Make Something Big
Summary
This week, I focused on understanding the design rules for CNC milling, especially for wood-based joints. I started by watching tutorials to understand the fundamentals of CAM programming in Fusion 360, including dog bone fillets, toolpath strategies, and how to calculate the correct feeds and speeds. I then applied this knowledge by designing and testing different types of joints and slot fits, working with parametric design to determine clearances. Through hands-on testing, I gained valuable insight into how CNC settings impact the final result—and how improper values can even damage tools.
Work Process Detail
Helpful Shortcuts and Workflow Tips for ShopBot CNC
Before moving on to the "Make Something Big" project, I’d like to share a few useful ShopBot shortcuts and tricks I learned during this week that significantly improved my workflow and machine handling.
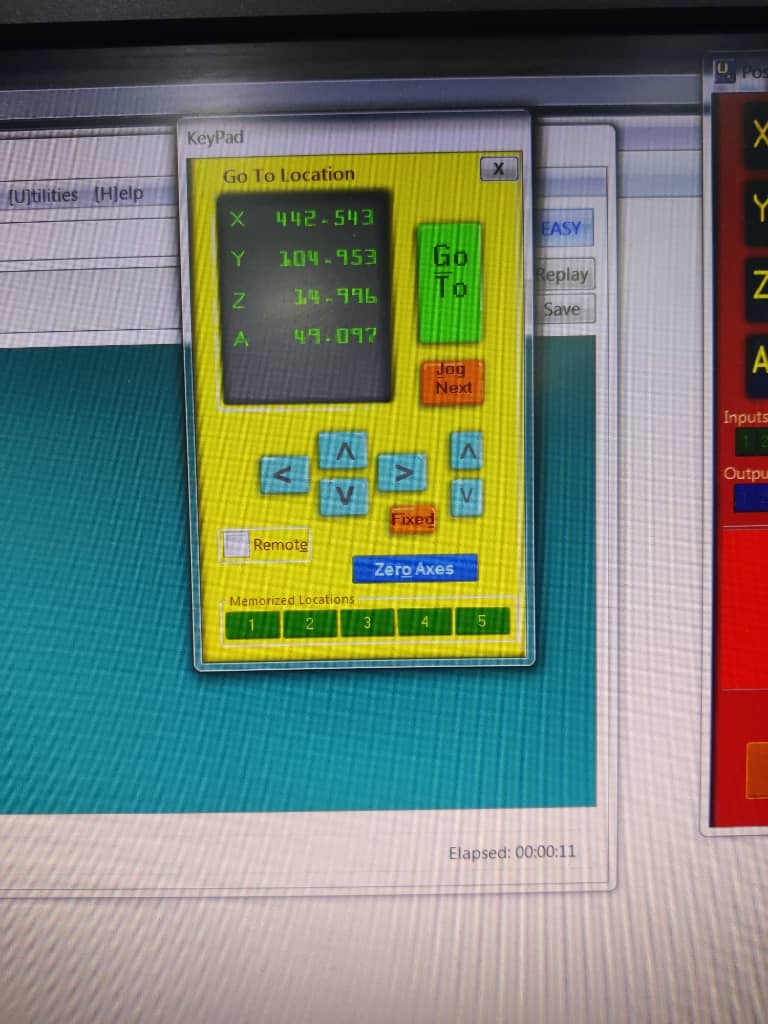
1. [K] – Keypad for Jogging
Pressing the K key opens the virtual keypad, which allows you to manually jog the CNC axes. This is especially helpful for fine-tuning the position of the tool before zeroing.

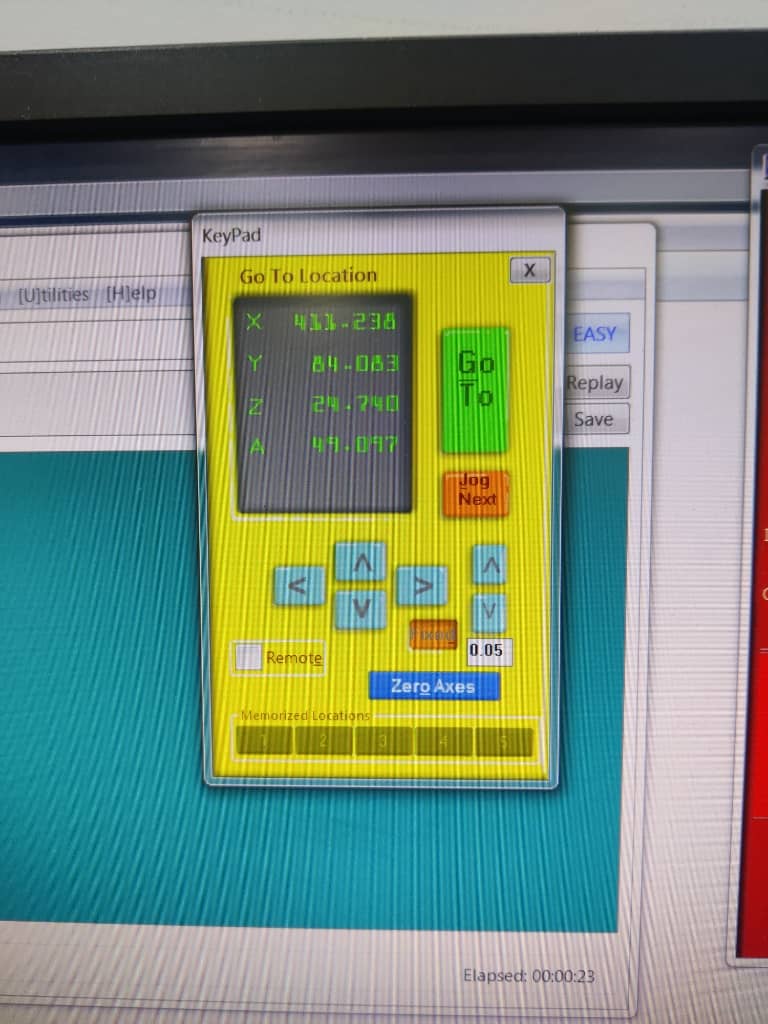
2. [D] – Precise Jogging Mode
The D key enables precise axis movement, allowing you to jog the machine in very small increments (e.g., 0.05 mm per step). This is ideal when aligning the tool with material edges or holes.
.jpg)
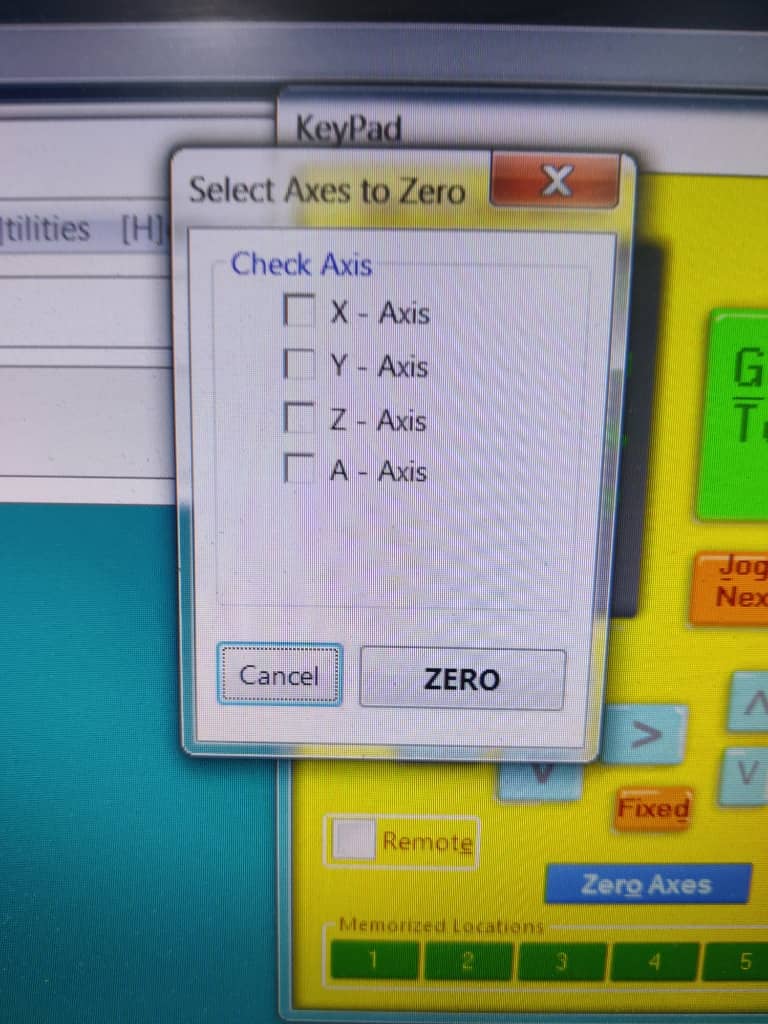
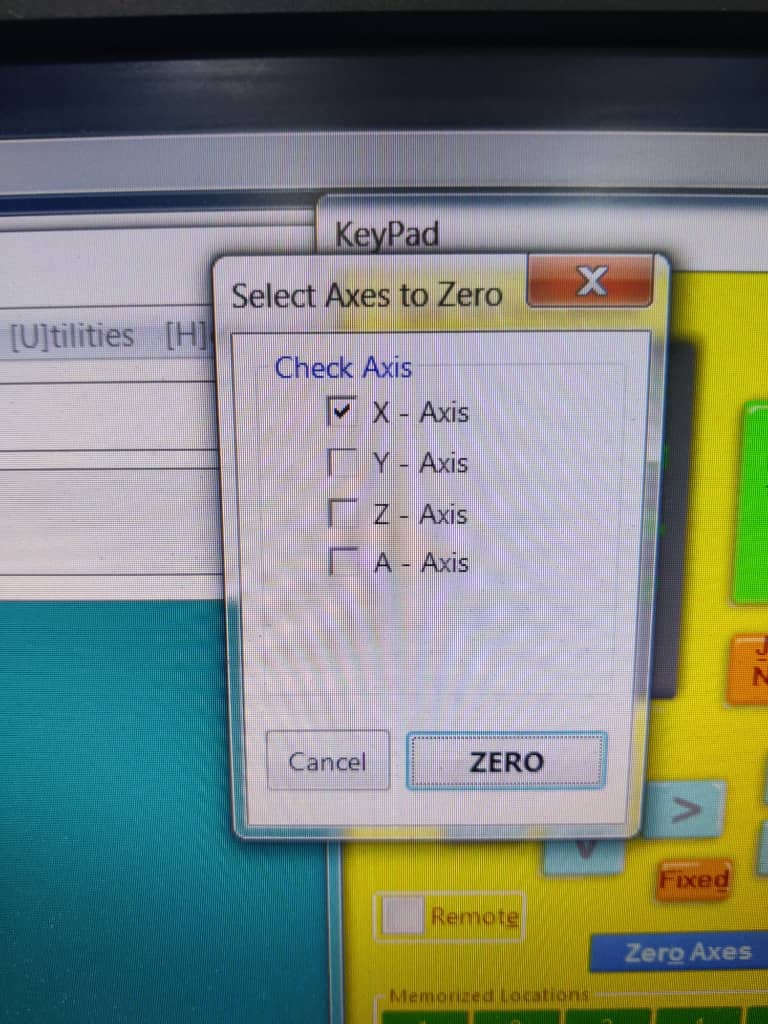
3. [O] – Axis Zeroing Options
The O key opens the zeroing interface, where you can choose which axis (X, Y, Z, or A) to zero.
Once the spindle is at the desired zero position, simply tick the corresponding axis box to set its coordinate to zero.

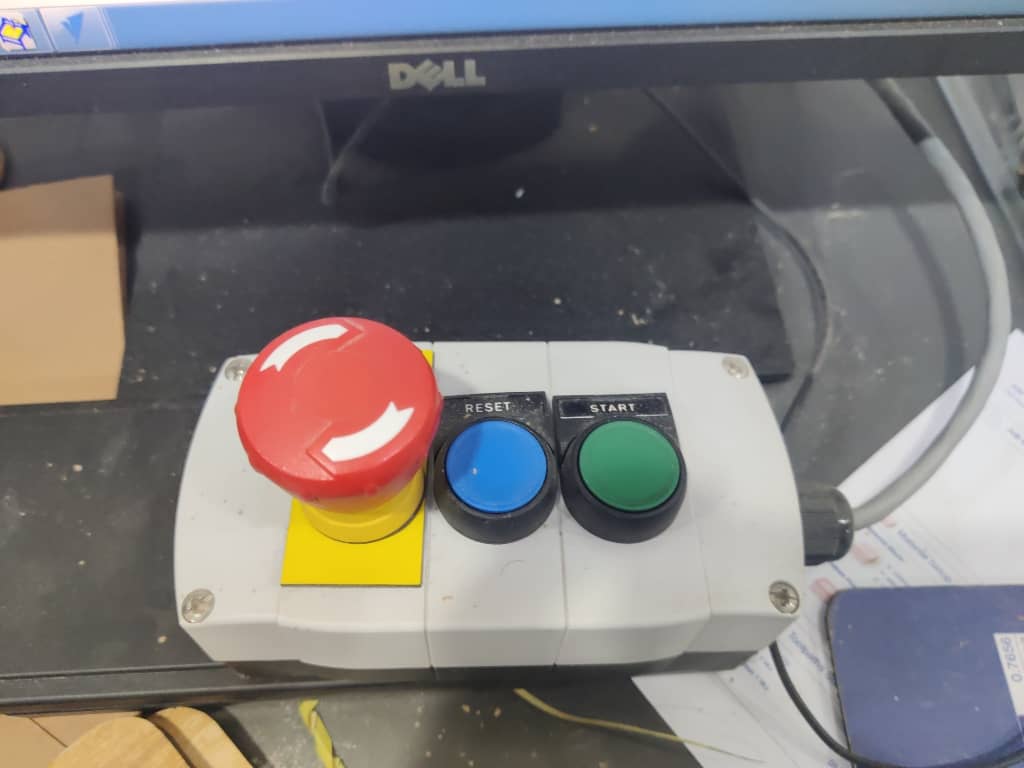
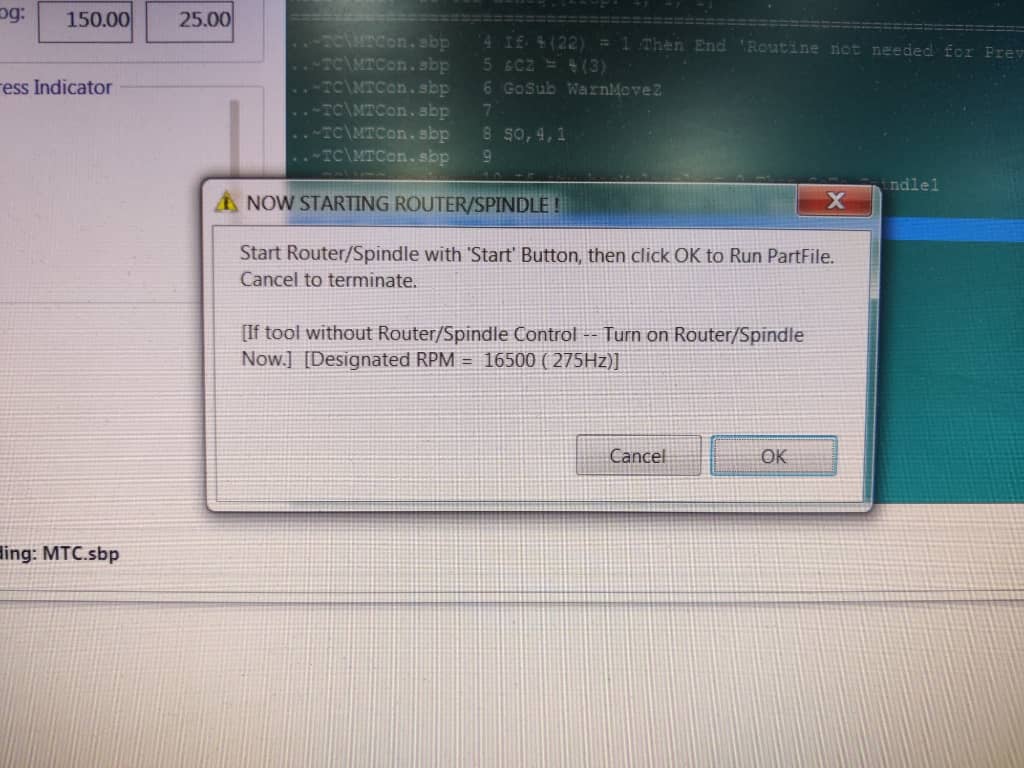
4. Spindle Start Warning
After sending a job to the machine, ShopBot prompts a warning reminding you to start the spindle manually.
Always confirm the spindle is spinning at the correct RPM before continuing with the cut by clicking “Start” on the control panel.


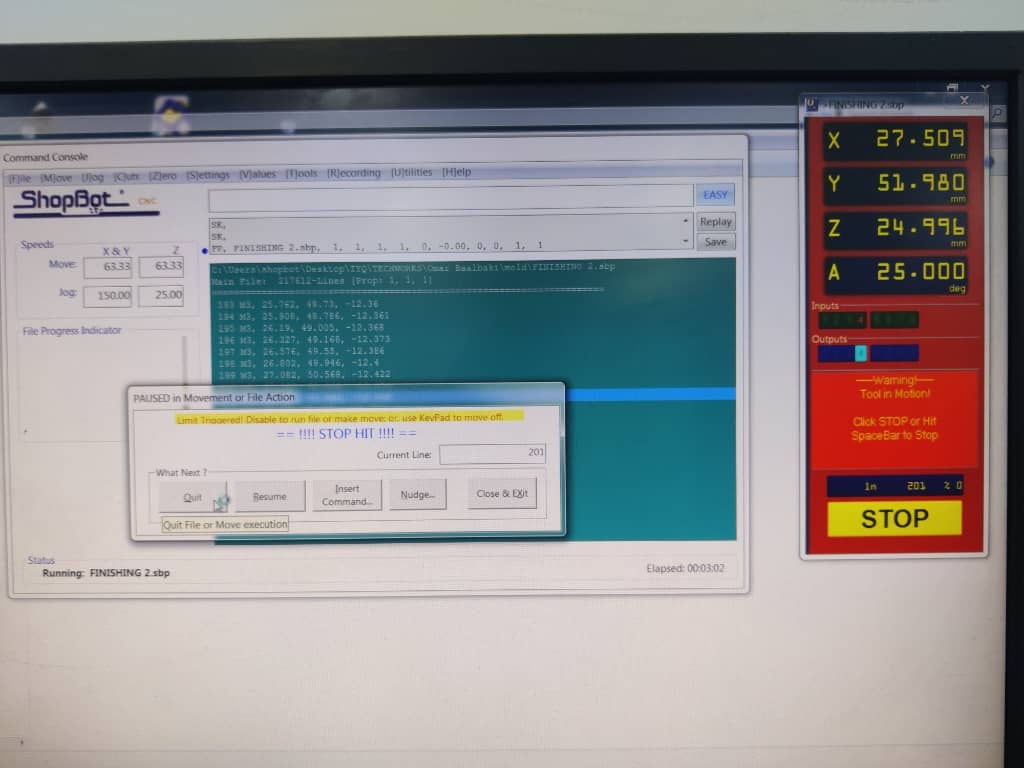
5. [Spacebar] – Pause & Resume
The spacebar serves as a pause/resume toggle.
This was especially helpful for long jobs (over 6 hours) when the lab had to close for the day. I paused the machine at night and resumed it the next morning.
Important: Do not move the axes during pause to preserve the exact coordinate positions. Moving any axis could cause the tool to lose its reference zero and misalign the rest of the job.
.jpg)
- Learning Phase
- Watched multiple YouTube tutorials to understand CAM workflows in Fusion 360.
- Learned about feed rate, spindle speed, and how to calculate optimal values using material specs and bit sizes.
- Studied the concept of dog bone fillets for inside corners in slots.

.avif)
- First Joint Test
- Designed a simple press-fit joint using parametric constraints with adjustable clearance.
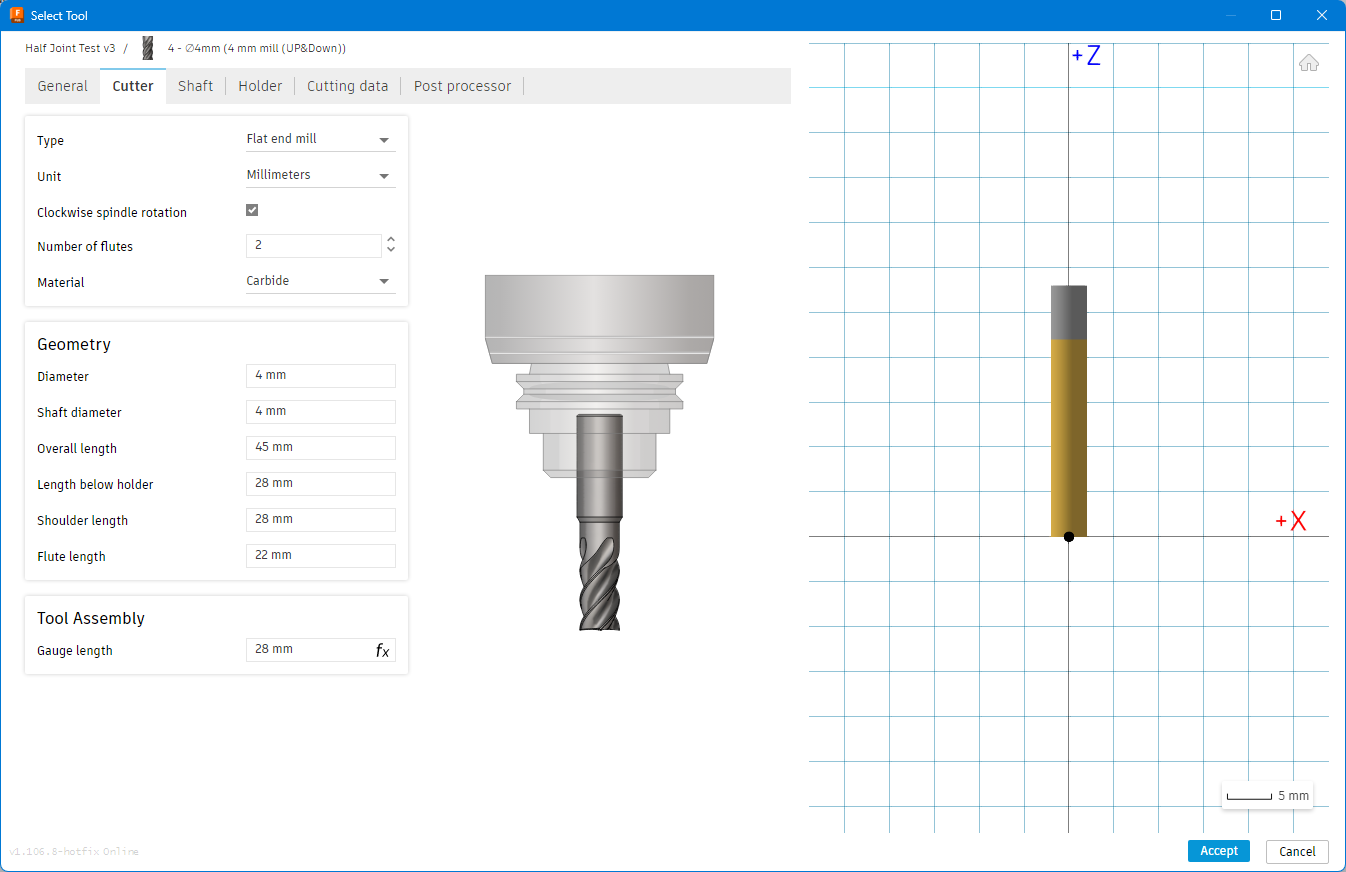
- Used Fusion 360 CAM to generate toolpaths with a 4 mm flat endmill.
- Ran the test cut and adjusted until I found the correct fit.
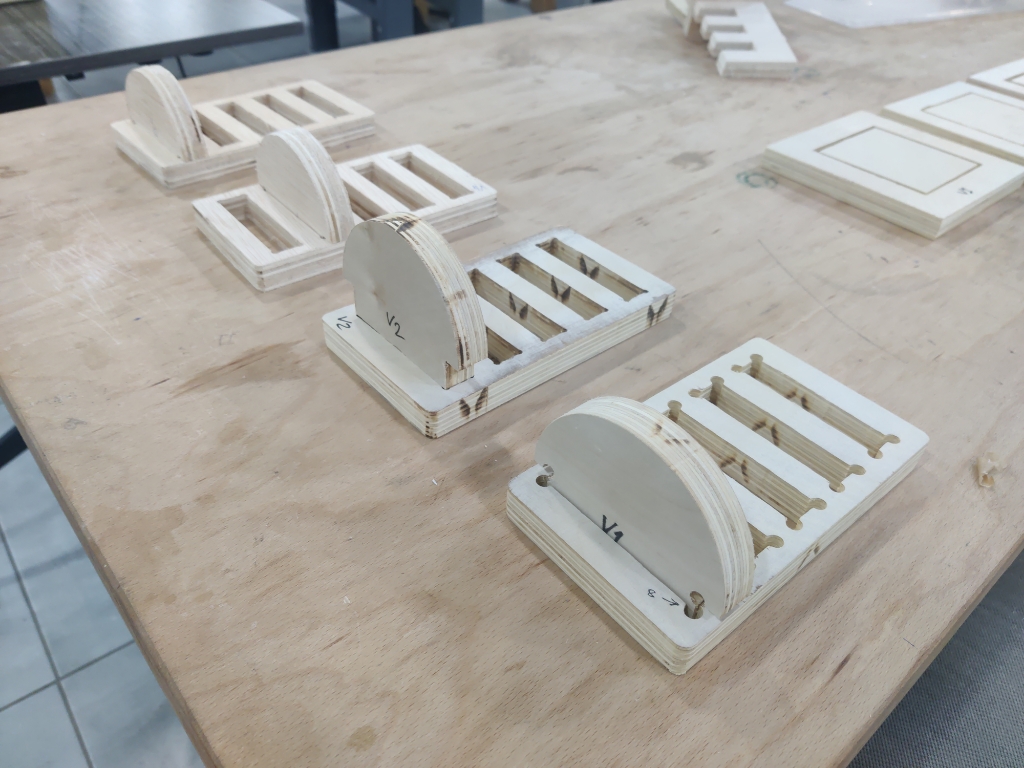

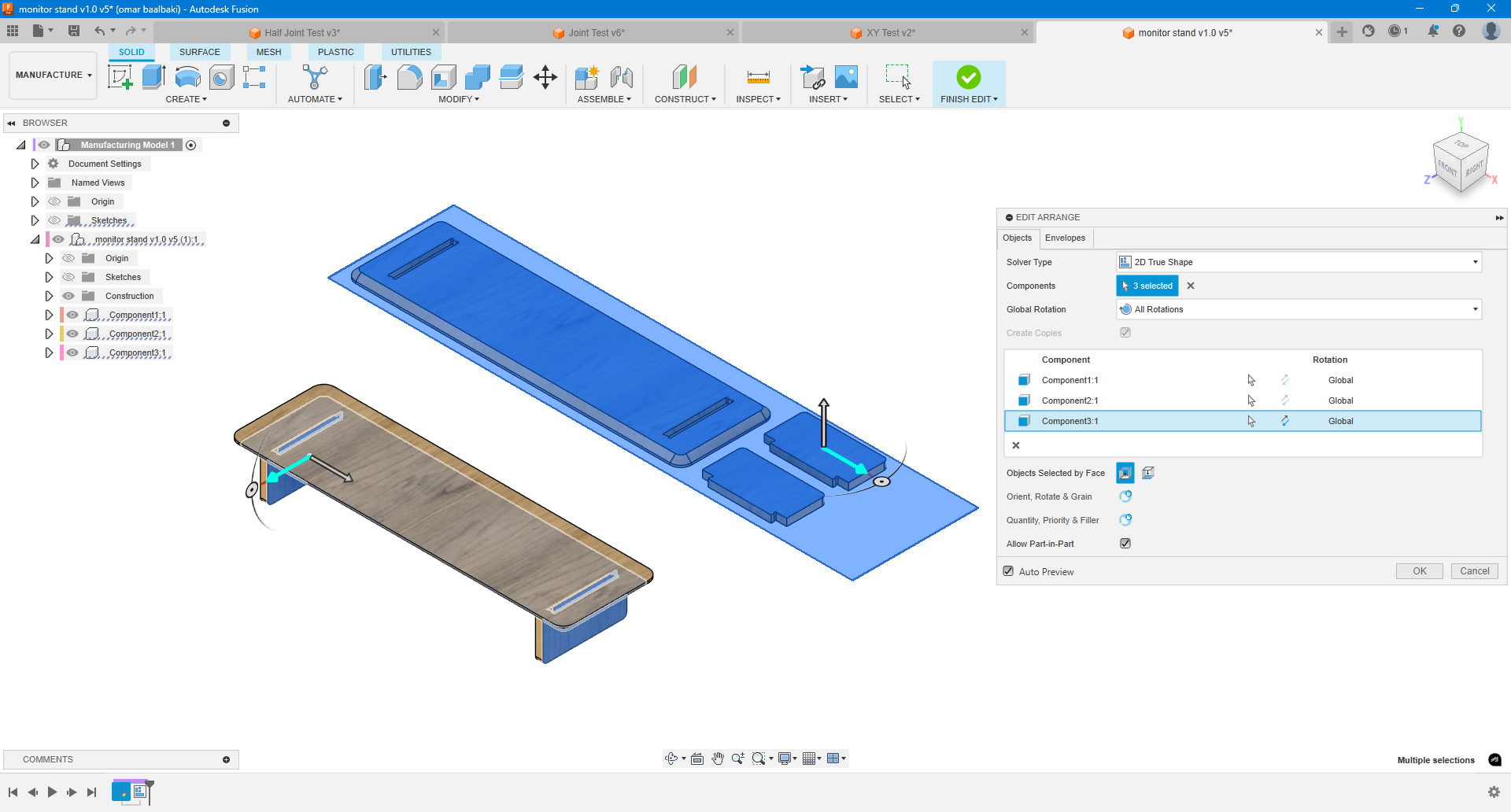
- Second Test – Slot Fit Joint + Design
- Designed a full-slot-fitting joint to test how parts insert vertically into pockets.
- Programmed it using CAM with dog bone fillets added for internal corners.
- After testing a few clearances, found the ideal tolerance for a snug, non-forceful fit.
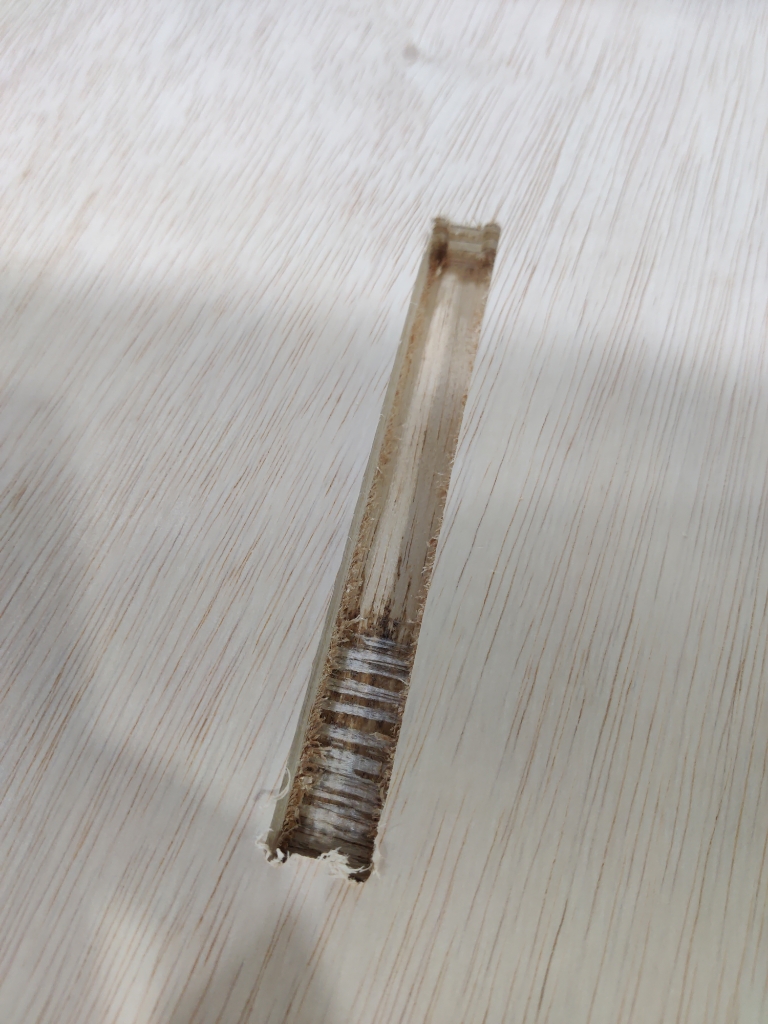


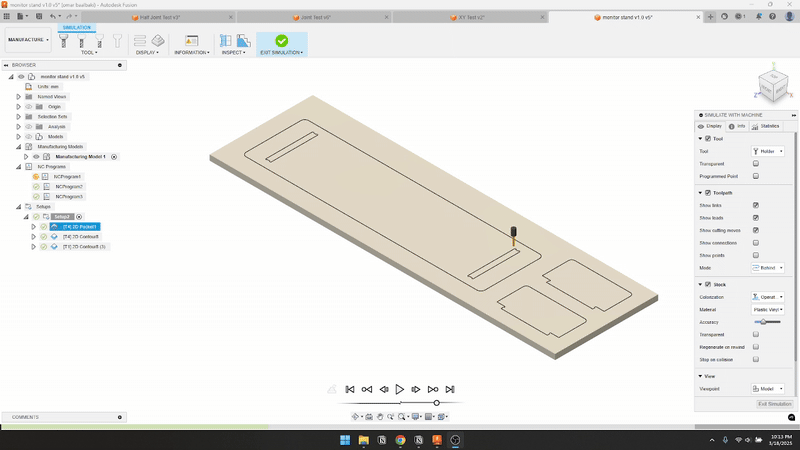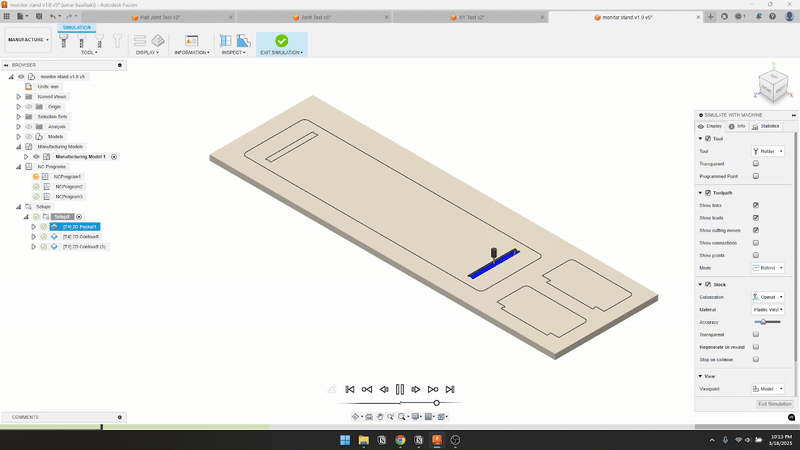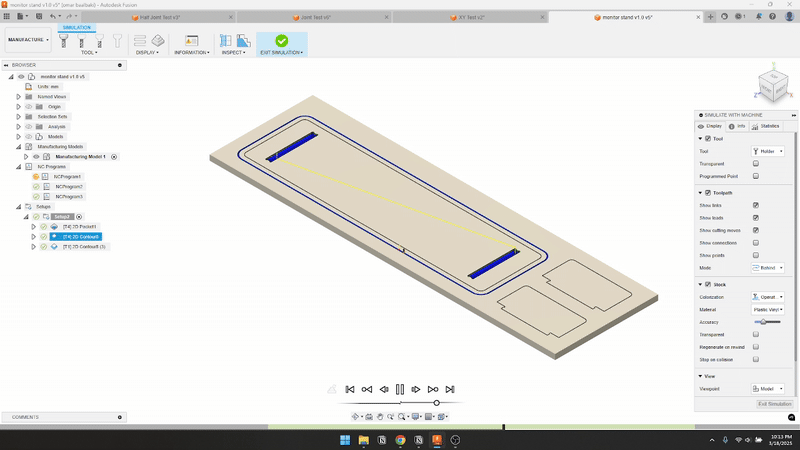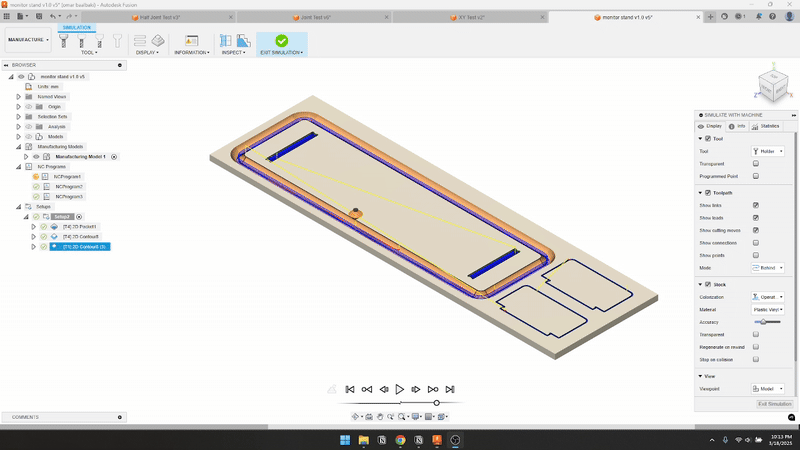
- Feed & Speed
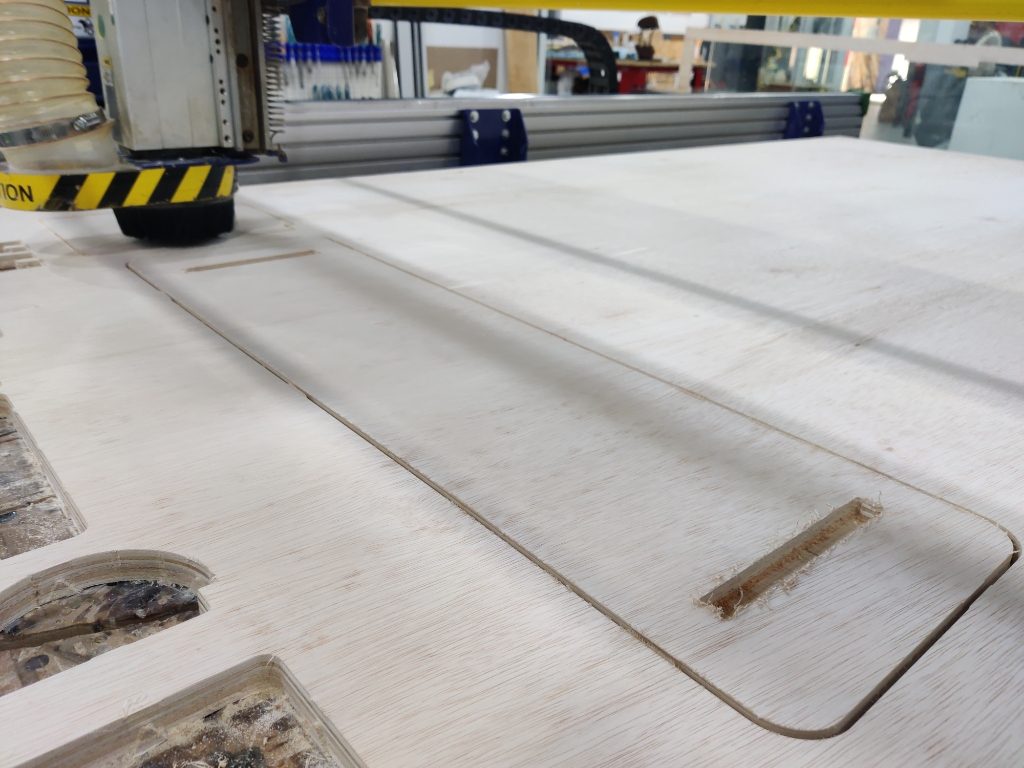
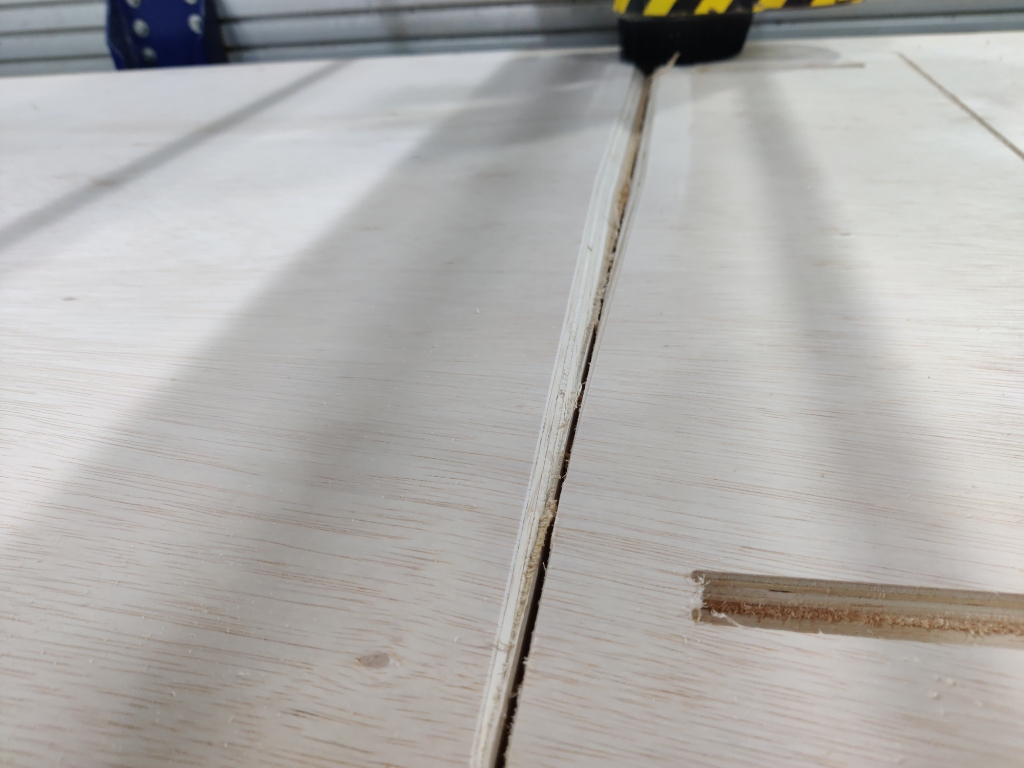
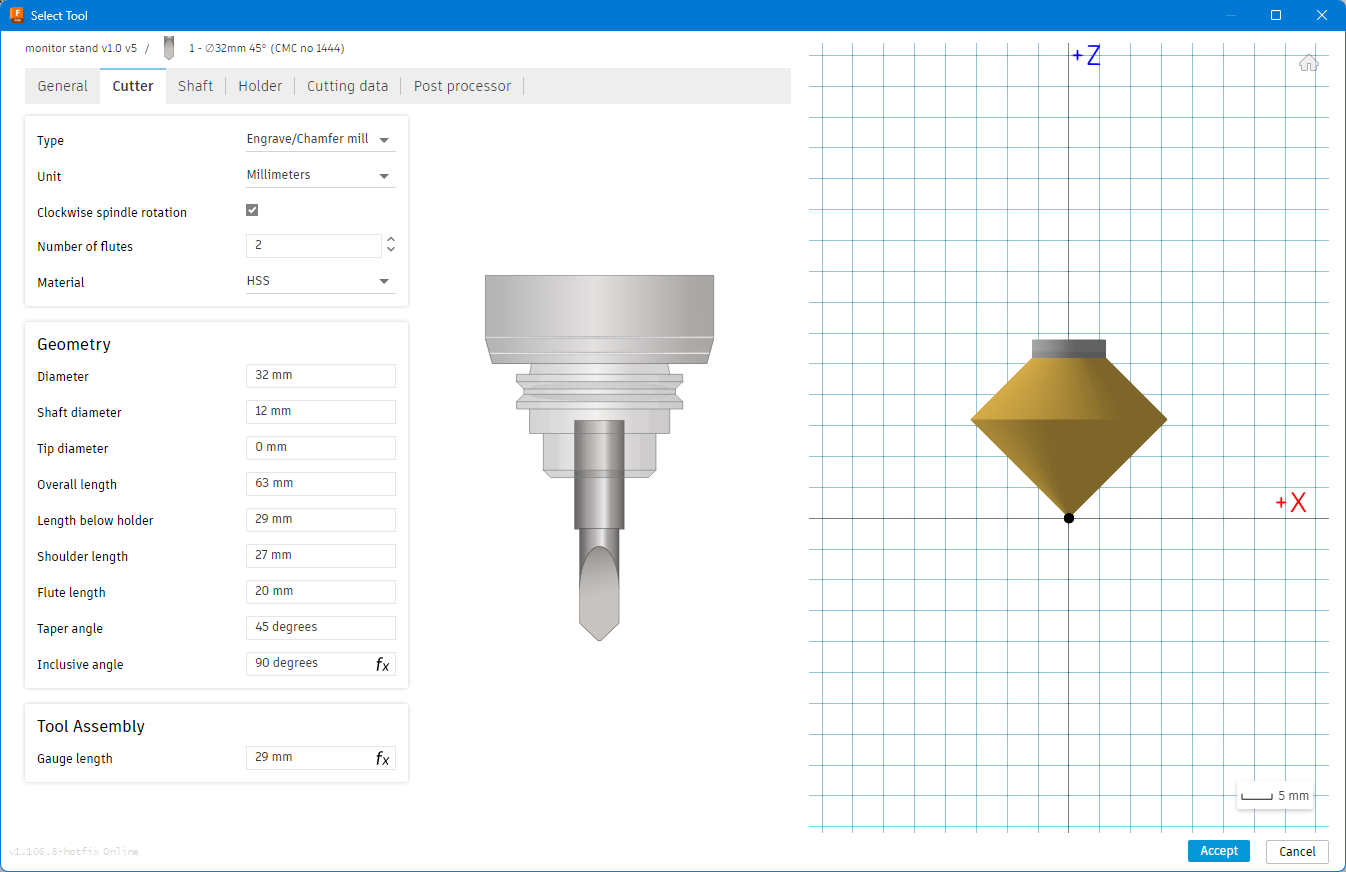
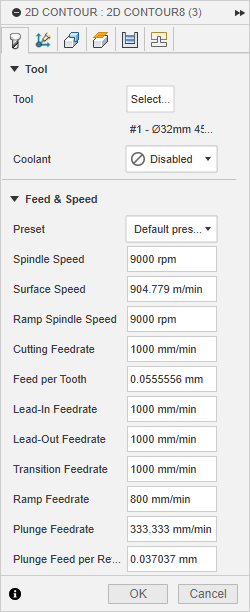

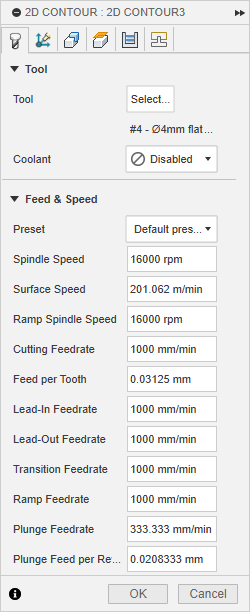
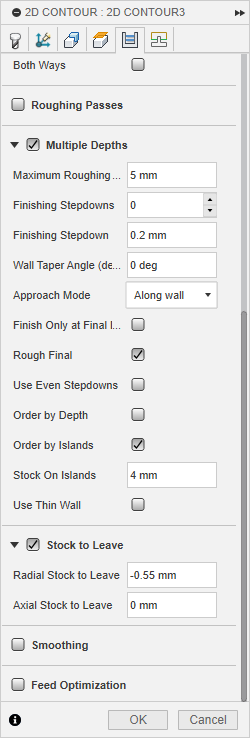


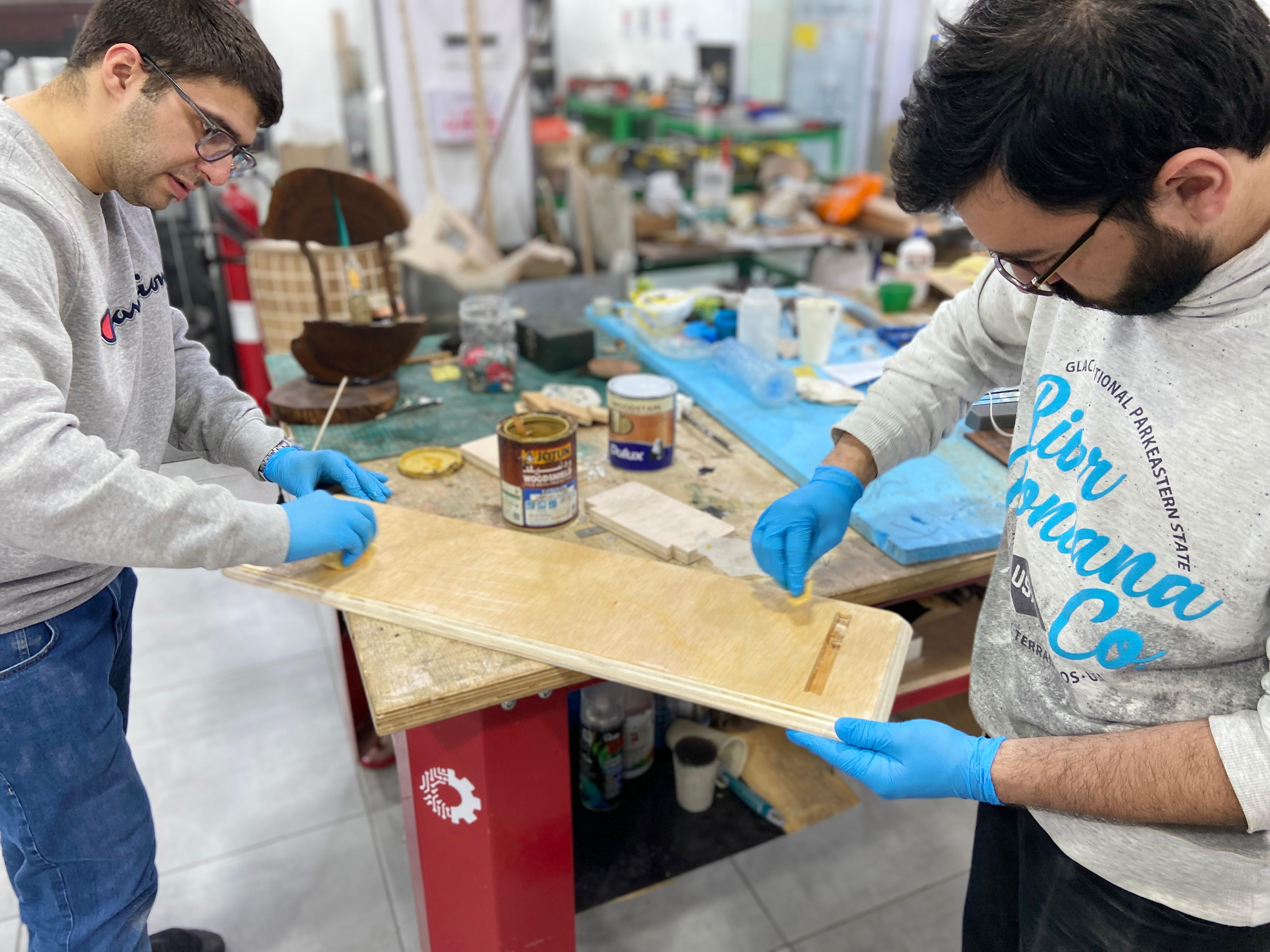
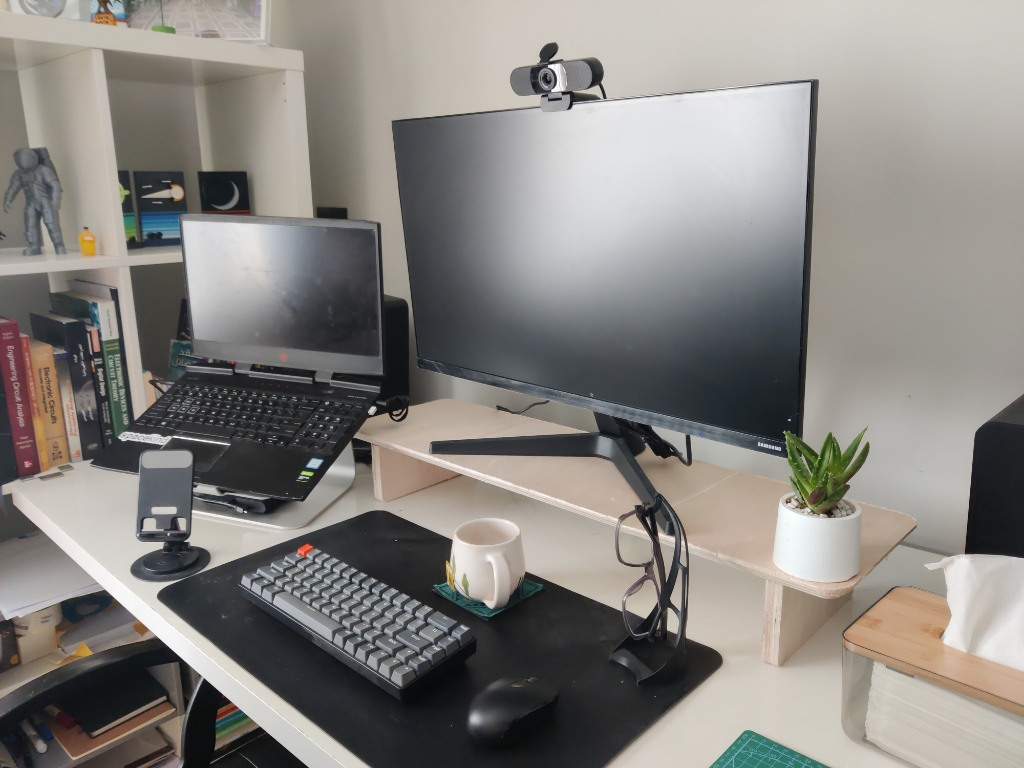
- Finally, after completing all the cuts, I applied a protective coat to the stand to enhance its appearance and durability. Then, I tested it out in my office—and it worked beautifully.


Learning Outcome
Through this process, I gained a solid understanding of the design and manufacturing rules for CNC milling. I learned how to create joints with proper tolerances, apply dog bone fillets, and adjust toolpath settings based on material and bit type. One of the most important lessons was how small mistakes in feed and speed settings can damage both the tool and the workpiece. This experience has prepared me to design smarter and safer CAM workflows for future projects.
