Week 1: Project Management and Git Tutorials
Git Tutorial
I worked through the Git tutorial to understand how version control works. Here's a brief breakdown of what I learned:
I was completely new in this kind of project management which was about documenting and tracking all progress of my work in Fab Academy. I started reading and reasearching about code editors and how to build a web page. I came to realise that there are several code editors that i could choose from but that I have to choose one that can meet the demands of digital fabrication with its use of enginering tools, software update extentions and can easily work with github. Below is a list of them:
- VS-Code - Visual Studio Code, often referred to as VS Code, has become a staple in the developer community. Its extensive extension marketplace allows for high customizability, making it a favorite among developers. Whether you're into web development, data science, or even game development, VS Code has something for everyone.
- Sublime Text - It’s known for its speed and simplicity. The editor's minimalist design and lightning-fast performance make it a popular choice for developers who prefer a no-frills coding experience. One of its most beloved features is the multiple selection tool, which allows you to make the same changes to multiple parts of your code simultaneously.
- Atom - Atom, developed by GitHub, is often praised for its hackability. The editor is built on web technologies, allowing developers to customize and extend its functionality using JavaScript, HTML, and CSS. This makes Atom highly flexible and adaptable to different workflows. [Source: https://toxigon.com/code-editor-feature-comparison]
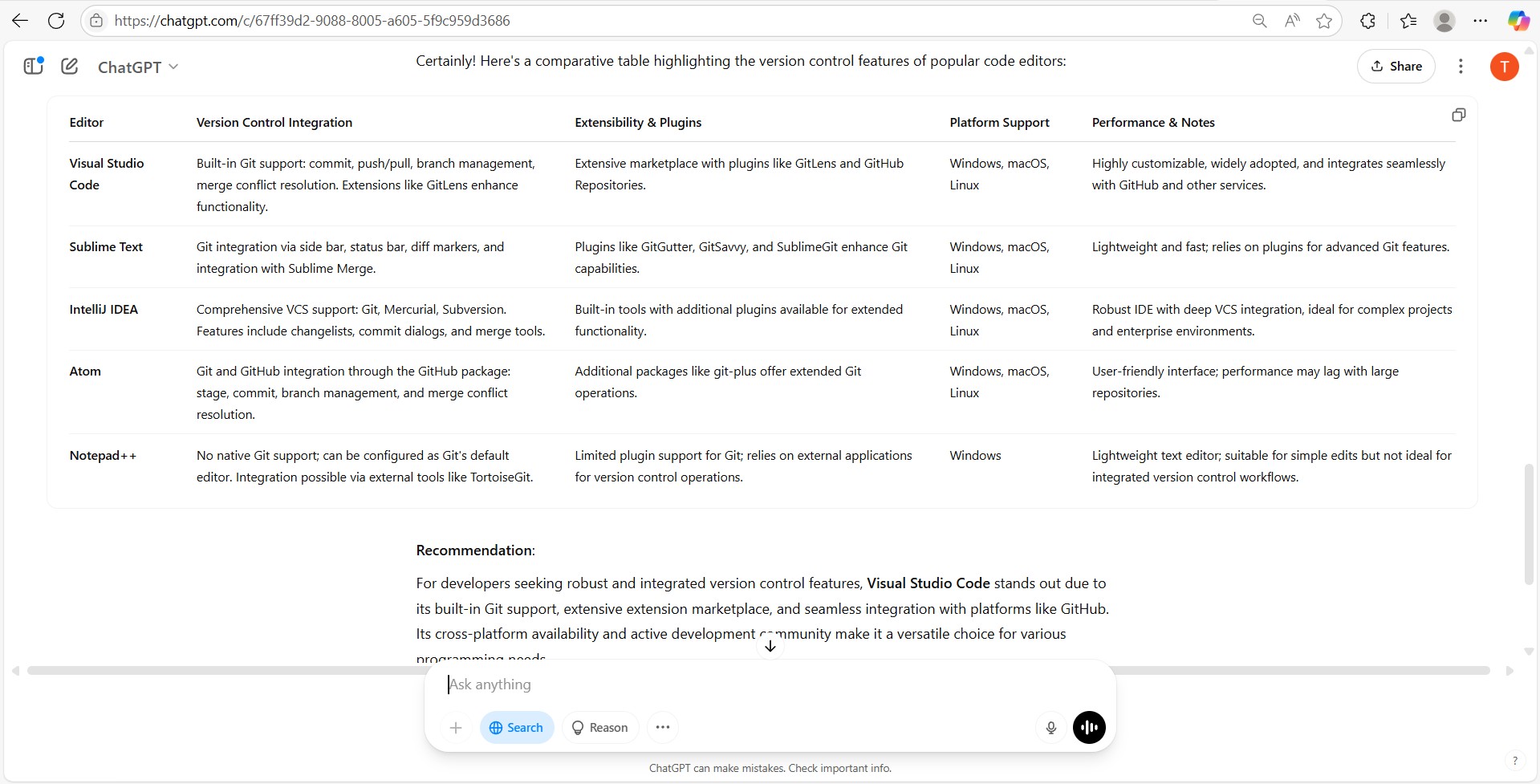
Click here for comparison of code editors
Screen short showing a comparison table for code editors and the final recommendation I finally chose vscode as the code editor of choice and I downloaded it as follows: Configuring your email in Git is essential for several reasons: To configure your email, use the following commands: SSH keys are used to authenticate yourself securely to a remote server or service, such as a Git repository (GitHub, GitLab, etc.) or a web server, without using a password. To generate an SSH key, follow these steps: Cloning a repository allows you to create a local copy of a remote repository on your machine. This enables you to work on the project locally and push changes back to the remote repository. To clone a repository, use the following command: Replace
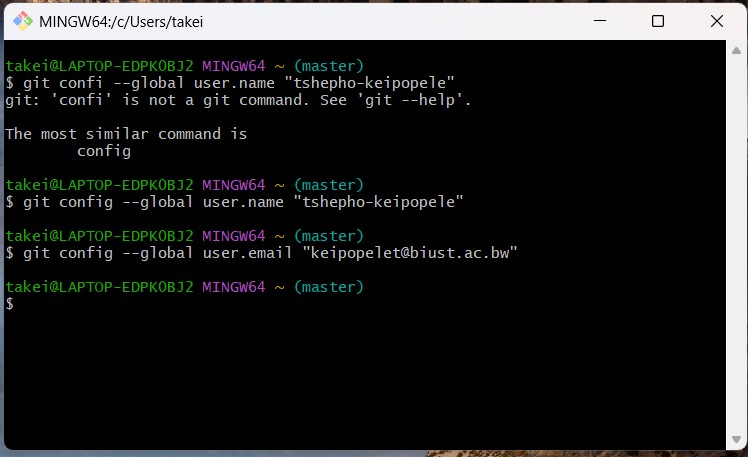
Configuring Git and SSH Keys
Configuring Email for Git
git config --global user.email "keipopelet@biust.ac.bw"
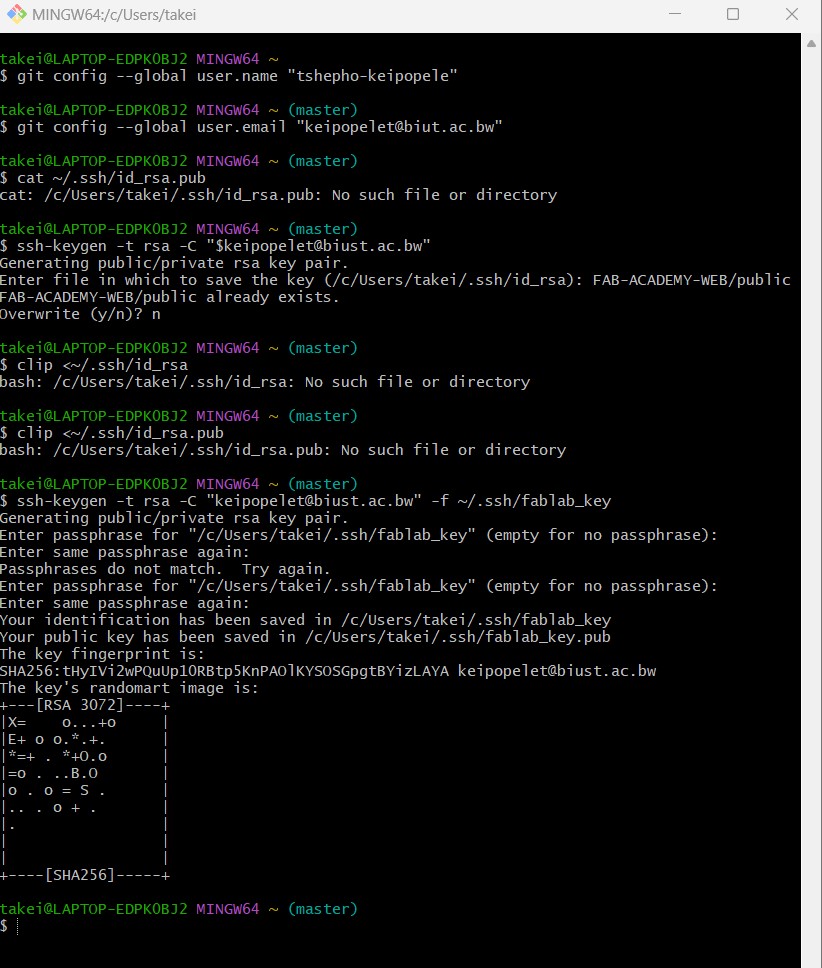
SSH Key Generation
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "cat ~/.ssh/fablab_key.pub"
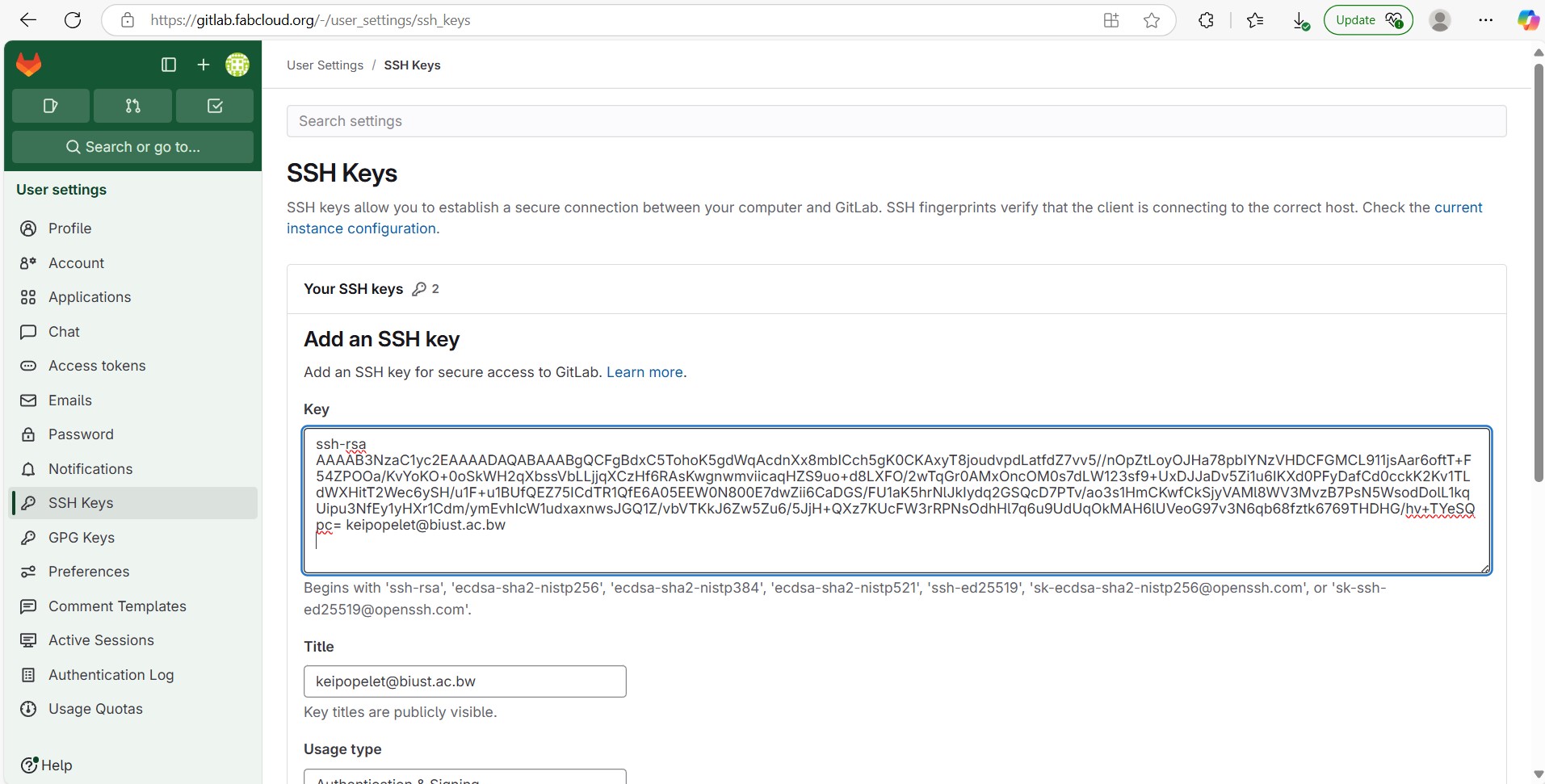
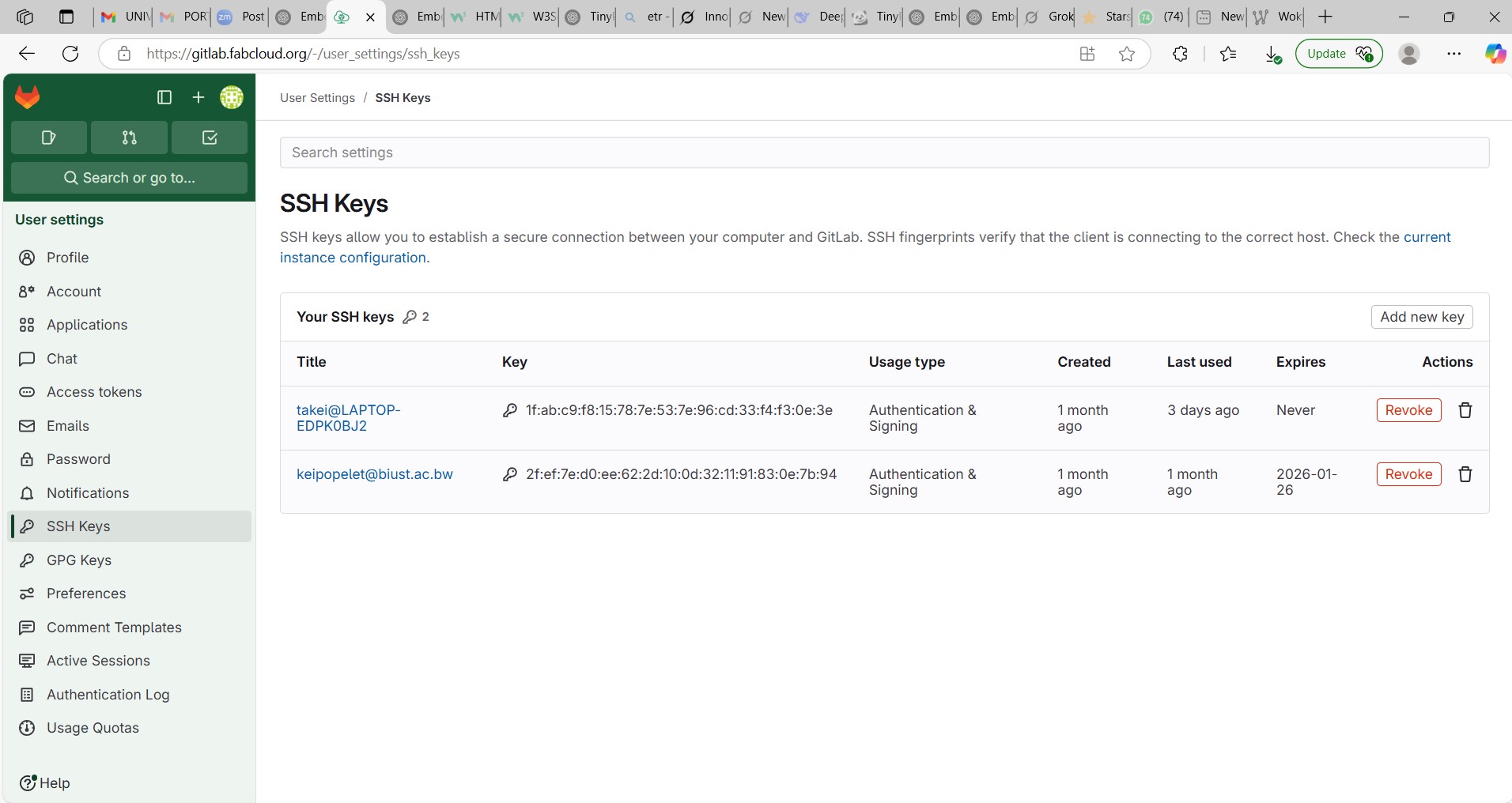
Cloning a Repository
git clone <repository-url>
<repository-url> with the URL of the repository you want to clone.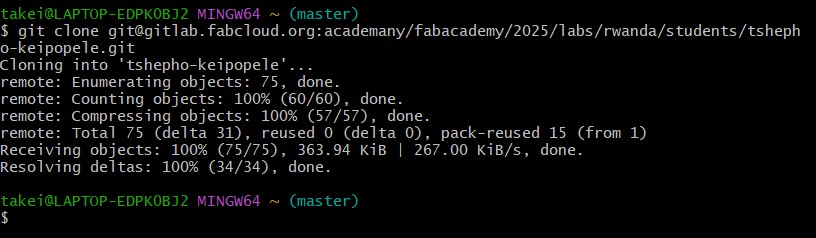
git init to initialize a new repository.git add to stage files for commit.git commit -m "message" to commit changes.git push to upload changes to a remote repository.
 br
br