Assignments
Week 3 – Computer-Controlled Cutting
Assignment
Group assignment
- Do your lab's safety training
-
Characterize your laser cutter:
- Focus
- Power
- Speed
- Rate
- Kerf
- Joint clearance
- Joint types
Individual assignment
- Cut something on the vinyl cutter
- Design, laser cut, and document a parametric construction kit, accounting for the laser cutter kerf
- Extra credit: Design it to be assembled in multiple ways
- Extra credit: Include elements that aren't flat
- Extra credit: Engrave as well as cut
What is a CNC Machine?
A CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine is a computer-controlled tool that performs precise movements based on a digital design. Depending on the tool or manufacturing process used, a CNC machine can perform different tasks.
For example, a CNC machine can work as:
-
3D printer, by depositing material layer by layer

-
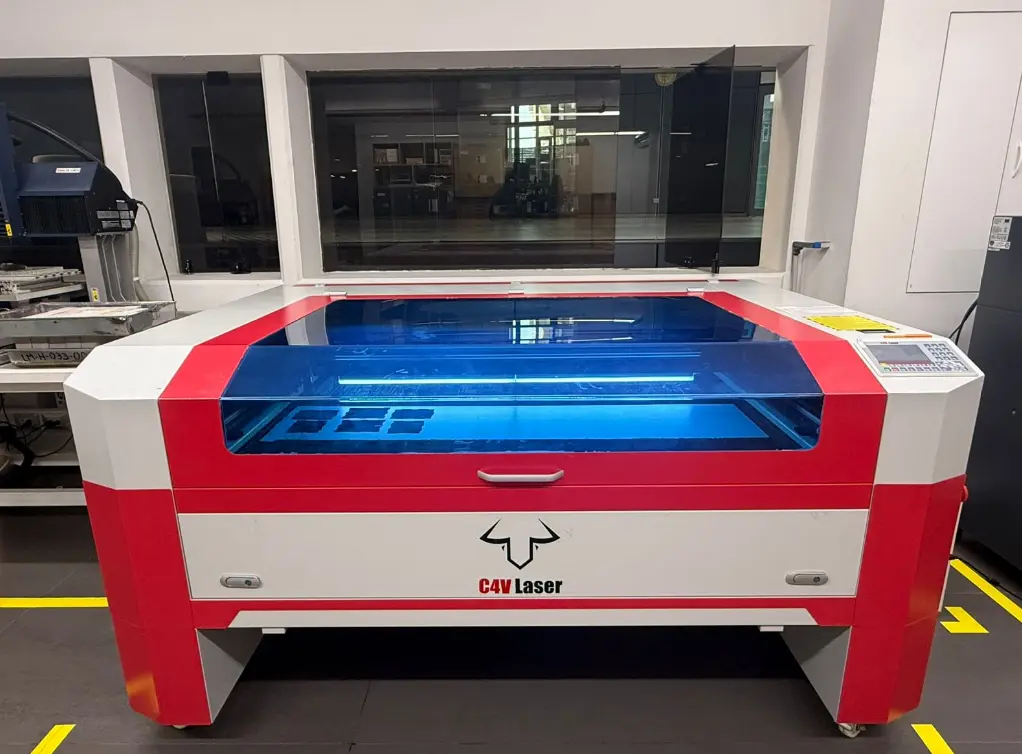
Laser cutter, by cutting material using a laser beam

-
Vinyl cutter, for thin and flexible materials

In all cases, the machine follows instructions generated from CAD/CAM software.
CNC Laser Cutter

The CNC laser cutter uses a CO₂ laser to cut and engrave materials such as MDF, acrylic, and cardboard. The laser follows vector paths generated from digital files, allowing high precision and clean cuts.
Fume Extraction System
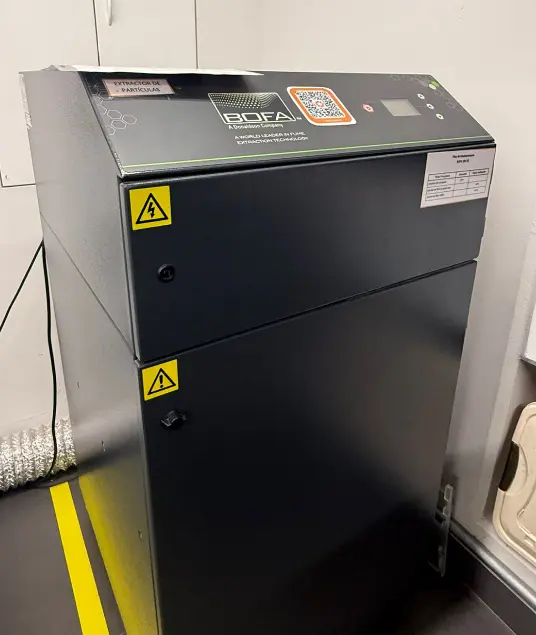

The fume extraction system removes smoke, gases, and particles produced during the laser cutting process. It is essential for maintaining a safe working environment and protecting both the user and the machine.
Water Chiller
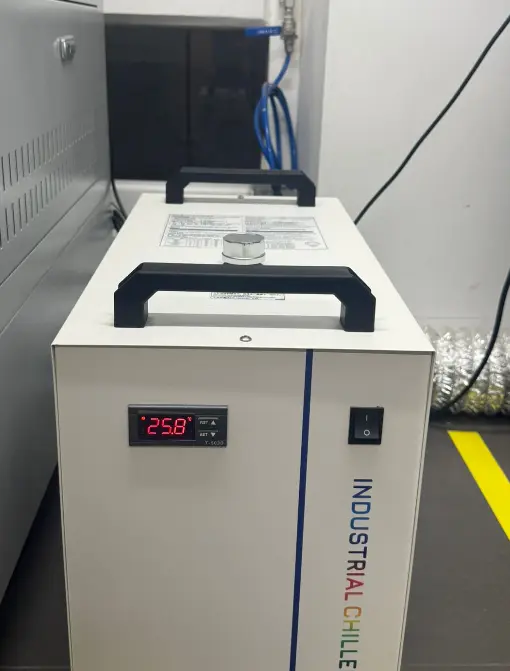

The water chiller is used to cool the laser tube while the machine is operating. It circulates cooled water to prevent overheating, ensure stable laser performance, and extend the lifespan of the laser system.
Compressed Air (Air Assist)
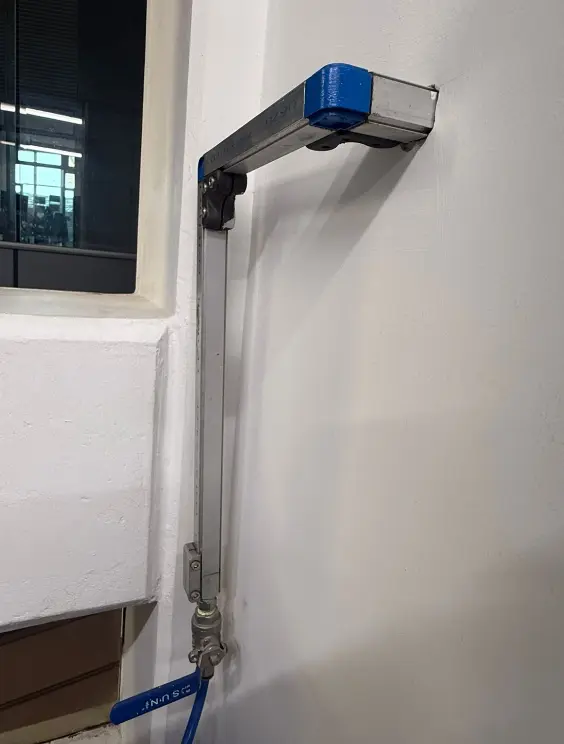

The laser cutter includes a compressed air system (air assist) that runs while cutting. This airflow helps prevent excessive burning and reduces the risk of fire inside the cutting area. The air blows directly onto the cut line to reduce charring and protect the machine during operation.
Safety Buttons
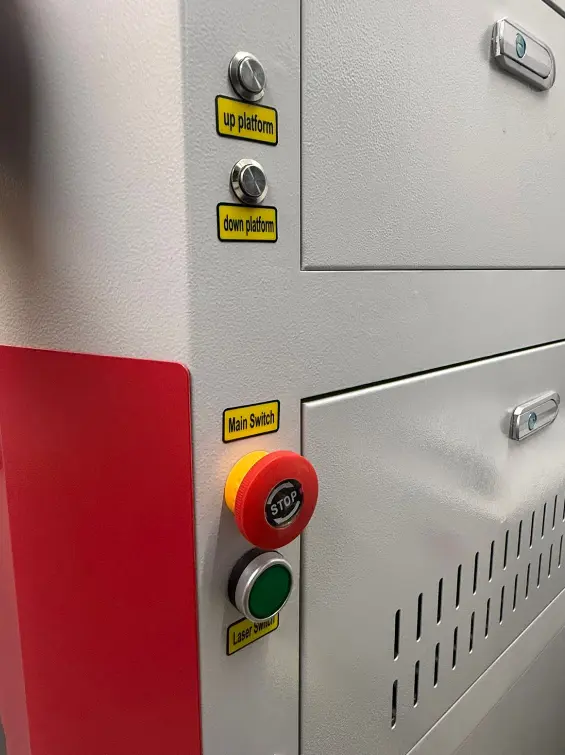

The UP and DOWN buttons raise or lower the cutting bed, allowing proper focus depending on material thickness. The main switch works as an emergency power control. The laser switch enables or disables the laser during setup and operation.
Group Assignment – Laser Engraving Test
Initial Design Preparation
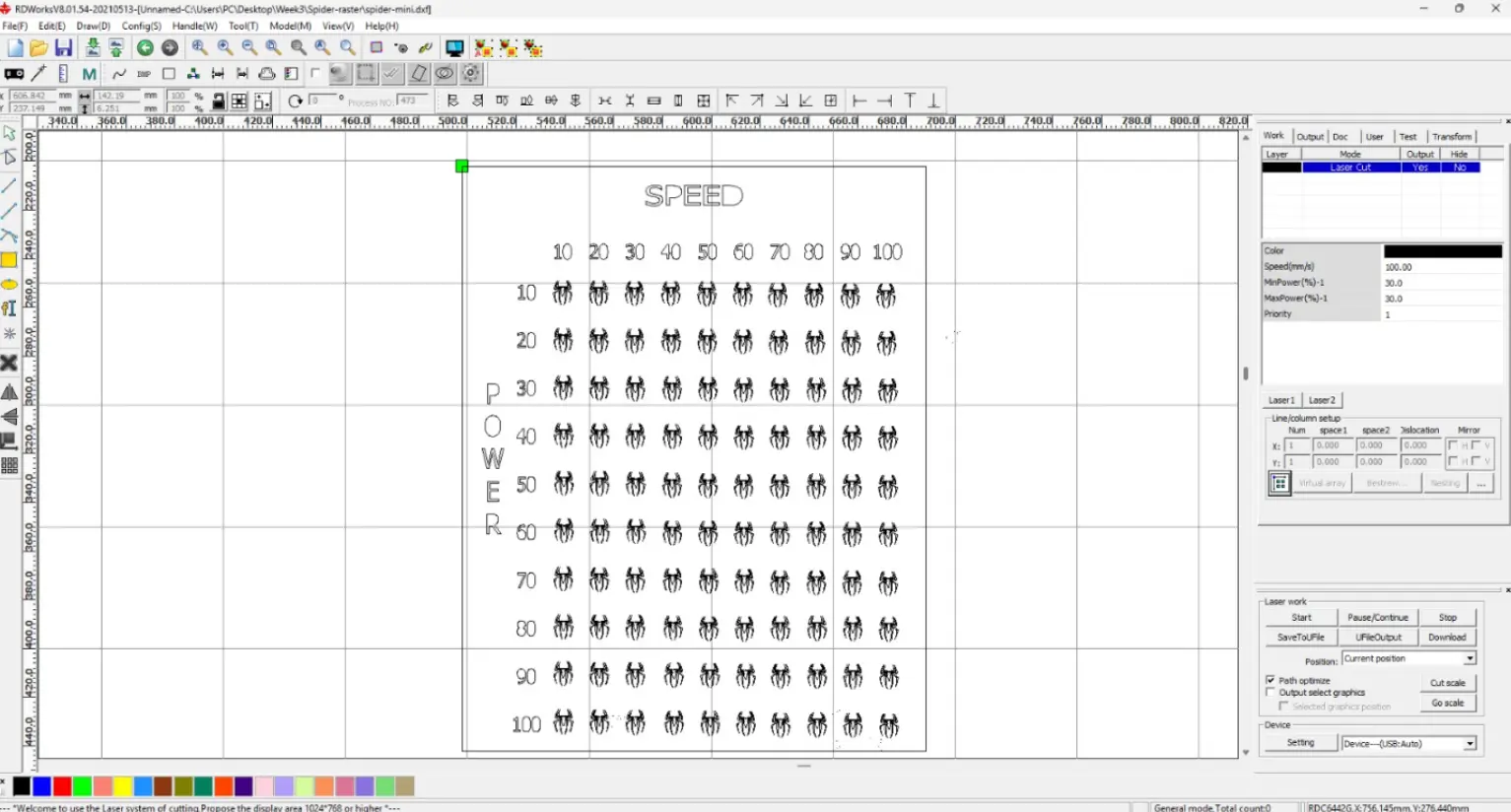
We prepared a small engraving test file to evaluate how different laser parameters affect the material. The design included multiple small figures arranged in a grid.
Parameter Variation Strategy
Each row and column of the design was assigned a different parameter. This allowed us to compare variations in engraving quality. The main variables tested were Speed and Power.
Color-Based Parameter Control
Different colors were assigned to the design elements. In the laser software, each color corresponds to specific speed and power settings. This allows multiple engraving configurations in a single job.
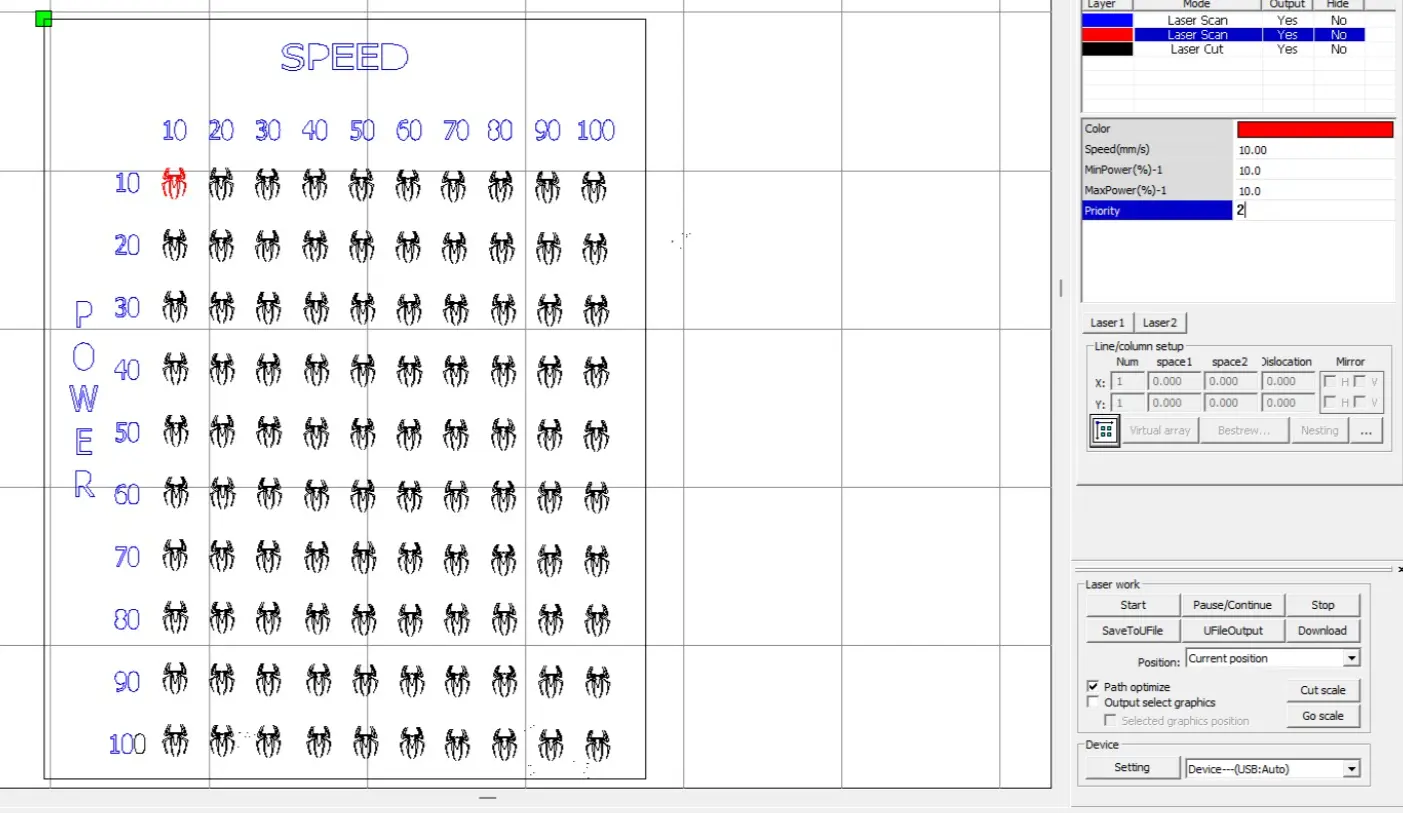
Laser Testing Process
After configuring the parameters, we executed the engraving test. Some low power values were not strong enough to produce visible engraving. The minimum effective power for our setup was identified through testing.
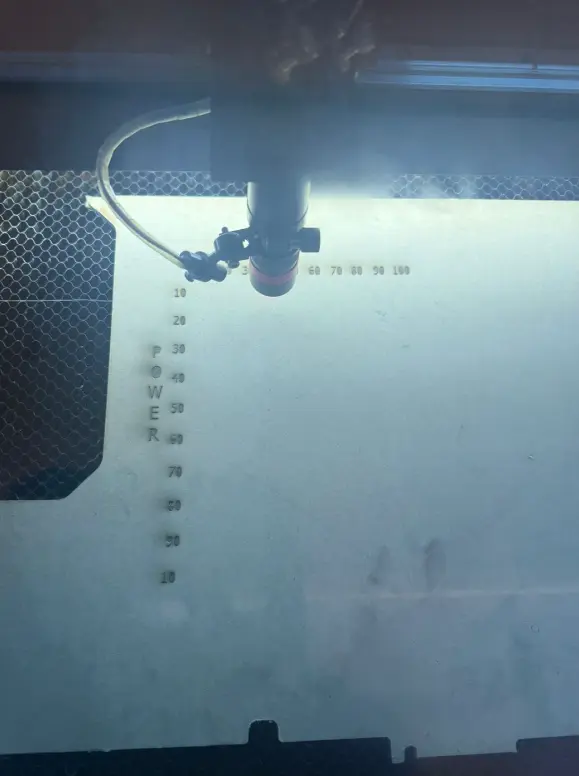
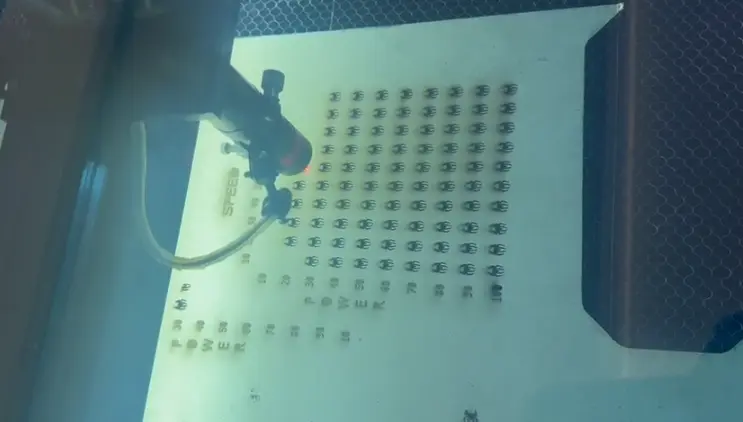
Final Result
The final engraved sample shows a clear comparison between speed and power variations. Higher power values produced darker engravings, while higher speed values reduced engraving intensity. This test helps define optimal settings for future projects.

Individual Assignment
Vectorizing an Image in Inkscape (Trace Bitmap)
I vectorized an image using Inkscape to transform a raster graphic into an editable vector. This is useful for digital fabrication because vectors keep clean edges and can be scaled without losing quality.
For this test, I tried different Trace Bitmap options to compare results and choose the cleanest output.

Workflow
- Import the image in Inkscape: File → Import.
- Open the vectorization tool: Path → Trace Bitmap.
- Choose the tracing method depending on the image (e.g., Single scan for silhouettes).
- Click Apply to generate a vector path.
- Compare and clean the vector, then delete the raster if needed.

More Vector Experiments
I tested different Spider-Man styles to see how vectorization behaves with various levels of detail and contrast. Each design produced a different tracing result.
Spider Symbol
Strong silhouette = clean vector result, ready for laser cutting.
Spider-Sense Effect
Thin lines and motion details helped evaluate how small strokes are captured.
Spider-Man with Headphones
More complex design; some node cleanup was needed but the result looked great.
.webp)
Spider-Man with Camera
Shading and small details required testing different settings to get the best result.
Vinyl Cutting
Exporting the File
Once the vector design was ready in Inkscape, I exported it as a DXF so it could be opened in Silhouette Studio.
Scaling the Design
After importing, the design was too large. I selected all vectors and scaled them to the desired dimensions while keeping proportions.
Machine Setup
The cutter was detected by the software. I adjusted blade depth, pressure, speed, and passes according to the material.
Preparing the Cutting Mat
I placed the adhesive vinyl on the cutting mat and pressed it firmly to avoid movement during cutting.

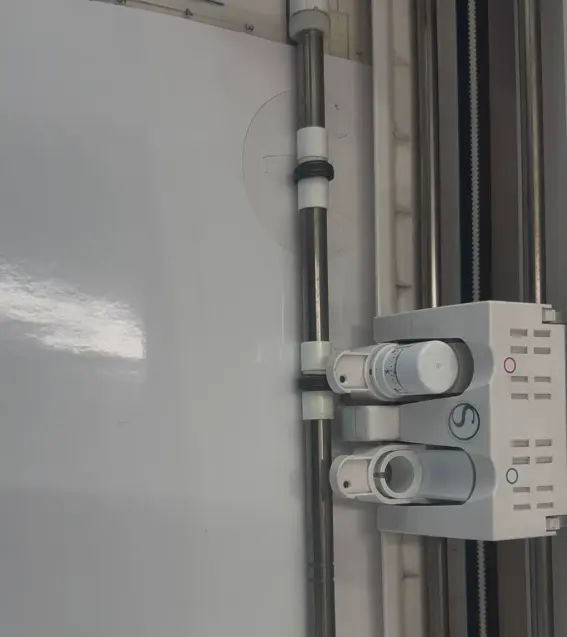
Sending the File to the Cutter
Once the material was ready, I sent the file to the cutter and the machine followed the vector paths.

Applying Transfer Tape
Transfer tape was applied on top of the vinyl to keep all parts aligned for placement.

Removing the Excess Material
I removed the excess vinyl carefully, especially small pieces, to avoid damaging the design.

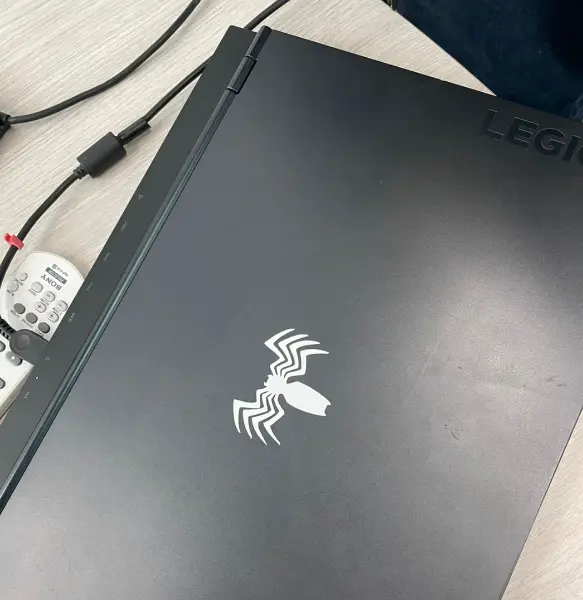
Final Application
Finally, the vinyl design was applied to a laptop surface.

Parametric Polygon Design
At first, I assumed that a parametric design should be created directly as a solid. However, this approach is not suitable when the main goal is to modify the number of sides. For this reason, the entire design was developed at the sketch level.
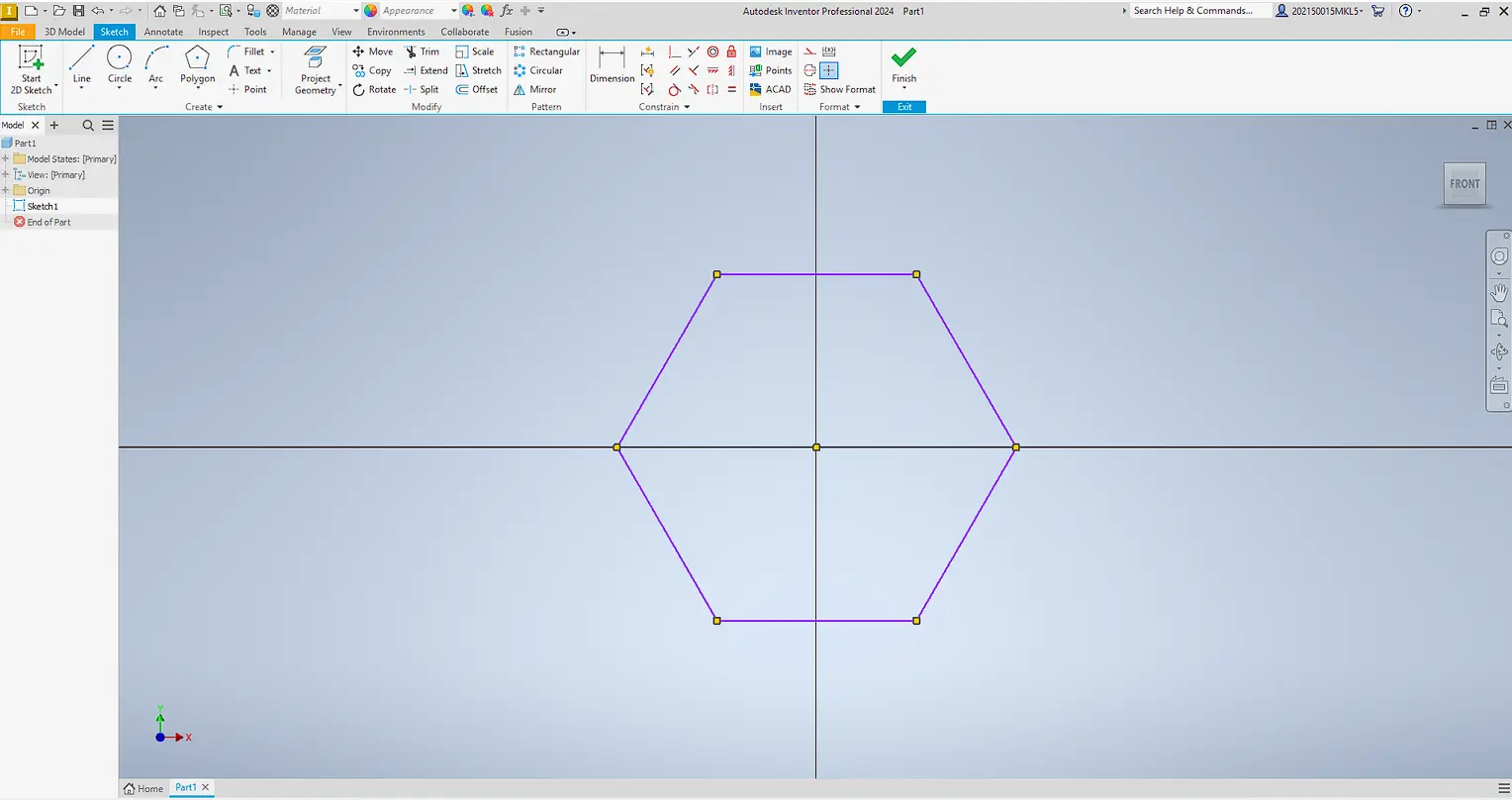
Instead of drawing the complete polygon, only one side of the geometry was modeled as a base module. By fully constraining this side, the polygon can be generated without redrawing geometry.
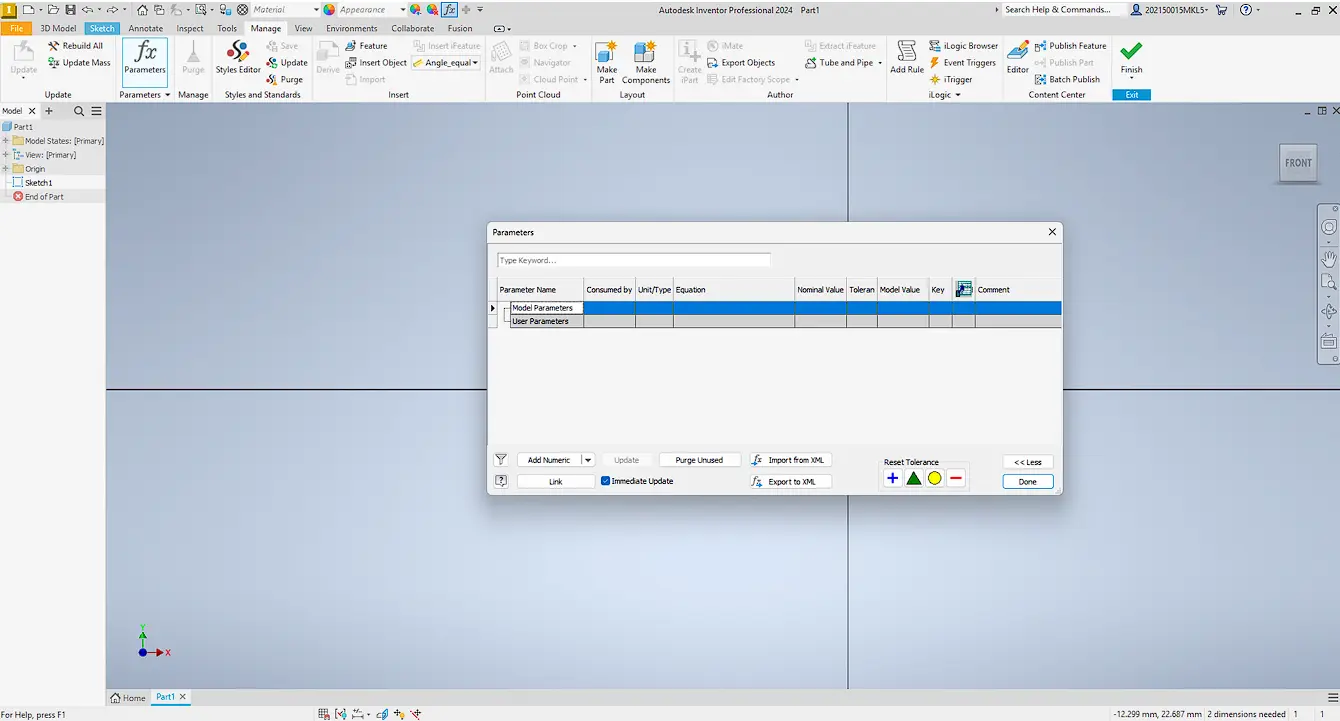
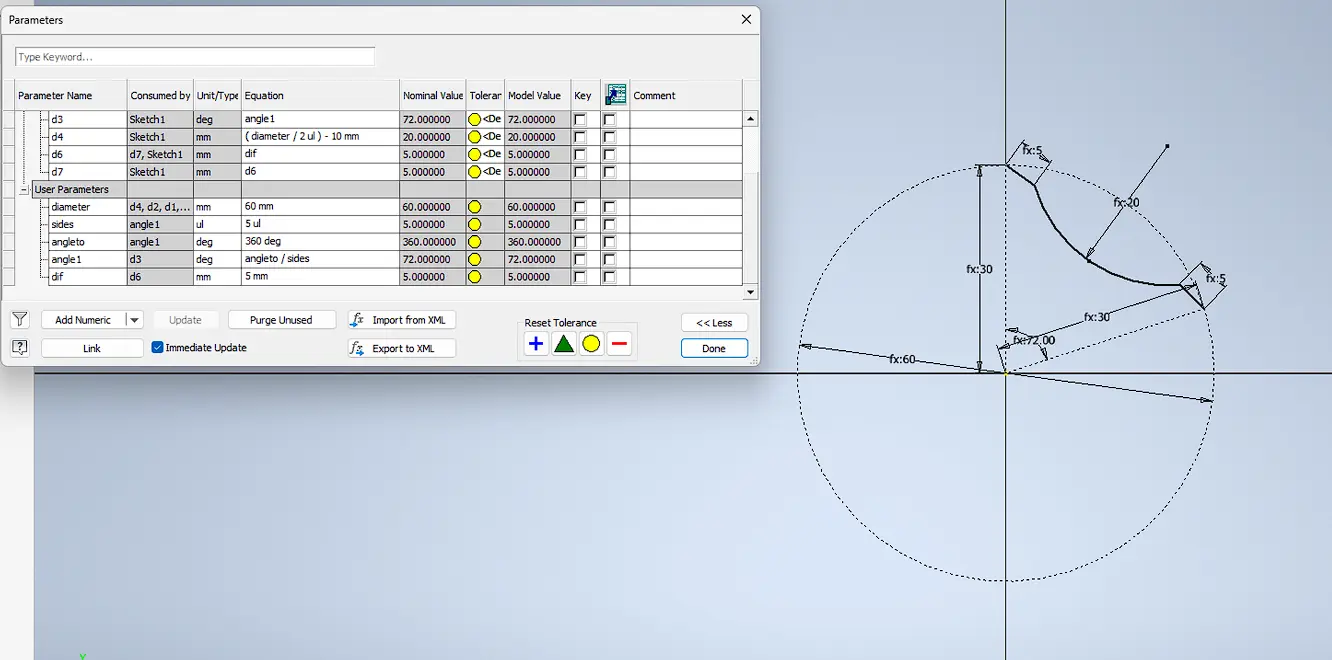
To control size, user parameters were created to define key dimensions and keep the sketch consistent.
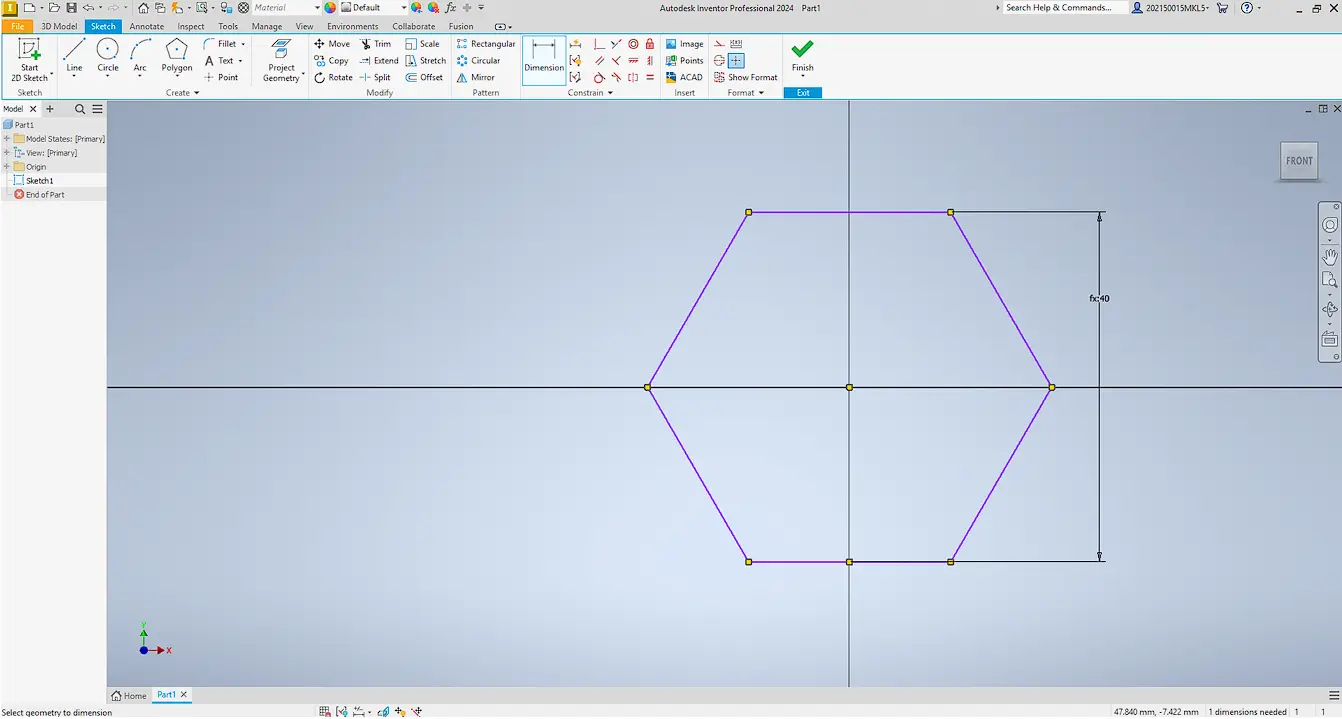
A construction line was added as a reference axis, and the angle was defined with: 360° / number of sides.
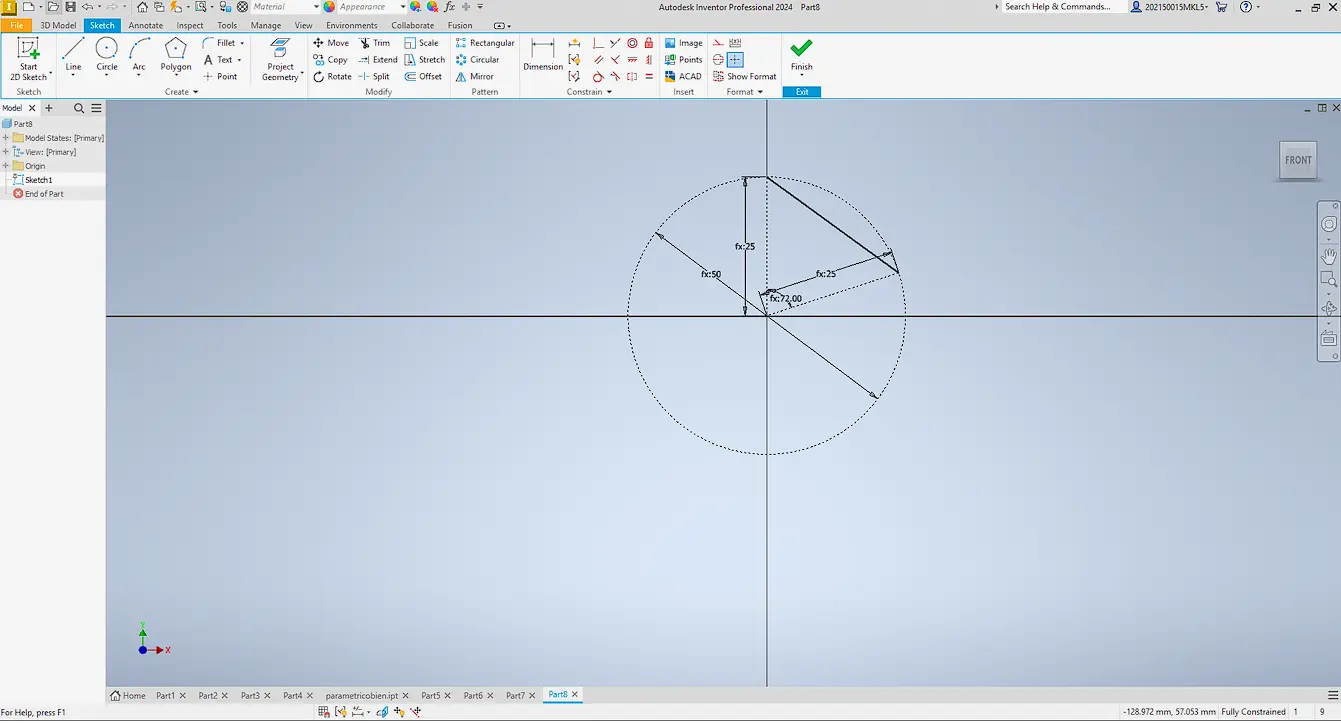
A circular pattern was applied around the sketch origin to replicate the side and generate the polygon.
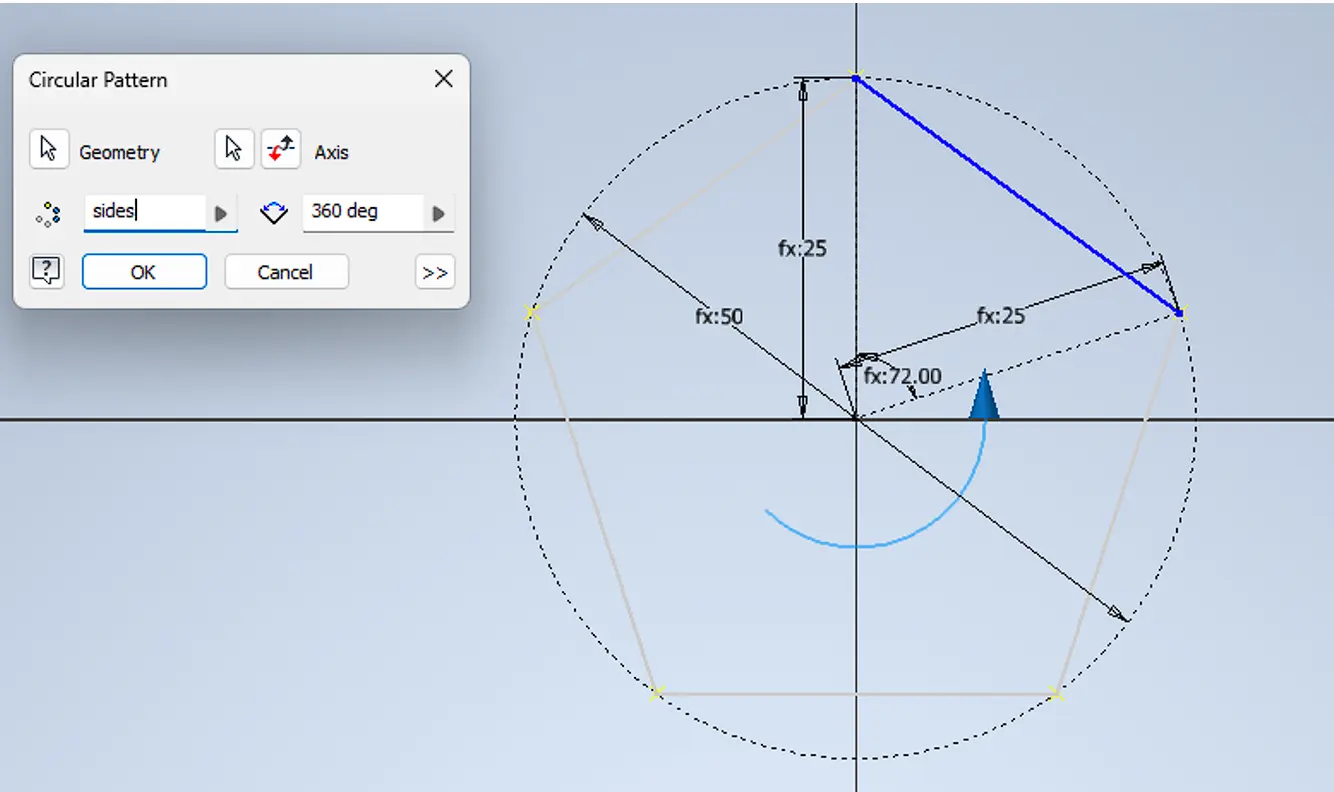
Finally, an internal circular feature was added following the same parametric logic.
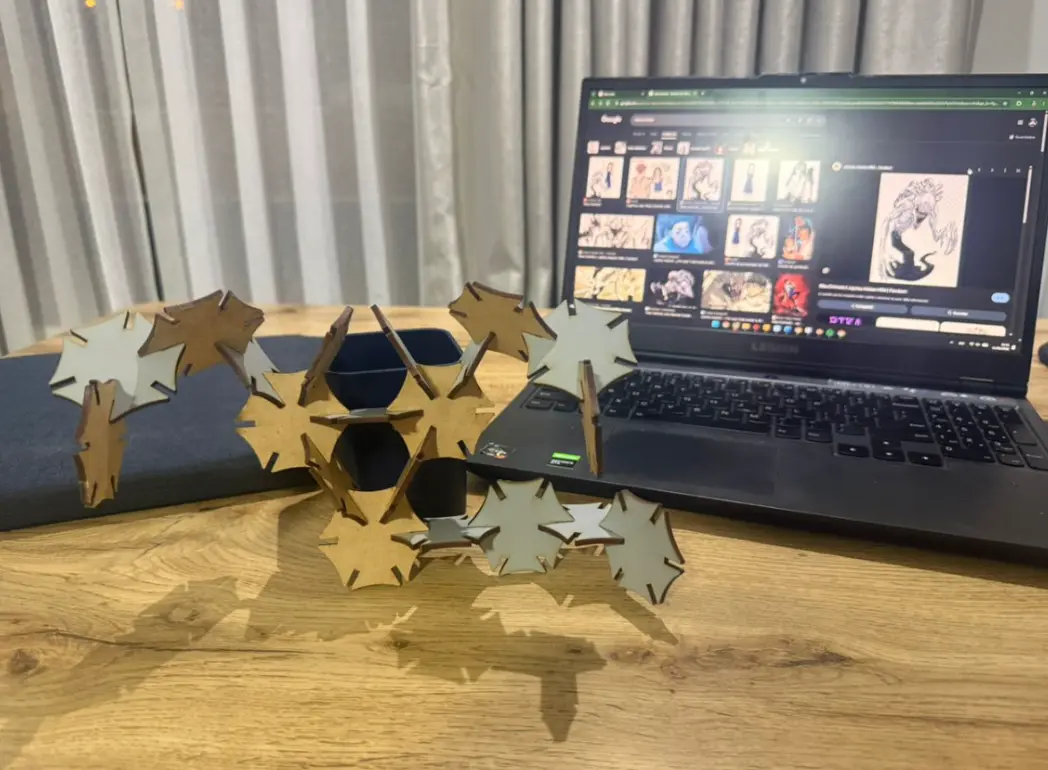
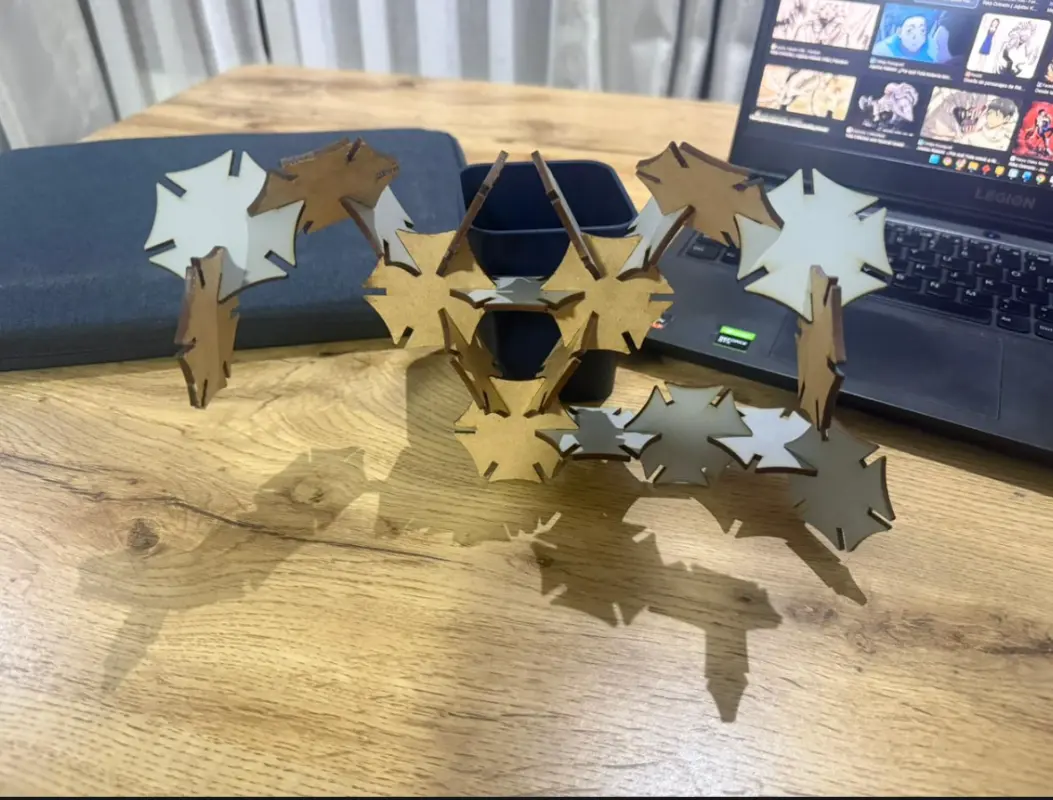
Structures Built with the 20-Piece Parametric Kit
Scorpion
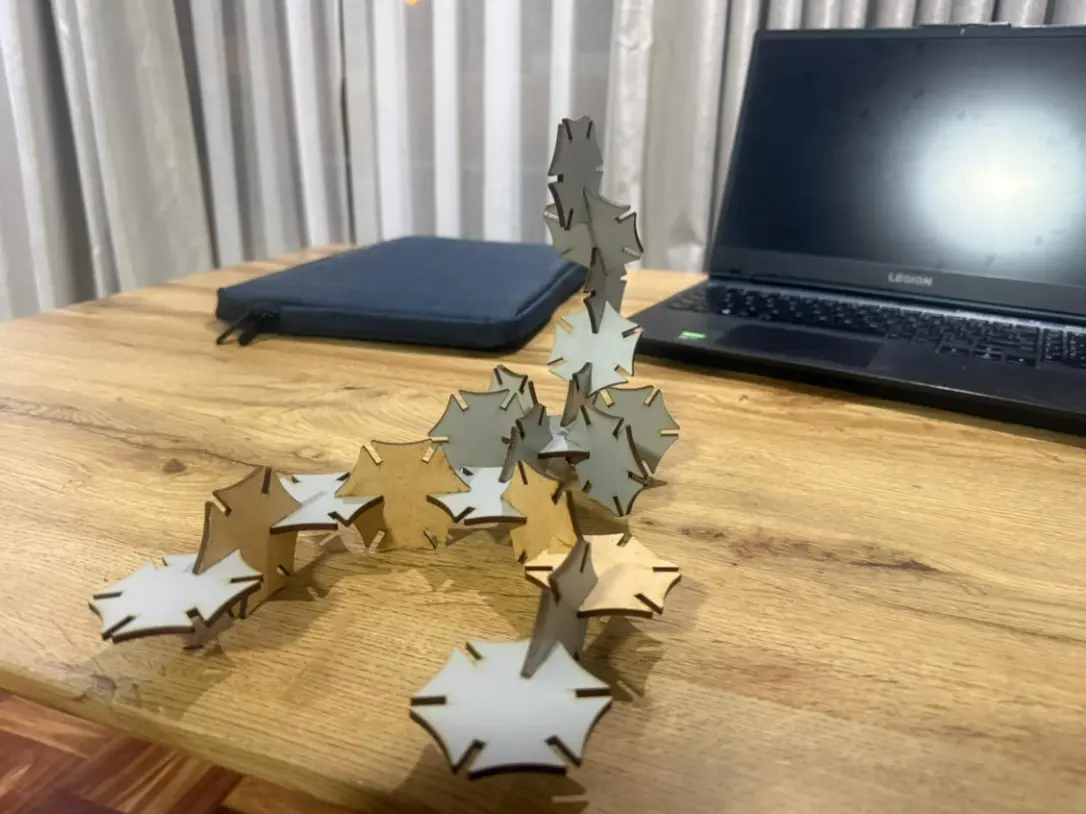
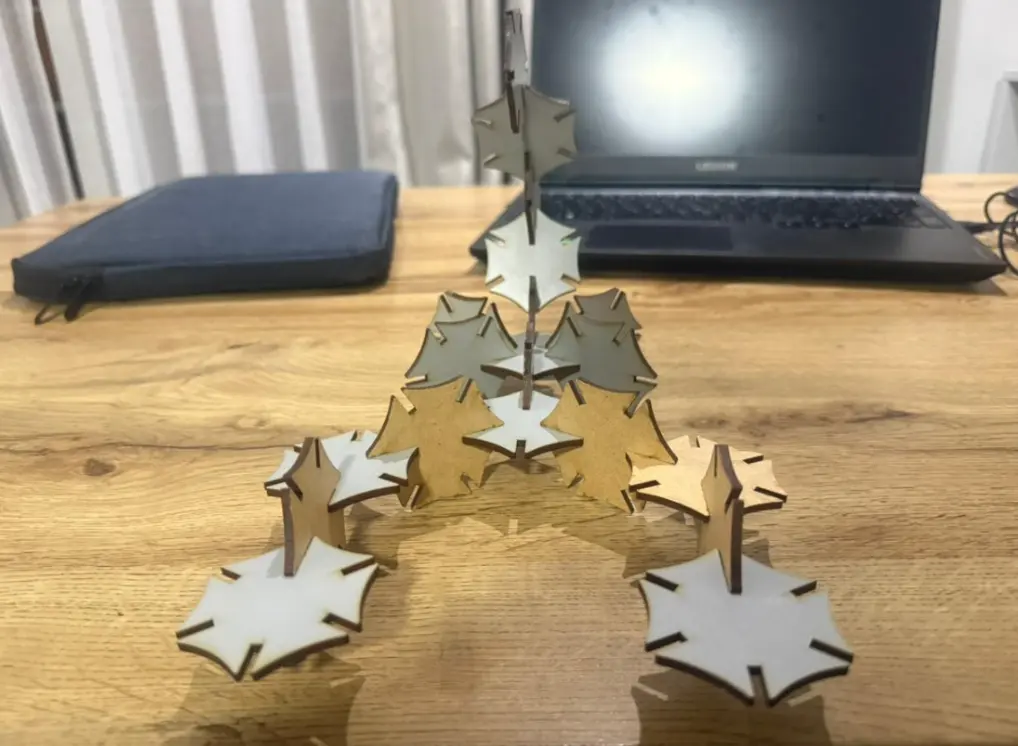


Black Widow Spider
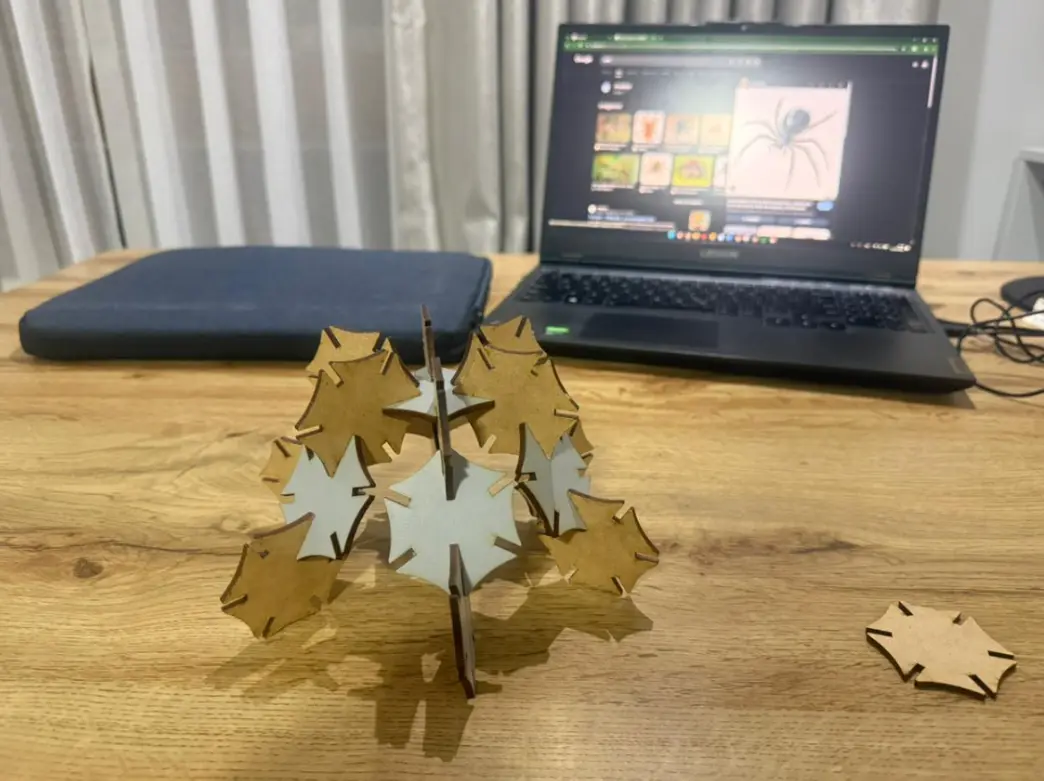
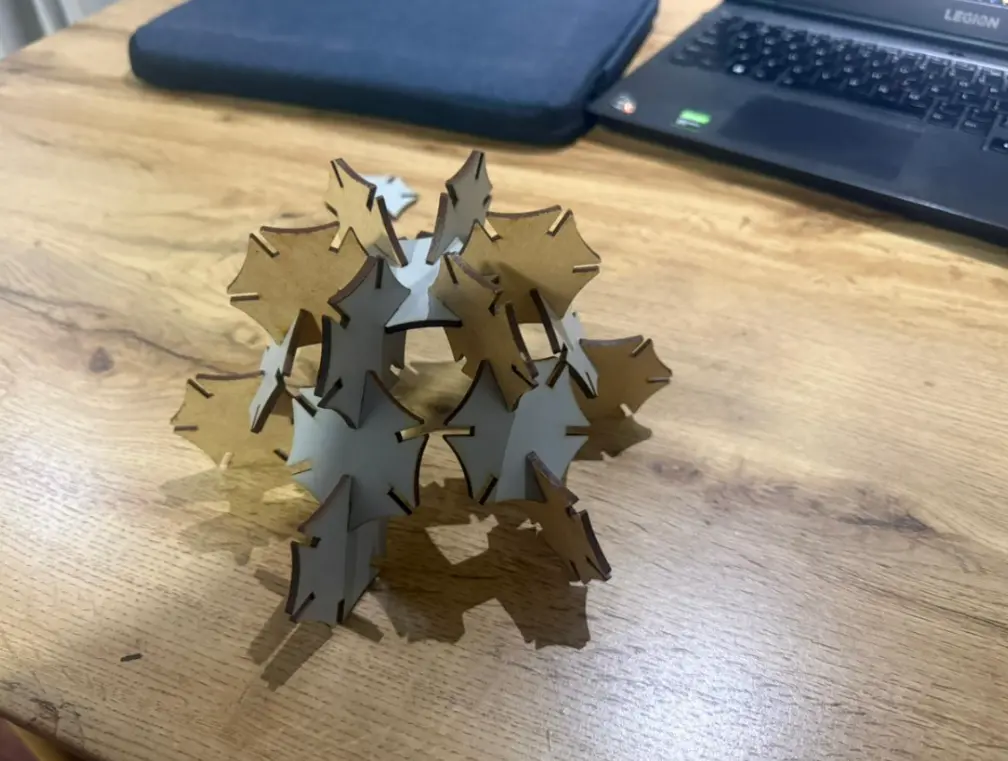


Turtle
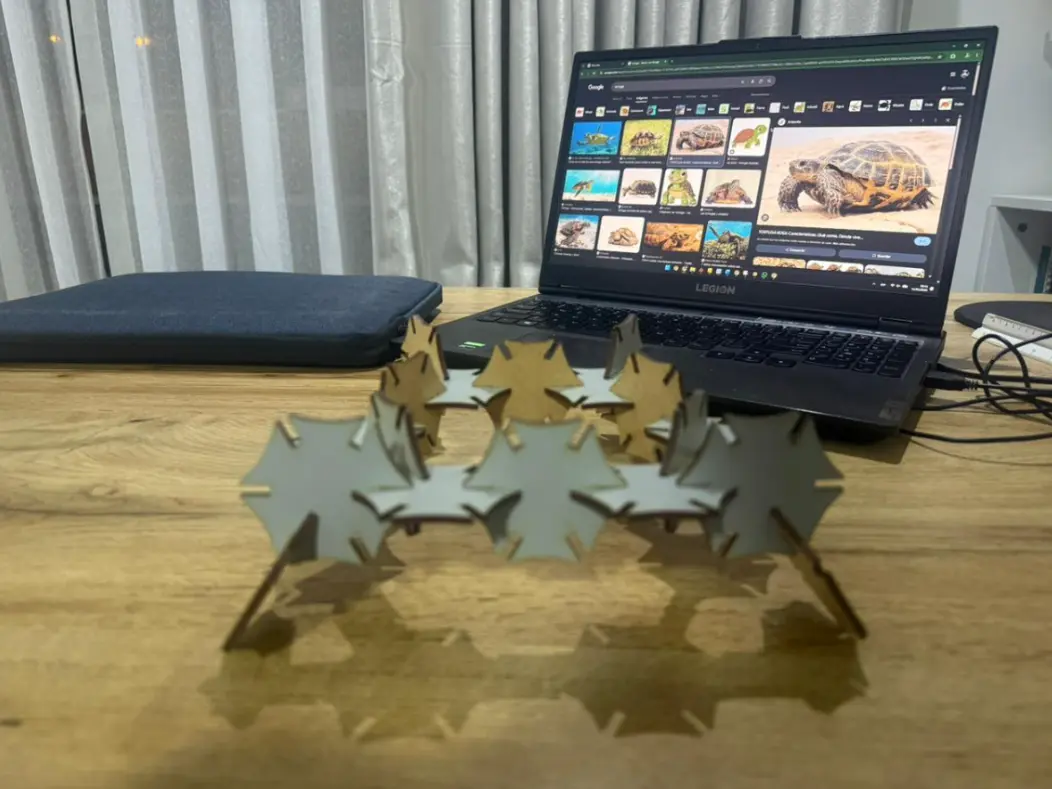


Pokémon (Maractus-inspired)
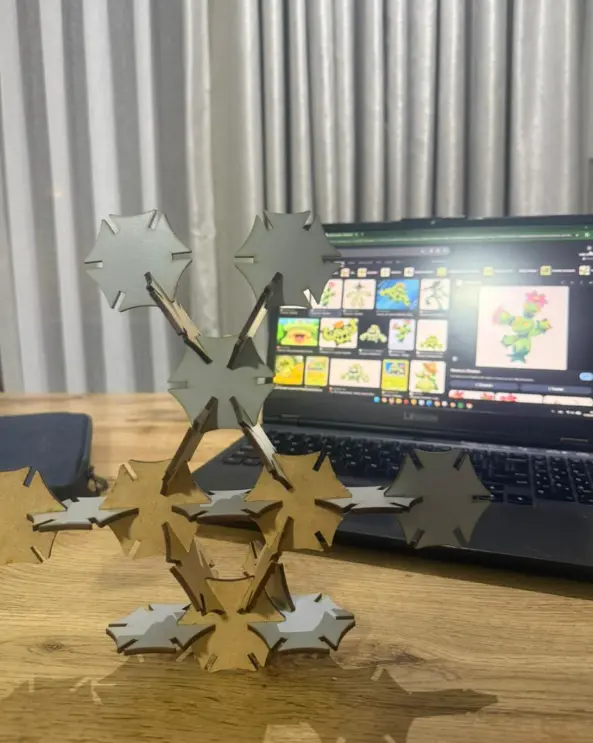

Pokémon (Ludicolo-inspired)
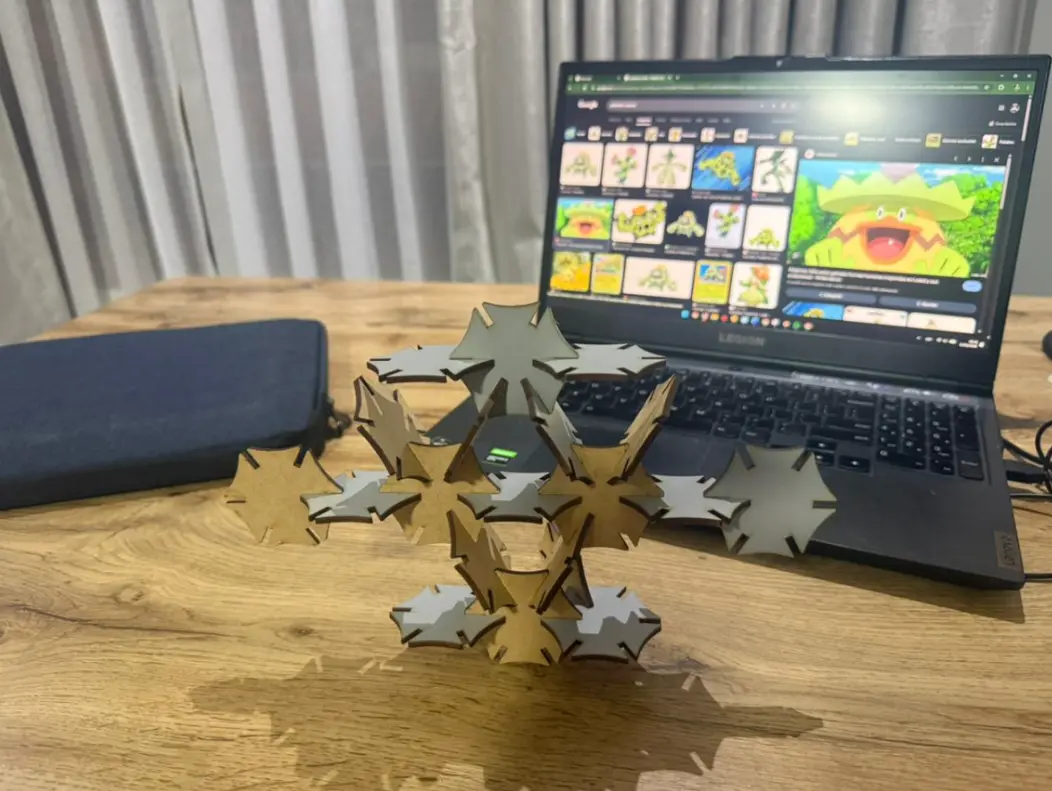

Rika Orimoto (Inspired Structure)

