MiniBank: Smart Saving for Kids
This project explores a smart mini bank system that goes beyond traditional saving to teach children how to save with purpose. While conventional piggy banks and school-led saving schemes encourage putting money aside, they rarely guide children on how to save strategically toward a goal. This project seeks to bridge that gap.
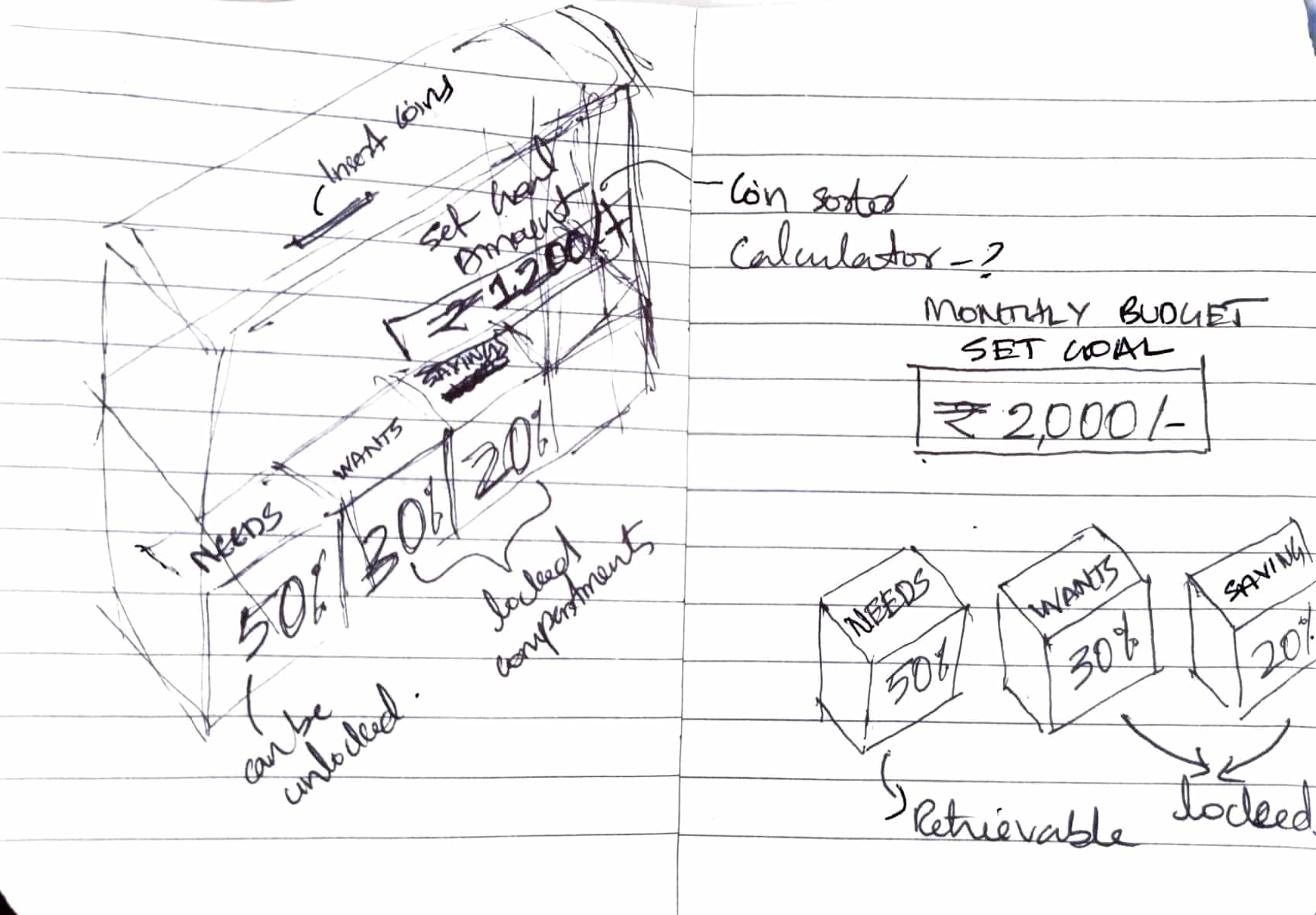
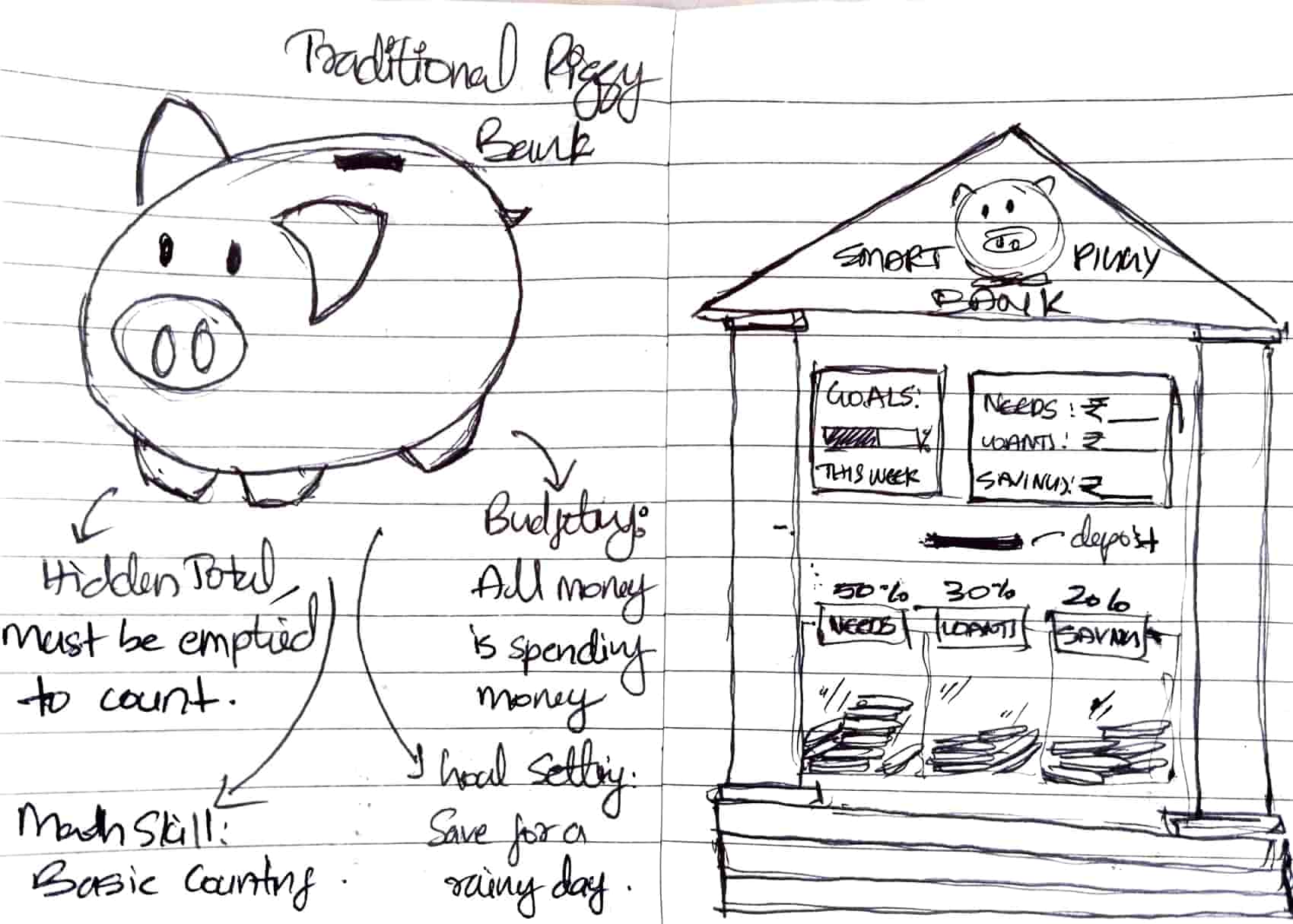
Inspired by how children learn arithmetic through everyday actions like adding coins or calculating change, this concept introduces structured, goal-based saving through interaction. The piggy bank functions as a mini banking system, internally organizing deposited coins to make savings visible and purposeful.
I am currently working with two conceptual approaches. The first is a goal-based model where a child sets a specific savings target and receives weekly guidance on how much to save. The second draws from the simplified 50–30–20 principle, where only a portion of the saved amount is accessible, encouraging discipline and delayed gratification. By combining saving with intention and planning, the piggy bank becomes an active learning tool rather than a passive container.
Concept & Rationale
Children are often told to save money, but rarely taught how to save wisely. Many accumulate coins without a clear purpose, leading to impulsive spending once the money is accessed. This pattern often continues into adulthood. I observed similar contrasts among colleagues on the same payroll—some struggled before month-end, while others managed comfortably. This raised a key question: why does saving feel intuitive for some, but not for others?
This reflection led to the idea of teaching children not just to save, but to save with intention.
The Smart Mini Bank introduces goal-oriented saving, where a child sets a specific target (with parental guidance) and works toward it through consistent contributions and delayed access to funds. Saving becomes a structured and intentional process rather than simple accumulation.
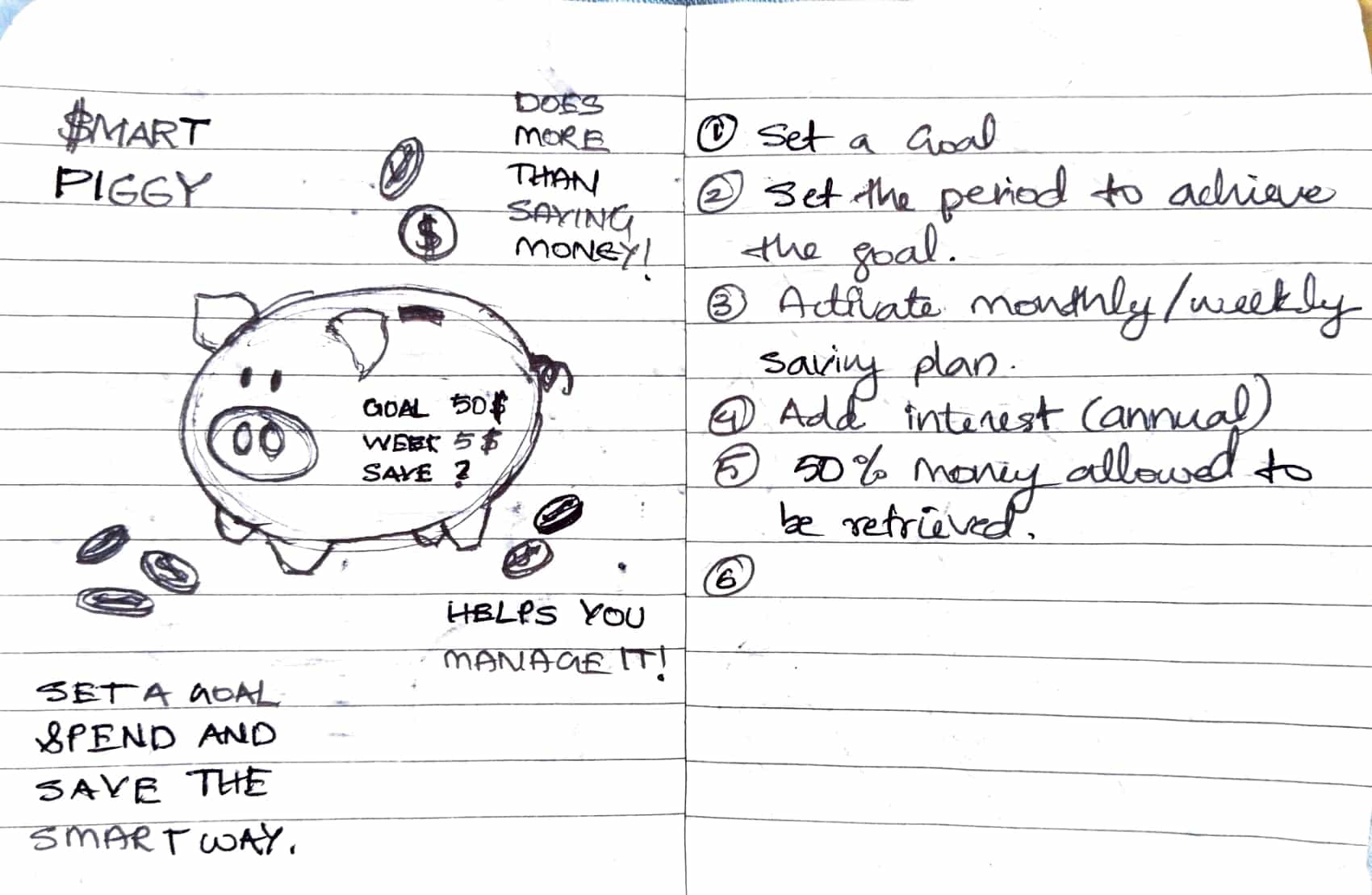
Through this process, the child learns:
- Restraint and patience
- Delayed gratification
- Foundational financial awareness
- An understanding of planning over impulsive spending
To reinforce positive saving behavior, the Smart Mini Bank rewards the child upon successful completion of a goal by adding a small amount of interest to the saved total, introducing simplified real-world financial principles in an age-appropriate manner. Parents act as facilitators rather than enforcers, guiding reflection and discussion instead of merely controlling access to money.
At its core, this project reimagines the traditional piggy bank as a Smart Mini Bank, an interactive system that encourages purposeful saving and helps children develop a healthy, intentional relationship with money from an early age.
Initial concept model on SketchUp
This model explores the early form of the Smart Mini Bank. The structure visualizes how the piggy bank could function as a small interactive system, combining physical coin storage with digital feedback elements. The model helped evaluate enclosure proportions, front interaction panels, and potential placement for sensors and outputs.
MiniBank – Final Project Development Plan
To organize the development of the MiniBank system, the project is structured into a series of stages covering research, system design, electronics development, fabrication, and integration. The following table outlines the planned workflow and expected outputs for each stage.
| Stage | Activity | Purpose | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concept Exploration | Initial idea of a coin sorting system based on the 50–30–20 money management model | Explore how physical coin allocation could support financial learning | Early concept sketches |
| Concept Refinement | Shift from mechanical coin sorting to goal-based saving | Align the system with behavioral learning objectives for children | Revised project direction |
| Context Research | Study variations in Indian coin diameter, thickness, and materials | Evaluate feasibility of physical denomination detection | Coin comparison dataset |
| Sensor Exploration | Investigate detection approaches including mechanical slots, IR sensing, load cells, and inductive sensing | Understand technical trade-offs between sensing methods | Sensor feasibility analysis |
| System Scope Definition | Analyze coin validation methods used in vending machines and banking systems | Define practical system boundaries appropriate for the project | Defined detection strategy and project scope |
| Interaction Design | Develop behavioral reinforcement model with micro rewards and milestone celebrations | Create a motivating saving experience for children | Interaction and reward system framework |
| System Architecture | Define input devices, processing unit, and output components | Translate the concept into a structured electronic system | System block diagram |
| Electronics Learning | Study PCB design workflow including schematic creation, component placement, and trace routing | Understand how to design and fabricate a custom PCB for the MiniBank electronics system | Foundational PCB design knowledge |
| Electronics Development | Design circuit connecting sensors, NeoPixel LEDs, servo motor, buzzer, and display | Create the hardware platform for the interactive system | Schematic and PCB layout |
| Mechanical Design | Design piggy bank enclosure and internal coin path | Integrate electronics with the physical structure | 3D CAD model of enclosure |
| Fabrication | Manufacture enclosure components using CNC or laser cutting | Produce the physical structure of the MiniBank | Fabricated enclosure components |
| Firmware Development | Implement coin detection logic, savings tracking, and milestone feedback | Enable interactive system behavior | Microcontroller program |
| System Integration | Assemble electronics, enclosure, and firmware | Validate complete system functionality | Working MiniBank prototype |
| Documentation | Record design decisions, experiments, fabrication processes, and results | Provide evidence of development and learning | Final project documentation |
Final Project Thinking Progression
Week 1 – Coin Sorting for Money Management Training
My initial concept was to design a coin sorting system based on the 50-30-20 money management model. The idea was to:
At this stage, I was thinking mechanically:
However, while mapping this idea to the real objective, I realized: The project is not about managing spending categories. It is about goal-based saving for children. Sorting coins added:
This week helped me identify a mismatch between concept and purpose.
I decided to pivot.
Week 2 – Shift to Goal-Based Digital Value Tracking
The project evolved from physical sorting to digital value accumulation.
New system requirement:
Detect coin → identify denomination → update total → display goal progress.
This was a conceptual shift from mechanical organization to intelligent tracking.
To implement this, I studied Indian coin characteristics:
I discovered that Indian coins are not standardized in a simple way. Different issues of the same denomination vary in material and design. This made denomination detection more complex than expected. This week was about understanding the physical reality of the problem.
Preliminary Diameter and Material Study for Coin Identification System Design
Since my final project involves designing a coin identification system that detects denomination and updates a running total, it was necessary to analyze whether Indian coin denominations are dimensionally consistent across different series. Accurate value computation depends on reliable physical identification; therefore, I first examined variations in diameter and material among commonly circulated coins.
Comparison across models
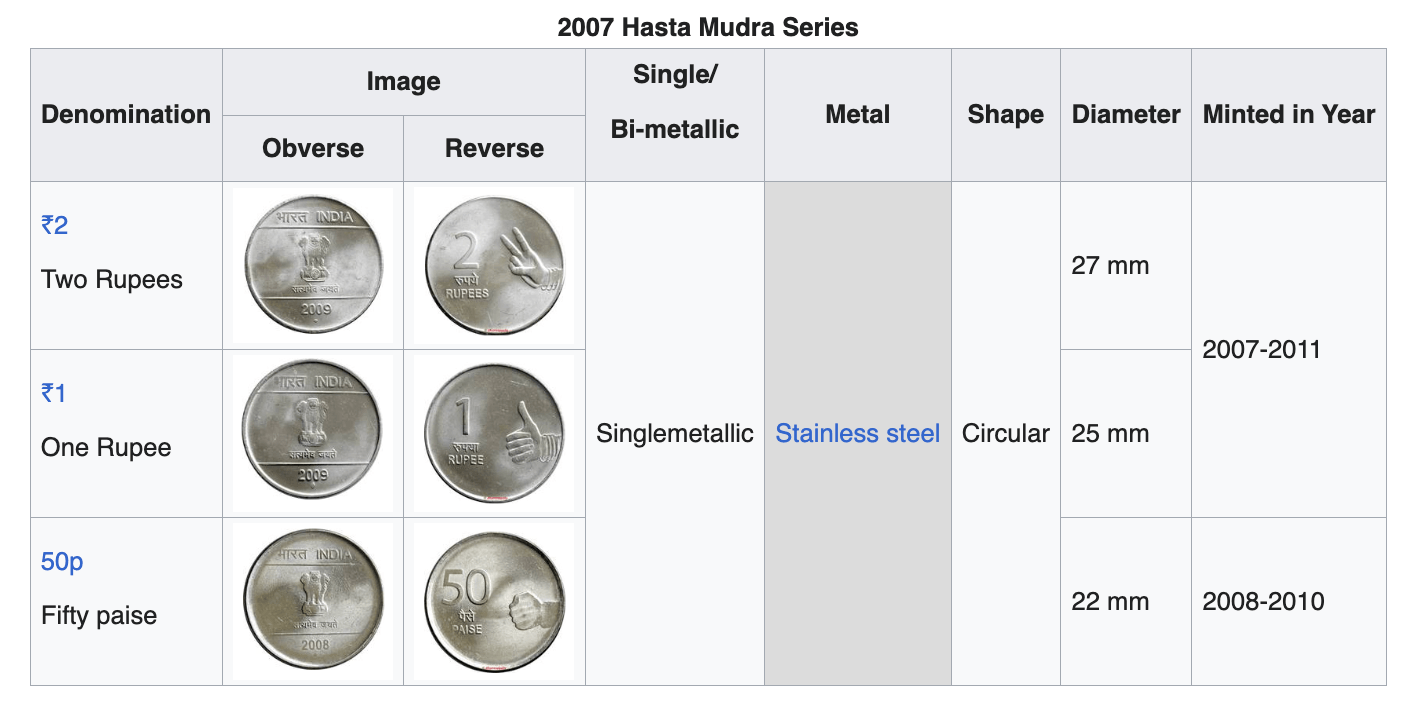
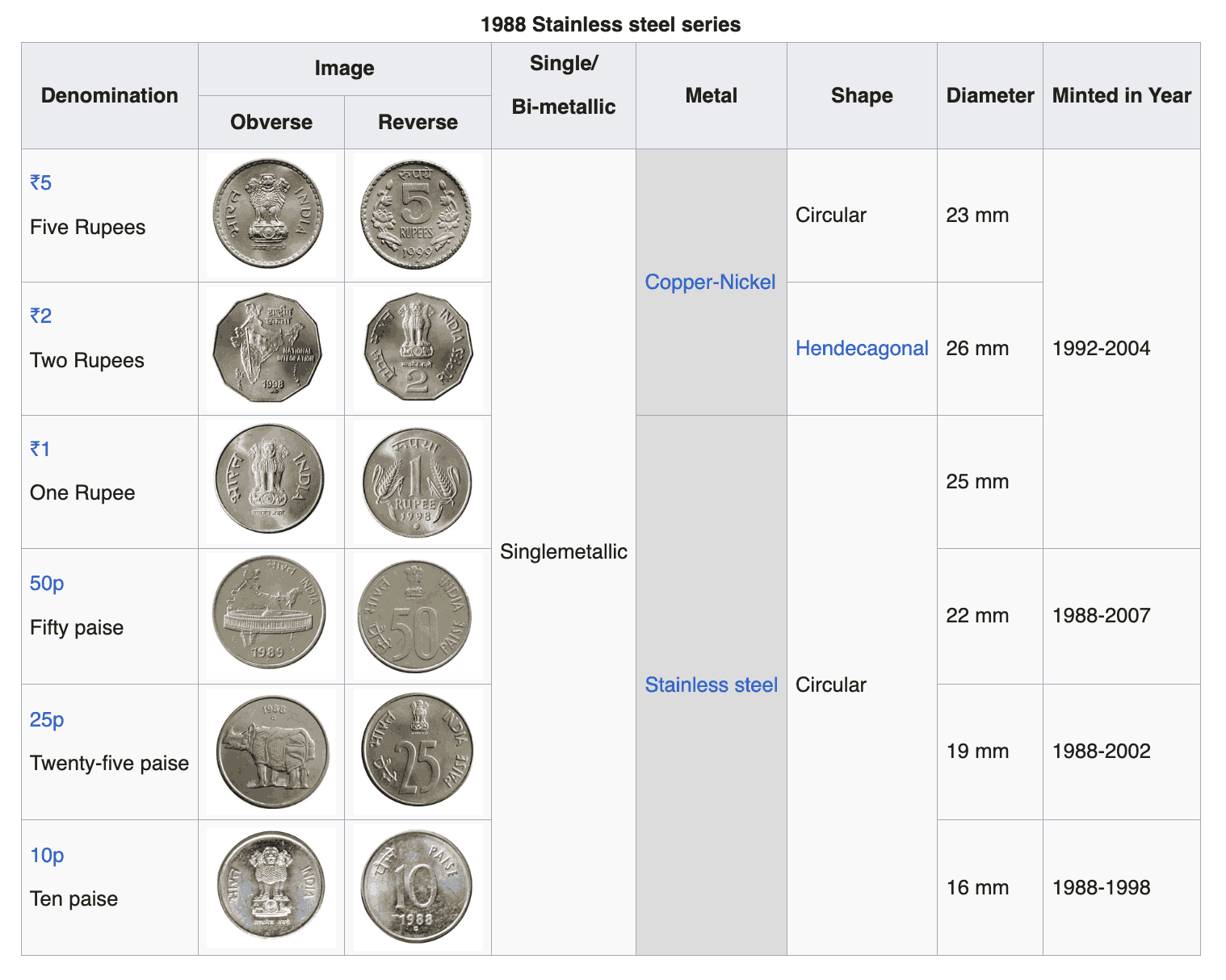
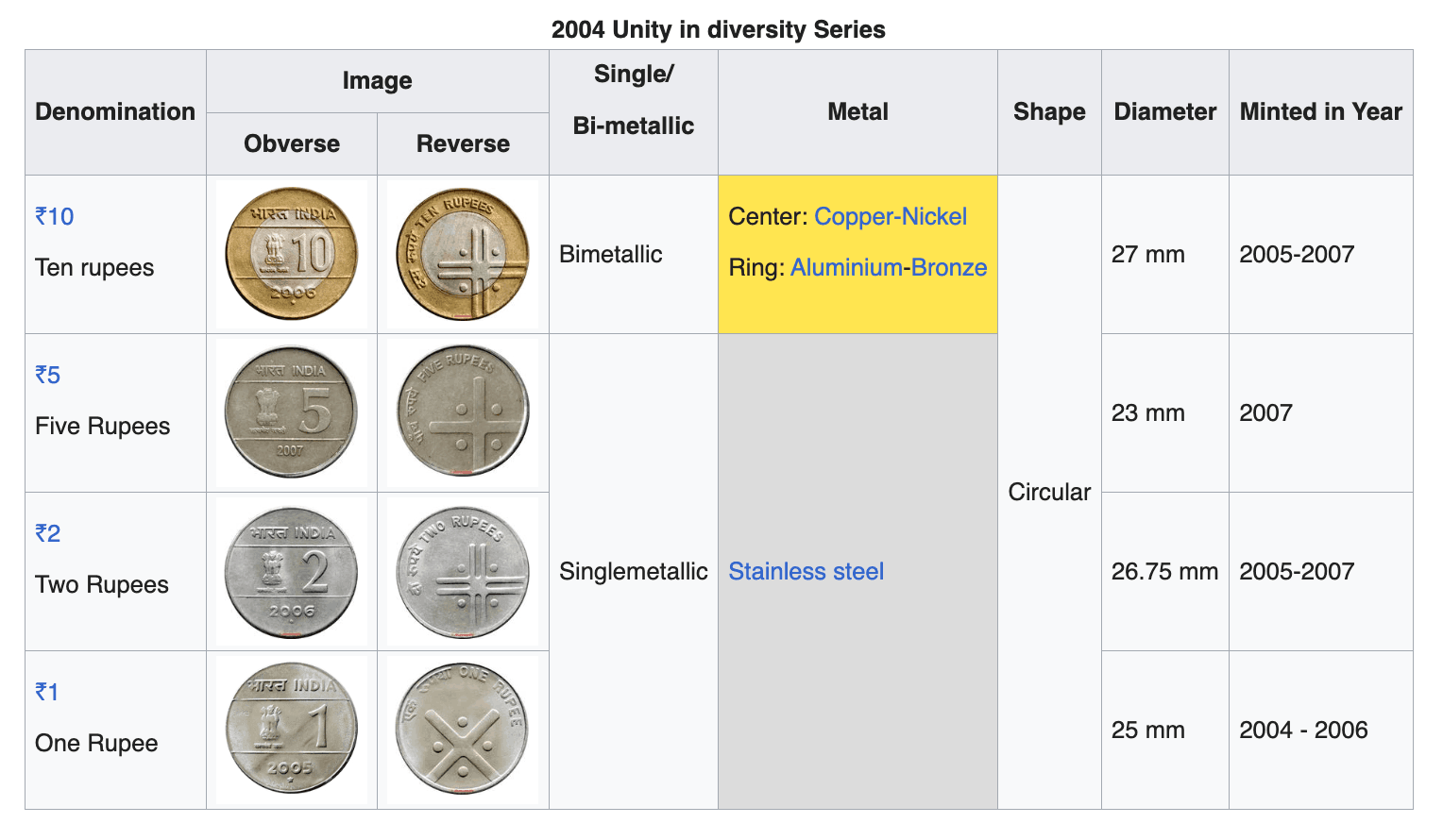

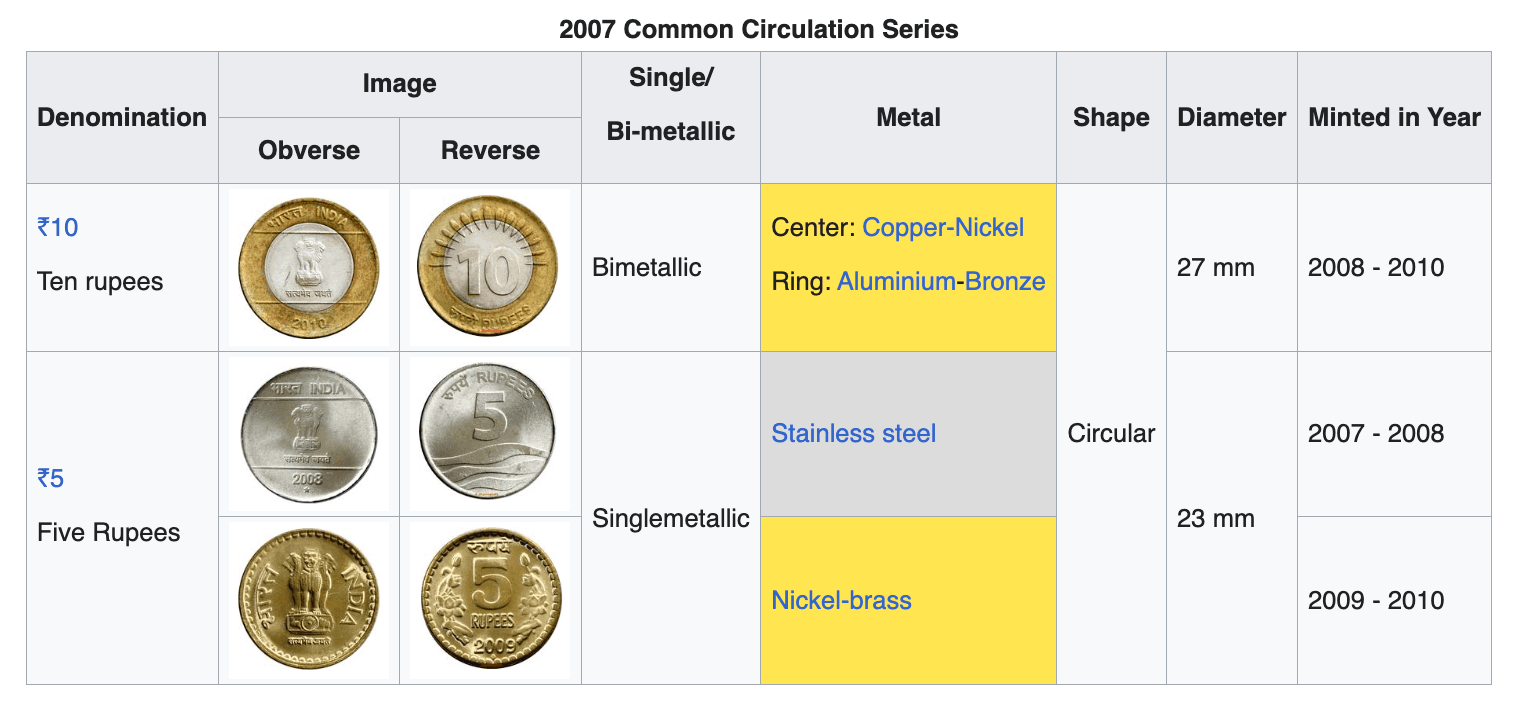


₹1 Coin Series Comparison
| Series | Diameter | Material | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1988 Stainless Series | 25 mm | Stainless Steel | Single |
| 2004 Unity | 25 mm | Stainless Steel | Single |
| 2007 Hasta Mudra | 25 mm | Stainless Steel | Single |
| 2011 Rupee Symbol | 21.93 mm | Stainless Steel | Single |
| 2019 Grain Series | 20 mm | Stainless Steel | Single |
₹2 Coin Series Comparison
| Series | Diameter | Material | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1988 Series | 26 mm | Copper-Nickel | Single |
| 2004 Unity | 26.75 mm | Stainless Steel | Single |
| 2007 Hasta Mudra | 27 mm | Stainless Steel | Single |
| 2011 Rupee Symbol | 25 mm | Stainless Steel | Single |
| 2019 Grain Series | 23 mm | Stainless Steel | Single |
₹5 Coin Series Comparison
| Series | Diameter | Material | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1988 Series | 23 mm | Copper-Nickel | Single |
| 2004 Unity | 23 mm | Stainless Steel | Single |
| 2007 Common (Steel) | 23 mm | Stainless Steel | Single |
| 2007 Common (Nickel-Brass) | 23 mm | Nickel-Brass | Single |
| 2011 Rupee Symbol | 23 mm | Nickel-Brass | Single |
| 2019 Grain Series | 25 mm | Nickel-Brass | Single |
₹10 Coin Series Comparison
| Series | Diameter | Material | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 Unity | 27 mm |
Center: Copper-Nickel Ring: Aluminium-Bronze |
Bimetallic |
| 2007 Common | 27 mm |
Center: Copper-Nickel Ring: Aluminium-Bronze |
Bimetallic |
| 2011 Rupee Symbol | 27 mm |
Center: Copper-Nickel Ring: Aluminium-Bronze |
Bimetallic |
| 2019 Grain Series | 27 mm |
Center: Copper-Nickel Ring: Aluminium-Bronze |
Bimetallic |
₹20 Coin Series Comparison
| Series | Diameter | Material | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 Grain Series | 27 mm |
Center: Nickel-Brass Ring: Nickel Silver |
Bimetallic |
Final Comparison Summary
| Denomination | No. of Varieties | Diameter Range | Materials Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| ₹1 | 5 | 20–25 mm | Stainless Steel |
| ₹2 | 5 | 23–27 mm | Copper-Nickel, Stainless Steel |
| ₹5 | 5 | 23–25 mm | Copper-Nickel, Stainless Steel, Nickel-Brass |
| ₹10 | 3 | 27 mm | Bimetallic (Cu-Ni + Al-Bronze) |
| ₹20 | 1 | 27 mm | Bimetallic (Ni-Brass + Ni-Silver) |
Week 3 – Sensor Exploration & Engineering Trade-offs
After studying the physical parameters of Indian coins, I moved into exploring different sensing mechanisms that could help identify denominations.
At this stage, I was not comparing industrial systems.
I was simply trying to understand:
What sensing approach is technically possible and practical for my context?
Since the project operates in a controlled environment and processes one coin at a time, I evaluated different sensors based on feasibility, complexity, and reliability.
Diameter Detection (Mechanical / Optical)
Measuring the width of the coin either through fixed mechanical slots or using optical sensors (such as IR break-beam) placed at defined spacing.
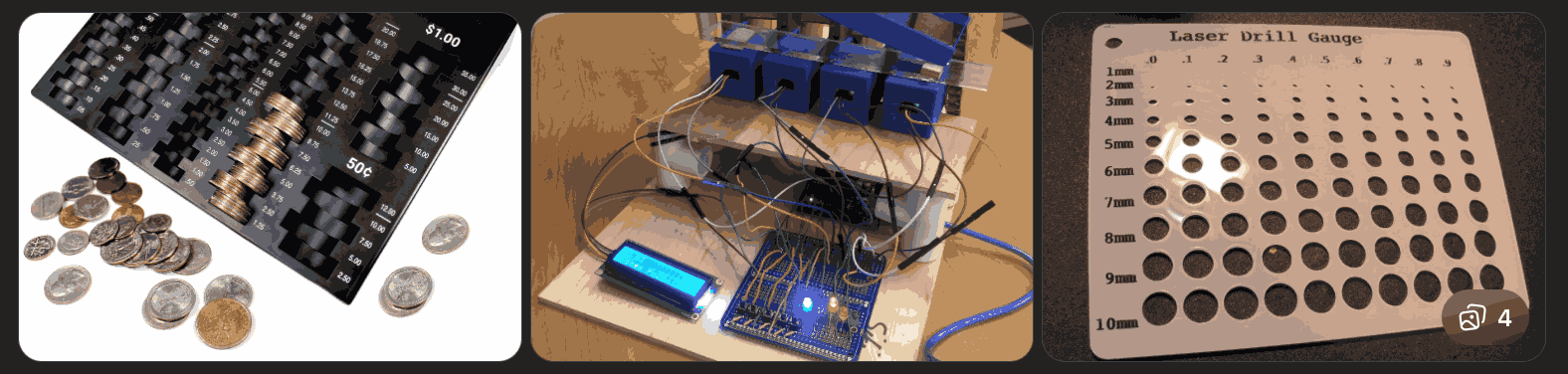
What This Is: A plate or ramp with multiple slots of different widths.
Each slot is calibrated to a specific diameter.
How It Works:
Limitation: Once fabricated, it cannot adapt. If coin size changes, redesign is required. This is purely mechanical detection, no electronics involved.

What This Is: An IR LED on one side and a receiver on the other.
When coin blocks the beam → signal changes.
What It Detects:
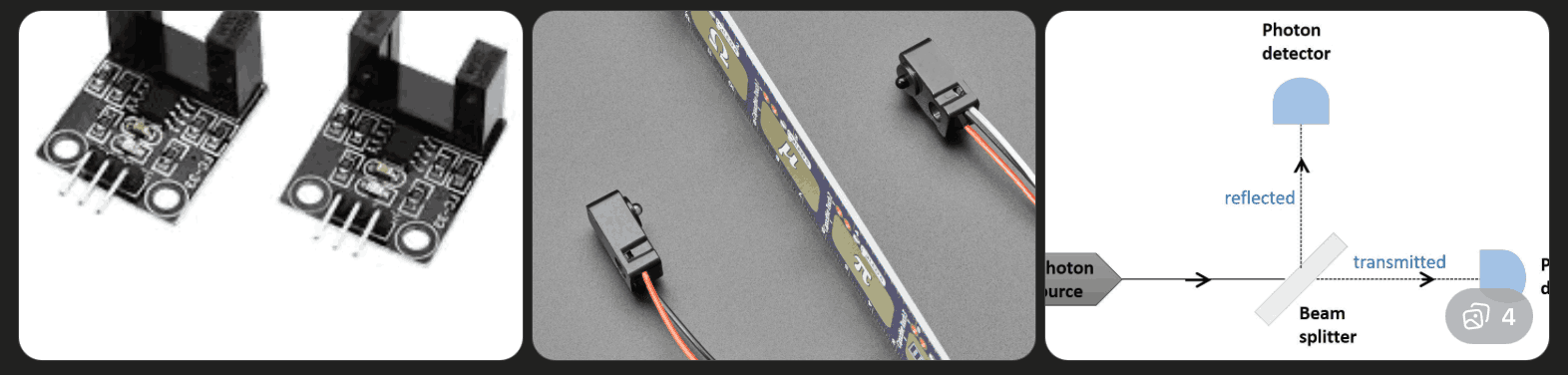
What This Is: Two IR beams placed a fixed distance apart.
How It Works:
Case 1 – Small coin:
Case 2 – Larger coin:
Microcontroller reads:
This allows approximate size classification without physical slot filtering.
Load Cell (Weight-Based Detection)
A load cell measures force using strain gauges. When a coin is placed on it, slight deformation generates a measurable electrical signal.
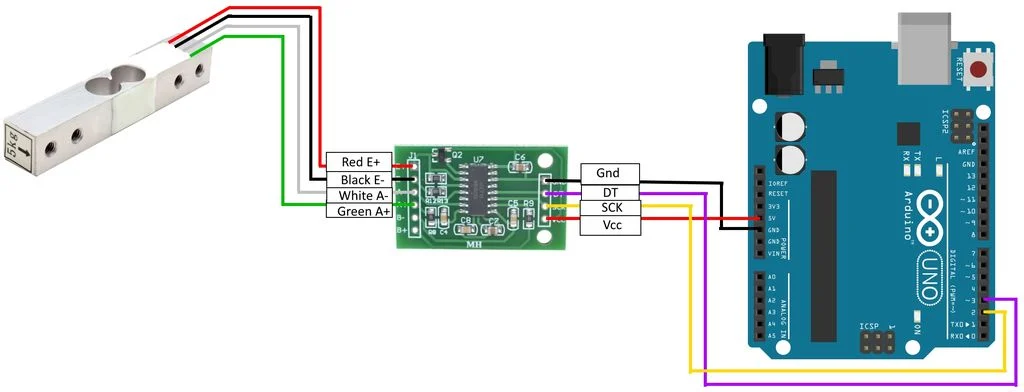
Why it could work:
Limitations:
IR-Based Detection Methods
IR Break-Beam Sensor (Object Detection)
What it is: An infrared LED (transmitter) and an infrared receiver placed opposite each other. The transmitter continuously emits invisible IR light toward the receiver.
How it works:
What it detects: Only presence of an object. Use in this project:Can detect coin insertion event reliably.
Limitation: Does not provide size or denomination information unless combined with additional logic.
IR Timing Analysis (Using Break-Beam Sensor)
What it is: A software-based method using the same IR break-beam sensor. Instead of only detecting interruption, the system measures: How long the beam remains blocked.
How it works: Coin enters → beam blocked → timer starts.
Coin exits → beam restored → timer stops.
Duration of blockage correlates to coin diameter (if insertion speed is controlled).
What it detects: Presence + approximate size.
Use in this project: Could help differentiate denominations based on interruption time.
Limitation: Highly dependent on insertion speed and user handling. Inconsistent movement may reduce reliability.
Inductive Sensing
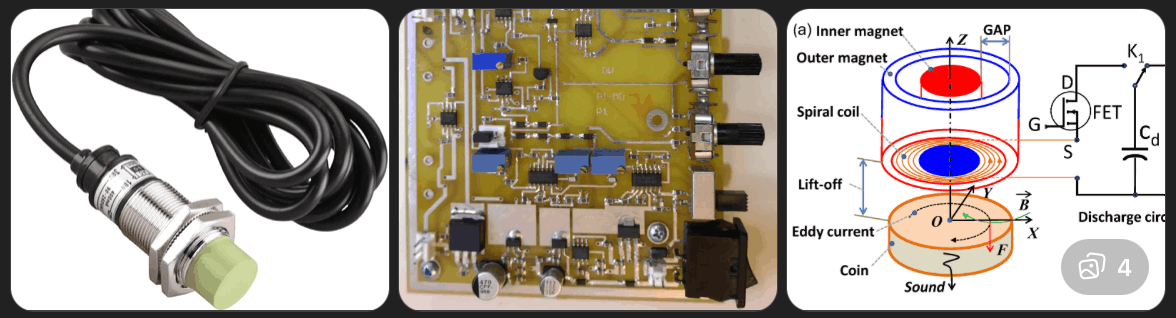
What it is: A coil generates a magnetic field. When a metal object passes through it, the inductance changes depending on material properties.
Why it could work:
Limitations:
This method is technically strong but increases system complexity significantly.
Magnetic Response Detection
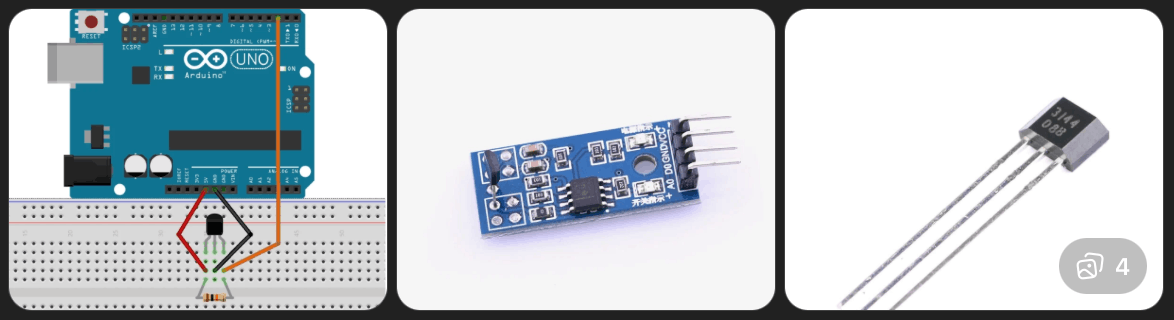
What it is: Using a Hall sensor or magnet to detect ferromagnetic properties of coins.
How It Works in Coin Detection
If a coin has ferromagnetic properties:
Limitations:
This would only work as a supporting parameter.
Insight
No sensing method is perfect on its own. Each approach introduces trade-offs between:
Week 4 – Learning from Vending Machines & Banks
I researched how real systems handle coin validation.

Findings:Industrial systems use multi-parameter validation, combining:
- Diameter
- Thickness
- Electromagnetic signature
- Magnetic properties
- Optical timing
Important realization:Real-world systems never rely on a single parameter. However, their priorities differ:
- Banks focus on authentication and counterfeit detection.
- Vending machines focus on transaction reliability.
- My project focuses on behavioral learning and goal tracking.
This comparison helped me clearly define boundaries.My system does not need:
- Anti-counterfeit security
- High-speed processing
- Industrial-grade validation
It needs:Reliable detection within a controlled environment. This week was about defining scope.
Week 5 – From Coin Detection to Interactive Behavioral System

At this stage, the project evolved beyond detection. The question became:
What should the child feel while using this system?
The project vision expanded into:
- Teaching goal-based saving
- Encouraging consistency
- Reinforcing delayed gratification
- Making learning invisible through play
Sensors (Input Layer)
- Coin insertion detection
- Denomination recognition
- Goal-setting button
Actuators (Output Layer)
- Servo motor (physical movement / progress indication)
- NeoPixel LEDs (visual progress)
- OLED display (goal + value)
- Speaker / buzzer (audio reinforcement)
Behavioral Design: Two-level reinforcement model
Micro Reward
- Every coin insertion acknowledged
- Soft tone + LED blink
Macro Reward
- Celebration at milestones (25%, 50%, 75%, 100%)
- Special sound
- Enhanced animation
- Physical servo movement
This balances continuous motivation with long-term goal orientation.
Microcontroller Consideration
Requirements:
- Control sensors
- Drive LEDs
- Control servo (PWM)
- Handle audio playback
- Manage milestone logic
Suitable options:
- ATmega328
- RP2040
- ESP32
Materials
| Qty | Description | Price | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material one | 22.00 $ | https://amazon.com/testoe | Order many |
| Material two | 22.00 $ | https://amazon.com/testoe | |
| Material three | 22.00 $ | https://amazon.com/testoe | |
| Material four | 22.00 $ | https://amazon.com/testoe |