Week 4: Embedded programming
Datasheet
A datasheet in electronics is a technical document provided by manufacturers that details the specifications, functionality, pinout, and physical characteristics of a component. It acts as a guide for engineers to design reliable circuits by defining operating parameters, electrical characteristics, and maximum ratings.
One of the assignments for this week was browse through the data sheet for a microcontroller. A microcontroller unit (MCU) is essentially a small computer on a single chip. It is designed to manage specific tasks within an embedded system without requiring a complex operating system. I chose the ESP32 WROOM 32 by Espressif Systems and a Raspberry Pi Pico by Raspberry Pi.
Classification of Microcontrollers by Number of Bits
Bit: Is the smallest unit of data in electronics and computing, representing a single binary value of either 0 or 1. It acts as the fundamental building block for all digital information, representing logical states like on/off, true/false, or high/low voltage.
- 8-bit Microcontrollers: Performs operations on 8 bits at a time. Ideal for basic simple tasks, such as timers, sensors, and motor control.
- 16-bit Microcontrollers: Performs operations on 16 bits at a time. They are ideal for real-time control, precision measurement and industrial applications.
- 32-bit Microcontrollers: Performs operations on 32 bits at a time. They offer high-performance processing, large memory addressing, and advanced peripherals, making them ideal for complex, power-efficient applications like IoT and industrial control.
Classification of Microcontrollers by Memory
- Embedded Memory Microcontroller: Is a compact, single-chip computer that integrates all the necesary components. integrating a processor core, program memory (Flash/ROM), data memory (SRAM), and peripherals.
- External Memory Microcontroller: Is a compact chip without on-chip integrated memory. It requires external program memory (Flash/ROM) and data memory (SRAM).
ESP32 WROOM 32
| Feature | ESP32 WROOM 32 |
|---|---|
| ROM | 448 KB |
| SRAM | 520 KB |
| SRAM in RTC | 8 KB |
| Wifi |
|
| Bluetooth |
|
| Peripherals |
|
| Analog Inputs | 18 Analog enabled pins |
| Operating Conditions |
|
Pinout
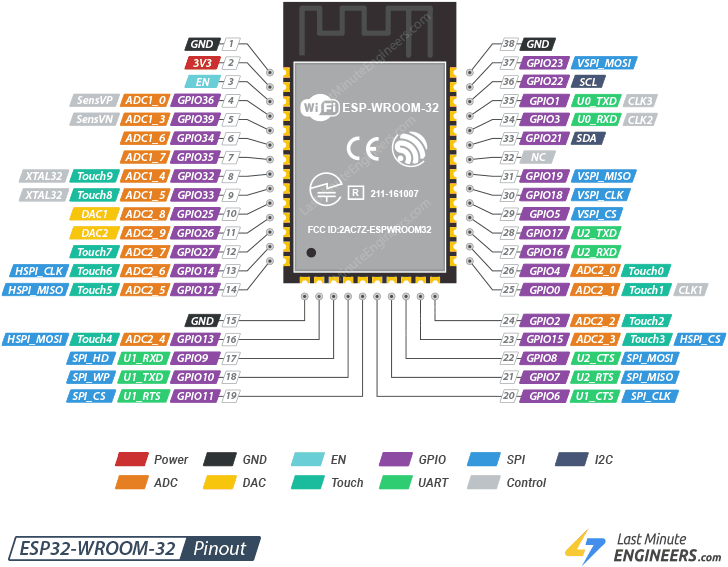
Power: These are the power supply pins, such as 3V3, which provide the necessary voltage for the module to operate.GND: Ground pins that act as the common reference point for the electrical circuit.EN: The Enable pin, used to boot, reset, or disable the chip.GPIO: General Purpose Input/Output pins that can be programmed to act as either digital inputs or outputs.SPI: Serial Peripheral Interface pins that are high-speed communication protocols for external devices like SD cards or displays.I2C: Serial Data (SDA) and Serial Clock (SCL). These pins allow microcontrollers to connect to multiple sensors or devices simultaneously using a master-slave architecture.DAC: Digital-to-Analog Converters used to output an analog voltage signal from the microcontroller.Touch: Capacitive touch sensors that can detect human touch on conductive surfaces without mechanical buttons.UART: Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter pins, typically used for serial communication with a PC or other microcontrollers.Control: Pins used for specific internal system functions or clock signals.Programming in C++
Programming in Python
Learning outcomes
This week, I read several microcontroller datasheets and concluded that the ESP32-WROOM-32 chip is the best choice for my project due to its integrated Bluetooth and Wi-Fi capabilities, as well as its large number of analog and digital pins. I also returned to programming in C++ and Python after some time without practicing, which allowed me to refresh my understanding of both languages.
In my opinion, C++ offers better performance because the program is compiled and executed as a whole, whereas Python is interpreted line by line. This makes C++ more efficient for real-time and embedded applications, where speed and hardware control are essential. Additionally, C++ provides greater control over memory management and system resources, which is important when working with microcontrollers. On the other hand, Python is more intuitive and easier to read, allowing faster development and testing of ideas. For this reason, I see Python as an excellent tool for prototyping, while C++ is better suited for final embedded implementations.
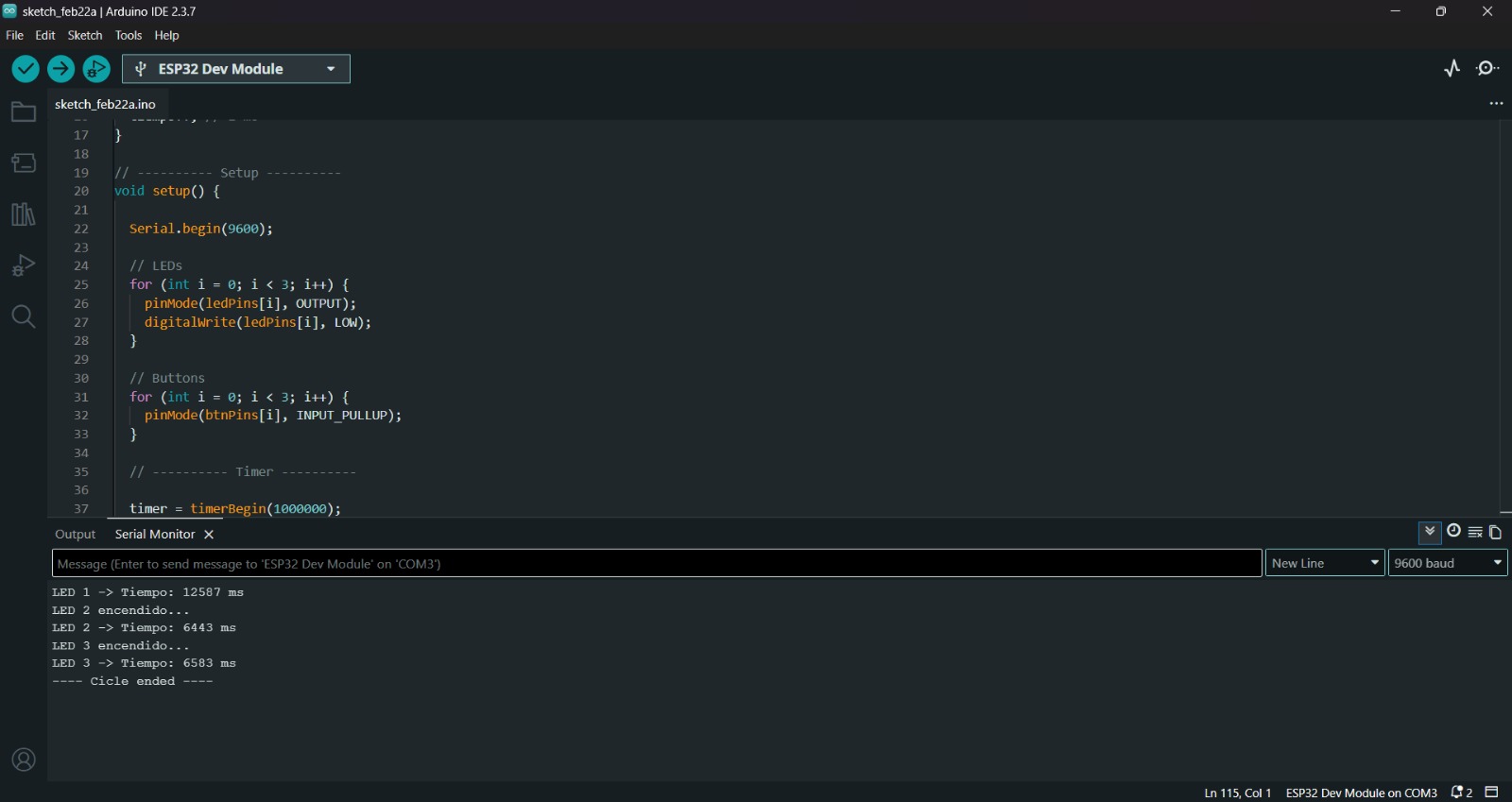
Understanding the ESP32 timer was particularly challenging and required significant time to fully grasp. My goal is to use this timer for a timing application in my boxing project.