

Toolchains, Development Workflows and Microcontroller Programming
Objective:
Demonstrate and compare the toolchains and development workflows for available embedded architectures.
Microcontrollers Analyzed:
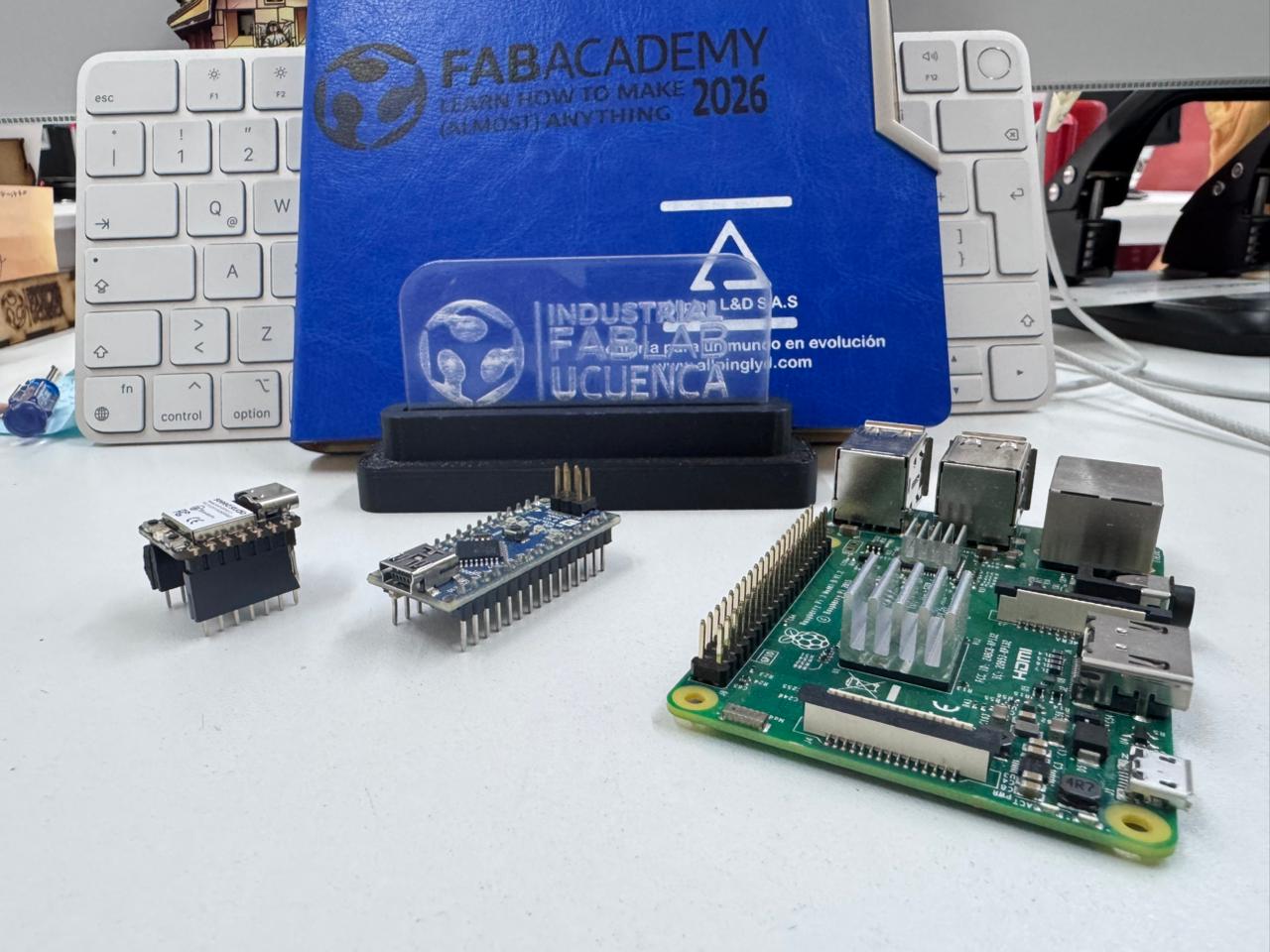

| Feature | ESP32-S2 | XIAO ESP32-C3 | Arduino Nano |
|---|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Xtensa LX7 (32-bit) | RISC-V (32-bit) | AVR (8-bit) |
| Clock Speed | Up to 240 MHz | 160 MHz | 16 MHz |
| Flash Memory | 4MB | 4MB | 32 KB |
| RAM | 320 KB | 400 KB | 2 KB |
| Wireless | WiFi | WiFi + BLE | None |
| Debug Interface | USB CDC / JTAG | USB CDC | UART Serial |

| Criteria | Arduino IDE | PlatformIO | ESP-IDF |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | High | Medium | Low |
| Flexibility | Medium | High | Very High |
| Compilation Control | Limited | Advanced | Full Control |
| Debugging Capabilities | Basic Serial | Integrated Debugger | Professional JTAG Debugging |
| Best For | Rapid Prototyping | Intermediate/Advanced | Industrial/Advanced IoT |
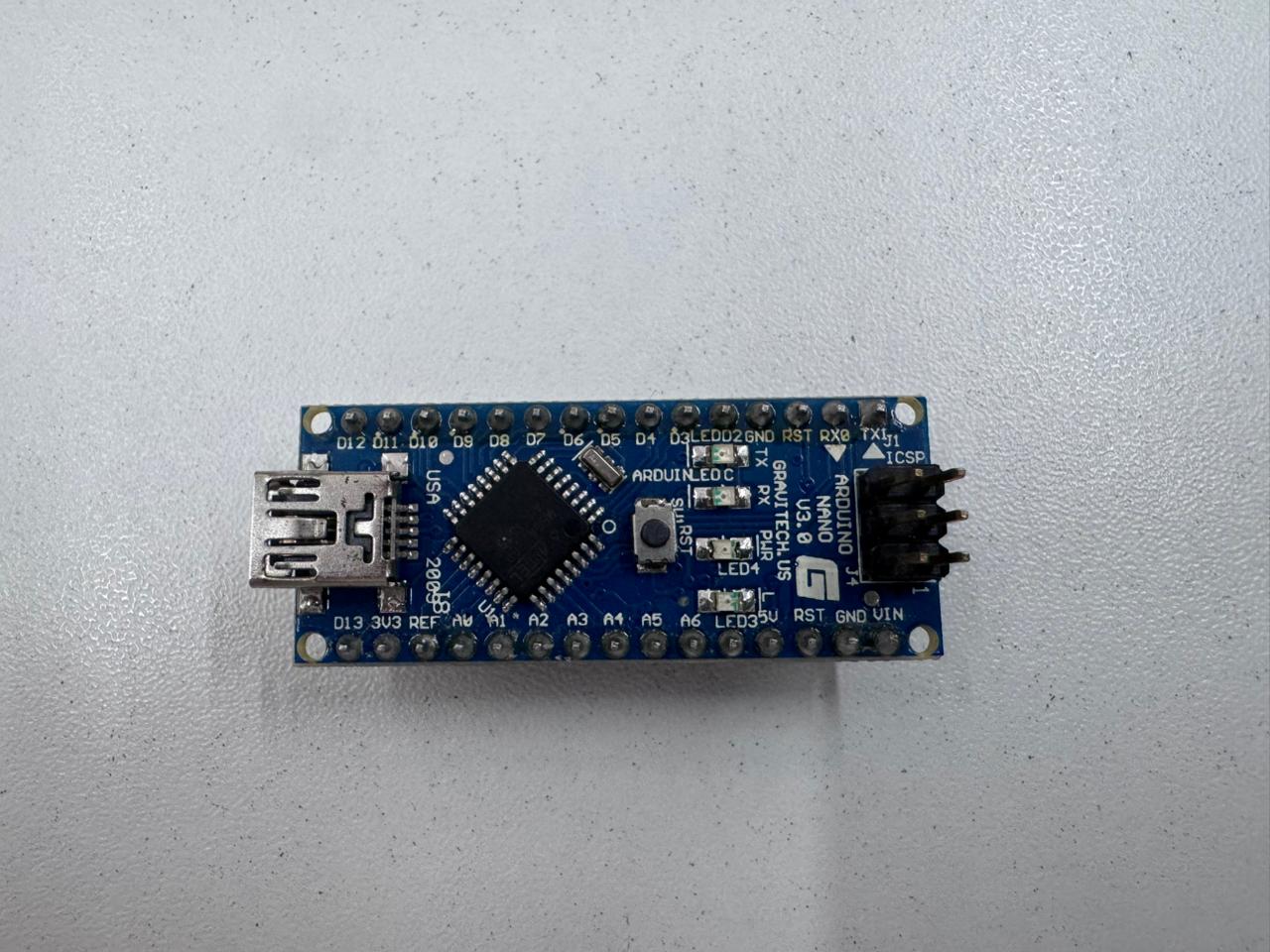
The ESP32 family allows advanced debugging using JTAG and FreeRTOS integration, while the Arduino Nano workflow is simpler but more limited in professional debugging tools.
The datasheet of the ATmega328P (Arduino Nano) and ESP32-S2 was reviewed. Key sections analyzed:
Understanding the datasheet allowed correct configuration of registers, communication interfaces, and peripheral usage.
A program was developed to:
const int buttonPin = 4;
const int ledPin = 2;
void setup() {
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(115200);
}
void loop() {
int buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin);
if (buttonState == LOW) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
Serial.println("Button Pressed - LED ON");
} else {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
Serial.println("Button Released - LED OFF");
}
delay(200);
}
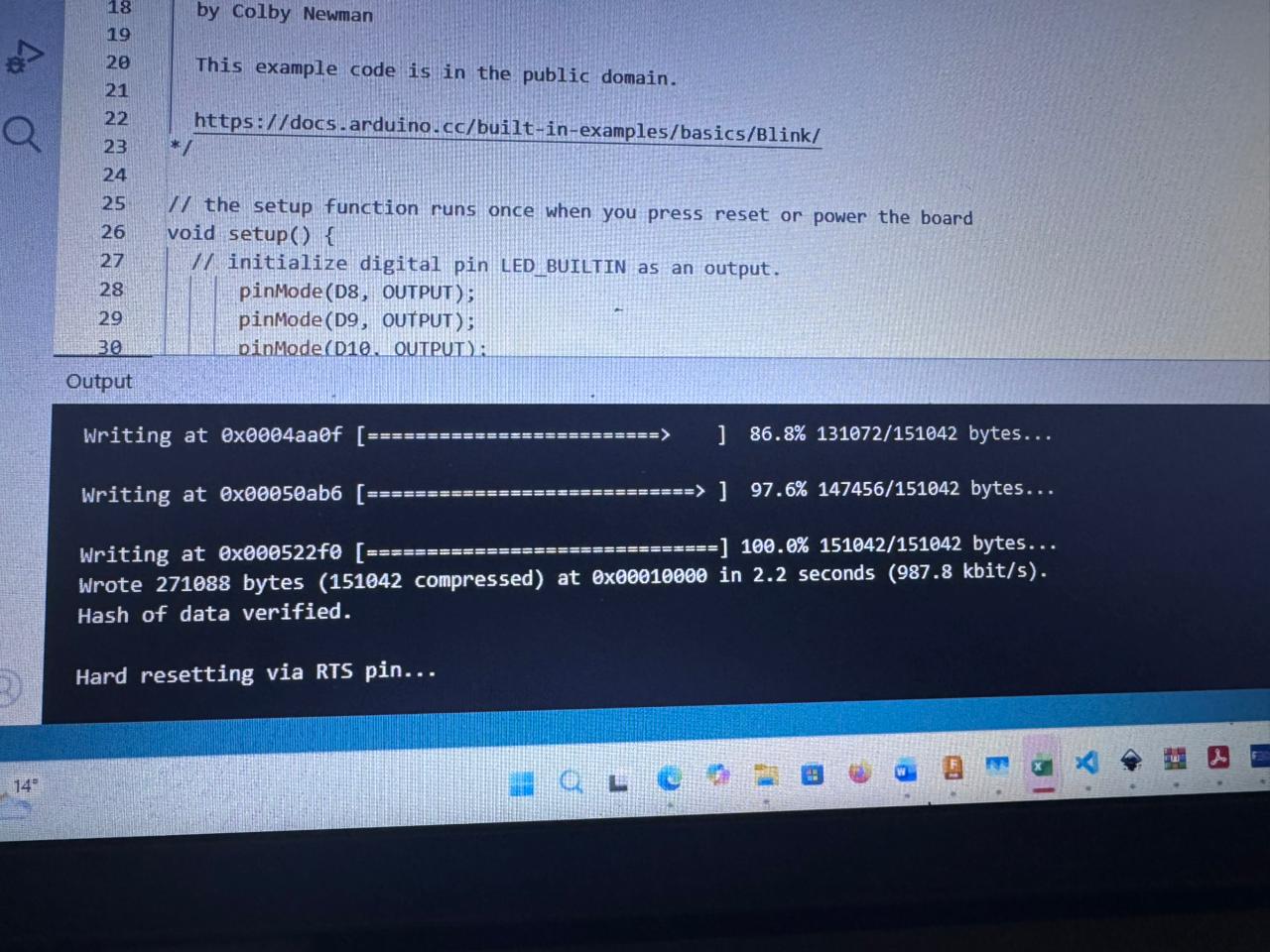
The system successfully interacted with physical input (button), controlled an output (LED), and communicated through USB serial.
Using ESP32 WiFi libraries, the board connected to a local network and transmitted status messages via TCP.
This demonstrates wireless embedded communication capability, which is not available on the Arduino Nano without additional modules.
Go to the official Arduino website and download the latest version for your operating system.
Run the installer and follow the installation wizard:
Tools → Board → ESP32 Arduino → Select "XIAO_ESP32C3"
Go to wokwi.com and create a new ESP32-C3 project.
| Component | Quantity |
|---|---|
| LED Red | 1 |
| LED Yellow | 1 |
| LED Green | 1 |
| Resistors (220Ω) | 3 |
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(D8, OUTPUT);
pinMode(D9, OUTPUT);
pinMode(D10, OUTPUT);
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("Hello, XIAO ESP32-C3!");
Serial.println("Welcome to Wokwi :-)");
}
void loop() {
Serial.println("Red");
digitalWrite(D8, HIGH);
delay(300);
digitalWrite(D8, LOW);
Serial.println("Green");
digitalWrite(D9, HIGH);
delay(300);
digitalWrite(D9, LOW);
Serial.println("Blue");
digitalWrite(D10, HIGH);
delay(600);
digitalWrite(D10, LOW);
}
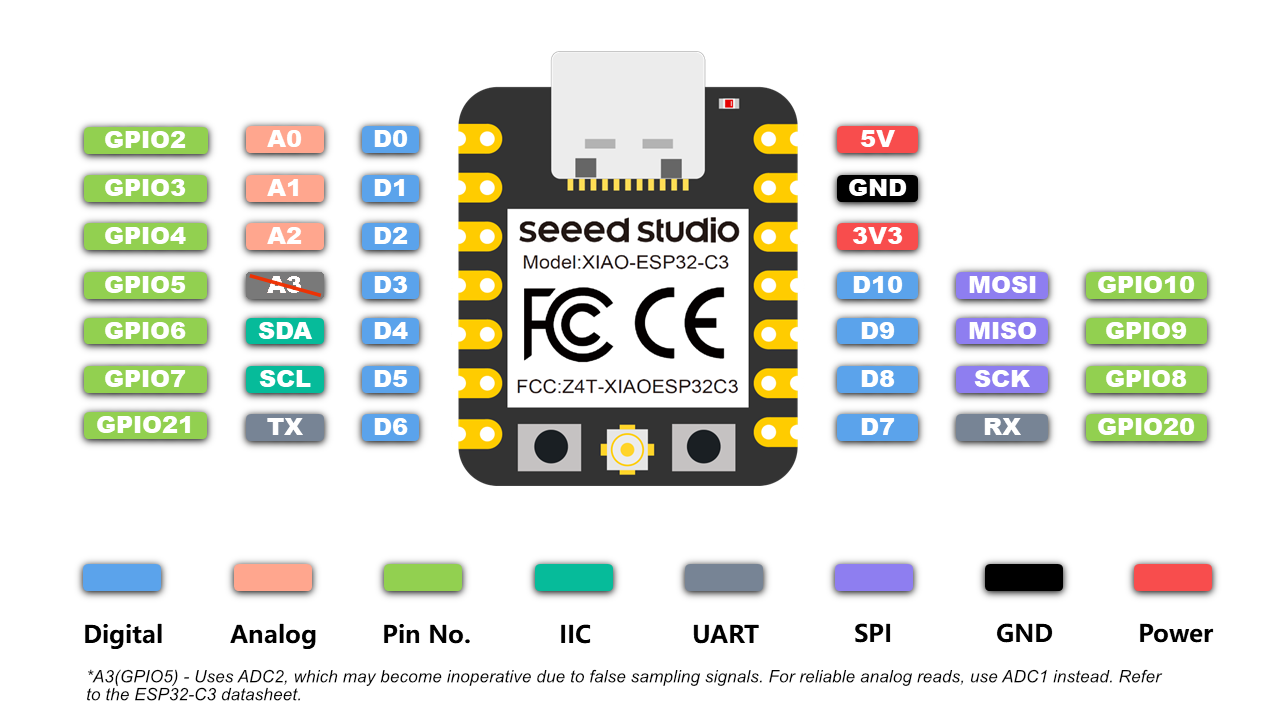
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| XIAO ESP32-C3 | Main microcontroller |
| LEDs | Red (D8), Yellow (D9), Green (D10) |
| Resistors | 220Ω current limiting resistors |
| Protoboard | Assembly platform |
| Jumper Wires | Connections |
This practice demonstrates embedded programming fundamentals including GPIO configuration, serial communication, digital output control, simulation before physical implementation, testing workflow, and debugging.
The workflow followed: Simulation → Code Debugging → Serial Monitoring → Physical Assembly → Final Validation.
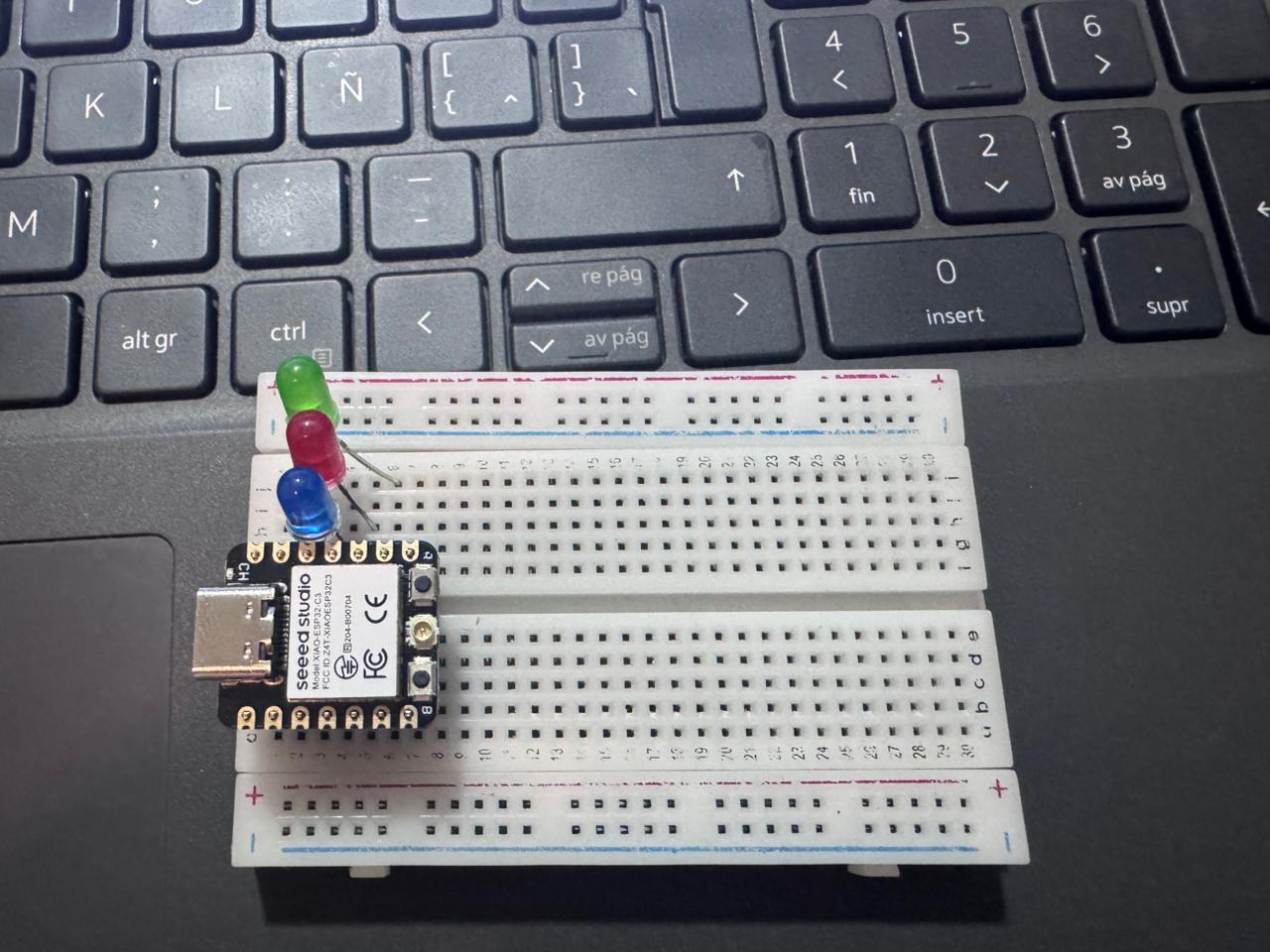
The embedded system was assembled on a breadboard including:
The hardware assembly was tested and validated before final code deployment.
Additional testing was performed using:
Differences observed: