Measuring Power Consumption
Summary
During the group assignment for Output Devices week, we focused on measuring the power consumption of two types of motors. We began with a simulated test to understand the wiring and expected performance, then moved on to a physical test setup. For each motor, we measured the current draw (in amperes) while operating under the same 12V power supply. The first motor drew approximately 0.415 A, while the second motor drew 0.25 A. Using the power formula, we calculated the power consumption of each motor, helping us compare their efficiency and suitability for different applications.
The group assignment Page :
Work Process Detail
Step 1: Simulation Setup
We began by simulating the motor wiring using a basic circuit diagram. This helped us understand the configuration before physical testing.
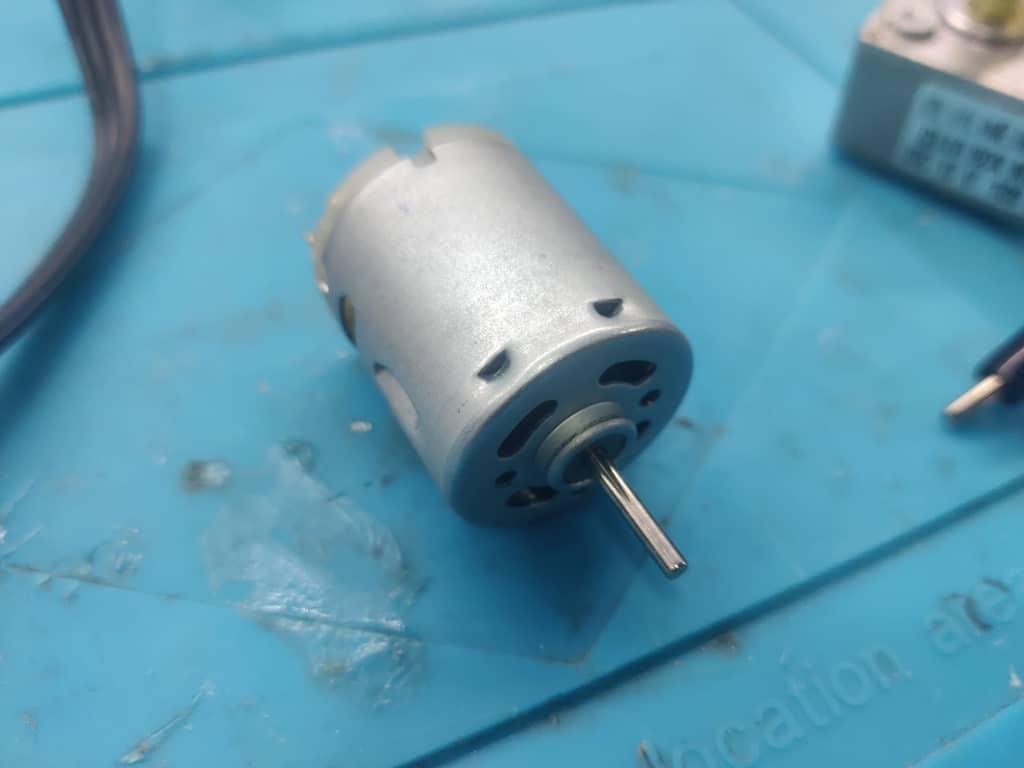
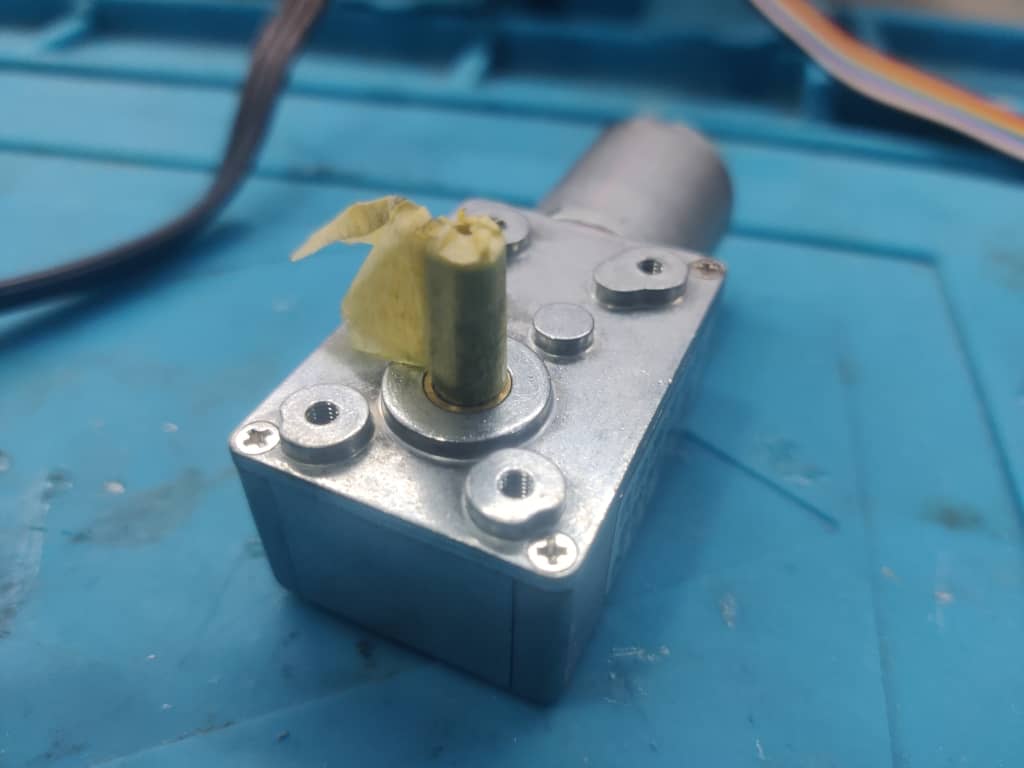
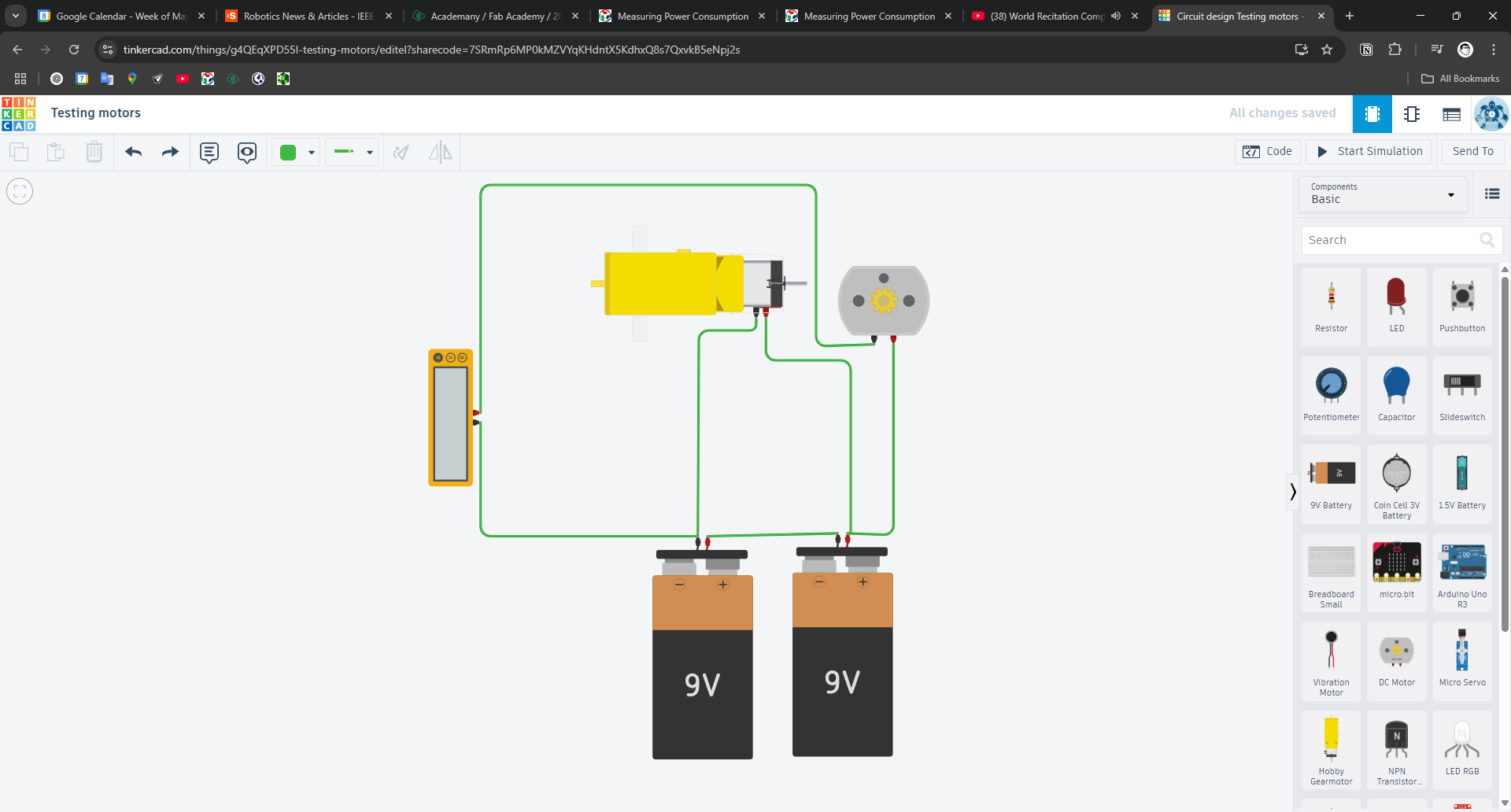
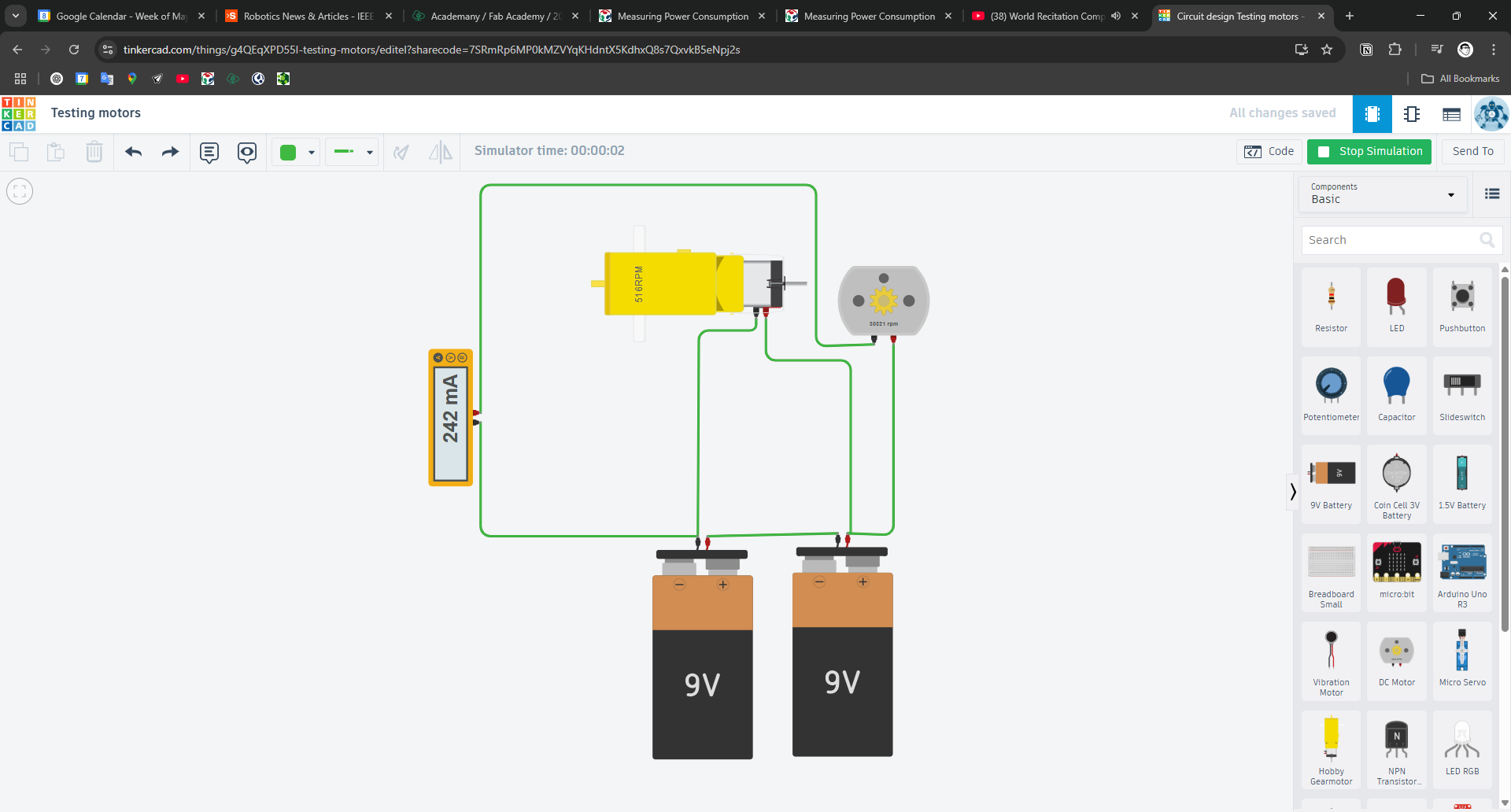


Step 2: Connecting the Motor
We connected the motors to a 12V power supply. The wiring was double-checked to ensure correct current flow.
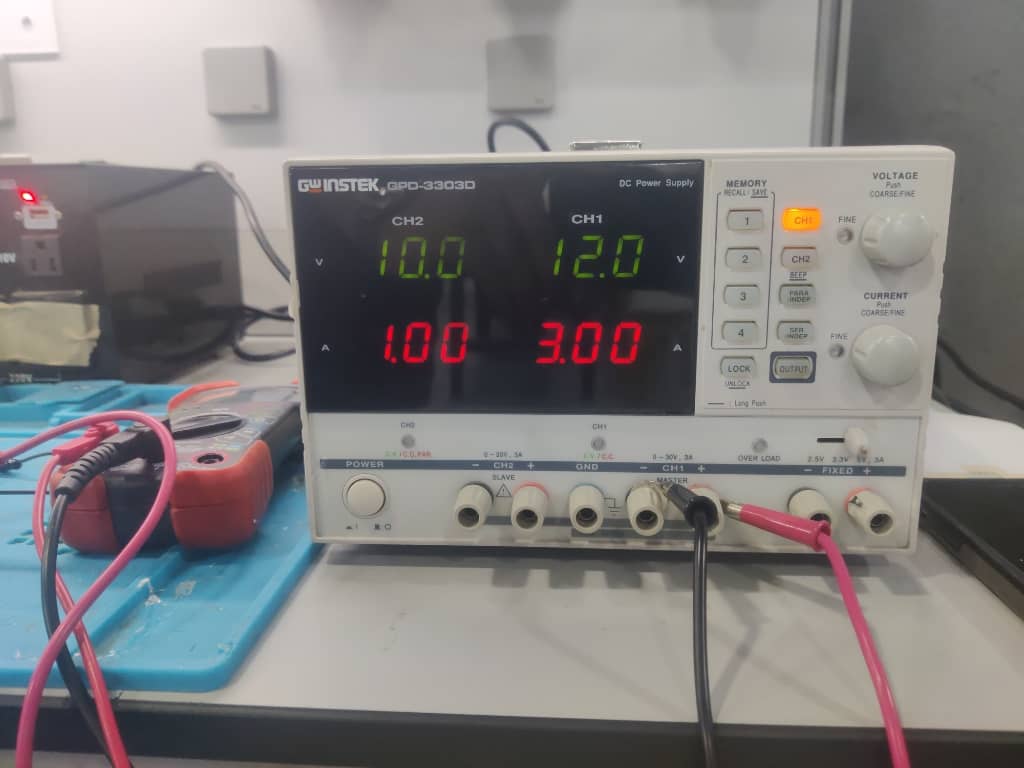

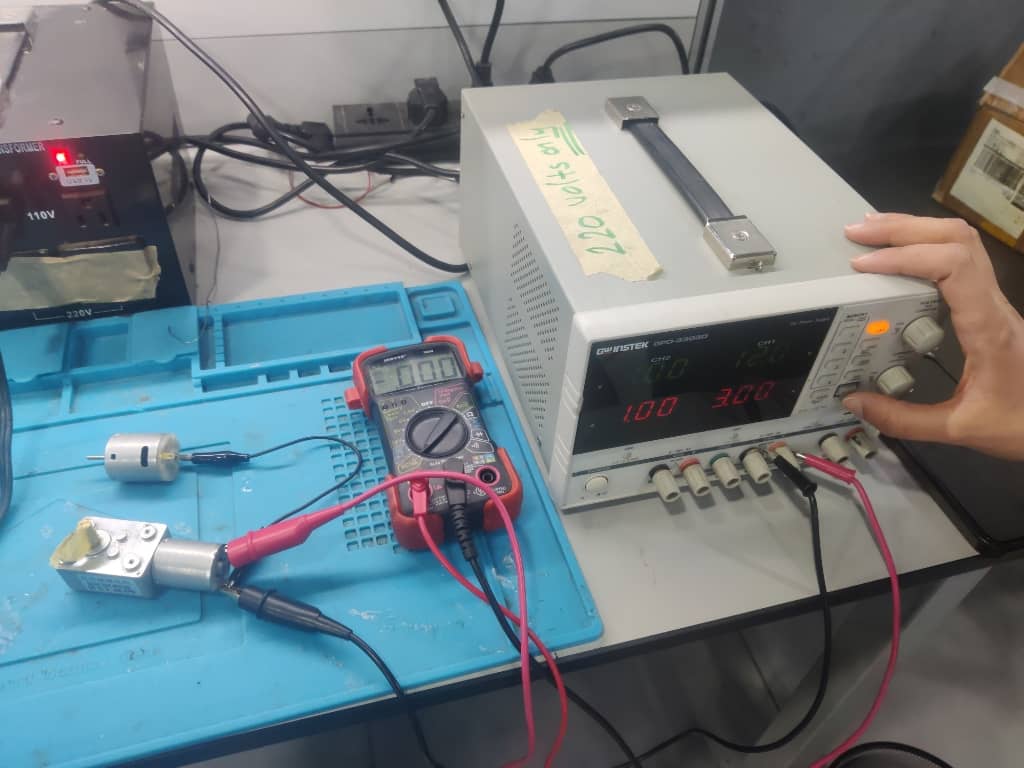

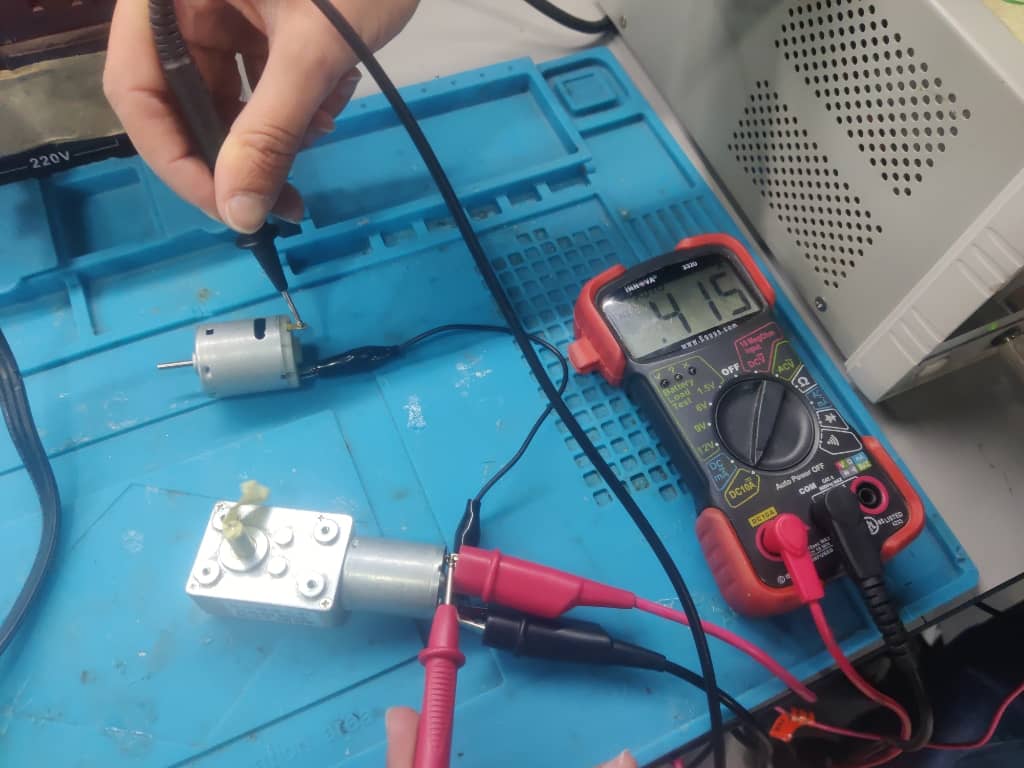
Step 3: Measuring Current for Motor 1
Using a digital multimeter, we measured the current drawn by Motor 1 during operation. The reading was 0.415 A.
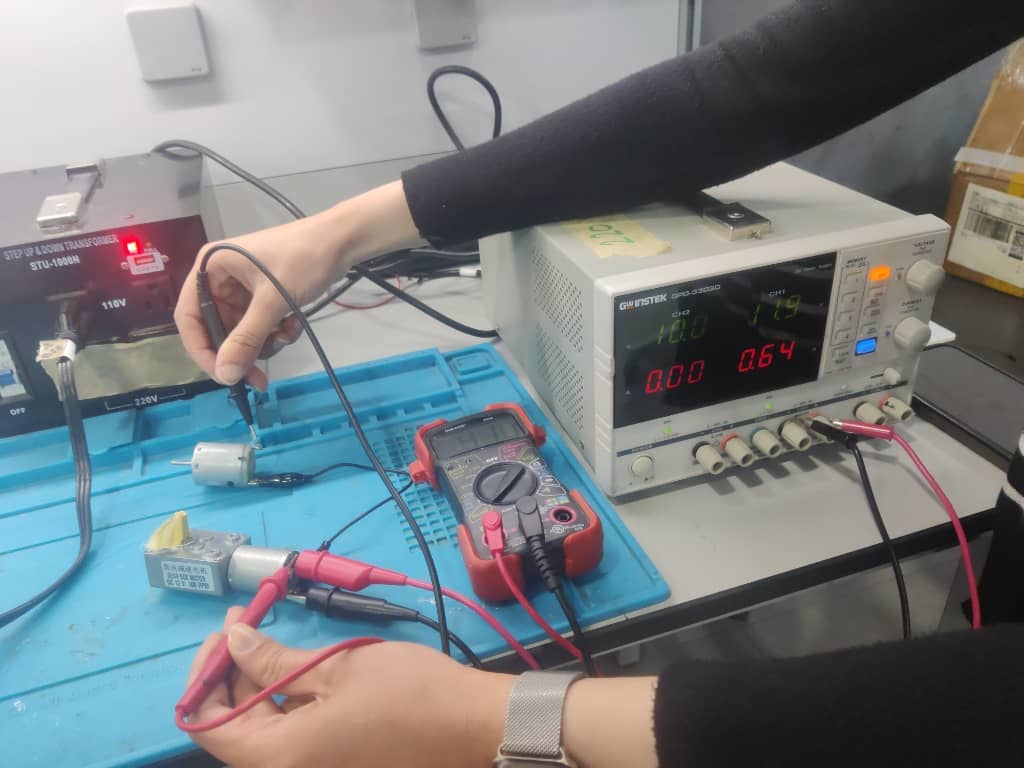
Step 4: Connecting the Second Motor
We connected Motor 1 and wired Motor 2 to the same power source. The wiring was slightly adjusted to match the motor’s terminals.
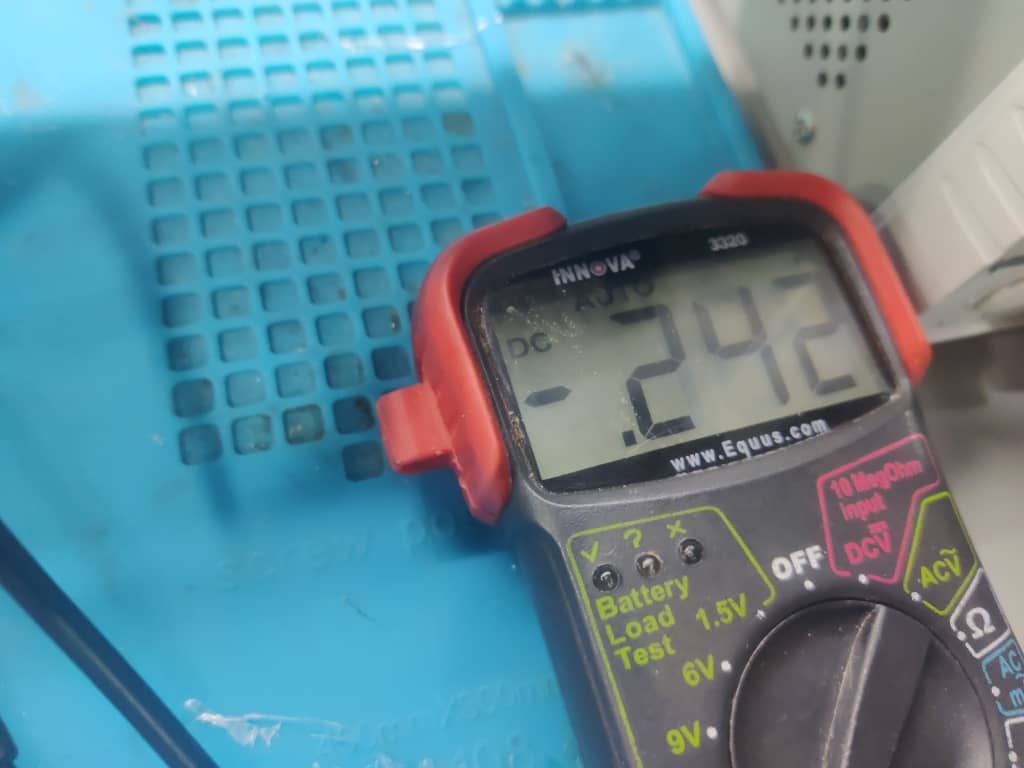
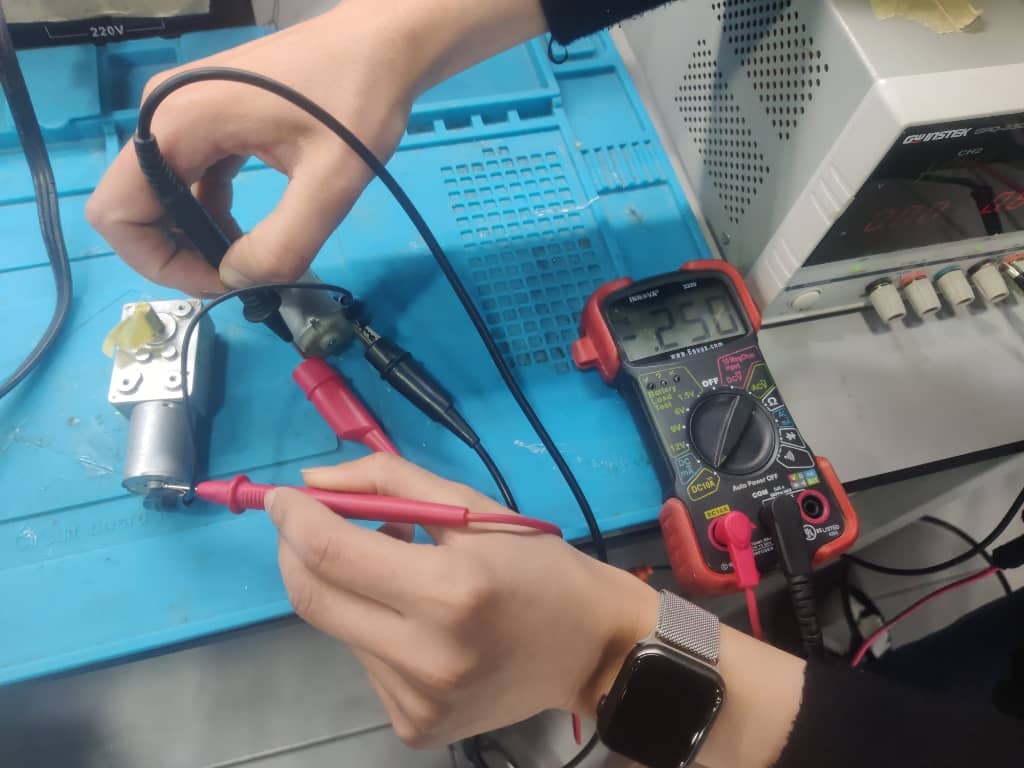
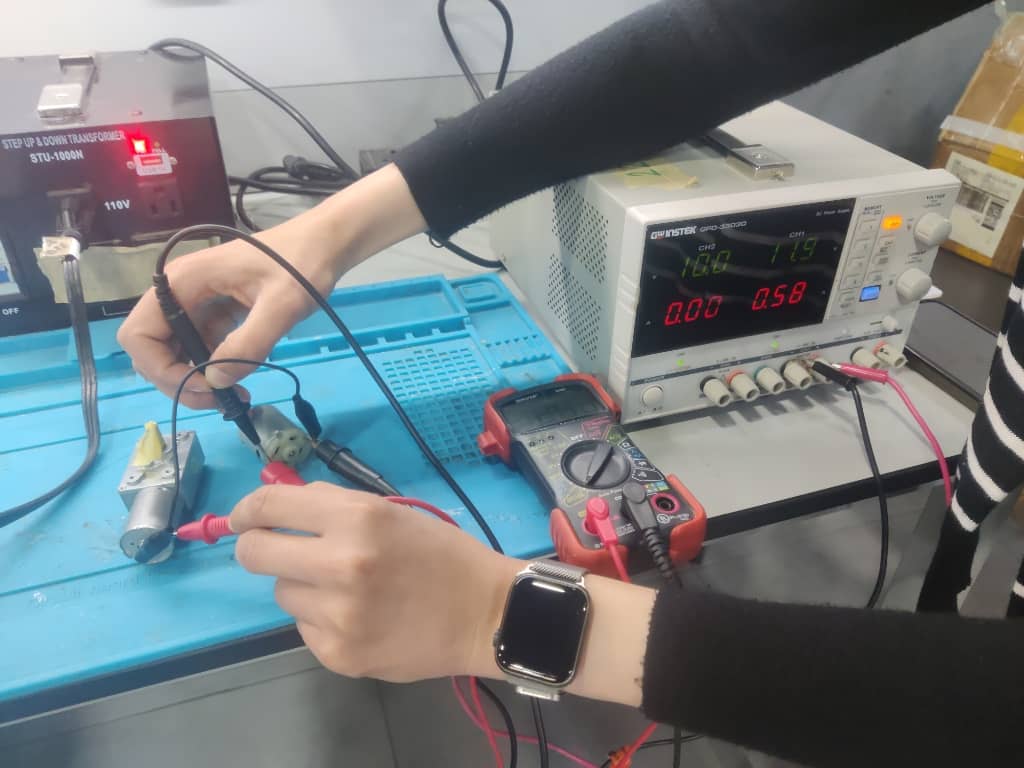
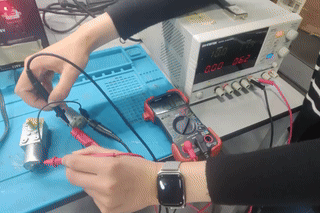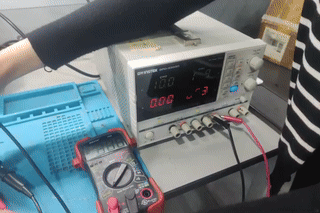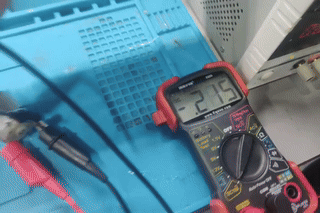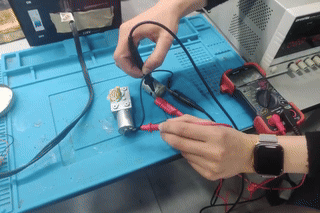
Step 5: Measuring Current for Motor 2
Motor 2 was tested under the same 12V supply. The measured current was 0.25 A, as shown on the multimeter.

Power Measurement Formula
To calculate the power (in watts) consumed by a device:
P = V × I
Where:
- P is the power in watts
- V is the voltage (in volts)
- I is the current (in amperes)
Example:
- Motor 1:
P = 12V × 0.415A = 4.98W
- Motor 2:
P = 12V × 0.25A = 3.00W
Learning Outcome
From this exercise, we learned how to measure and compare power consumption across different output devices. We understood how current draw varies based on wiring and motor type, and how to apply a basic electrical formula to compute power usage. This knowledge is crucial for optimizing energy efficiency in future electronic and mechatronic systems.