Week 02 — Digital Design Tools
Fab Academy 2026 · Jenny Rojas · Industrial FabLab UCuenca
Introduction
During Week 02 of Fab Academy, the focus is on understanding and applying a wide range of digital design tools that support the complete workflow from ideation to fabrication and documentation. As a student, I explored 2D raster and vector software, parametric and non-parametric 3D modeling tools, AI-assisted design platforms, and video documentation software. Each tool was evaluated based on its role within a possible final project and its relevance to Fab Academy requirements.
Software Overview Table
| Category | Type | Software |
|---|---|---|
| 2D | Raster | GIMP |
| 2D | Raster | MyPaint |
| 2D | Vector | Inkscape |
| 2D | Vector | Adobe Illustrator |
| 2D | Vector | CorelDRAW |
| 3D | Program | Tinkercad |
| 3D | Program | Fusion 360 |
| 3D | Program | Blender |
| 3D | AI Software | Text to CAD |
| 3D | AI Software | DALL·E |
| Audio/Video | Video | Audacity |
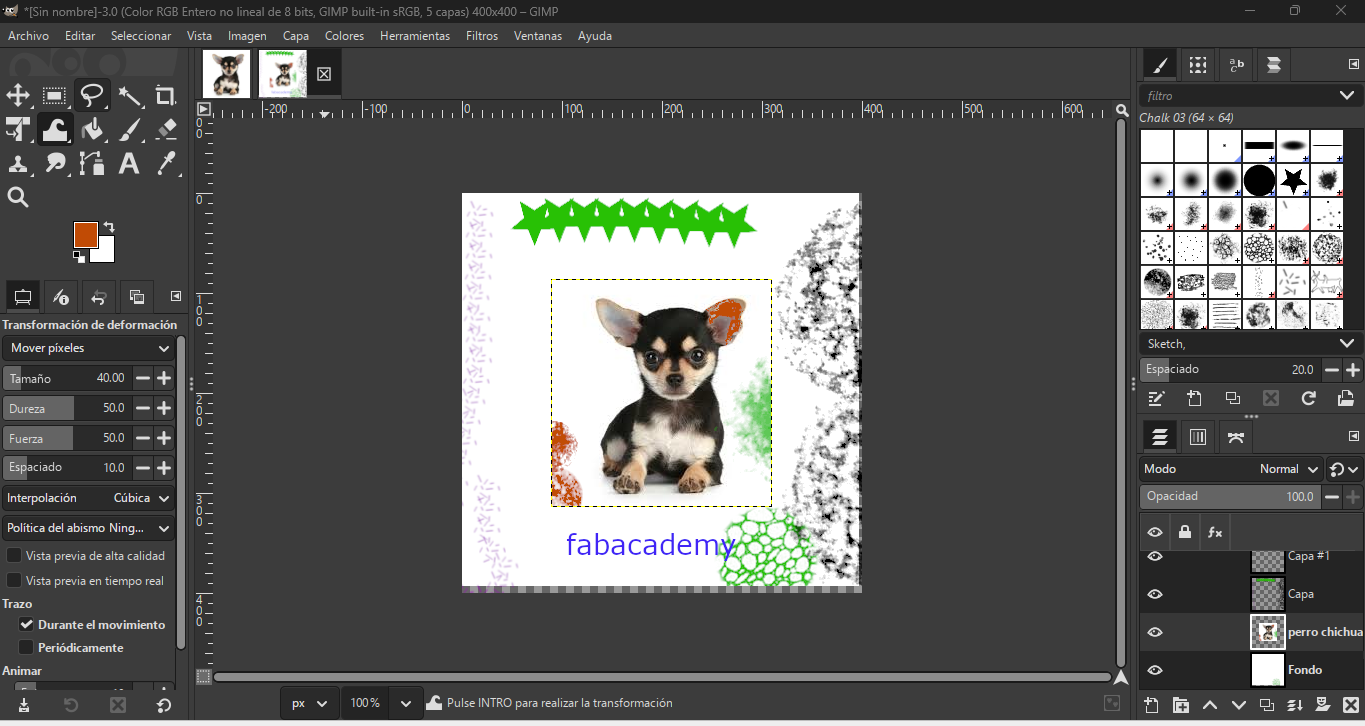
GIMP — 2D Raster Image Editing
GIMP is used extensively for image editing and technical documentation. As a Fab Academy student, I rely on GIMP to process screenshots, annotate fabrication steps, adjust contrast, and compress images for web publication while preserving clarity.
Workflow
- Import raw screenshots from design software.
- Crop unnecessary areas and adjust brightness/contrast.
- Add annotations using text and arrow tools.
- Resize image for web documentation.
- Export as optimized JPG or PNG.
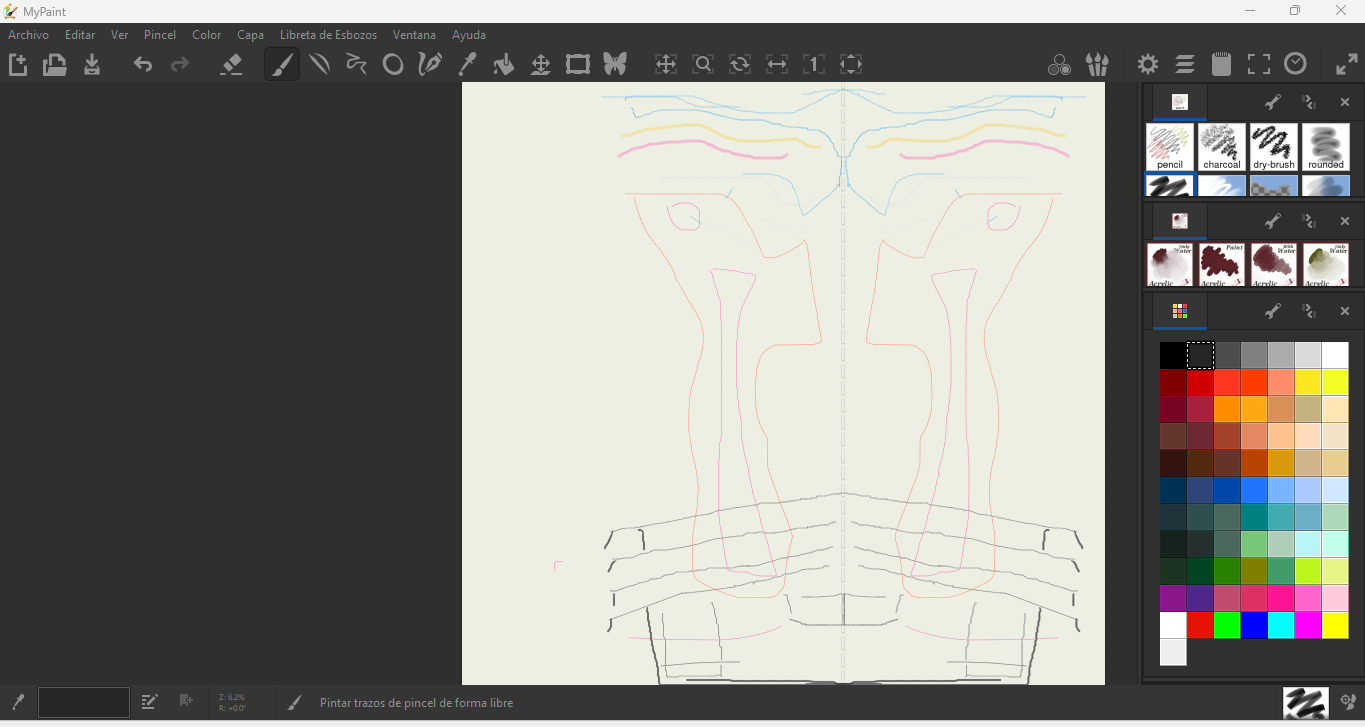
MyPaint — Concept Sketching
MyPaint functions as a digital sketchbook during early ideation. I use it to freely sketch mechanisms, enclosures, and interaction ideas before moving into precise CAD environments.
Workflow
- Create a new canvas with appropriate resolution.
- Select brush type depending on sketch style (pencil, ink, soft brush).
- Draw initial conceptual ideas without dimensional constraints.
- Refine main shapes and interaction elements.
- Export sketch as PNG or JPG for documentation or CAD reference.
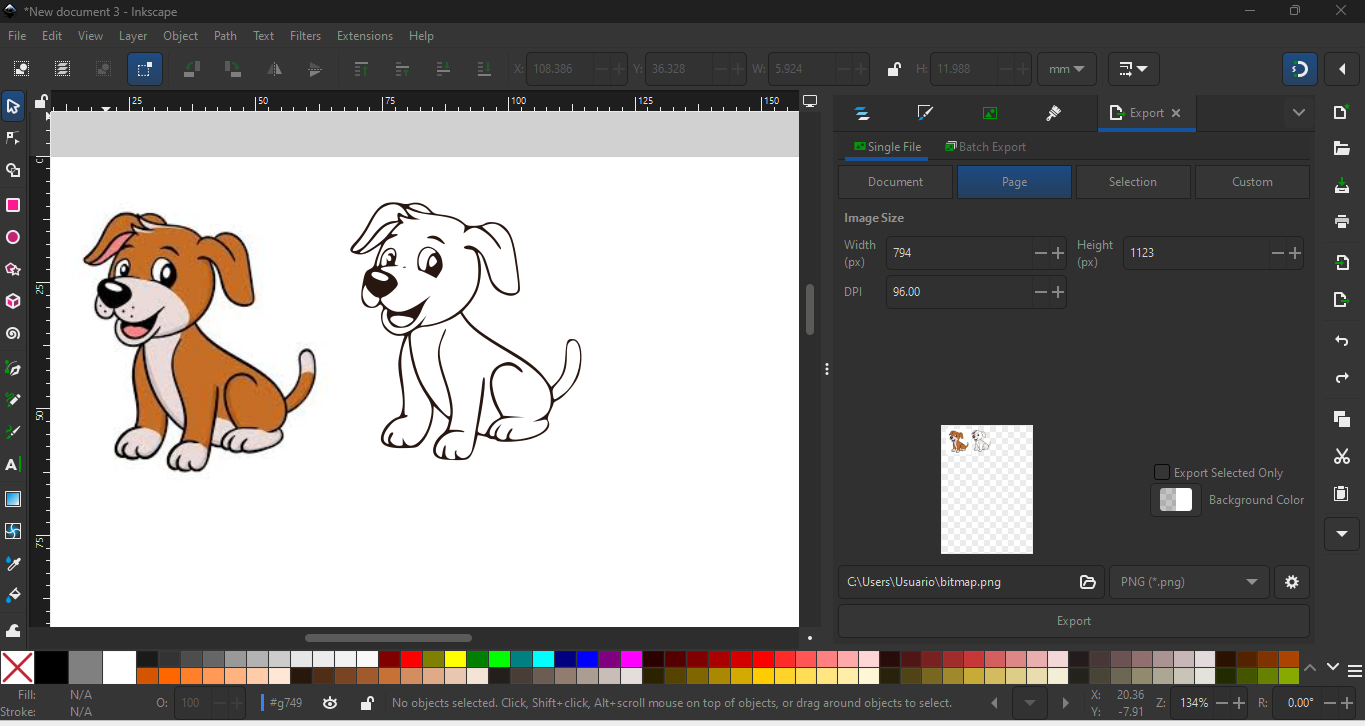
Inkscape — 2D Vector Design
Inkscape is a core Fab Academy tool for producing fabrication-ready vector files for laser cutting and vinyl cutting. I use layers and precise path operations to separate cutting, engraving, and reference geometry.
Workflow
- Create new document with correct dimensions.
- Draw vector geometry using path tools.
- Apply stroke colors for cut/engrave separation.
- Organize layers for fabrication clarity.
- Export as SVG or DXF for CAM use.
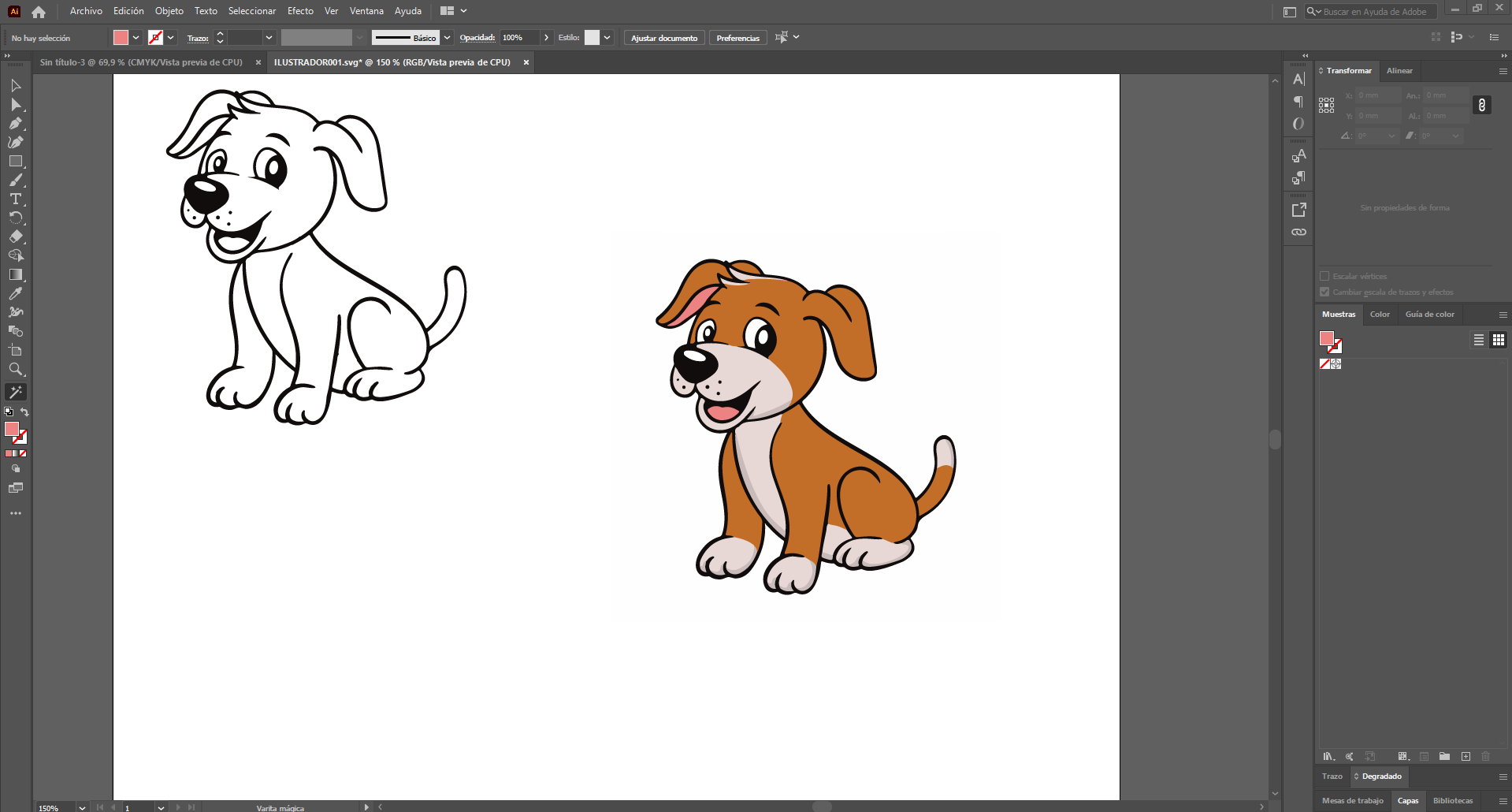
Adobe Illustrator — Visual Communication
Illustrator is mainly used for graphic layout, diagrams, and visual assets that support technical documentation. It enhances clarity and presentation quality.
Workflow
- Create new document with defined artboard size.
- Import vector or raster reference images.
- Use pen tool and shape tools to create diagrams.
- Apply consistent typography and color palette.
- Export final layout as PDF, SVG, or PNG for web.
CorelDRAW — CAM Vector Preparation
CorelDRAW is used for preparing CAM-ready files, particularly for laser cutting workflows commonly found in Fab Labs.
Workflow
- Import or create vector design.
- Convert objects to curves.
- Adjust line thickness to hairline (laser requirement).
- Assign color coding for cut and engrave operations.
- Export file in DXF, AI, or directly send to laser software.
Tinkercad — Introductory 3D Modeling
Tinkercad is used for quick parametric modeling and early prototyping of simple parts such as holders and enclosures.
Workflow
- Create new design project.
- Drag basic shapes into workspace.
- Adjust dimensions numerically.
- Group shapes to form final geometry.
- Export STL file.
Fusion 360 — Parametric CAD
Fusion 360 is the primary tool for parametric and mechanical design. I document sketches, constraints, and modeling steps to ensure reproducibility.
Workflow
- Create parametric sketch with constraints.
- Define dimensions and relationships.
- Extrude or revolve geometry.
- Apply fillets and chamfers.
- Export STL or STEP file for fabrication.
Blender — Organic Modeling
Blender is used for freeform and organic shapes, especially when aesthetic or ergonomic considerations are dominant.
Workflow
- Create base mesh primitive.
- Switch to sculpt mode for organic shaping.
- Refine topology using modifiers.
- Apply materials for visualization.
- Export STL or OBJ file.
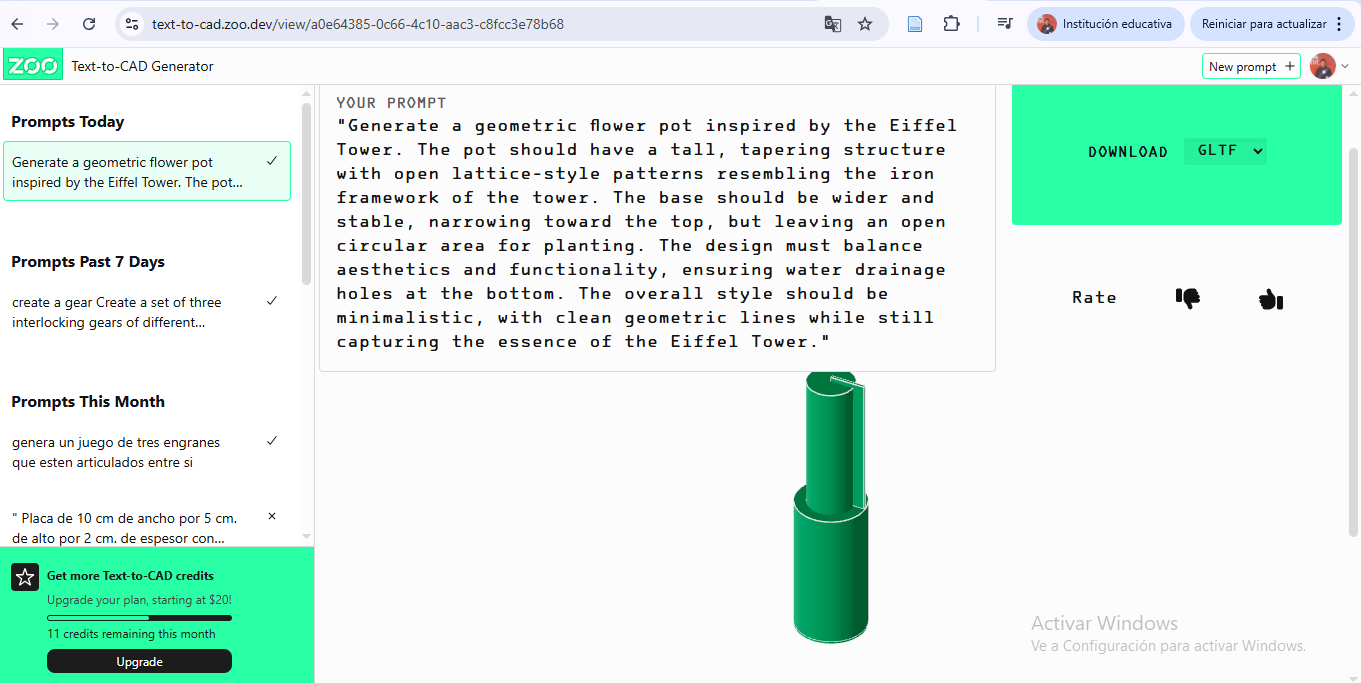
Text to CAD — AI Assisted Modeling
Text to CAD tools are explored for conceptual modeling and rapid idea generation using natural language descriptions.
Workflow
- Write detailed prompt describing object dimensions and purpose.
- Generate CAD proposal automatically.
- Review generated geometry for accuracy.
- Export editable CAD file (STEP or STL).
- Refine model manually in parametric CAD software if needed.
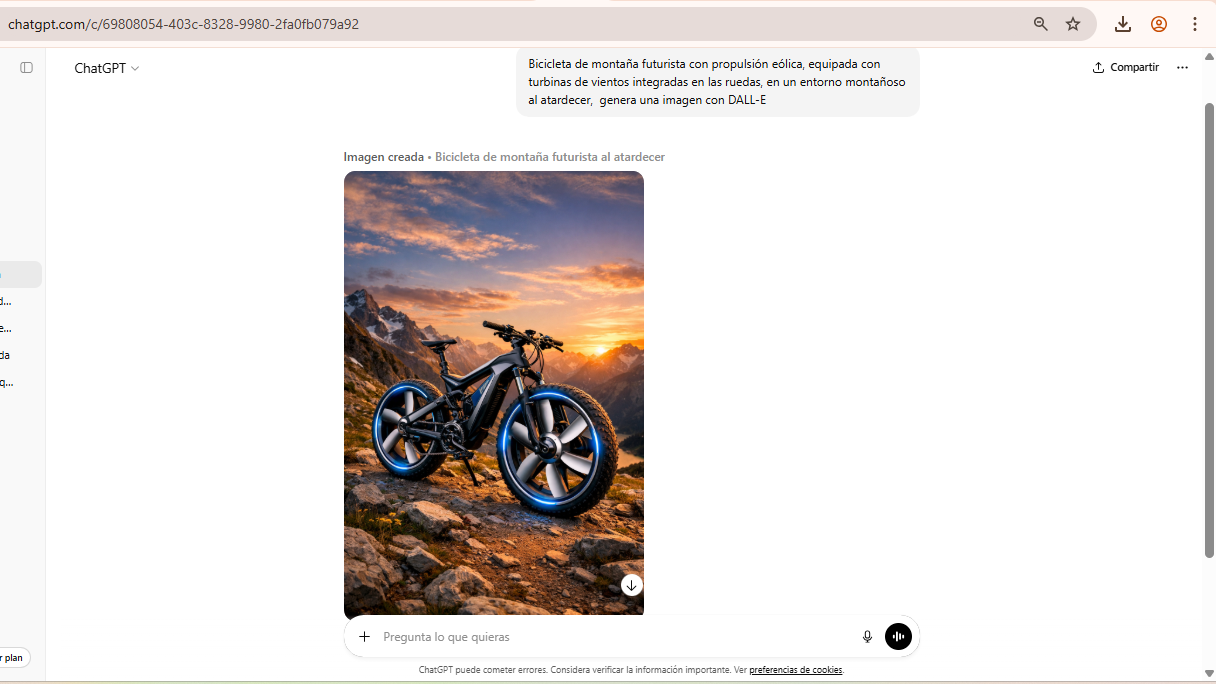
DALL·E — AI Concept Visualization
DALL·E is used to generate conceptual reference images that support early design decisions and aesthetic exploration.
Workflow
- Write detailed prompt describing concept.
- Generate multiple image variations.
- Select best visual direction.
- Refine prompt for improved detail.
- Download final reference image.
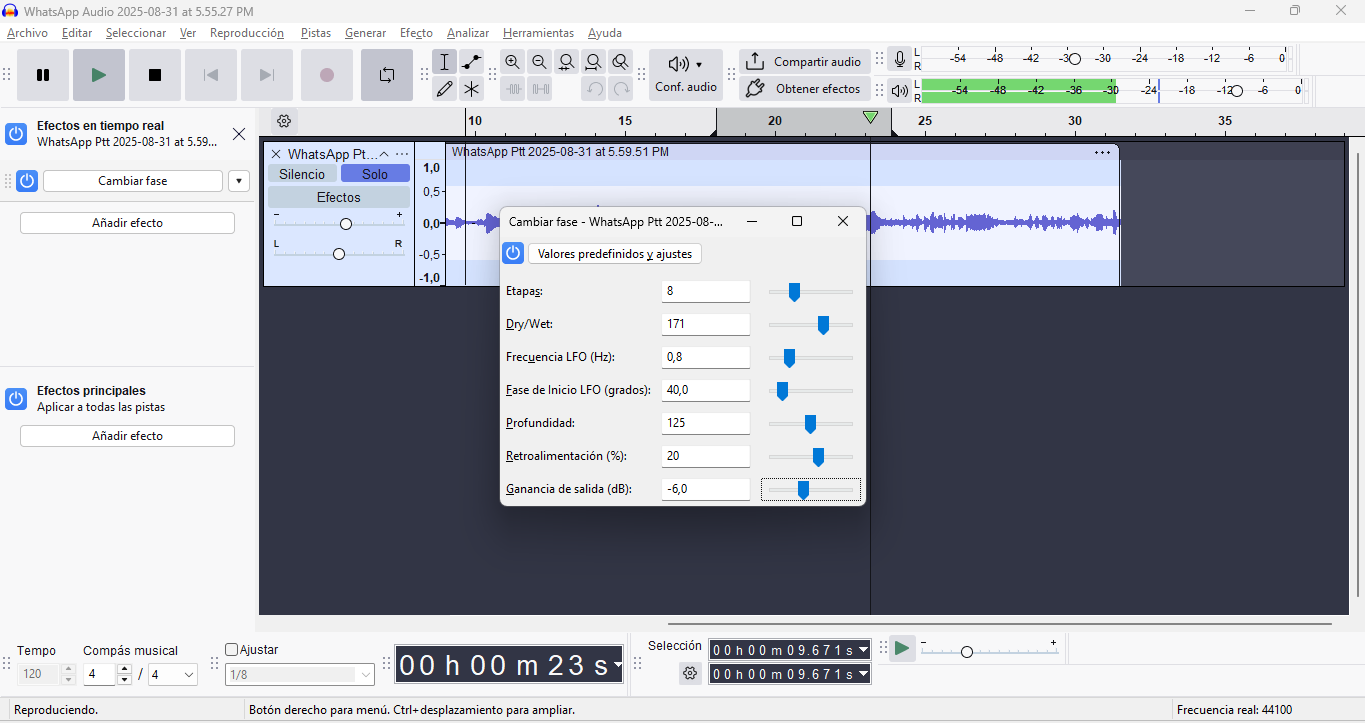
Audacity — Video Documentation
Audacity is the go-to open-source audio editor for recording, refining, and post-producing documentation videos, ensuring compliance with Fab Academy's publishing standards.
Workflow
- Record narration using microphone.
- Remove background noise.
- Trim silence and adjust levels.
- Apply compression and normalization.
- Export as MP3 or WAV.
Comparative Analysis of Digital Design Tools
The following table compares all the software tools explored during this week based on criteria relevant to Fab Academy workflows. The evaluation reflects my experience as a student and focuses on practical usability rather than theoretical capability.
| Software | Ease of Use | Accessibility | Cost | Compatibility | Collaborative Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GIMP | Medium | High | High | High | Low |
| MyPaint | High | High | High | Medium | Low |
| Inkscape | Medium | High | High | High | Low |
| Adobe Illustrator | Medium | Medium | Low | High | Low |
| CorelDRAW | Medium | Medium | Low | High | Low |
| Tinkercad | High | High | High | Medium | Medium |
| Fusion 360 | Medium | Medium | Medium | High | Medium |
| Blender | Low | High | High | High | Low |
| Text to CAD | High | Medium | Medium | Low | Low |
| DALL·E | High | Medium | Low | Low | Low |
| Audacity | Low | Low | Low | High | Low |
Image Compression Workflow
Image compression is a critical requirement in Fab Academy documentation to ensure fast website loading times while maintaining sufficient visual clarity for evaluation. For this purpose, I selected an online tool that balances quality, accessibility, and ease of use.
Selected Tool: Squoosh
Squoosh is a web-based image compression tool developed by Google. It is particularly suitable for Fab Academy students because it is free, does not require account creation, and runs entirely in the browser.
Compression Procedure
- Capture screenshots or export images from design software at full resolution.
- Open the Squoosh web application in a browser.
- Upload the image by dragging it into the interface.
- Select an appropriate format (PNG for diagrams, JPG for photos).
- Adjust the quality slider until visual clarity is preserved.
- Preview the compressed result and verify readability.
- Download the optimized image and place it in
images/w02/.
Result: This workflow significantly reduces file size while maintaining documentation quality, ensuring compliance with Fab Academy web guidelines.
Fab Academy Checklist
- ✔ Modelled experimental objects and parts of a possible final project in 2D and 3D
- ✔ Explained the process using text, images, and screenshots
- ✔ Documented image and video compression
- ✔ Included original design source files