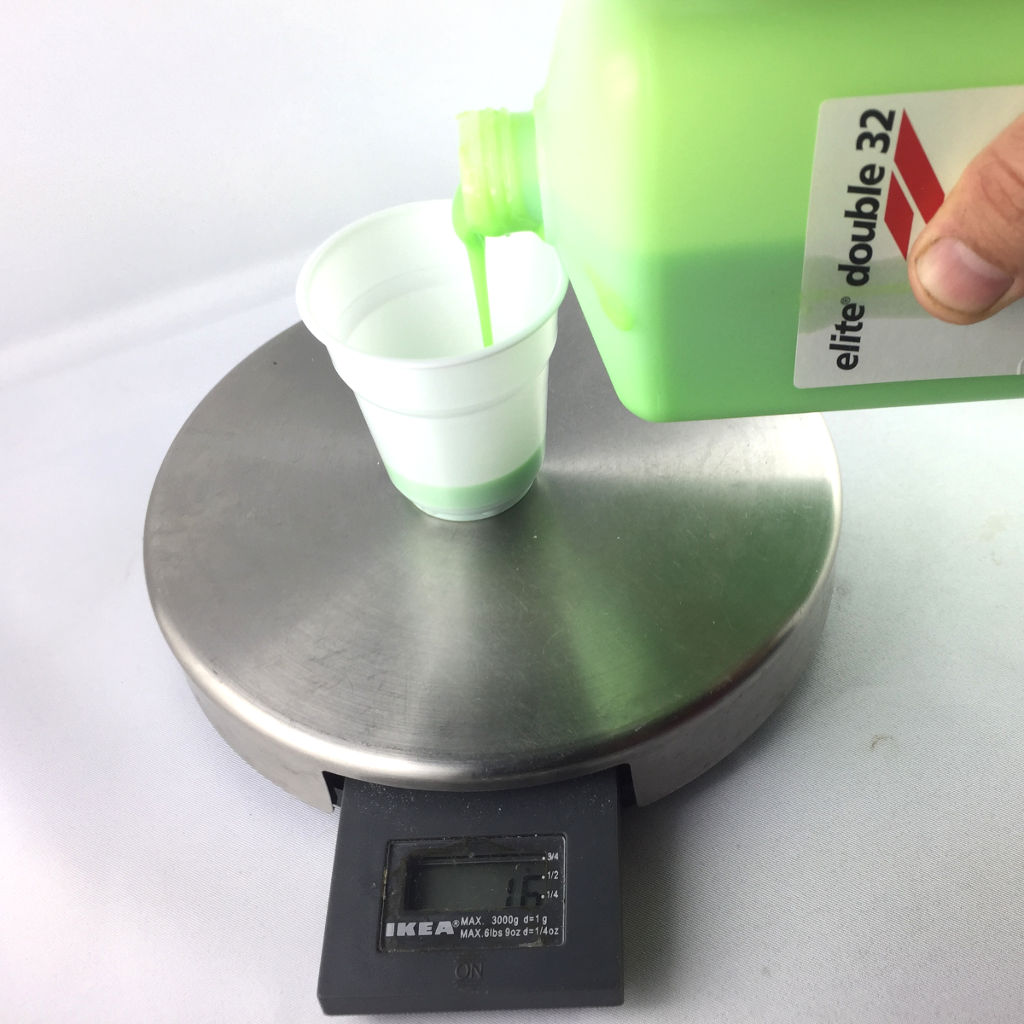
- Scale
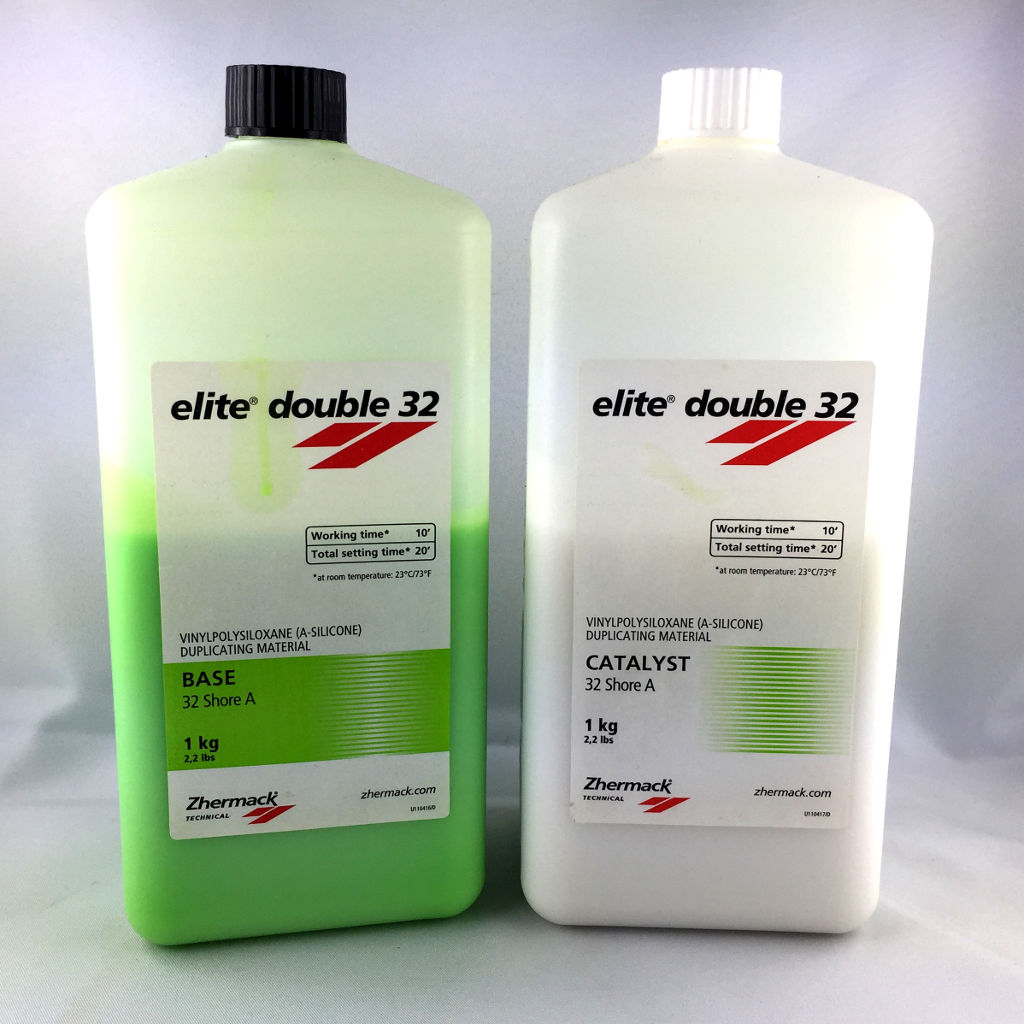
- Silicone based polymer (fast curing)
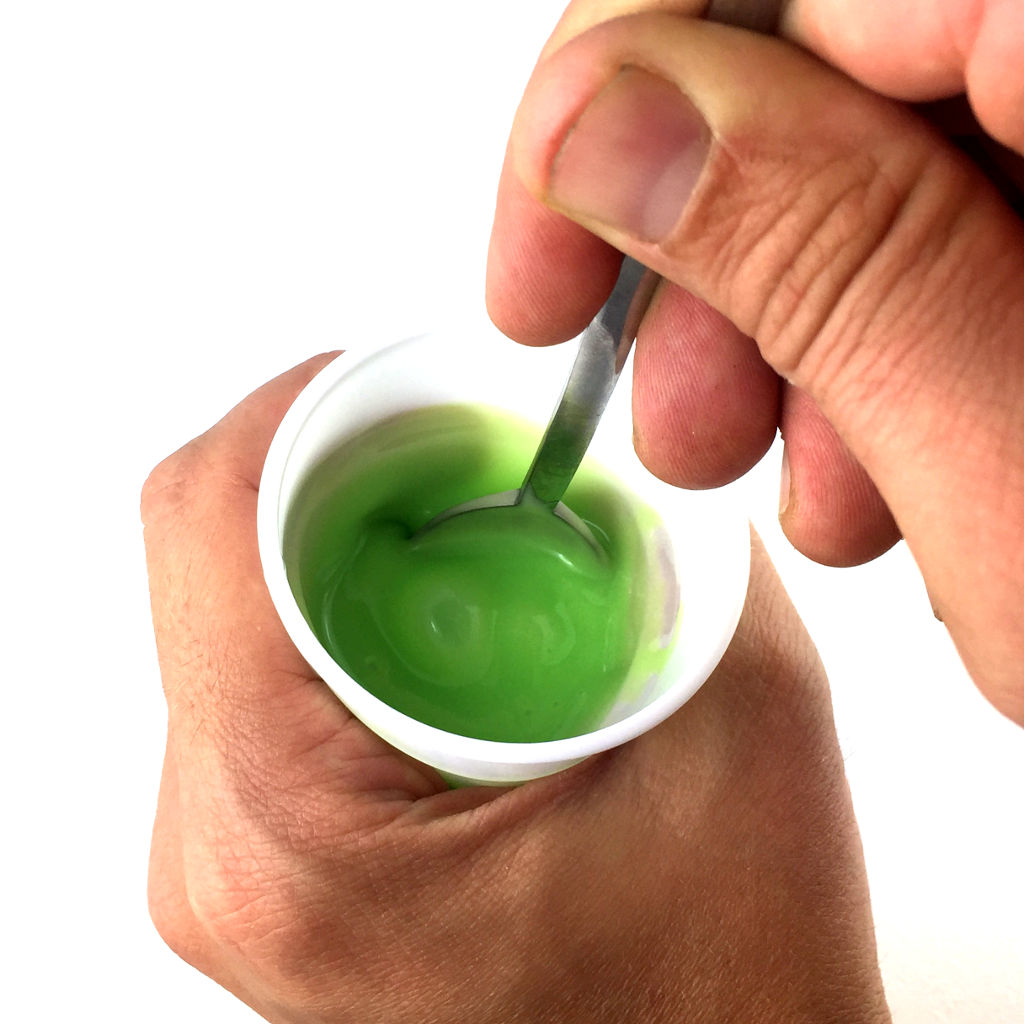
- Mixing cups
- Mixing sticks
Machine
- Laser cutter
Designing the mold
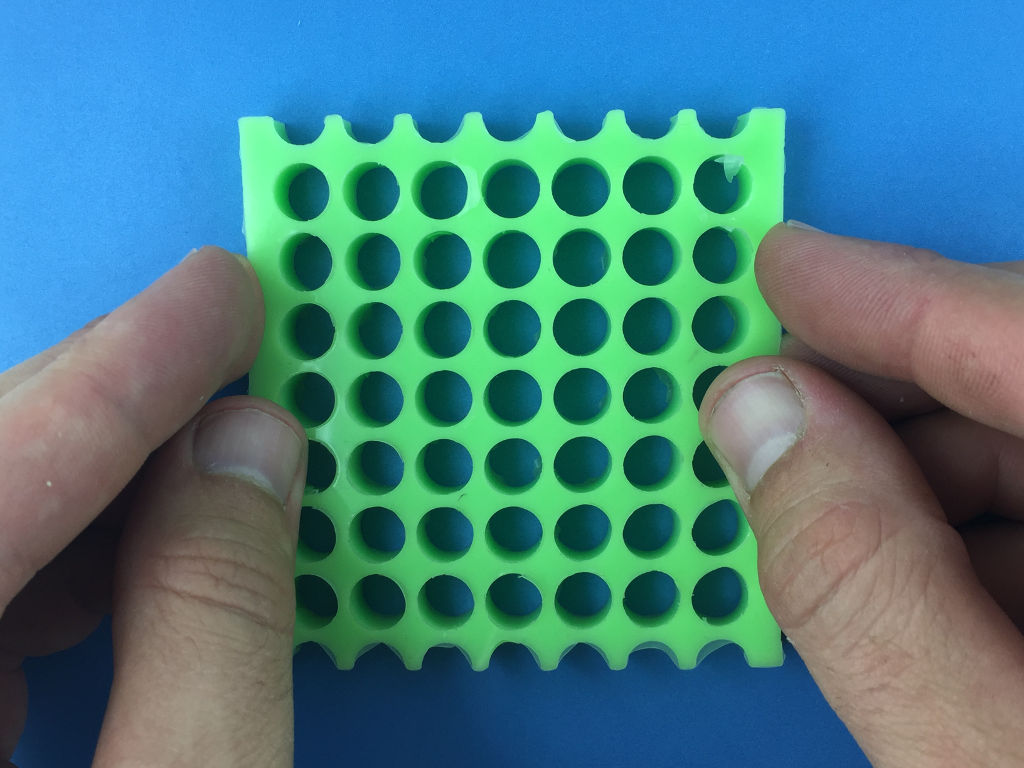
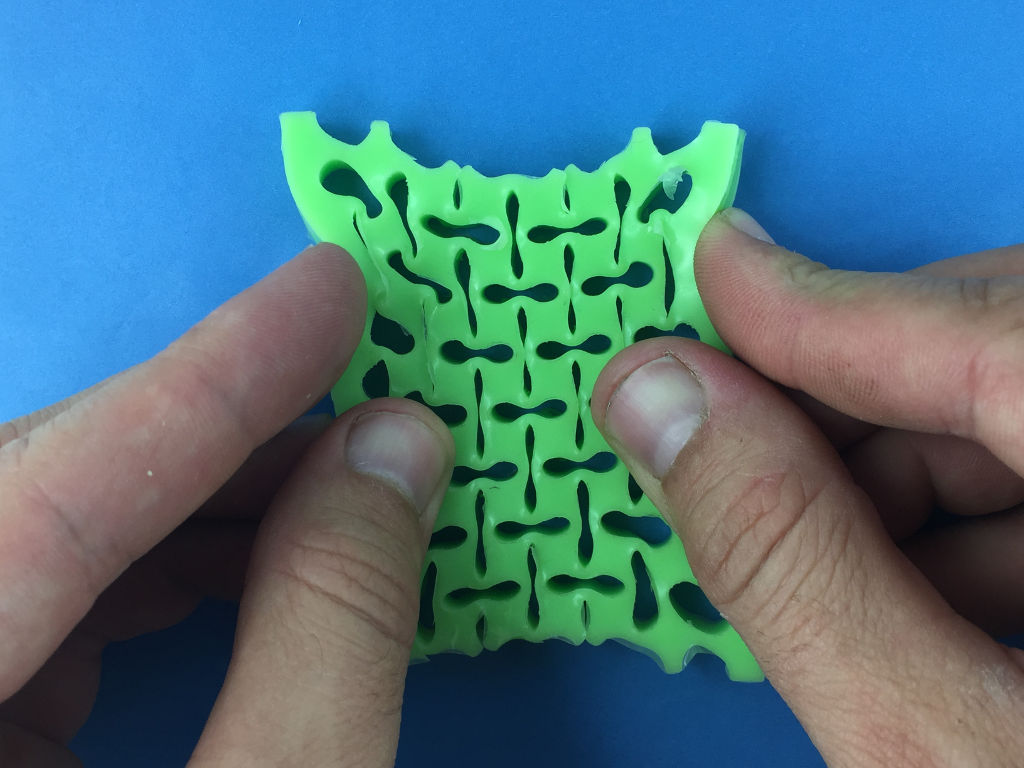
In this workshop unit, you will design and fabricate by molding and casting 2D auxetic mechanical metamaterials.
Using openSCAD, a free software, the first step is to design the mold. The mold is made of three laser cut acrylic plates (upper, middle, lower) and dowel pins (see photo below).
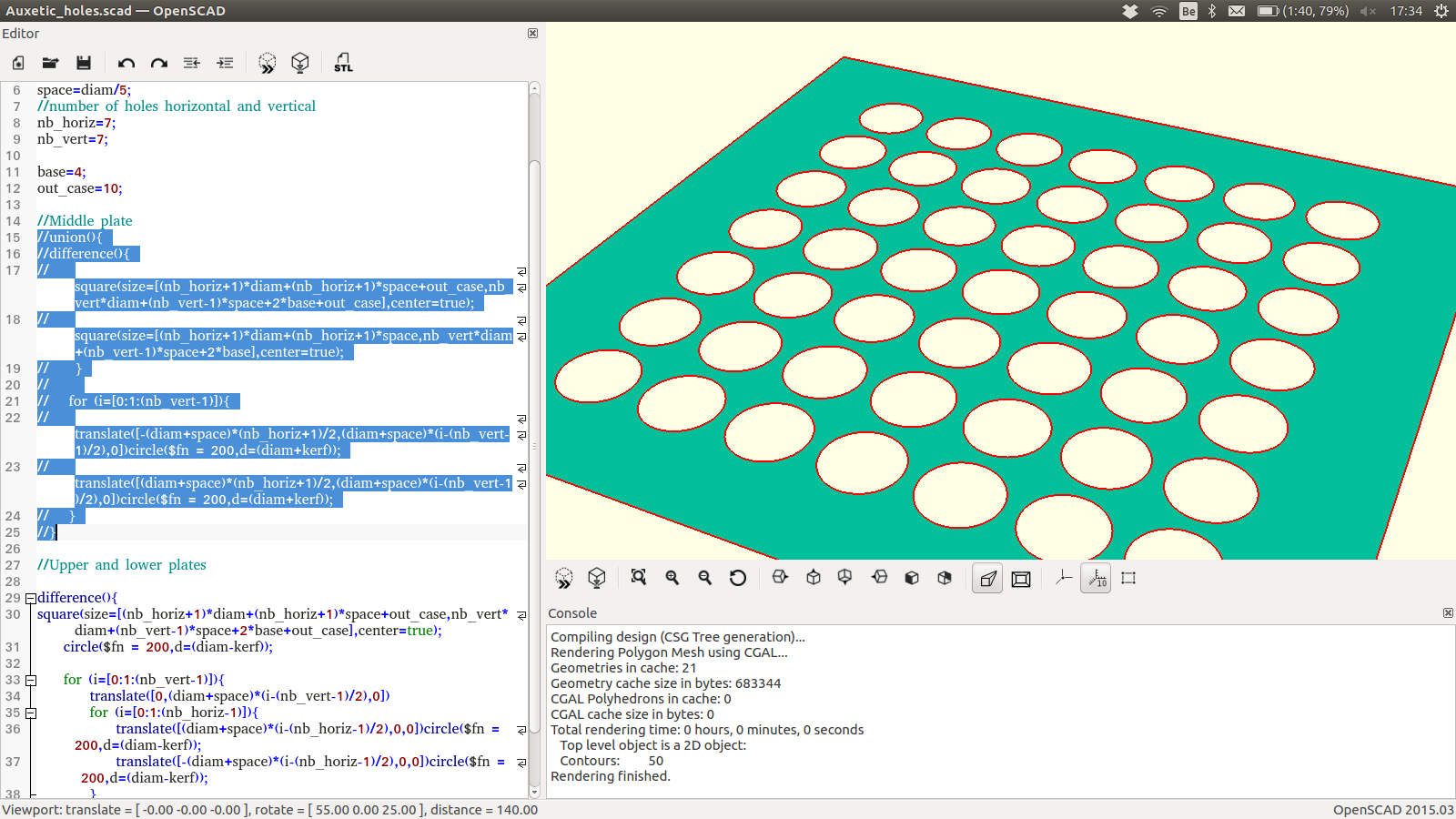
Here is the openscad code for parametrically designing the upper and lower plates:
/*
// FILE : Auxetics Metamaterials with holes - Upper and lower plates
// VERSION : 0.1 (draft)
// LICENSE : M.I.T. (https://opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.php)
// AUTHOR : Denis Terwagne
// TARGET : OpenSCAD
*/
kerf=0;
//dowel pins diameter
diam=8;
//space in between holes
space=diam/5;
//number of holes horizontal and vertical
nb_horiz=7;
nb_vert=7;
base=4;
out_case=10;
//Upper and lower plates
difference(){
square(size=[(nb_horiz+1)*diam+(nb_horiz+1)*space+out_case,nb_vert*diam+(nb_vert-1)*space+2*base+out_case],center=true);
circle($fn = 200,d=(diam-kerf));
for (i=[0:1:(nb_vert-1)]){
translate([0,(diam+space)*(i-(nb_vert-1)/2),0])
for (i=[0:1:(nb_horiz-1)]){
translate([(diam+space)*(i-(nb_horiz-1)/2),0,0])circle($fn = 200,d=(diam-kerf));
translate([-(diam+space)*(i-(nb_horiz-1)/2),0,0])circle($fn = 200,d=(diam-kerf));
}
}
}
Here is a SVG image example:
Here is the openscad code for the middle plate:
/*
// FILE : Auxetics Metamaterials with holes - Middle plate
// VERSION : 0.1 (draft)
// LICENSE : M.I.T. (https://opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.php)
// AUTHOR : Denis Terwagne
// TARGET : OpenSCAD
*/
kerf=0;
//dowel pins diameter
diam=8;
//space in between holes
space=diam/5;
//number of holes horizontal and vertical
nb_horiz=7;
nb_vert=7;
base=4;
out_case=10;
//Middle plate
union(){
difference(){
square(size=[(nb_horiz+1)*diam+(nb_horiz+1)*space+out_case,nb_vert*diam+(nb_vert-1)*space+2*base+out_case],center=true);
square(size=[(nb_horiz+1)*diam+(nb_horiz+1)*space,nb_vert*diam+(nb_vert-1)*space+2*base],center=true);
}
for (i=[0:1:(nb_vert-1)]){
translate([-(diam+space)*(nb_horiz+1)/2,(diam+space)*(i-(nb_vert-1)/2),0])circle($fn = 200,d=(diam+kerf));
translate([(diam+space)*(nb_horiz+1)/2,(diam+space)*(i-(nb_vert-1)/2),0])circle($fn = 200,d=(diam+kerf));
}
}
Here is a SVG image example:
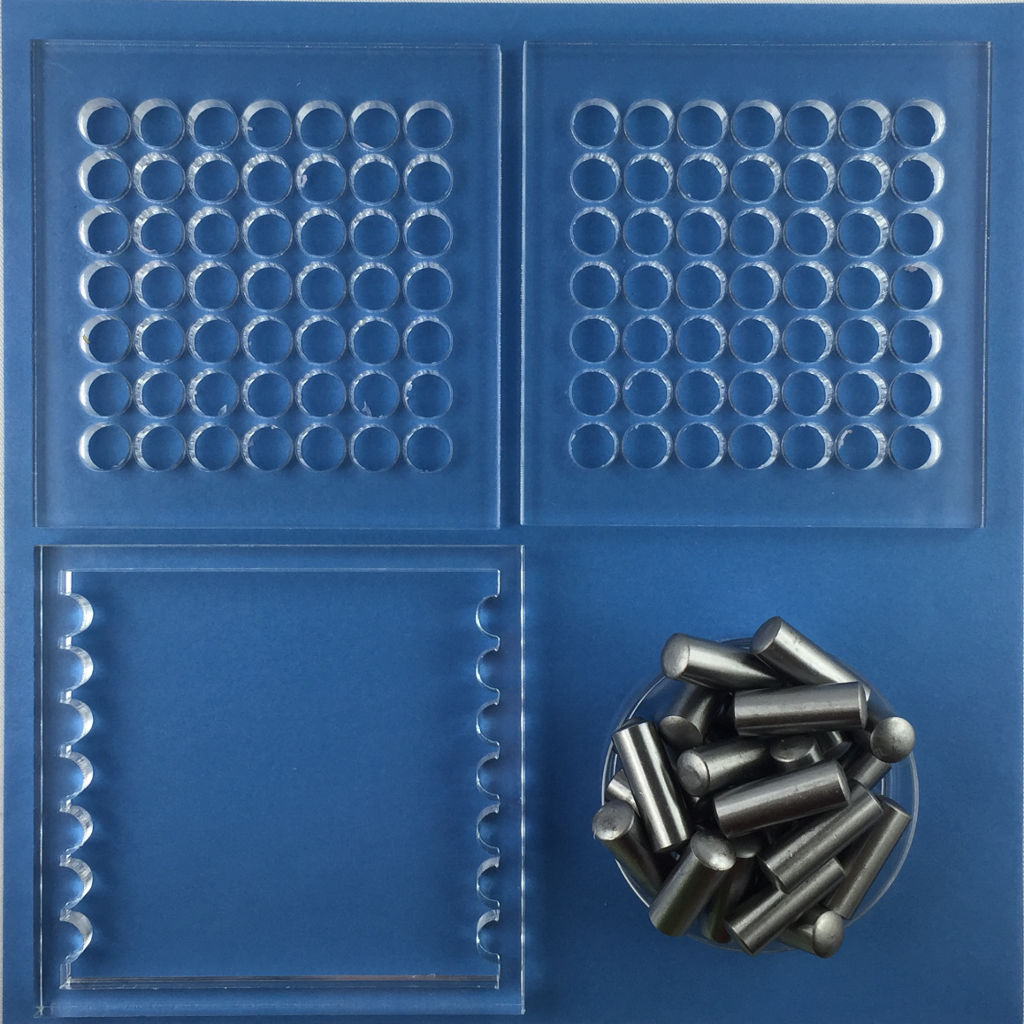
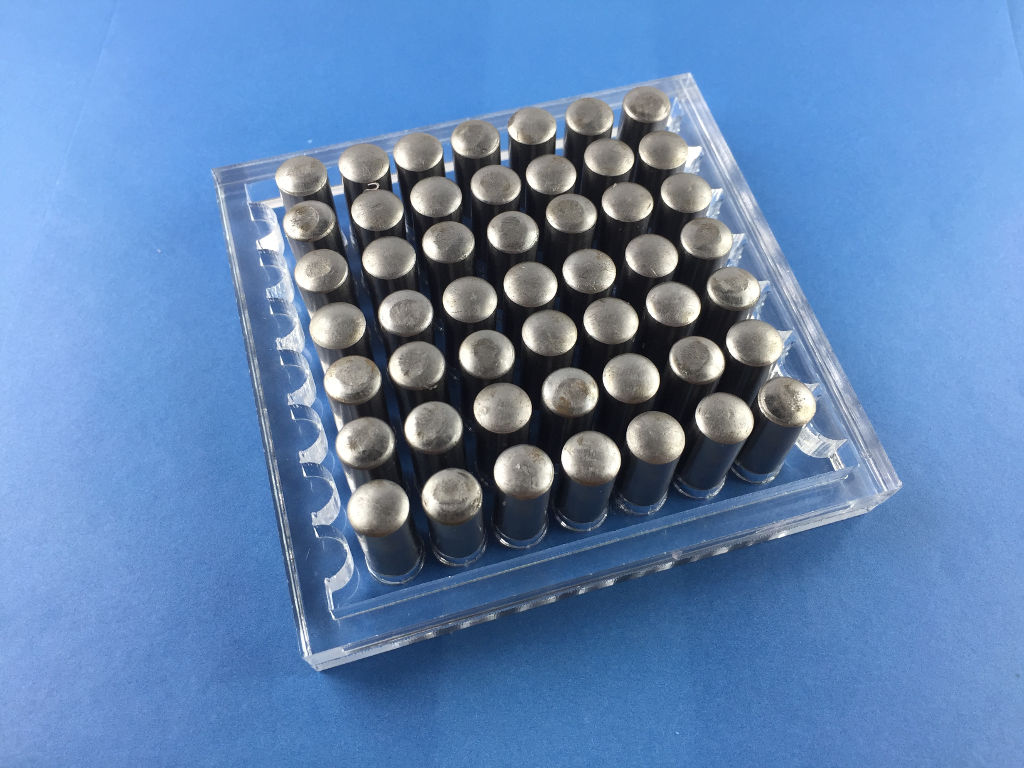
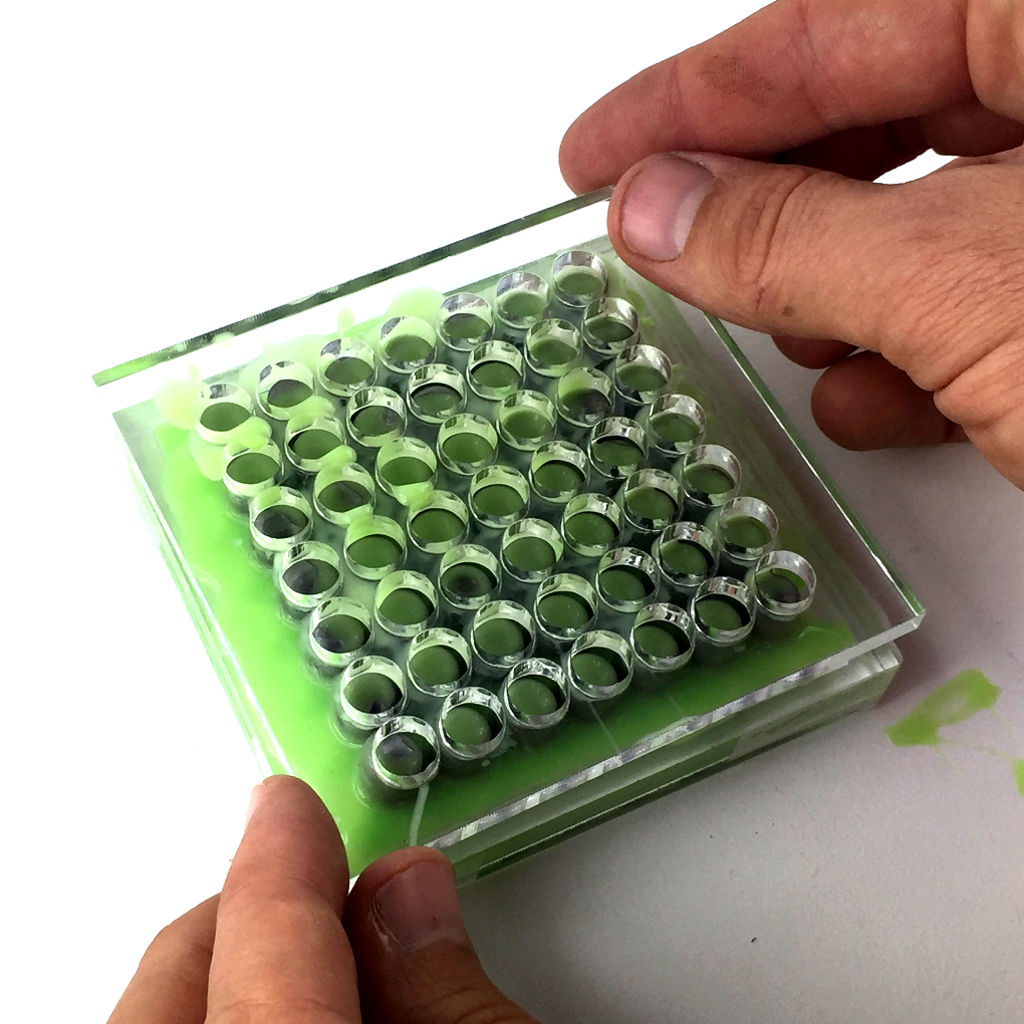
Fabricating the mold
To make the mold, laser cut the 3 acrylic plates and prepare a number of dowel pins.


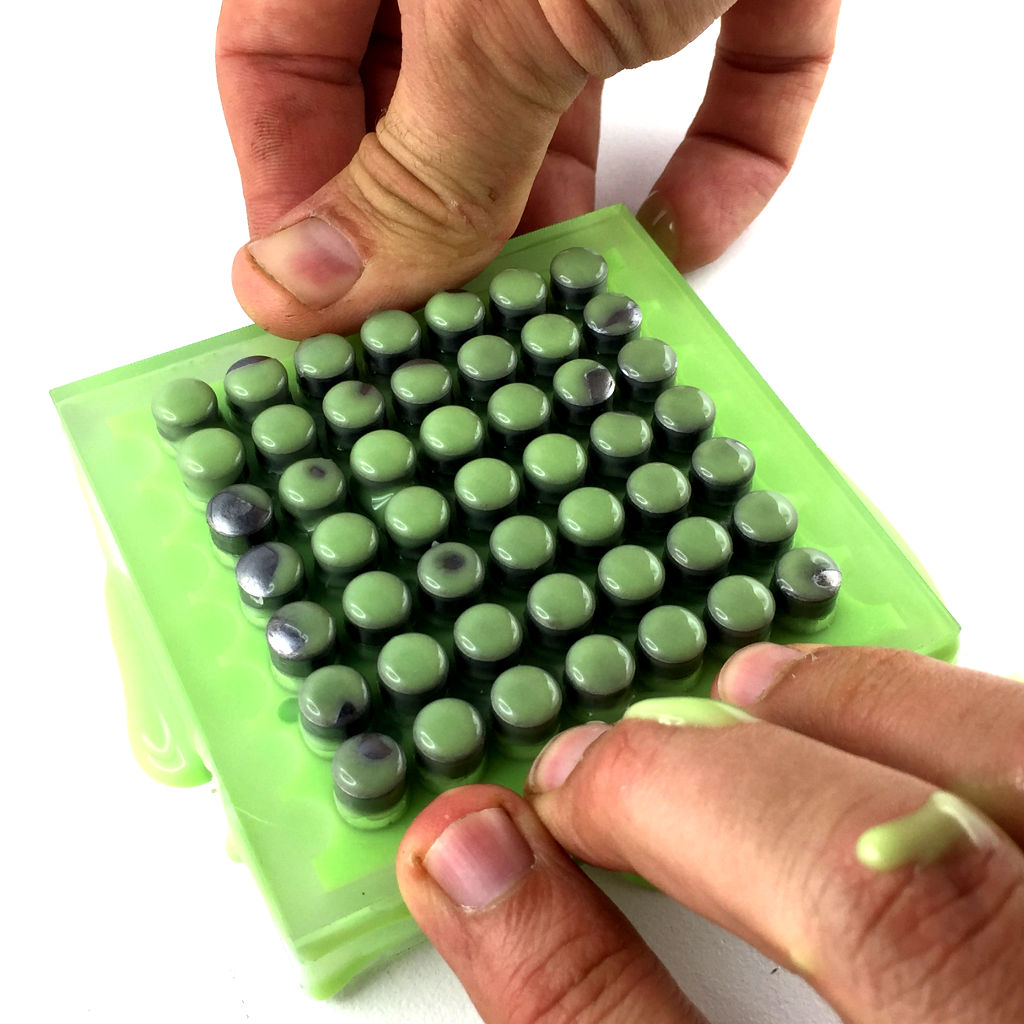
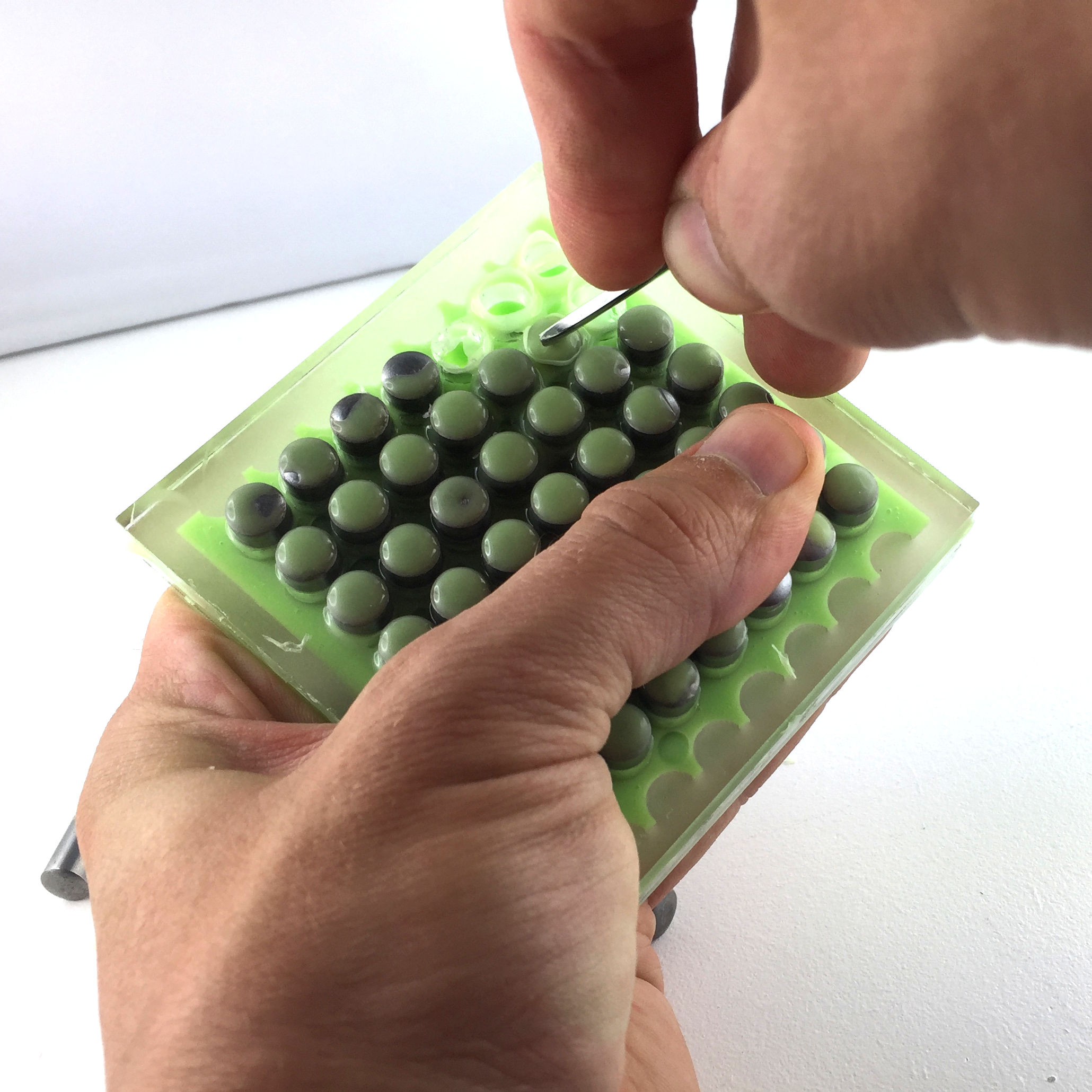
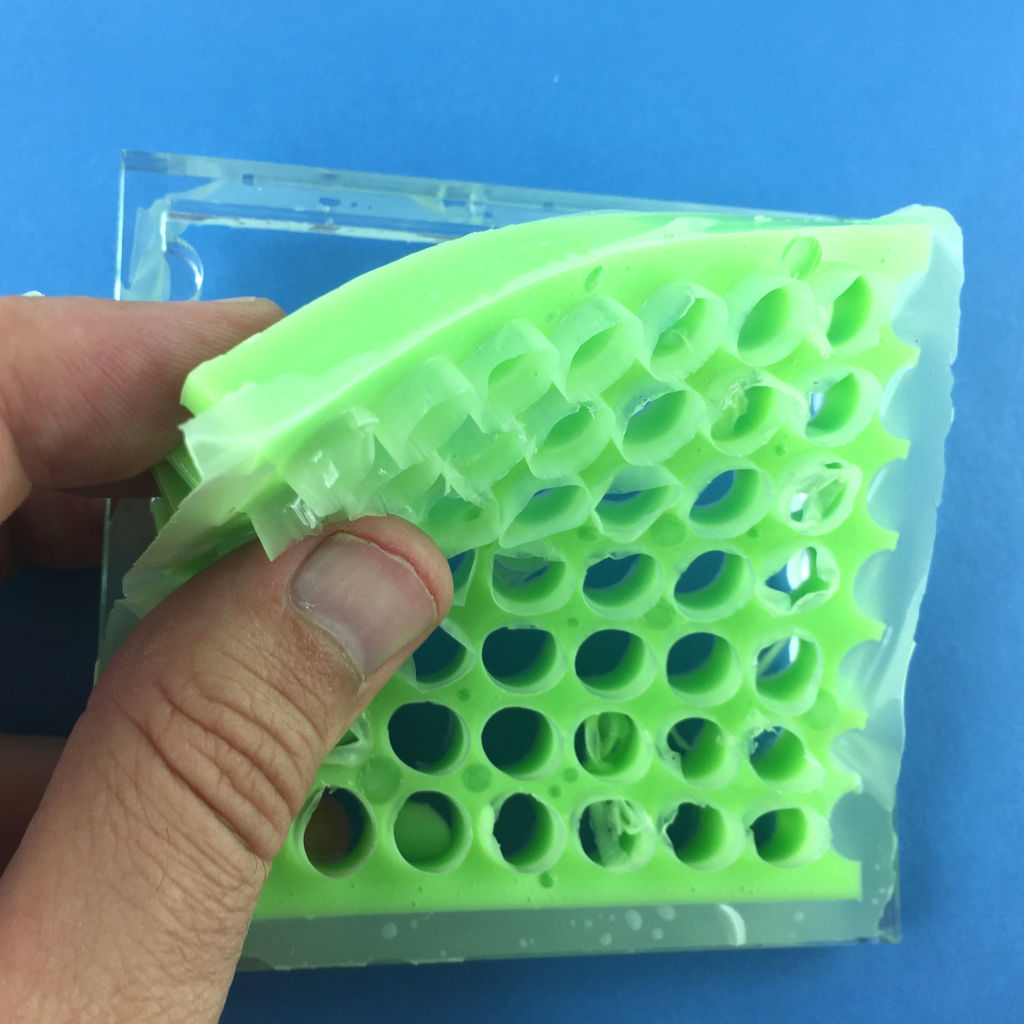
Molding the material
Now, it's time to cast our structure. To do this, follow these steps :







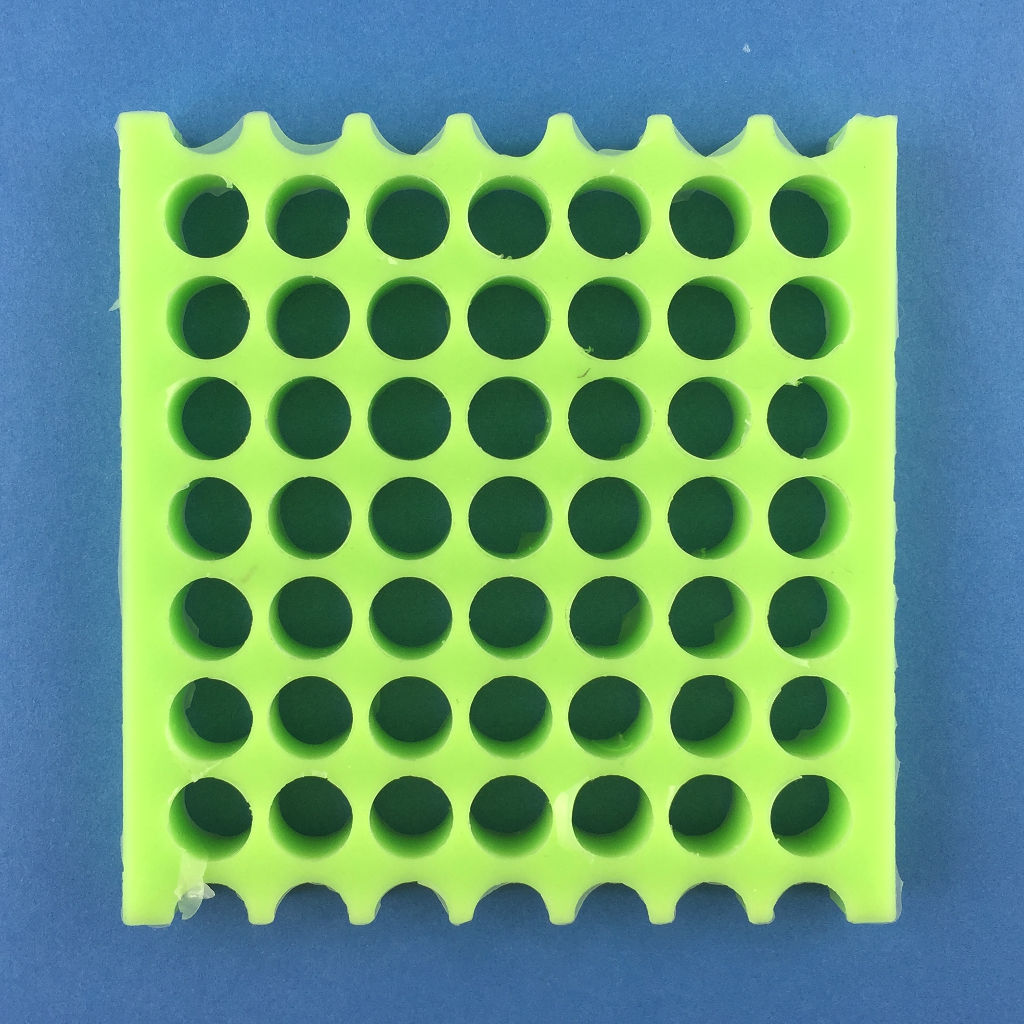
Testing the strutures