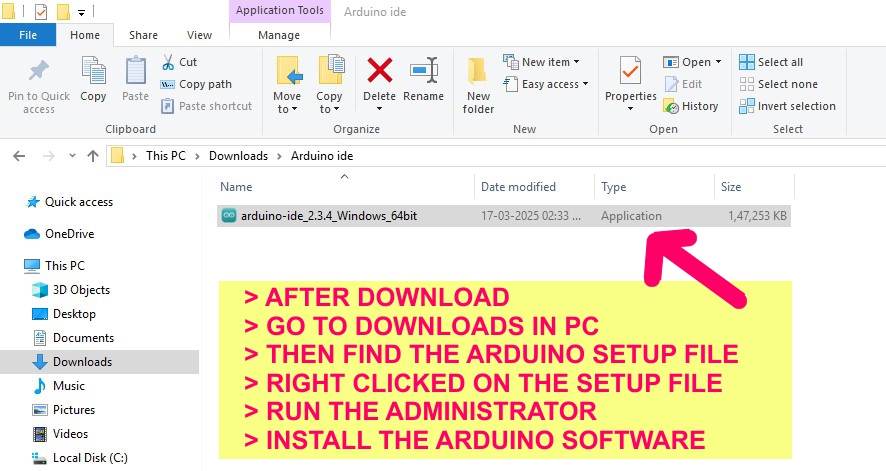
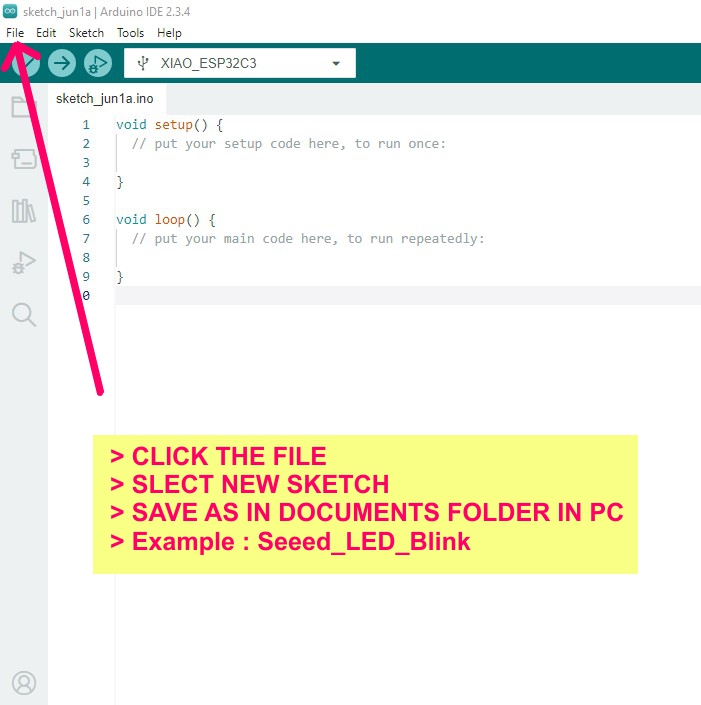
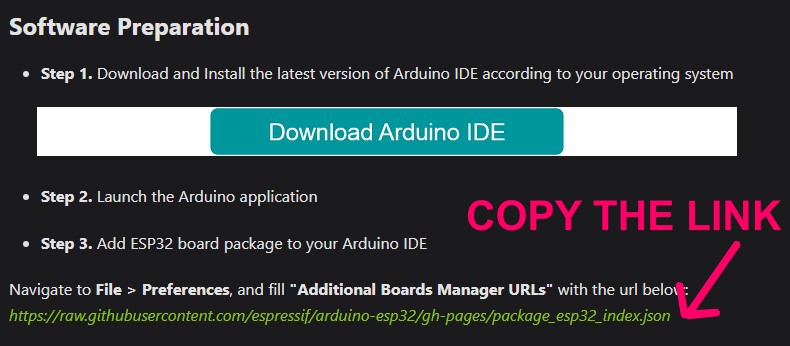
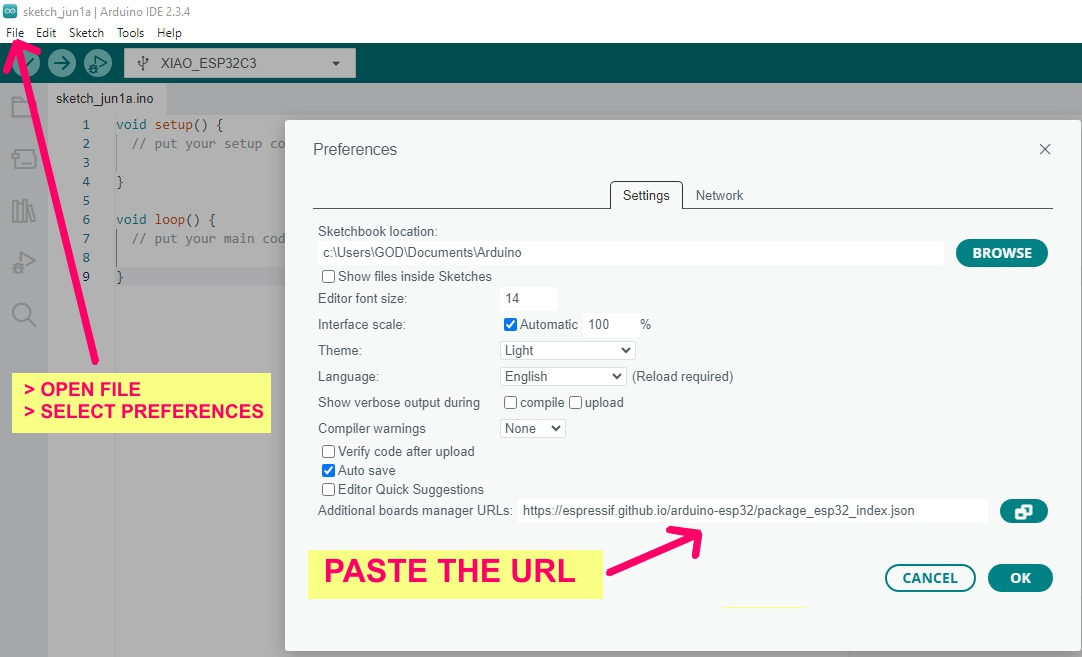
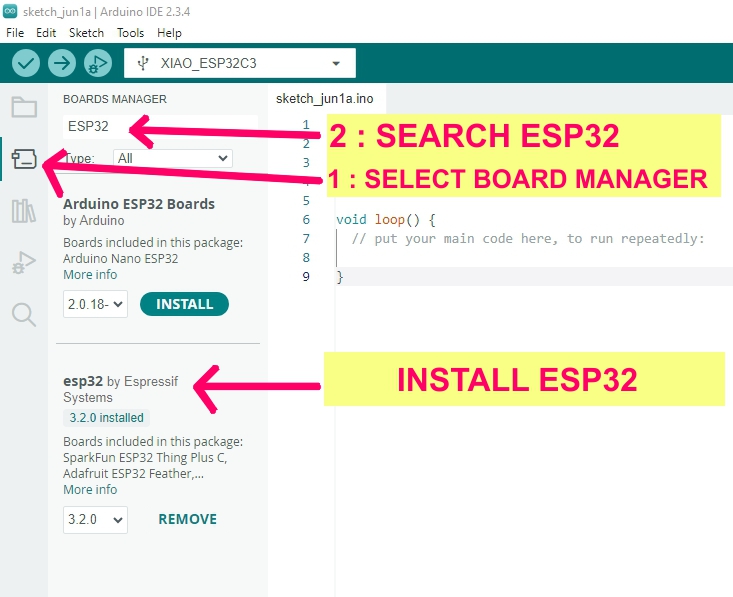
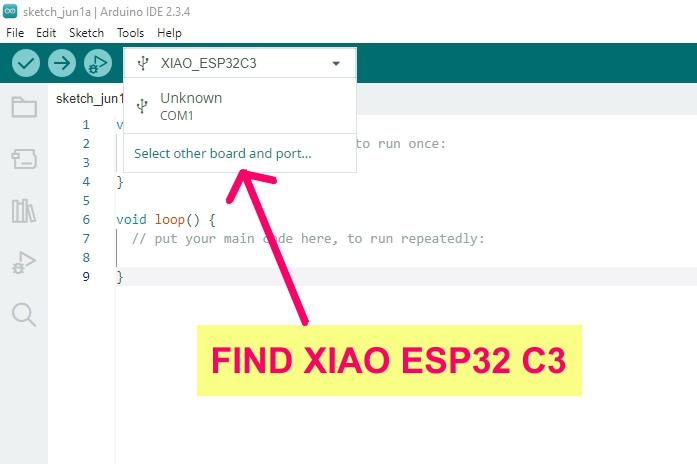
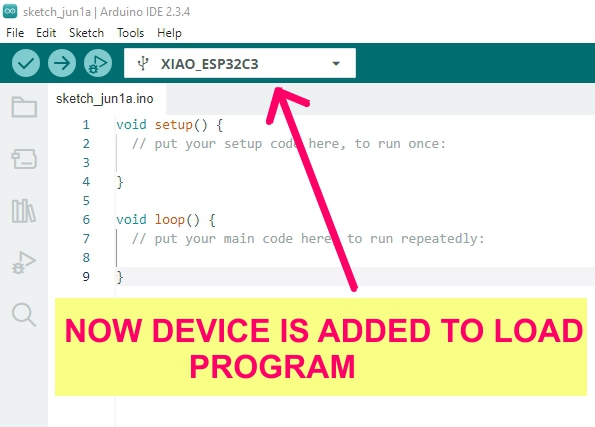
Group Assignment:
Probe an input device(s)'s analog levels and digital signals.
Document your work on the group page and reflect on your individual page what you learned.
A sensor is a device that detects or measures a physical property and converts it into a signal.
In simple words:
A sensor is like a human sense organ (eyes, ears, skin). It helps machines or systems "sense" their
surroundings.
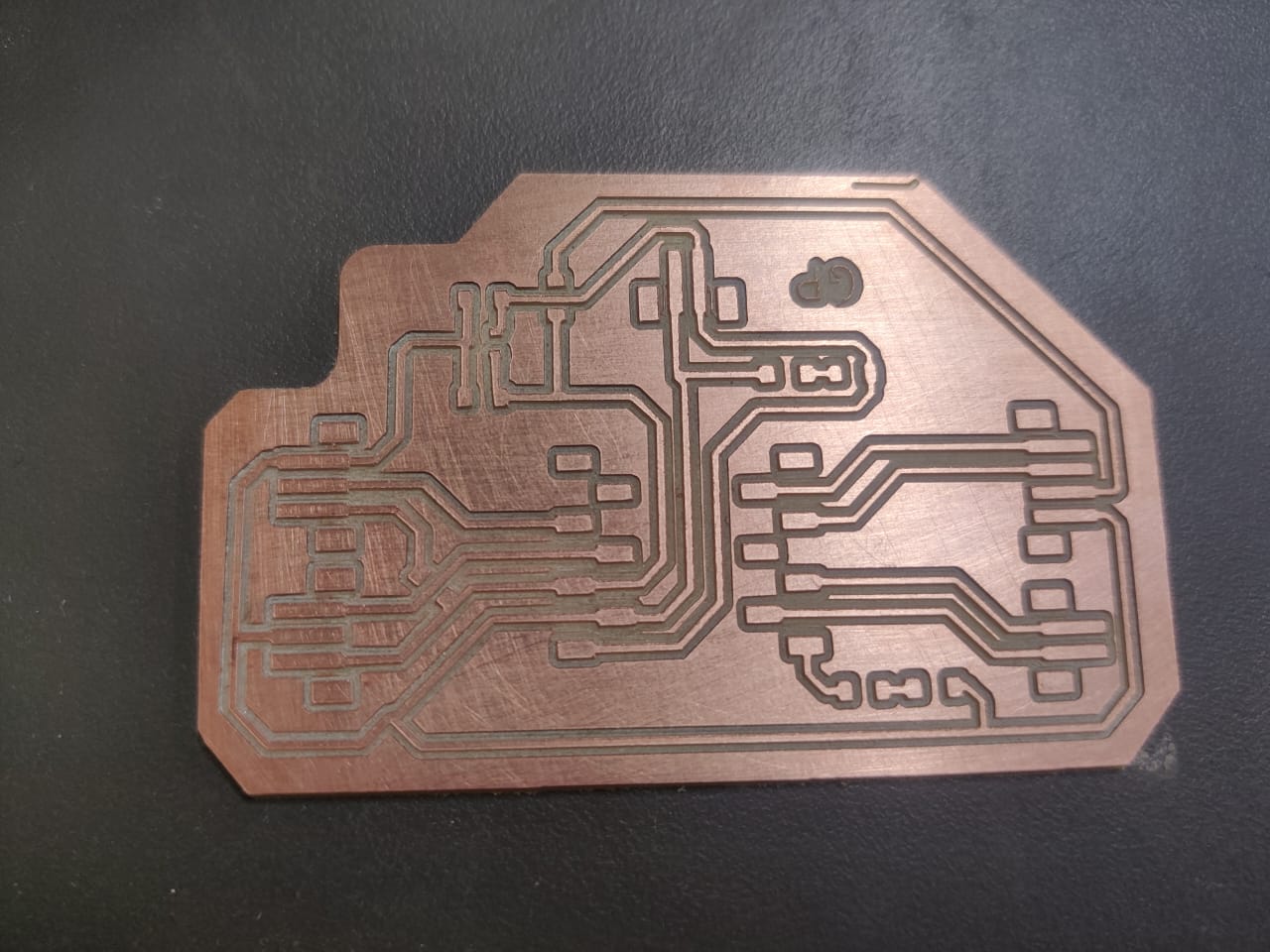
The objective of this project is to design, develop, and test an electronic input device using an Infrared (IR) sensor to control an RGB LED. As part of my Fab Academy 2025 assignment on input devices, this project demonstrates how sensor data can be used to influence output behavior. The IR sensor detects the presence or proximity of an object and sends an analog or digital signal to a microcontroller. This signal is then interpreted to control the color or intensity of an RGB LED, enabling real-time interaction between input and output components. The project involves designing a custom PCB in KiCad, programming the microcontroller to read IR sensor data, and writing logic to control the RGB LED based on sensor input. This assignment enhances my understanding of sensor integration, analog/digital signal processing, and embedded control, contributing to my overall goal of mastering digital fabrication and interactive electronics.
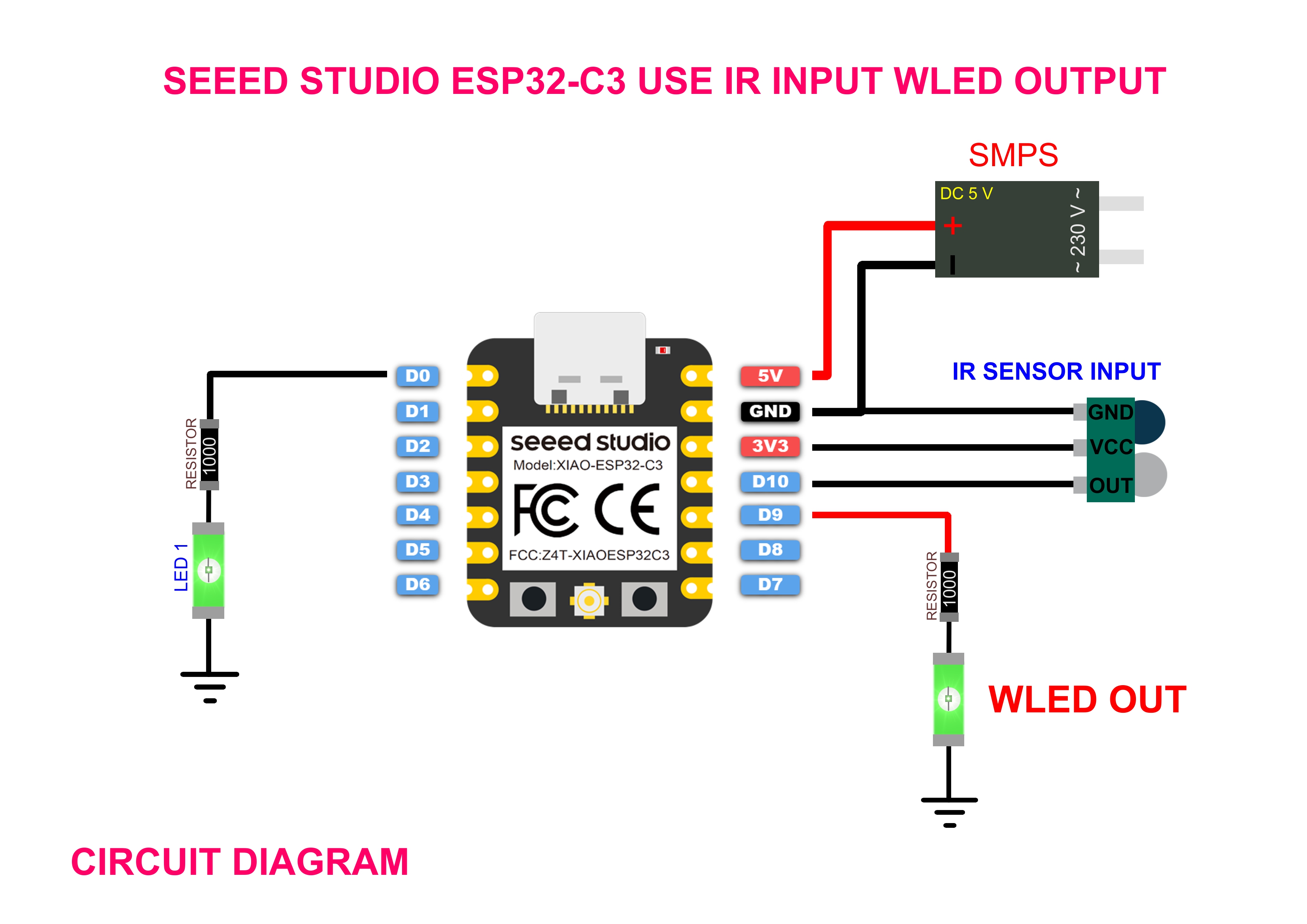
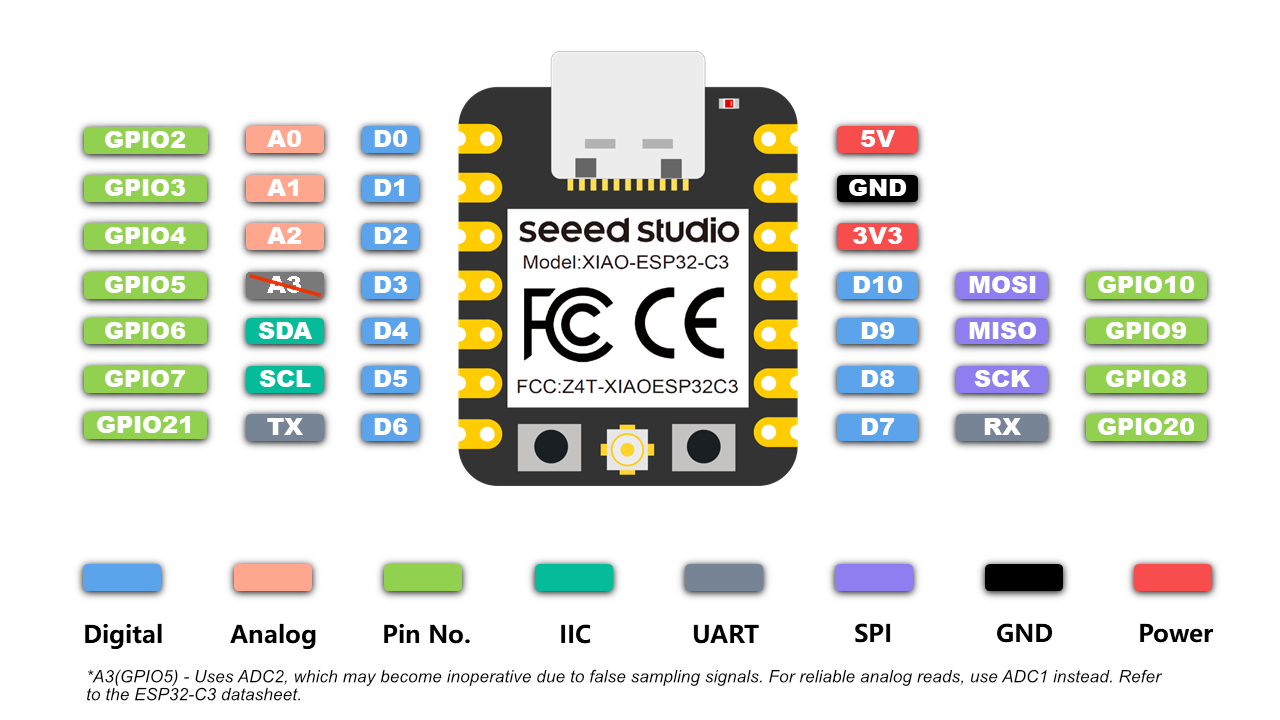
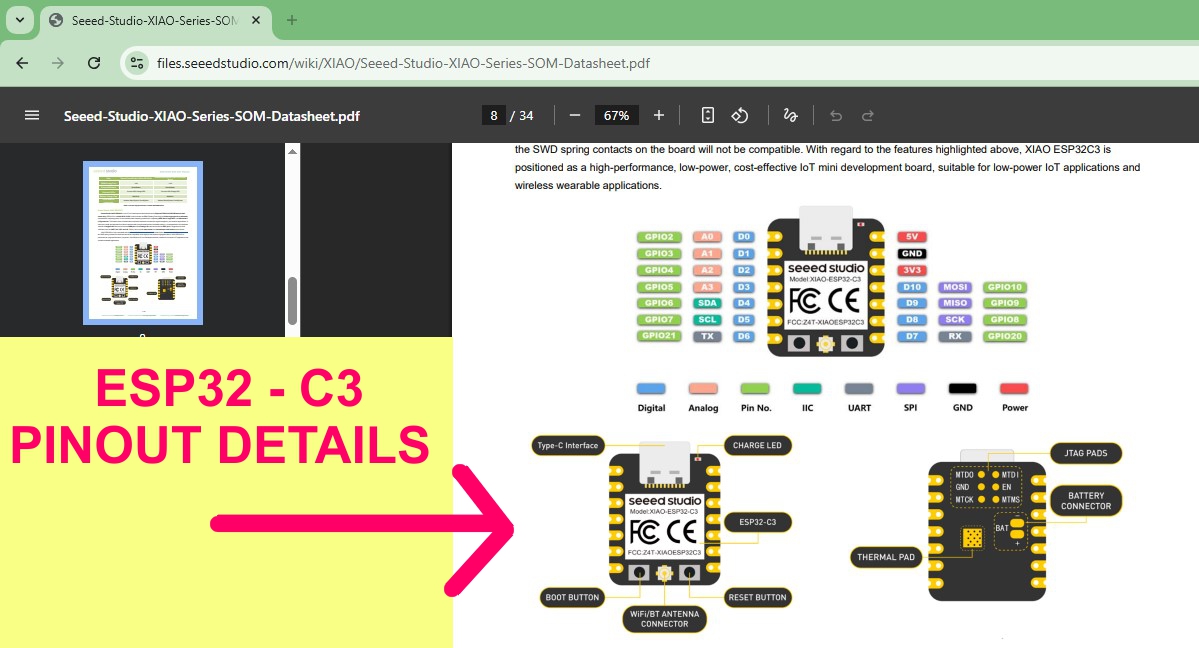
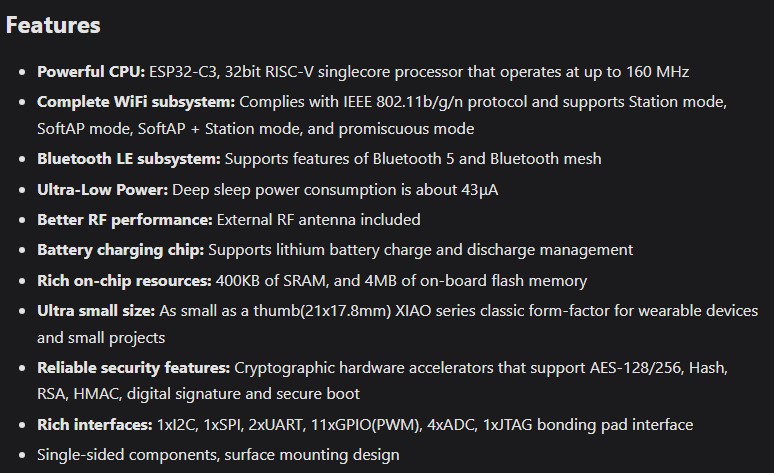
Why I Used ESP32-C3 for Input Week I selected the ESP32-C3 module as the microcontroller for input device testing due to its robust wireless communication, rich peripheral support, and efficient processing capabilities. It supports multiple input interfaces like analog sensors, joysticks, and buttons, enabling real-time data acquisition and wireless transmission.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| CPU | 32-bit RISC-V single-core @ up to 160 MHz |
| SRAM | 400 KB |
| ROM | 384 KB |
| Flash Memory | External (typically 4 MB via SPI) |
| EEPROM | Not available (can be emulated in flash) |
| Operating Voltage | 3.0V to 3.6V |
| Wi-Fi | 2.4 GHz, IEEE 802.11 b/g/n (up to 150 Mbps) |
| Bluetooth | Bluetooth 5.0 LE (Mesh, Long Range) |
| Digital I/O Pins | 22 GPIOs (GPIO0–GPIO21) |
| ADC | 12-bit resolution, 6 channels (GPIO0 to GPIO5) |
| UART | 2 UART interfaces |
| SPI | 2 (SPI0 reserved for flash, SPI1 for general-purpose use) |
| I2C | 1 (SDA/SCL can be mapped to any GPIOs) |
| PWM | Available on all GPIOs |
| Timers | Multiple hardware timers |
| USB | Native USB 2.0 Full-Speed (GPIO19: D-, GPIO20: D+) |
| Security | Flash Encryption, Secure Boot v2, AES, SHA, RSA, ECC |
| Power Consumption | Active ~130 mA, Light Sleep ~0.8 mA, Deep Sleep ~5 µA |
| Package | QFN32 (5 mm × 5 mm) |
| Supported Tools | ESP-IDF, Arduino IDE, PlatformIO, MicroPython |
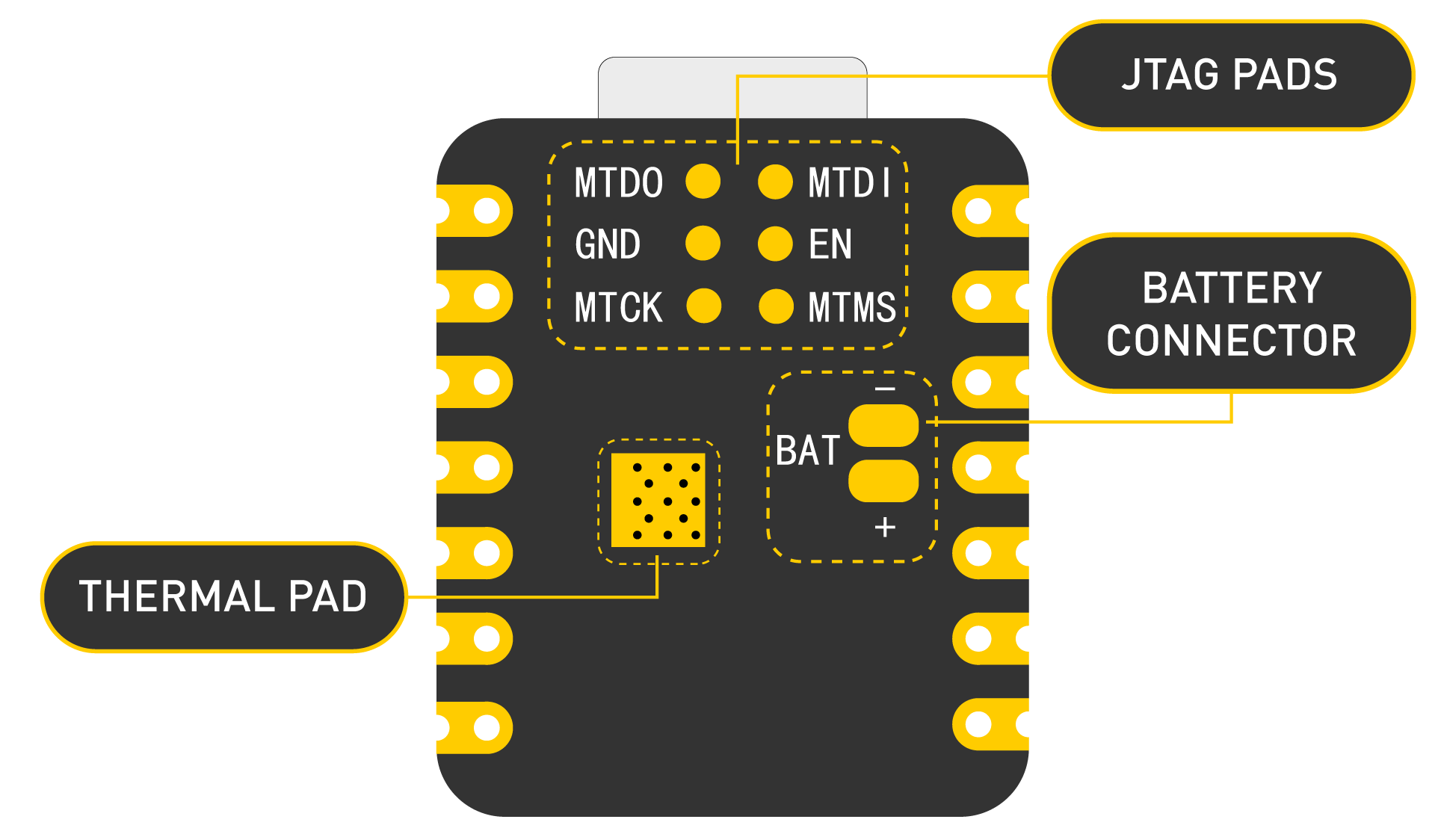
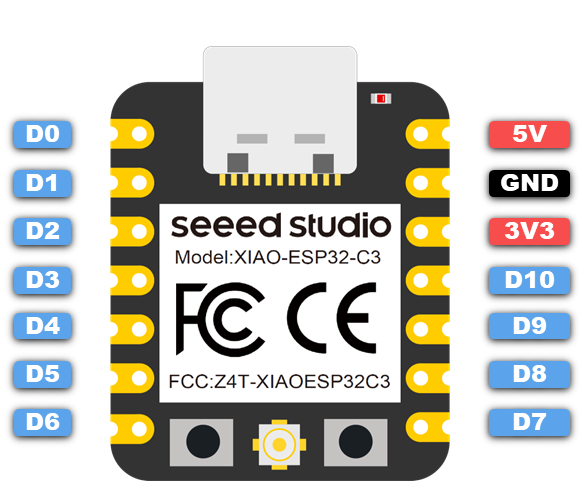
The Seeed Studio XIAO Series offers ultra-compact, powerful microcontroller boards ideal for rapid prototyping and embedded projects in FabLabs and personal studios. With variants like XIAO RP2040, ESP32C3, and nRF52840, they provide built-in USB, multiple GPIOs, and support for Arduino, CircuitPython, and PlatformIO. Their tiny form factor (21x17.5 mm) and versatile features make them perfect for wearables, IoT, and interactive devices. Each board includes castellated pads for easy soldering to custom PCBs. **Download the official Seeed Studio XIAO Series PDF here:** [https://files.seeedstudio.com/wiki/XIAO\_SERIES/res/XIAO-Series-Datasheet.pdf](https://files.seeedstudio.com/wiki/XIAO_SERIES/res/XIAO-Series-Datasheet.pdf)
The Seeed Studio XIAO Series System on Module (SoM) user manual provides comprehensive guidance for using compact, high-performance microcontroller boards designed for prototyping, embedded applications, and educational use. The XIAO series includes variants like XIAO SAMD21, XIAO RP2040, XIAO ESP32C3, and XIAO nRF52840, each offering unique features such as built-in USB, low power consumption, wireless connectivity (Wi-Fi, BLE), and versatile development environment support (Arduino, PlatformIO, CircuitPython). The manual covers essential topics such as pin configuration, power management, memory specs, programming modes, and firmware flashing procedures. With castellated edges and a small form factor (21 x 17.5 mm), XIAO modules are ideal for wearable electronics, IoT devices, and student projects. The document also includes hardware schematics, PCB layout, and application guidelines to support integration into custom designs, making it a valuable reference for FabAcademy students.




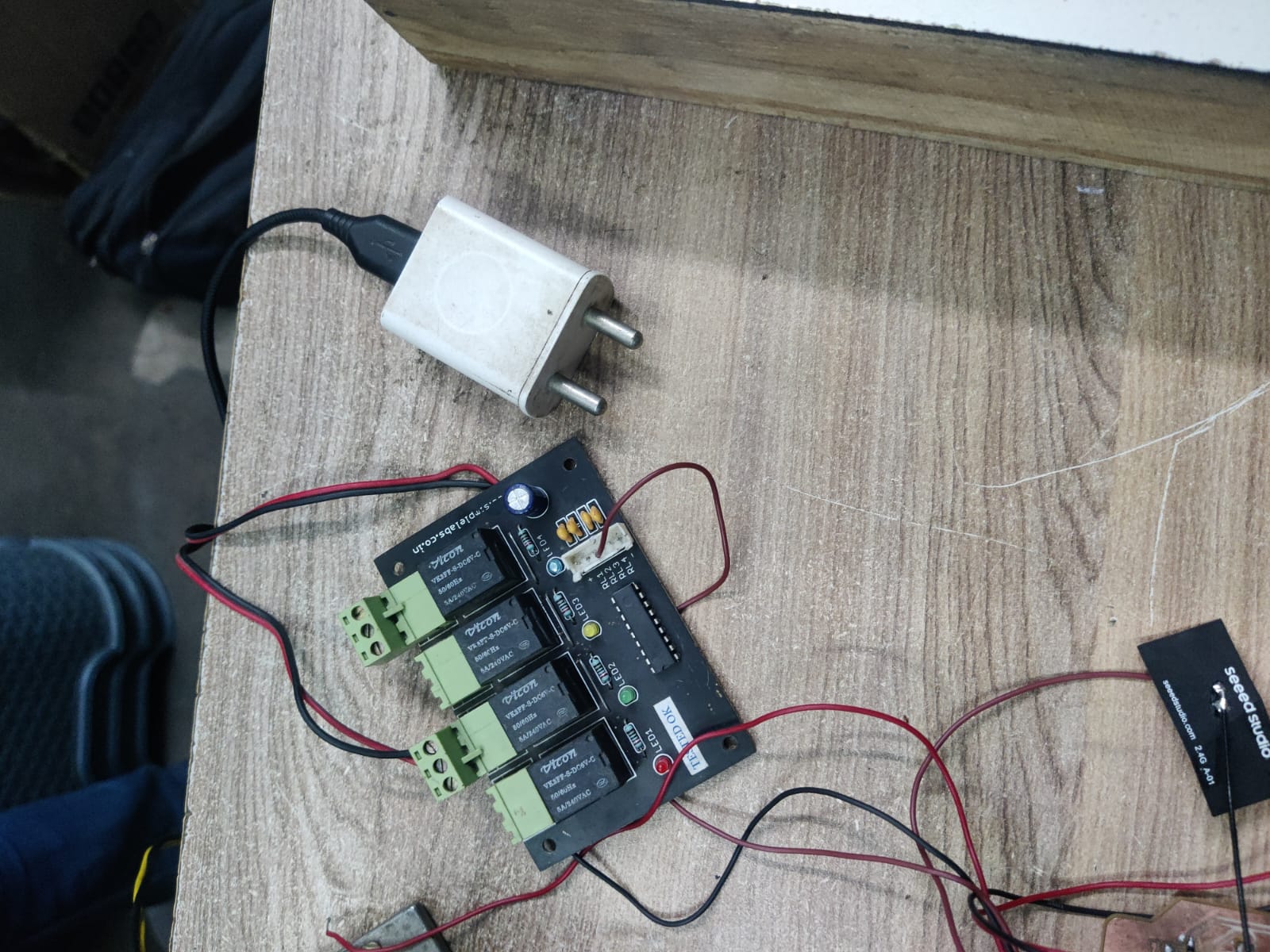
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Seeed Studio XIAO ESP32-C3 | A compact Wi-Fi + BLE microcontroller that reads input signals from the IR sensor and controls output devices like RGB LEDs and a relay. |
| 2. IR Sensor Module | Acts as the input device. Receives infrared signals (e.g., from a remote) and sends data to the ESP32 for processing. |
| 3. Common Cathode RGB LED | A 4-pin LED capable of emitting Red, Green, and Blue light. Controlled using PWM signals from the ESP32 to create various colors. |
| 4. Relay Module (5V) | Allows the ESP32 to control high-power AC/DC devices. Acts as an electrically isolated switch. |
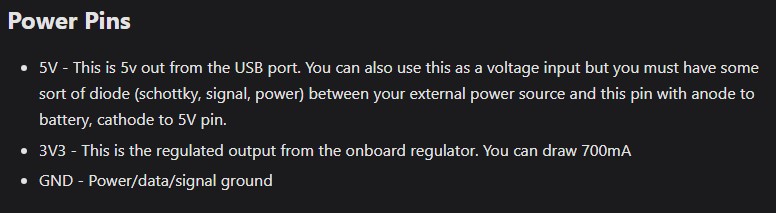
| 5. Buck Converter (e.g., LM2596) | Steps down battery voltage (e.g., from 7.4V or 12V) to 5V or 3.3V to safely power the ESP32 and other components. Ensures stable voltage supply. |
| 6. Custom PCB Board | A soldered board that organizes and connects all components. Useful for compactness, durability, and debugging. |
| 7. Battery (Li-ion or 2S Pack) | Supplies raw DC voltage (often higher than needed). Used with a buck converter to provide regulated voltage to the circuit. |
| 8. Resistors (220Ω–330Ω) | Protect the RGB LED by limiting current. Connected in series with each color pin. |
| 9. Capacitors (e.g., 0.1µF) | Help filter noise and stabilize the ESP32’s power supply, especially important when using relays or motors. |
| 10. Male/Female Header Pins | For modularity and easy replacement of components during testing. Useful for sensors or RGB LED connection. |
| 11. Jumper Wires / Connectors | For flexible connections, especially between the buck converter output and ESP32 power input (3V3 or 5V). |
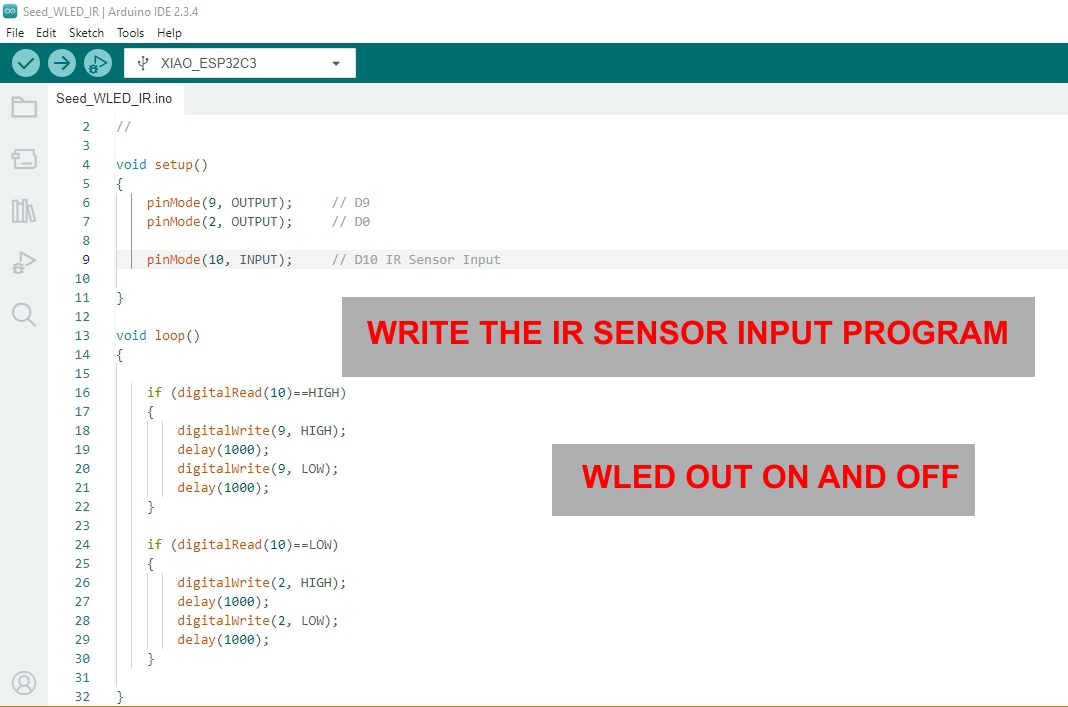
This Arduino project reads a digital input from pin 10 and controls two LEDs connected to pin 9 and pin 2. Depending on the input state, the appropriate LED blinks every second.
INPUT, used to detect a digital signal (e.g., from a switch).OUTPUT, turns ON/OFF when input is HIGH.OUTPUT, turns ON/OFF when input is LOW.
void setup()
{
pinMode(9, OUTPUT); // Output 1
pinMode(2, OUTPUT); // Output 2
pinMode(10, INPUT); // Input
}
void loop()
{
if (digitalRead(10) == HIGH)
{
digitalWrite(9, HIGH);
digitalWrite(2, LOW); // Ensure other LED is off
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(9, LOW);
delay(1000);
}
else
{
digitalWrite(2, HIGH);
digitalWrite(9, LOW); // Ensure other LED is off
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(2, LOW);
delay(1000);
}
}
Note: If using a pushbutton or switch on pin 10, ensure proper pull-up or pull-down resistors are used to prevent floating input states.
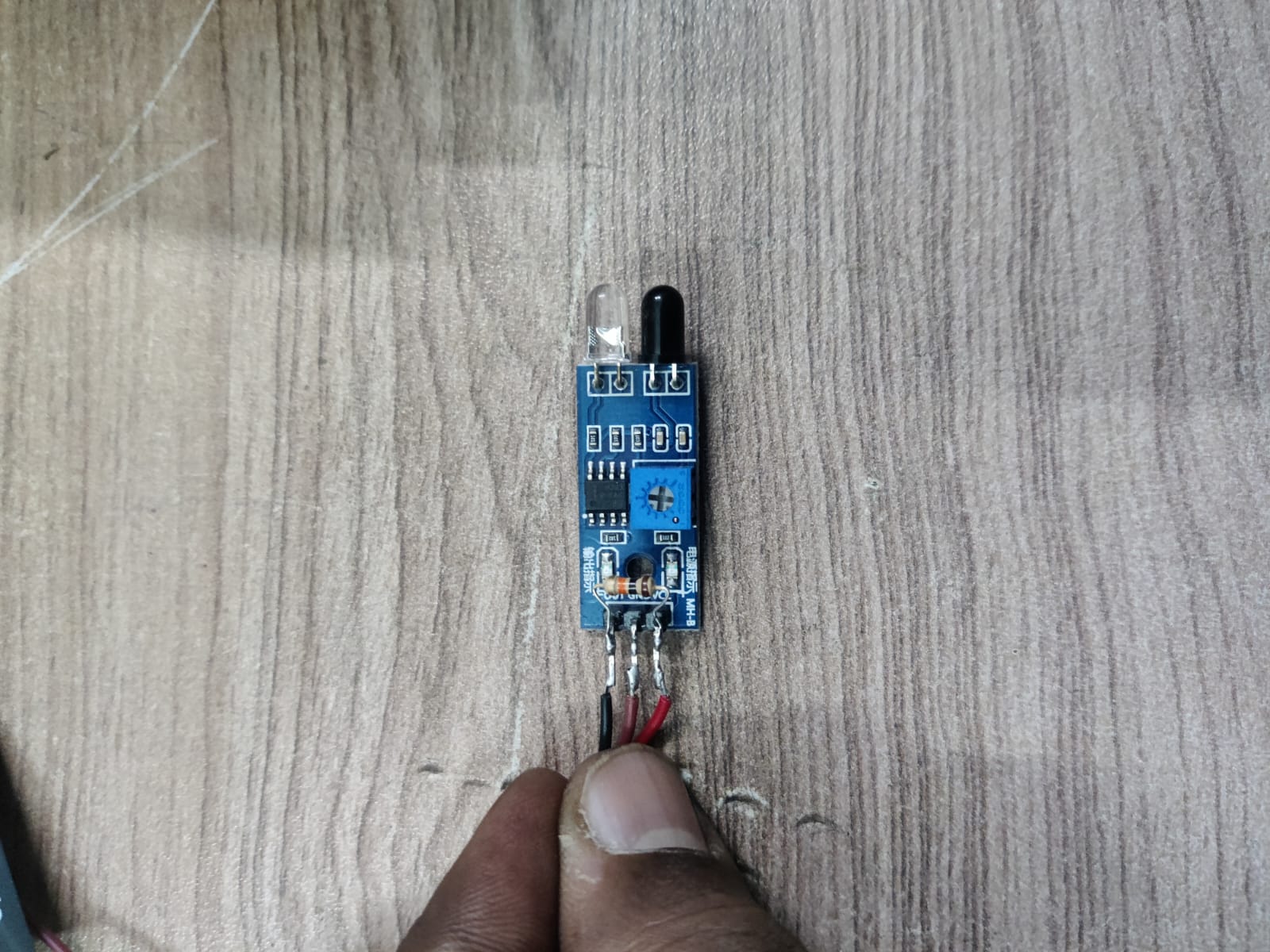

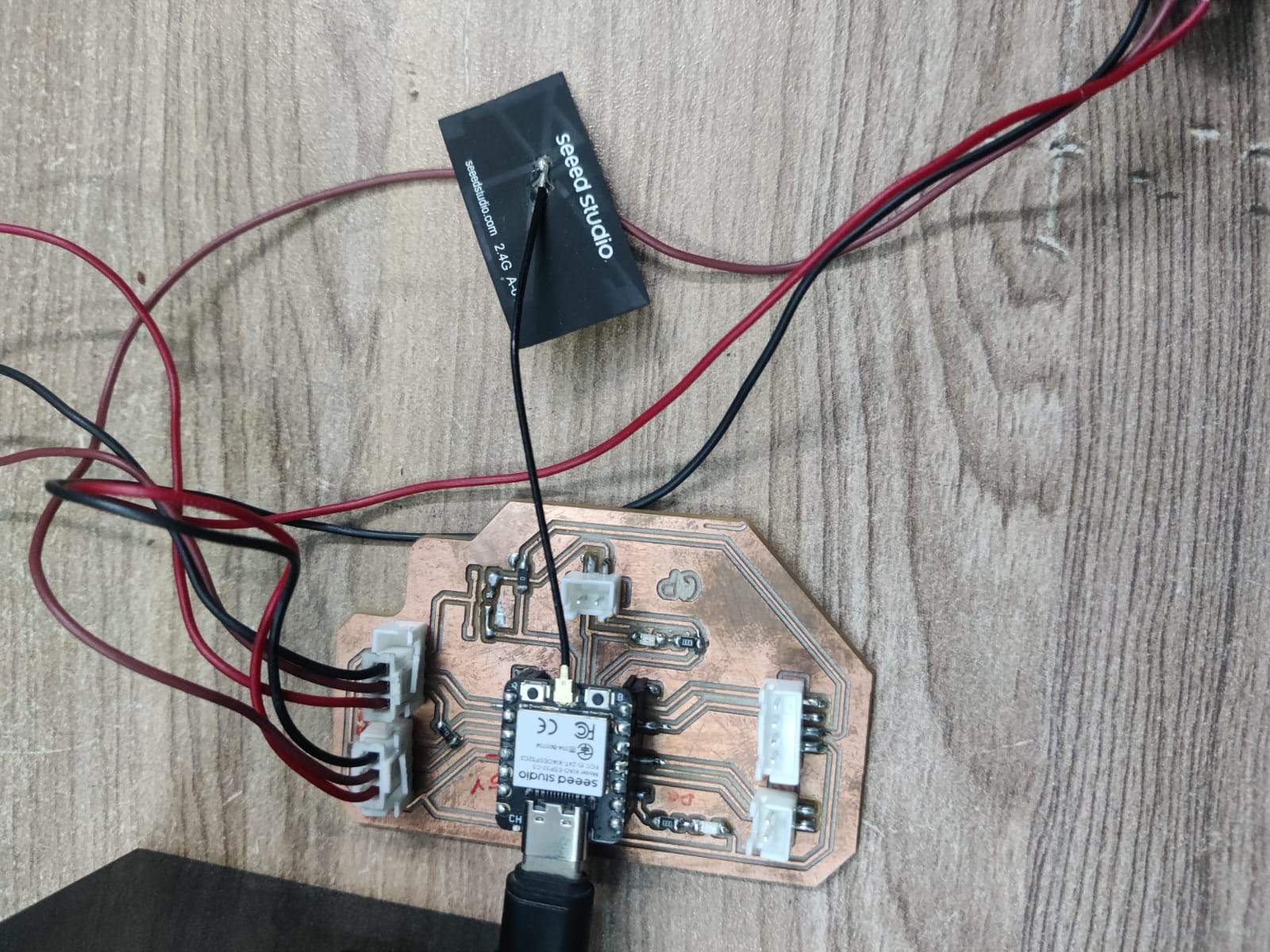
For my Fab Academy Input Devices assignment, I designed a simple interactive system using an IR (Infrared) sensor to control an RGB LED light strip. The IR sensor acts as the input device, continuously emitting and detecting infrared signals. Under normal conditions, when the IR beam is not obstructed, the system interprets this as a "clear" state. In response, the RGB LED light strip remains active, cycling through colors or blinking continuously using PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signals controlled by the Seeed Studio XIAO ESP32-C3 microcontroller.
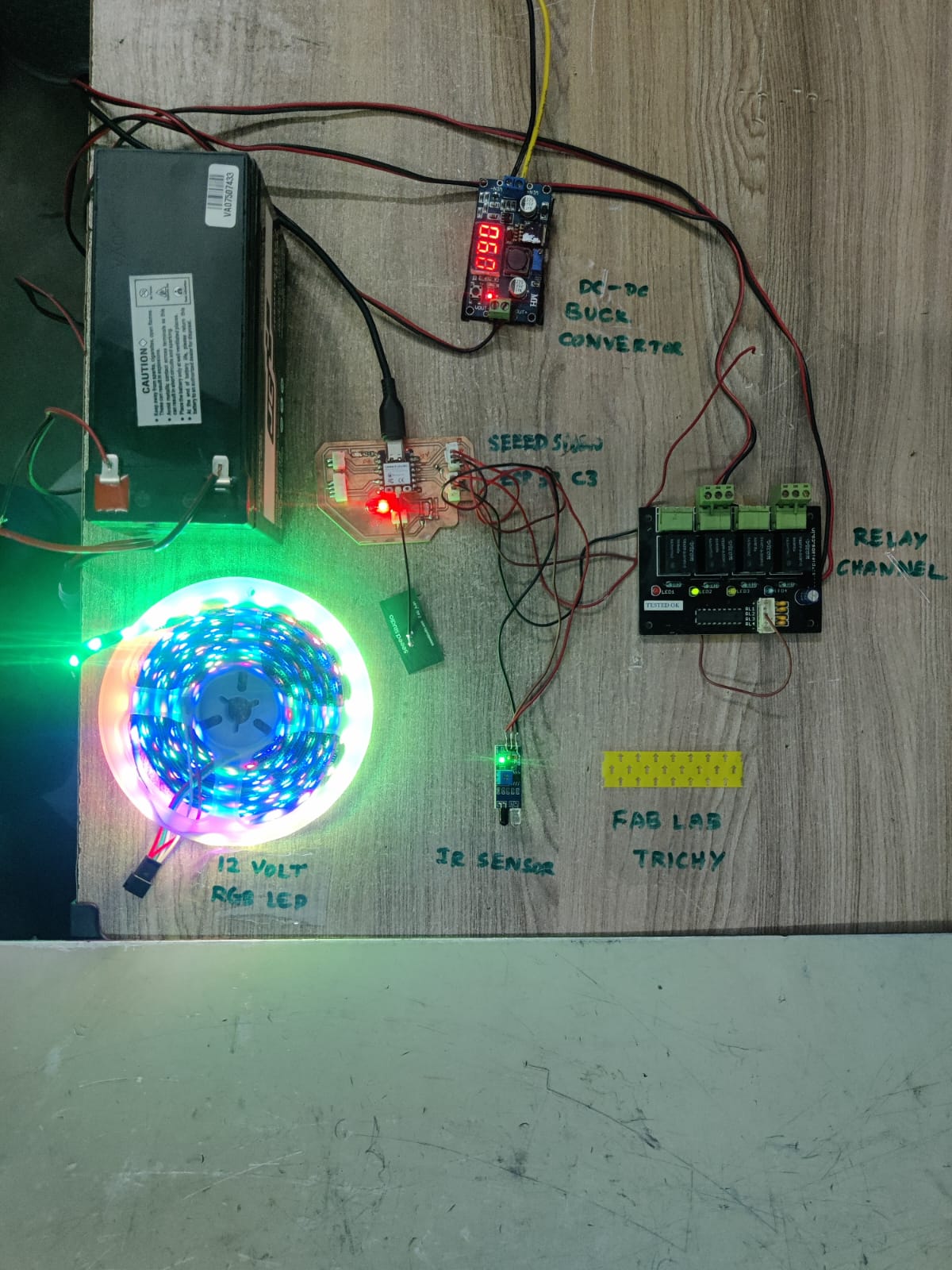

When an object blocks the IR sensor (such as a hand or any solid object), the IR receiver detects the absence of the reflected signal. This triggers a change in logic on the ESP32, which is programmed to immediately turn off the RGB LED strip. This simulates an interactive response where user presence or motion alters the lighting behavior. The RGB LED remains off until the IR sensor is no longer blocked. This project demonstrates how digital input sensing and PWM-controlled outputs can be combined in real-time interaction using simple components. It also highlights the practical use of microcontrollers to bridge input sensing and visual feedback in creative applications.
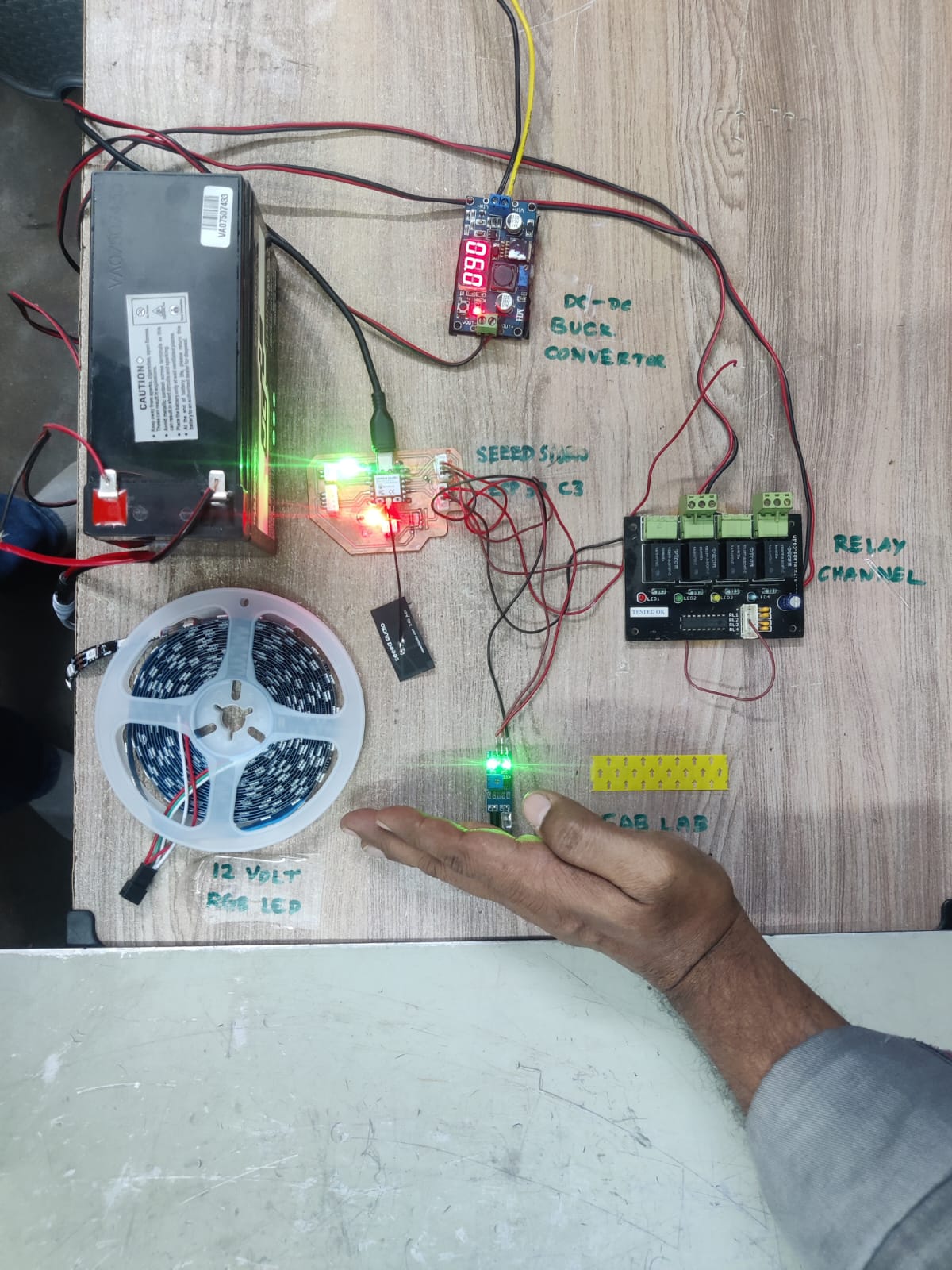
During my input device assignment, I integrated both low-power input (IR sensor) and high-power output (12V RGB LED strip) components. This required careful voltage management and safe control circuitry. Here are the problems I faced and the solutions I implemented:
Problem:
I used a 12V, 7A sealed lead-acid battery to power the entire setup. While this was suitable for the RGB LED strip, my microcontroller (ESP32-C3) and sensor required 3.3V and 5V respectively. Supplying the wrong voltage could damage components.
Fix:
I added a buck converter (DC-DC step-down regulator) to derive both 5V and 3.3V outputs from the 12V battery:
This allowed all components to operate off a single 12V battery without compromising safety.