Group Assignment:
Use the test equipment in your lab to observe the operation of a microcontroller circuit board (as a minimum, you should demonstrate the use of a multimeter and oscilloscope)
Document your work on the group work page and reflect what you learned on your individual page
In our group assignment, we collaboratively tested various tools for circuit board design, including KiCad and EasyEDA. We experimented with different methods for schematic capture, footprint assignment, and PCB layout. As a team, we compared the outputs and discussed design constraints like trace width, clearances, and DRC (Design Rule Check). We also practiced using the milling machine to fabricate a simple board and identified key workflow steps for PCB production.
My Reflection
Through this assignment, I learned the complete workflow of electronic design—from schematic creation to PCB fabrication. Using KiCad, I practiced creating schematics, assigning footprints, and routing the PCB layout. I gained confidence in following design rules and understanding electrical connections. Collaborating with my peers helped me identify errors and improve my designs. Testing the milled board taught me the importance of proper trace clearance and drill size selection. This experience strengthened my understanding of electronic components and design constraints, preparing me for more advanced electronic projects in the future. I now feel more comfortable with both the software and hardware aspects.
Individual assignment:Hero Shot
Use an EDA tool to design a development board that uses parts from the inventory to interact and communicate with an embedded microcontroller
Learning outcomes
Select and use software for circuit board design
Demonstrate workflows used in circuit board design
What is EDA tool?
An EDA tool, or Electronic Design Automation tool, is a software or hardware tool used to design and test
electronic
systems. EDA tools are also known as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD) tools.
What EDA tools do?
Design: Create circuit designs
Model: Create models of circuit designs
Simulate: Predict the results of circuit designs before testing
Test: Test the correctness of designs
Analyze: Analyze circuit designs
What are EDA tools used for?
Designing integrated circuits (ICs)
Designing printed circuit boards (PCBs)
Designing systems for data communications, the internet, transportation, and consumer devices
How do EDA tools help?
Increase productivity
Improve power, performance, and area (PPA)
Reduce time to market (TTM)
Anticipate chip performance
Assemble circuit elements
Predict circuit behavior
Capacitors (C) – Store and release electrical energy. Measured in farads (F).
Inductors (L) – Store energy in a magnetic field when current passes through. Measured in henries (H).
Diodes (D) – Allow current to flow in only one direction.
2. Active Components These components require a power source to function. Transistors (Q) – Act as switches or amplifiers. Types: Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) and Field Effect Transistor (FET).
Operational Amplifiers (Op-Amps) – Used for signal amplification, filtering, and other functions.
Integrated Circuits (ICs) – Contain multiple electronic components within a single package, like microcontrollers or logic gates.
3. Electromechanical Components Switches (S) – Manually or electronically control the circuit's on/off state.
Relays – Electrically operated switches that use electromagnets.
Transformers – Transfer electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction.
4. Power Components Batteries – Store and supply DC power.
Voltage Regulators – Maintain a stable voltage supply.
Transformers – Step up or step down AC voltage.
5. Sensors & Display Components LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) – Emit light when current flows through them.
LCD/OLED Displays – Show information in digital circuits.
Temperature, Pressure, and Motion Sensors – Detect changes in the environment and provide input to circuits.
Weekly Goal: Development Board
Objective:
For this week, my goal is to design, mill, and test a custom development board using the SAMD11 microcontroller.
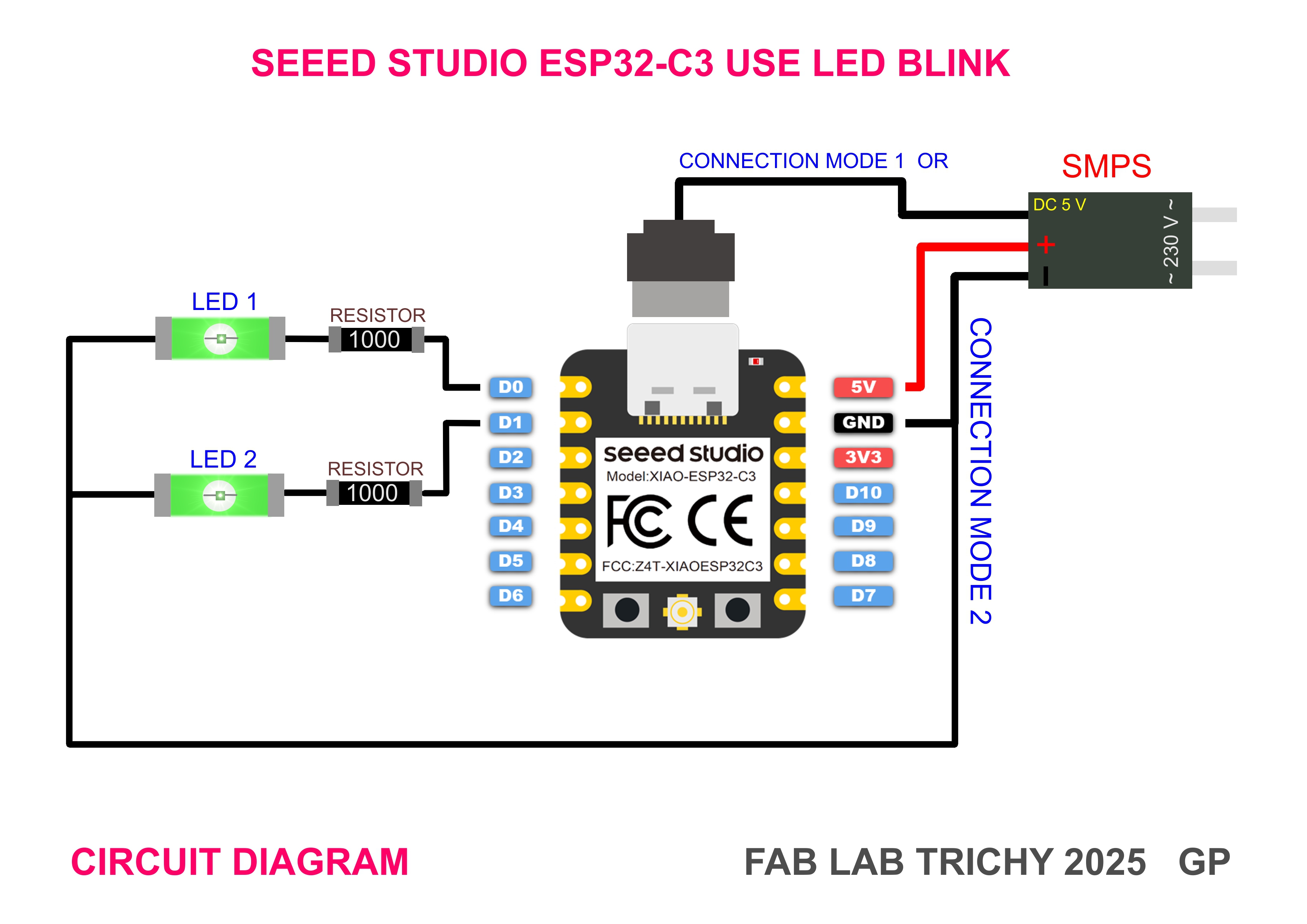
>The XIAO ESP32S3 is a compact yet powerful development board developed by Seeed Studio, based on the Espressif ESP32-S3 SoC. It is part of Seeed’s XIAO series, known for their small footprint and versatile functionality. Here’s a concise description with key features:
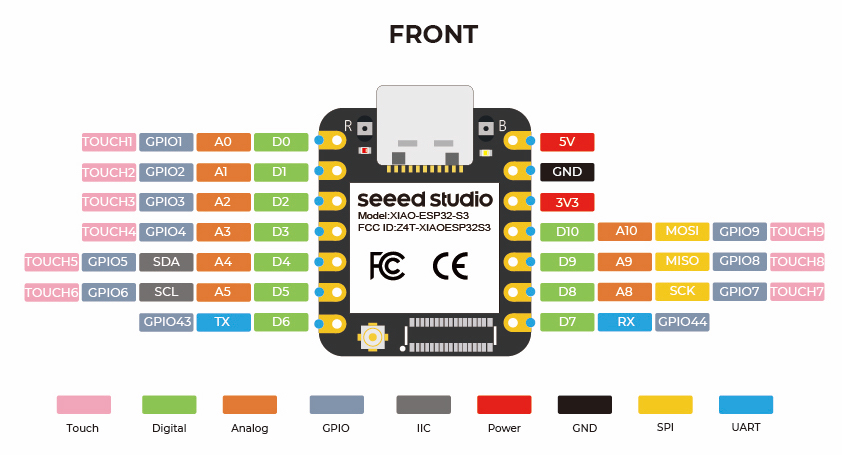
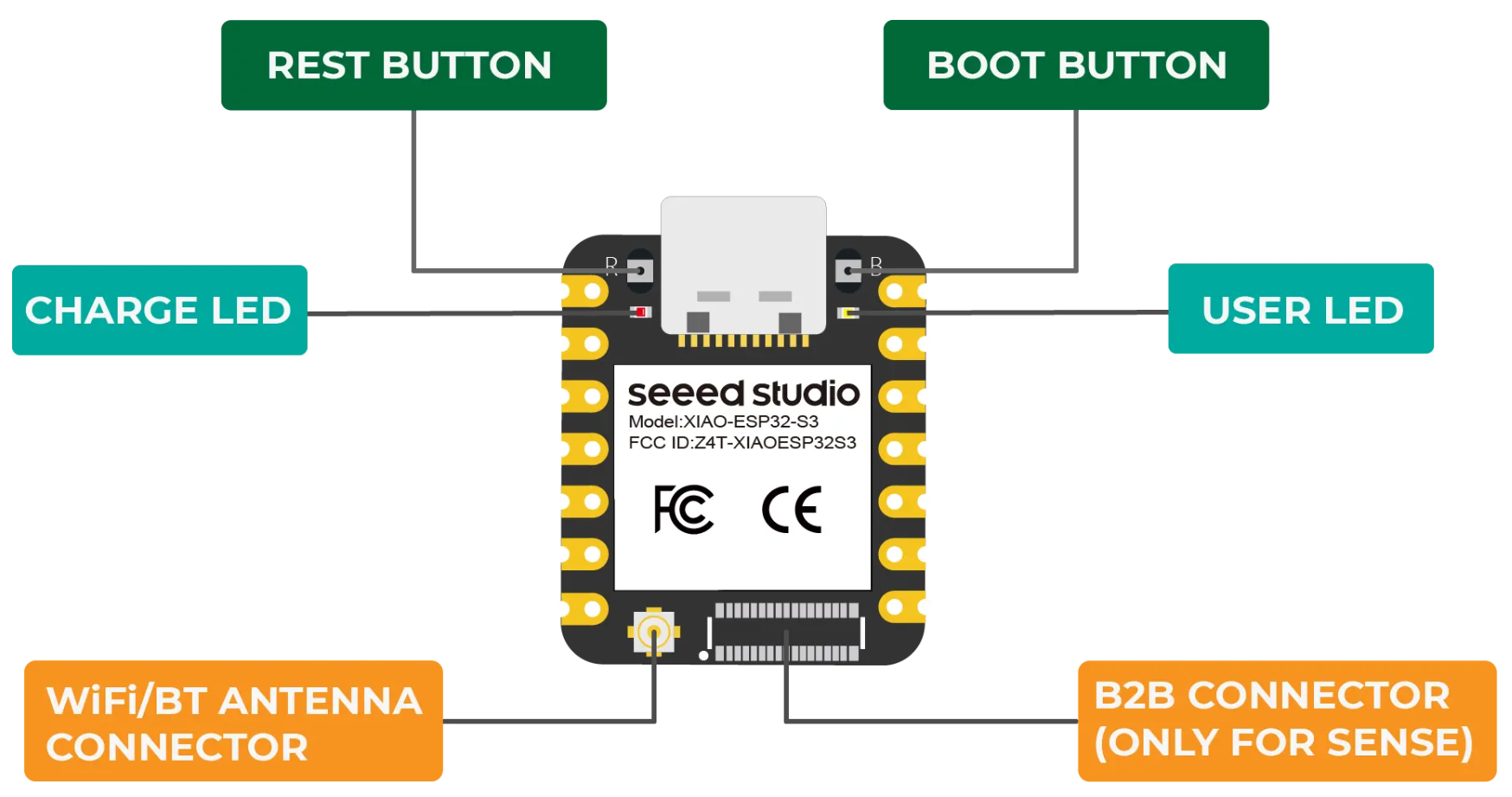
XIAO ESP32S3 Overview Hardware Specifications
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Flash & PSRAM | 8 MB Flash 8 MB PSRAM |
| Wireless Connectivity | Wi-Fi 802.11 b/g/n Bluetooth® 5 (LE) |
| USB Support | Native USB-C (supports USB OTG, device and host modes) |
| Form Factor | Extremely compact: 21 × 17.5 mm Compatible with XIAO series shields |
| GPIOs | 11 multifunctional GPIOs Supports ADC, SPI, I2C, UART, PWM, and DAC |
| Camera Interface | Dedicated 8-bit parallel camera interface (DVP) Suitable for AI and vision applications |
| AI Capability | Supports TensorFlow Lite, ESP-DL, and other AI frameworks on edge |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V logic level |
| Power Supply | USB-C or 5V input through pins |
| Battery Support | Built-in battery charging circuit (Li-Po charging via USB-C) |
| Ideal For |
- Wearable and IoT applications - Edge AI (e.g., simple image classification, gesture recognition) - DIY embedded projects with space constraints - USB-enabled devices or HID applications |
Designing the Development Board
Microcontroller Choice: SAMD11
The development board will be based on the SAMD11, a compact and capable ARM Cortex-M0+ microcontroller, ideal for embedded development and experimentation.
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Microcontroller | ATSAMD11D14A |
| Core | ARM Cortex-M0+ |
| Flash Memory | 16 KB |
| SRAM | 4 KB |
| Operating Voltage | 1.62V – 3.63V |
| Clock Speed | 48 MHz |
| USB Interface | Yes, USB Device |
| Package | SOIC-14 |
PCB Design Using KiCad
Overview of KiCad
KiCad is an open-source EDA (Electronic Design Automation) tool used for schematic capture and PCB layout. A typical KiCad project includes various files such as:
- Project file (
.proor.kicad_pro) - Schematic file (
.sch) - PCB layout file (
.kicad_pcb) - Supporting libraries (symbols, footprints)
- Optional: simulation files, BOMs, and netlists
Schematic Design Process
The first step in the workflow is creating a schematic. This involves:
- Selecting components from standard or custom libraries
- Connecting components with wires to define electrical relationships
- Annotating components for clarity and organization
Create a New Project
Open KiCad → Click on “File > New Project”.
Choose a name and location for your project.
2. Schematic Design (Eeschema)
Open Schematic Editor.
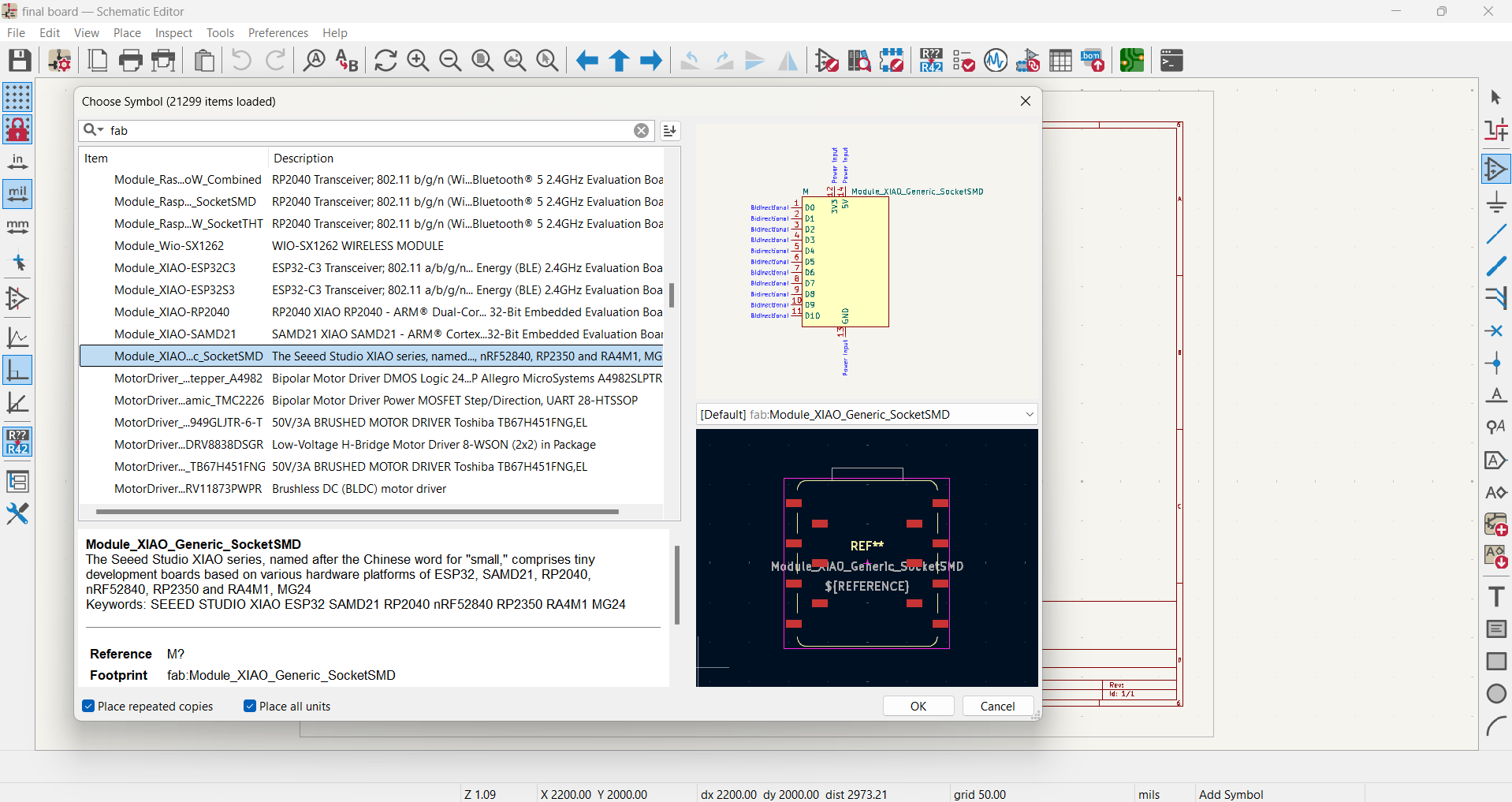
Place components using the “Place Symbol” tool.
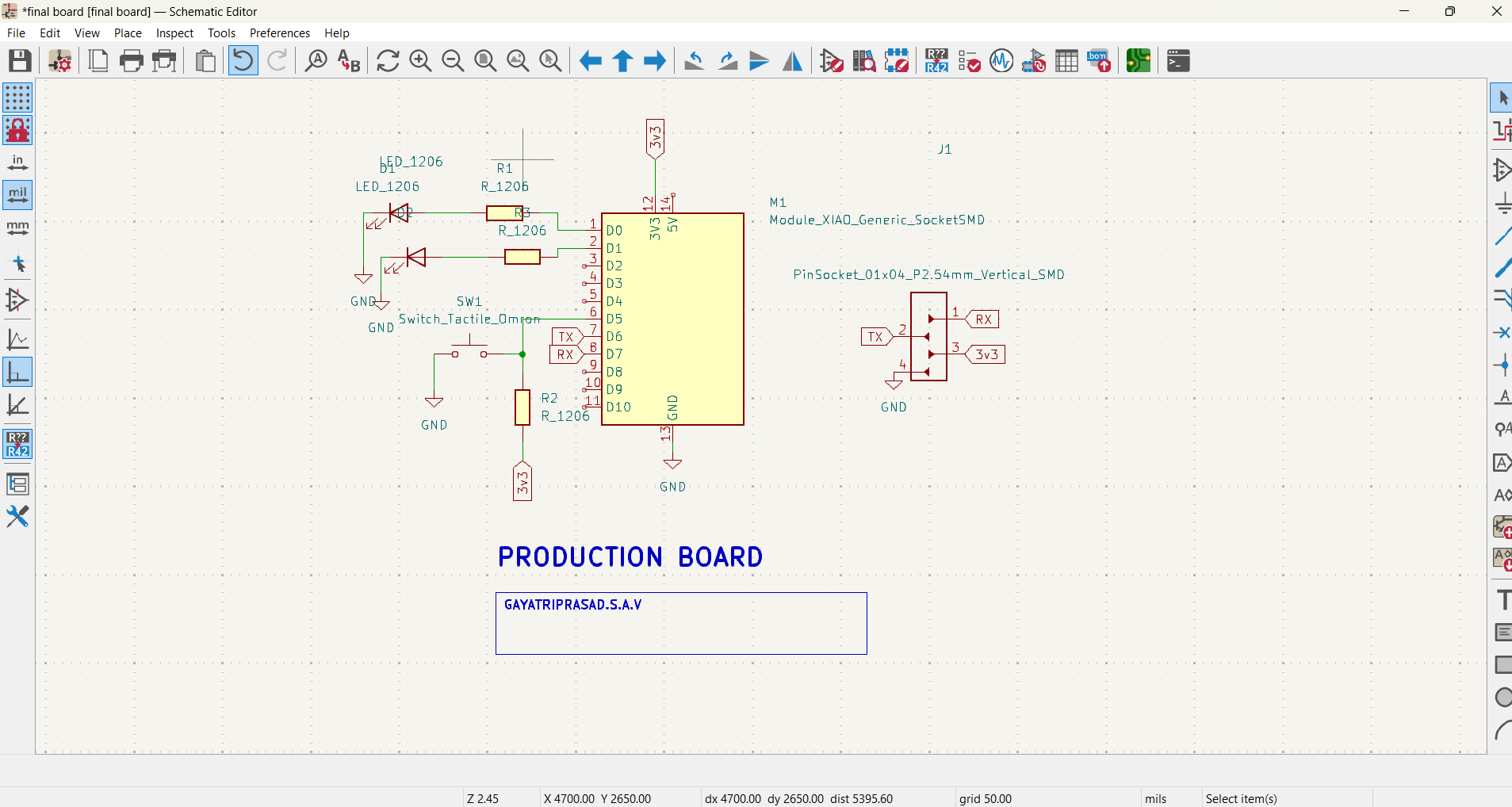
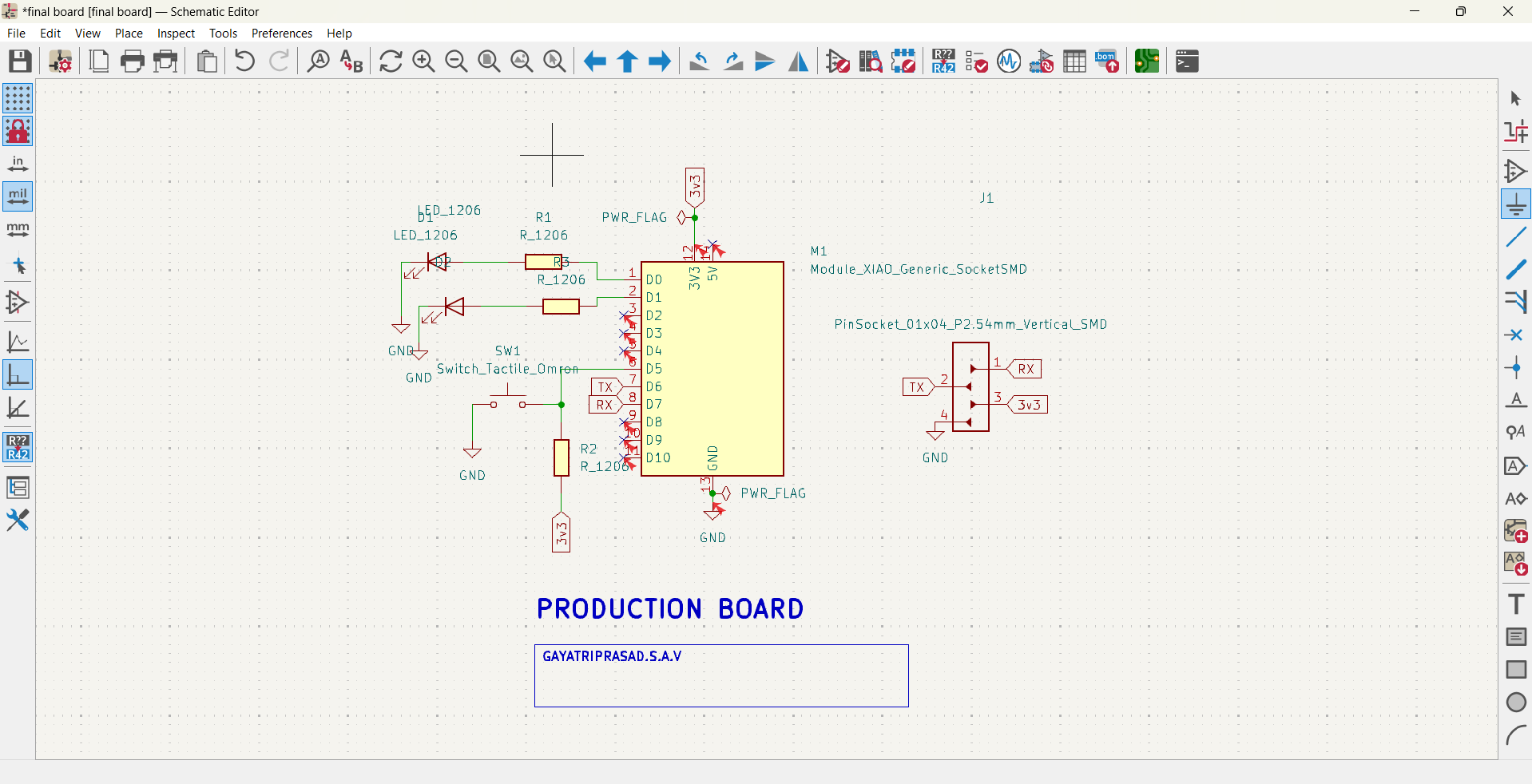
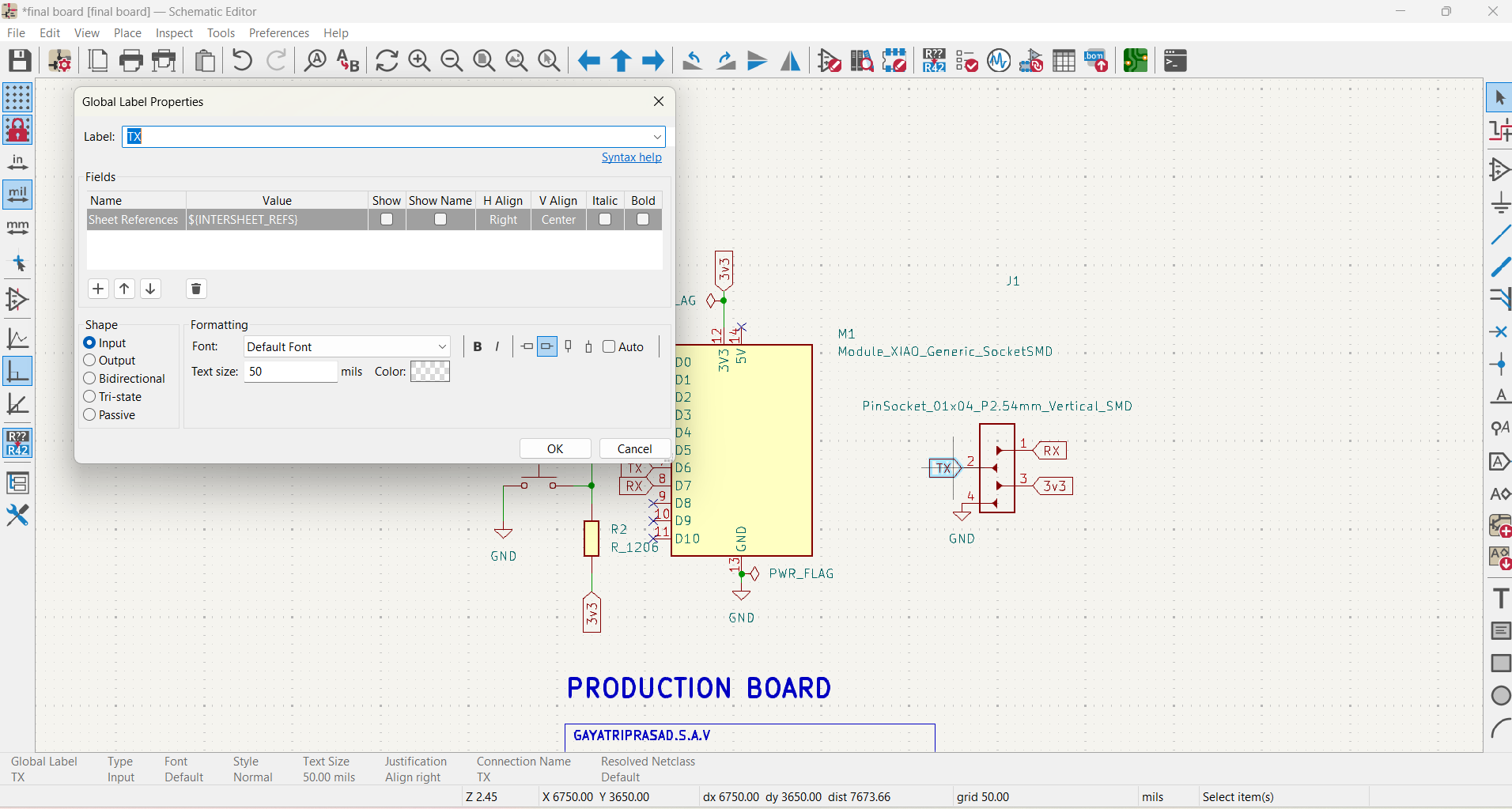
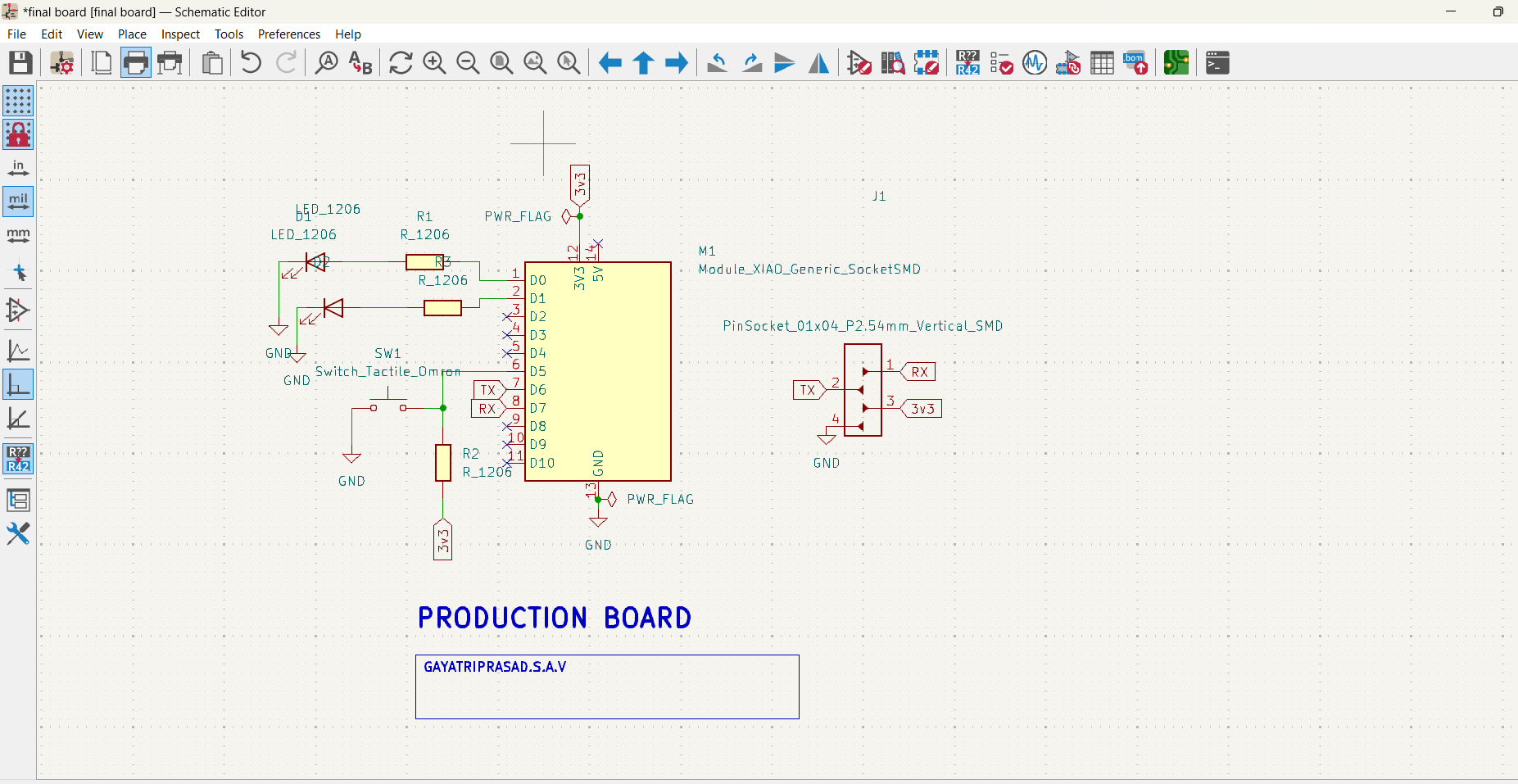
Wire the components using the “Place Wire” tool.
Add power and ground symbols where needed.
3. Assign Footprints
Open “Assign PCB Footprints” tool.
Match each symbol to its appropriate footprint (e.g., resistor to 0603 footprint).
4. Electrical Rules Check (ERC)
Run ERC to check for missing connections or issues.
Fix warnings/errors if needed.
- Assign Footprints: Link each schematic symbol to a corresponding physical footprint.
- Electrical Rules Check (ERC): Run ERC to verify all connections and catch potential schematic errors.
- Generate Netlist / Update PCB: Click “Update PCB from Schematic” to transfer schematic data to the PCB layout editor.
- PCB Layout (Pcbnew):
Fix warnings/errors if needed.
• Open the PCB editor
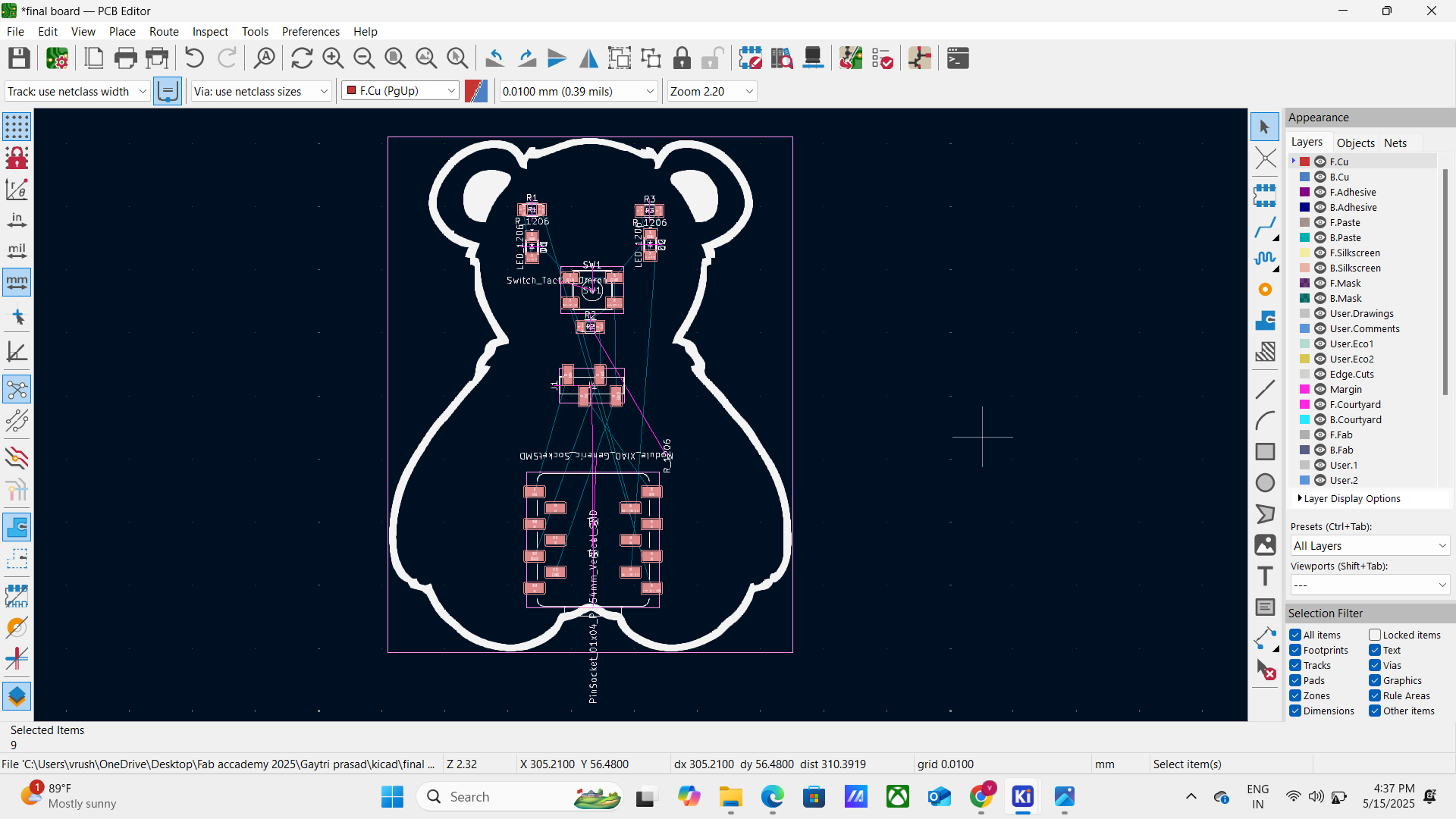
• Import component footprints
• Arrange components logically
• Draw the board outline
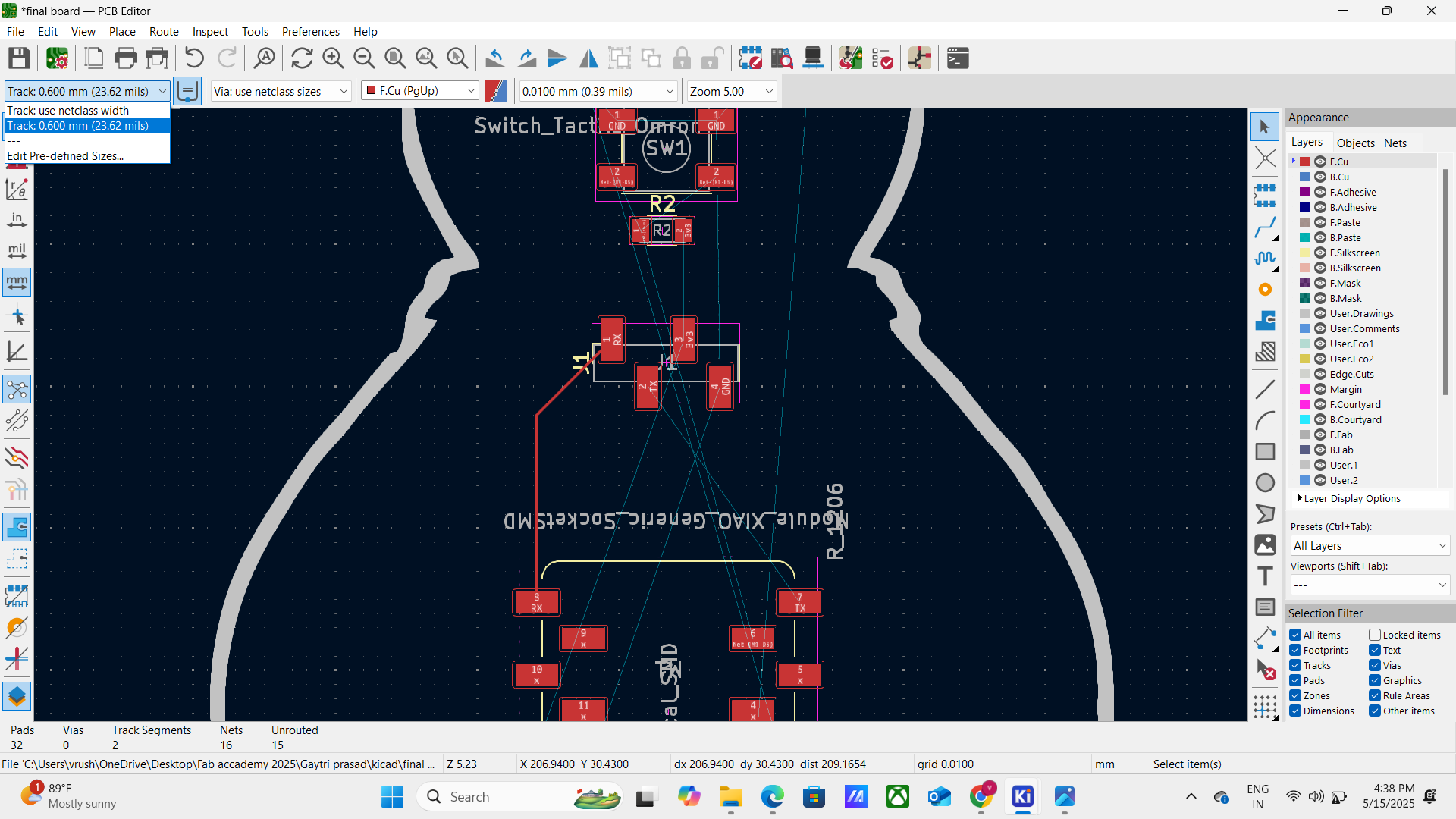
• Route tracks manually (or use autorouter, if available) - Design Rule Check (DRC): Run DRC to detect spacing, clearance, and overlap violations.
- Add Silkscreen, Text, and Logos: Place reference labels, orientation marks, and optional branding or logos.
- Generate Gerber Files: Use the “Plot” tool to export Gerber and drill files for PCB fabrication.
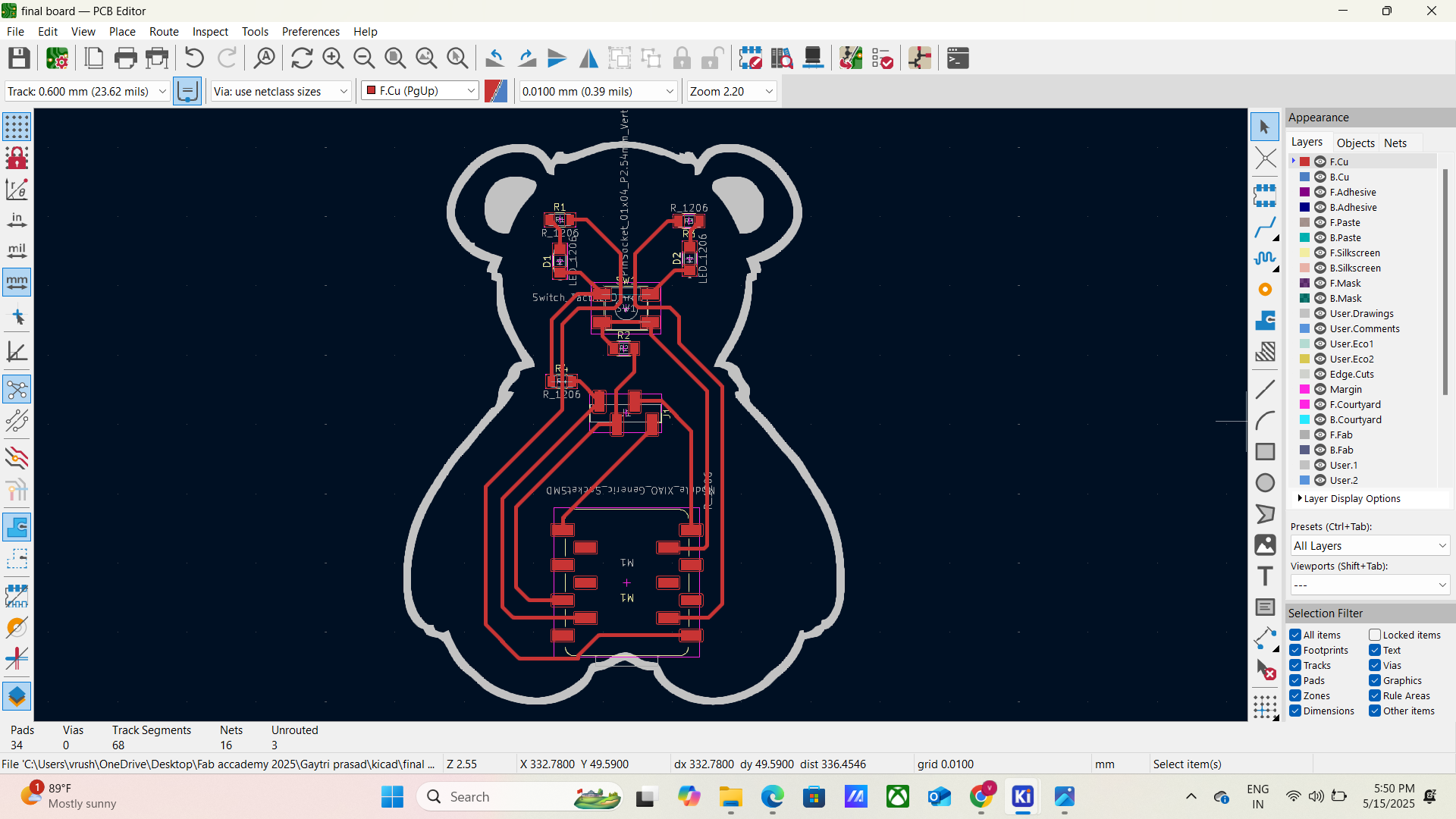
Final Output
3d view of my board
File svg