Week 01 — Project Management
Fab Academy 2026 · Jenny Rojas · Industrial FabLab UCuenca
1. Thought Process
Overview and Motivation
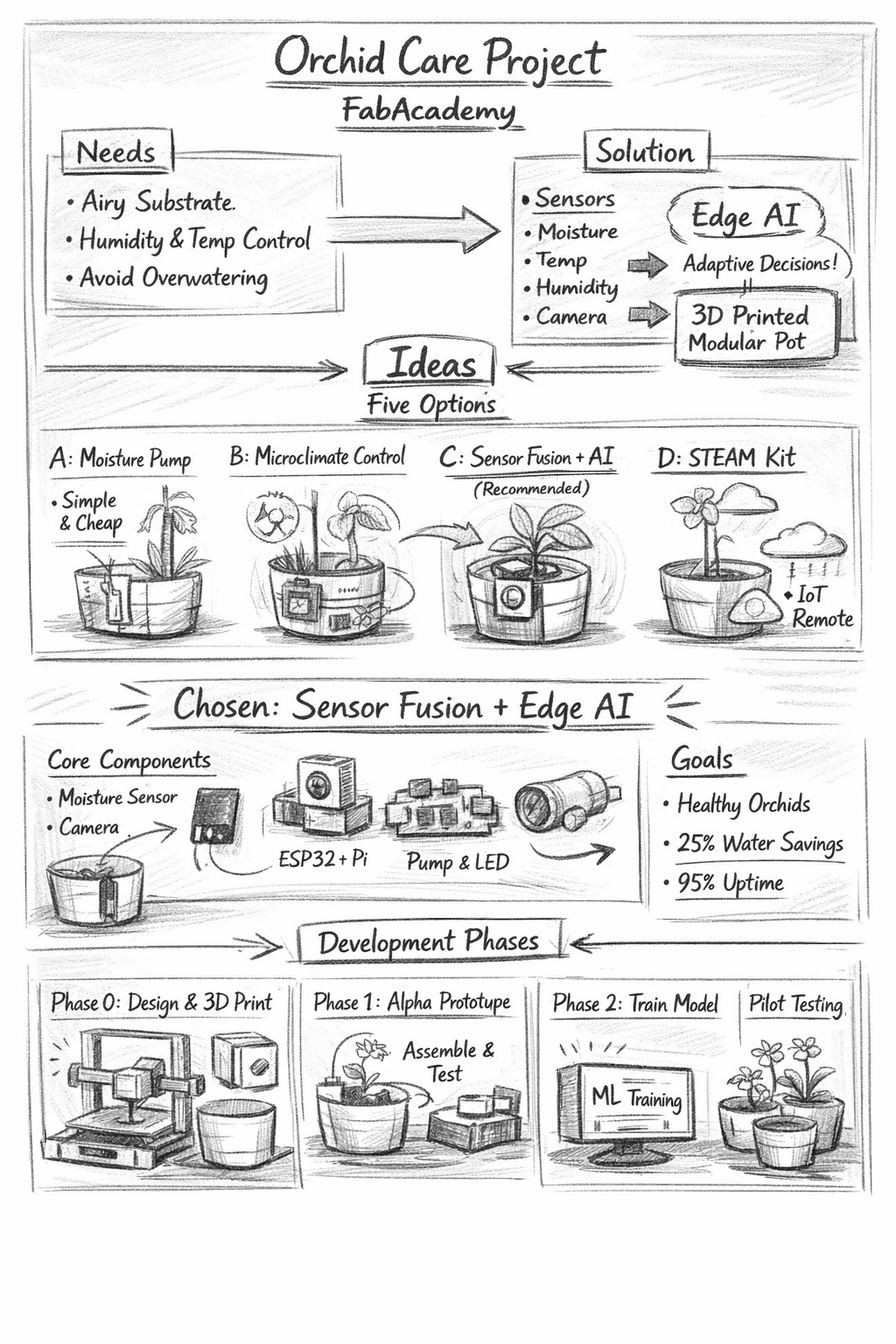
Orchids have specific cultural needs: airy substrates such as bark and sphagnum, high sensitivity to overwatering (which increases root rot risk), and a strong dependence on stable humidity and temperature cycles for healthy growth and flowering.
The central challenge is to provide water in a way that keeps both the substrate and the plant healthy while minimizing water waste and human intervention.
The proposed solution combines multiple data sources — substrate moisture, ambient humidity, temperature, and camera-based visual monitoring — with an AI decision engine that adapts watering volume and timing.
Evidence basis: Research in precision irrigation and IoT shows that sensor-driven systems using machine learning improve water efficiency and plant outcomes. Orchid horticultural guidelines provide target humidity ranges and substrate recommendations.
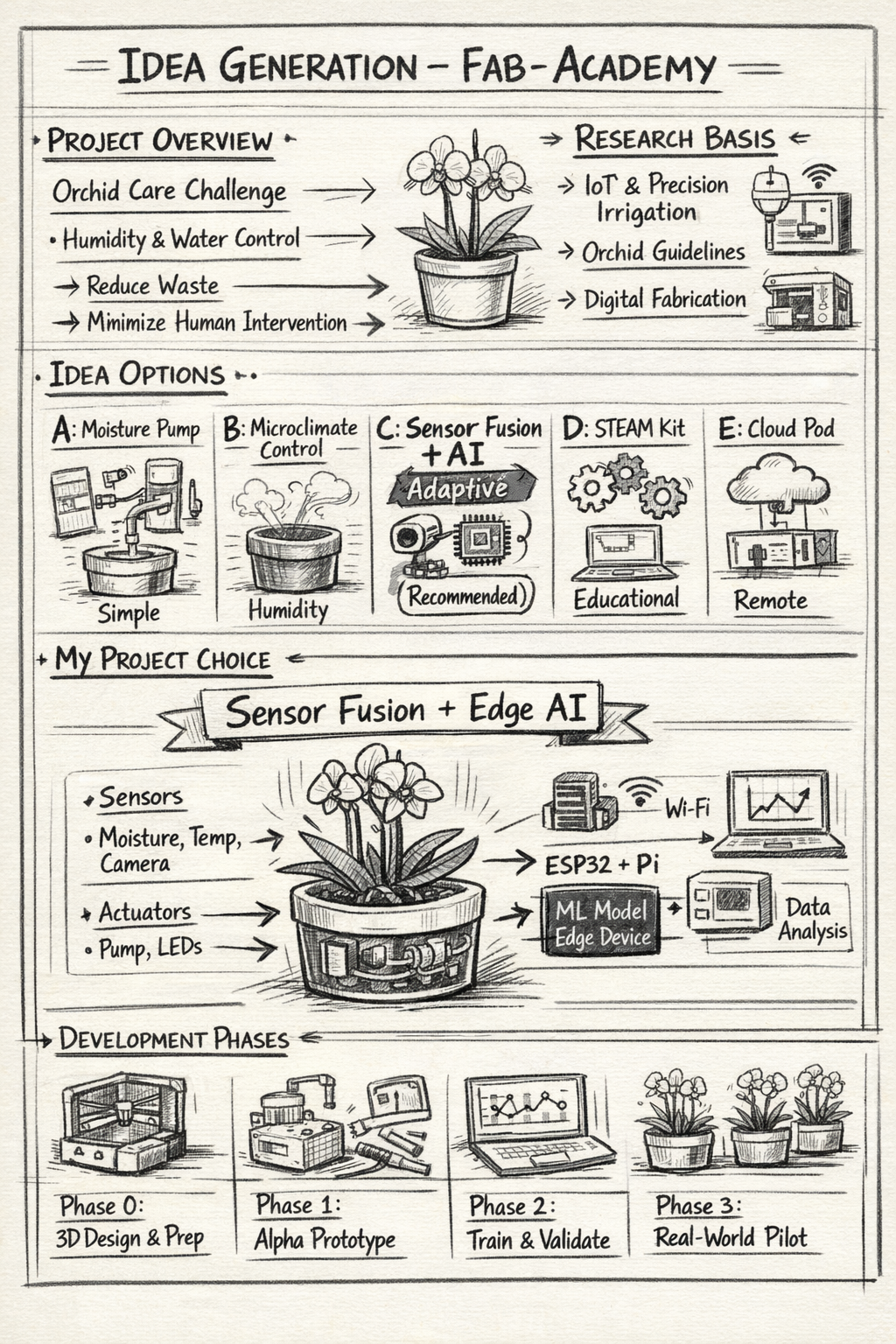
2. Project Ideas Exploration
Option A — Threshold-based Moisture Pump
A simple system where a substrate moisture sensor activates a micro-pump when readings fall below a fixed threshold.
Pros: Low cost, easy to build, fast to prototype.
Cons: Not adaptive; risk of overwatering.
Option B — Microclimate Controller
Controls ambient humidity using a nebulizer and fan, while watering remains manual or semi-assisted.
Pros: Good for epiphytic orchids.
Cons: Higher energy use and complexity.
Option C — Sensor Fusion + Edge AI (Selected)
Combines moisture, humidity, temperature, and camera data processed by a lightweight AI model running on an edge device.
Pros: Adaptive decisions, visual diagnostics.
Cons: Higher hardware and software complexity.
Option D — Educational STEAM Kit
Modular kit designed for classrooms where students assemble and program the system.
Pros: Educational, low cost.
Cons: Not fully autonomous.
Option E — Cloud-connected Commercial Pod
Full system with cloud analytics, dashboards, and predictive maintenance.
Pros: Advanced analytics.
Cons: Cloud dependency and higher cost.
3. Defining My Project
Chosen Option: Sensor Fusion + Edge AI
The goal is to build an autonomous orchid pot that automates watering decisions using fused sensor inputs and visual monitoring.
- Sensors: Capacitive moisture, temperature & humidity, water level, camera
- Actuators: Peristaltic pump, LEDs or buzzer
- Compute: ESP32 + Raspberry Pi or Jetson Nano
- Connectivity: Wi-Fi (MQTT), local storage
- Safety: Low-water lock, emergency stop, watchdog timer
Success criteria: Healthy orchids over a 6-week trial, at least 25% water savings, and system uptime above 95%.
4. Experimentation Plan
- Phase 0: CAD design, 3D printing, sensor calibration
- Phase 1: Alpha prototype and data collection
- Phase 2: ML training and edge inference deployment
- Phase 3: Real-world pilot and comparative analysis
5. Conclusion
Sensor fusion combined with edge AI enables a robust autonomous orchid pot that optimizes water usage, reduces root rot risk, and adapts to environmental variation. Digital fabrication ensures reproducibility and educational impact.
References
- Abioye et al. (2022). Precision irrigation management using machine learning.
- Aydın et al. (2021). AI and IoT for precision irrigation.
- American Orchid Society. Humidity and watering guidelines.
- Penn State Extension (2023). Orchids as houseplants.