3
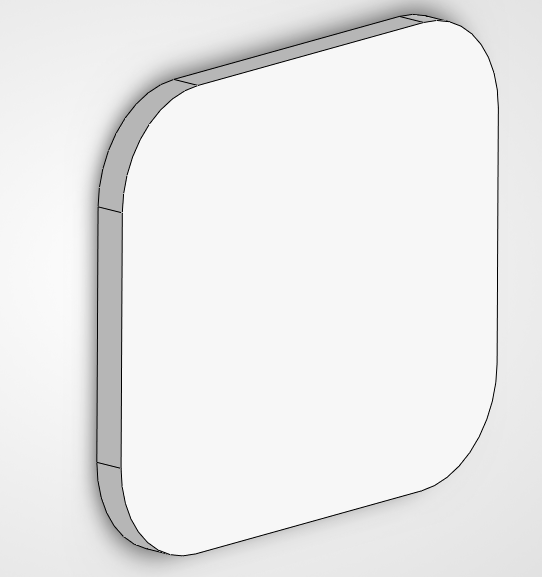
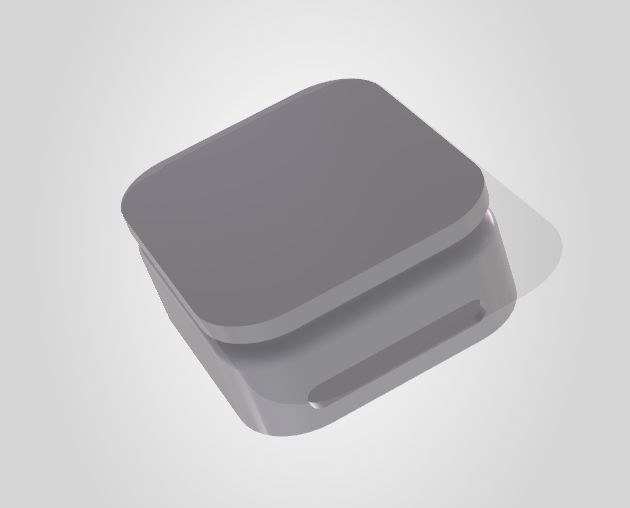
Modeling the SafePath-RM Induction Dock
In this section, we are going to build the induction charging dock from scratch.
Step 1: Workspace & First Sketch
We'll start by opening a new design. In Fusion 360, everything begins with a sketch.
We'll pick the Top Plane (the floor) because we want our dock to sit flat on a table.
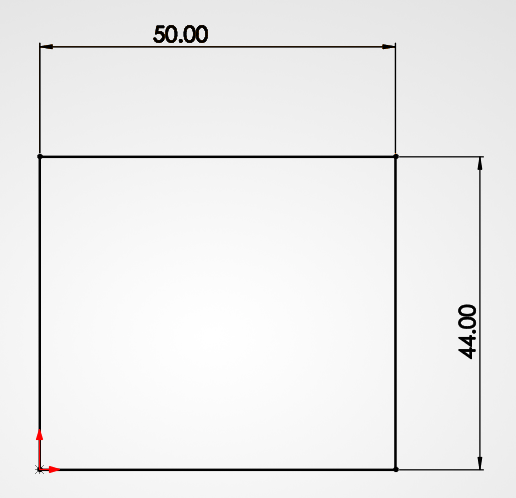
Using the Center Rectangle tool: it keeps everything centered on the origin, which makes the whole design much more organized.
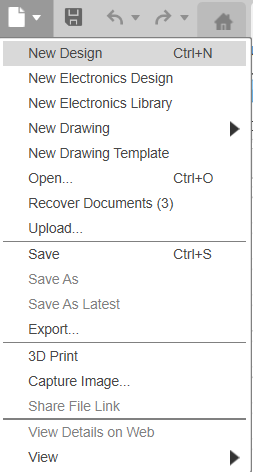
Starting a new design file.
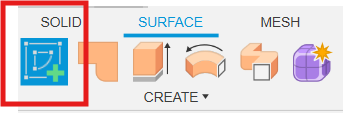
Selecting the 'Create Sketch' icon.
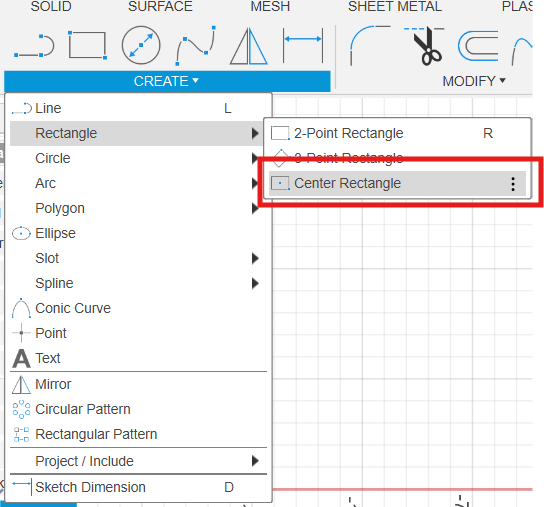
Using Center Rectangle for symmetry.
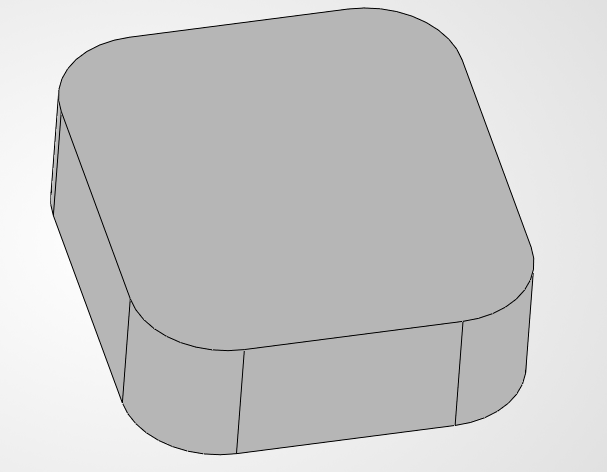
Step 2: Creating the Solid Base
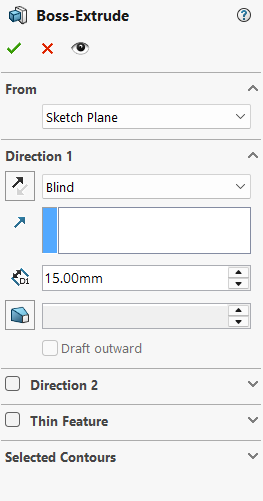
Now we define the size: 60 x 70 mm. Once the sketch is ready, we use the Extrude tool to turn that rectangle into a 3D block. We're going for 18 mm in height to give it enough weight and presence on the desk.
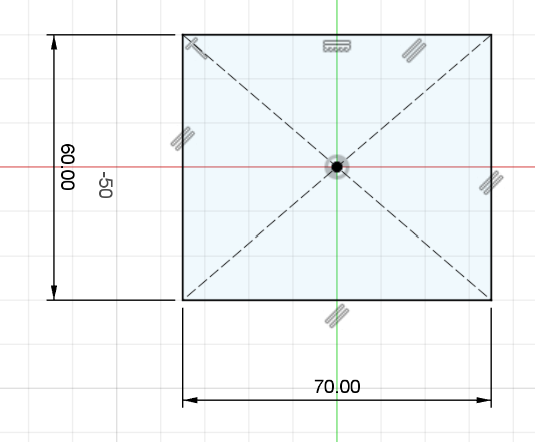
Setting the 60x70mm footprint.
Switching to the Extrude tool (E).
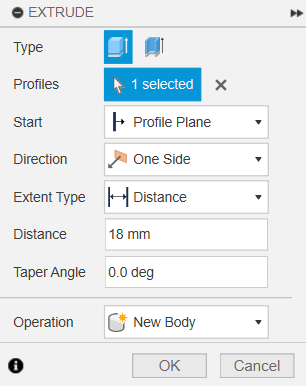
Setting the height to 18 mm.
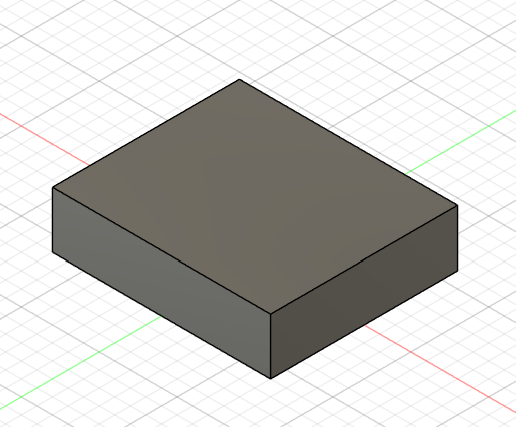
Our first 3D solid base is ready.
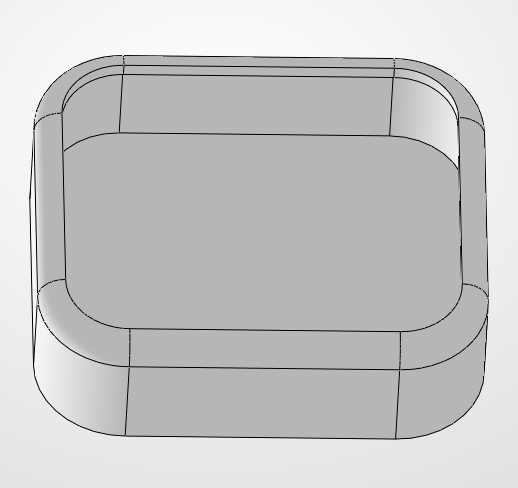
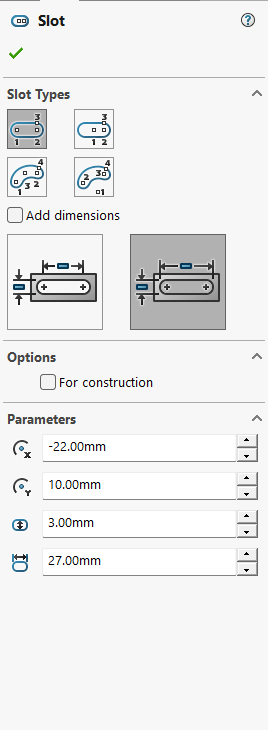
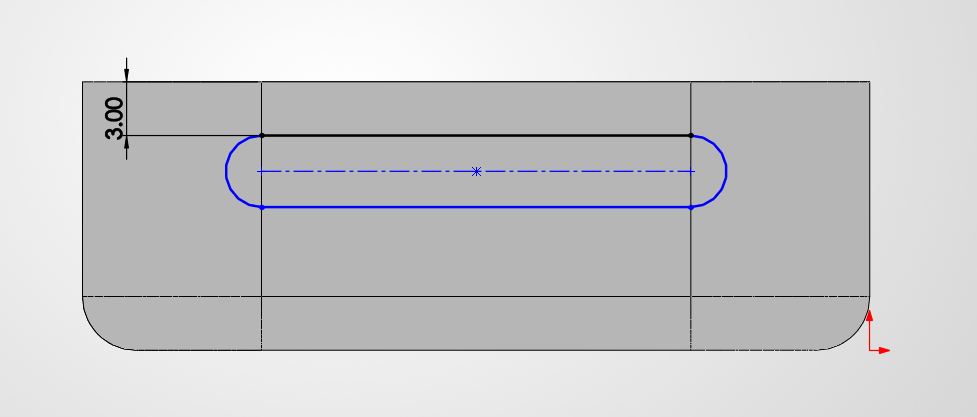
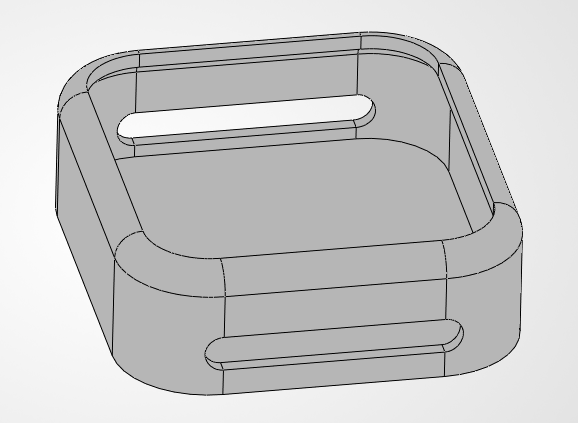
Step 3: The "Nest"
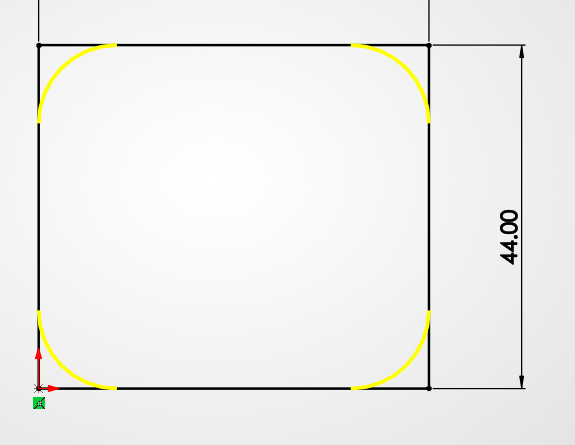
We need a hole where the watch will sit. We'll draw another rectangle (44.4 x 50.4 mm) right on top of our block. To make it easy to use, we'll use a -5° Taper Angle in the cut operation. This creates a "slanted" wall that guides the watch right into the center even if you drop it slightly off-target.
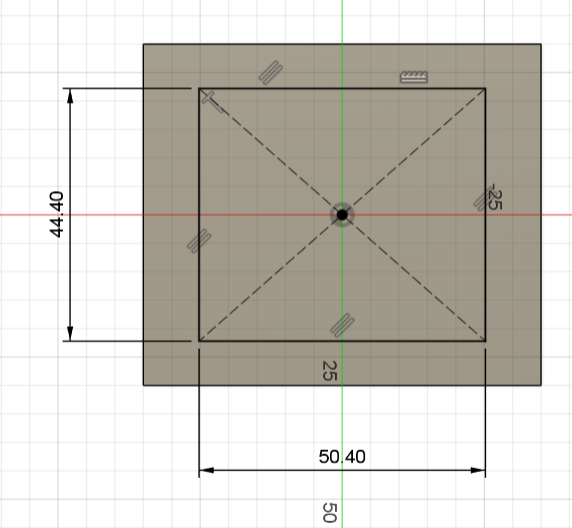
Sketching the cavity with 0.4mm tolerance.
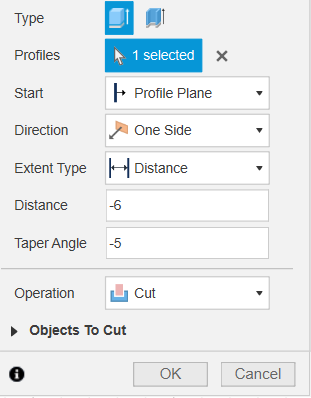
Cutting 6mm deep with a -5° angle.
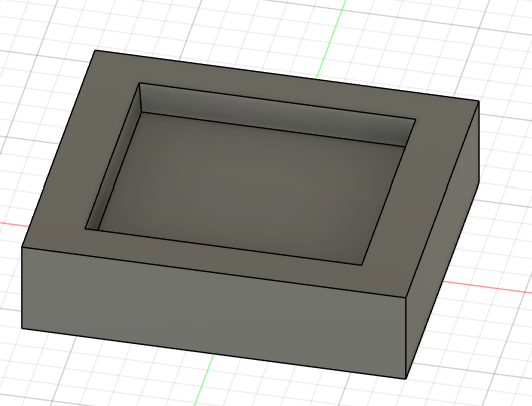
This "funnel" effect is great for accessibility.
Step 4: Preparing for Wireless Charging
Flip the dock over. We need to get the induction coil as close as possible to the top.
We'll draw a 30 mm circle and cut into the bottom.
We are leaving a thin 1.2 mm wall to making the energy transfer work.
Selecting the Circle tool for the coil.
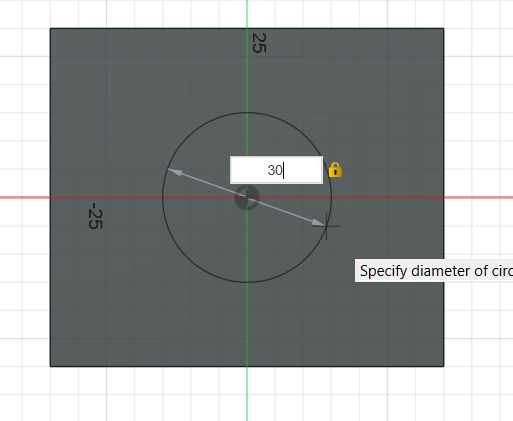
Drawing the 30mm diameter on the bottom face.
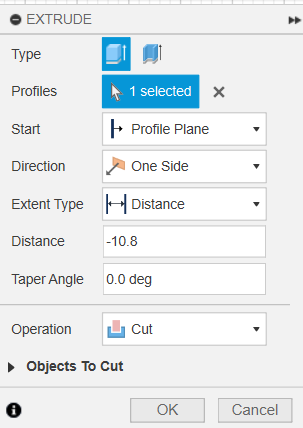
Cutting -10.8mm deep into the base.
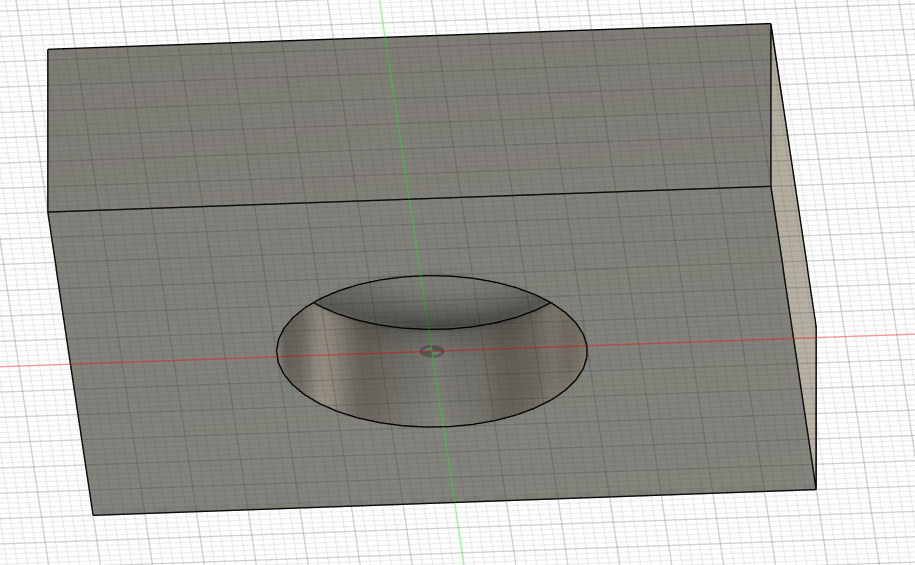
The internal housing is now finished.
Step 5: Modeling the Cable
We will use the Fit Point Spline tool. This lets us draw a curvy, natural path.
Once we have the "skeleton" of the cable, we use the Pipe tool to give it a 3.5 mm thickness.
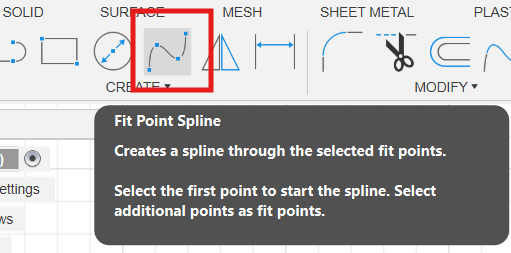
Drawing the wire path with the Spline tool.
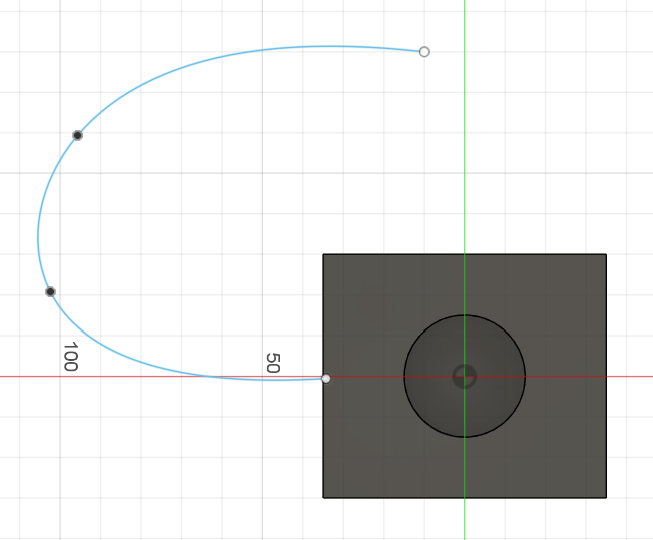
Creating an organic curve for the cable.
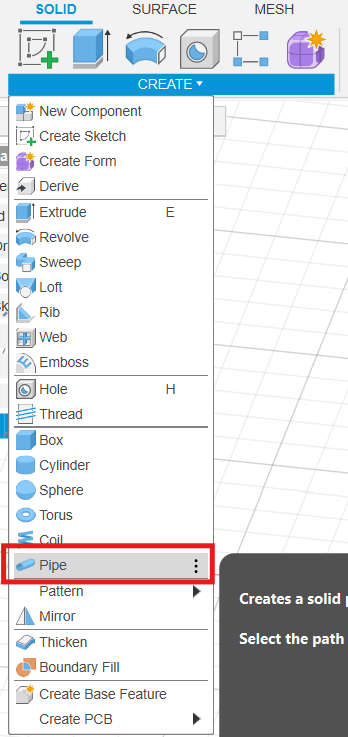
Finding the Pipe tool in the Create menu.
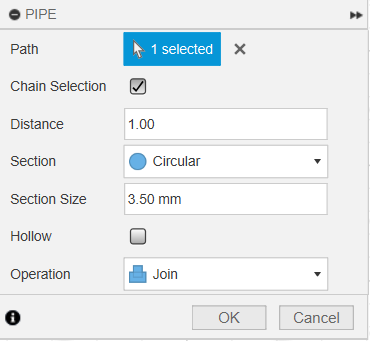
Setting the section size to 3.50 mm.
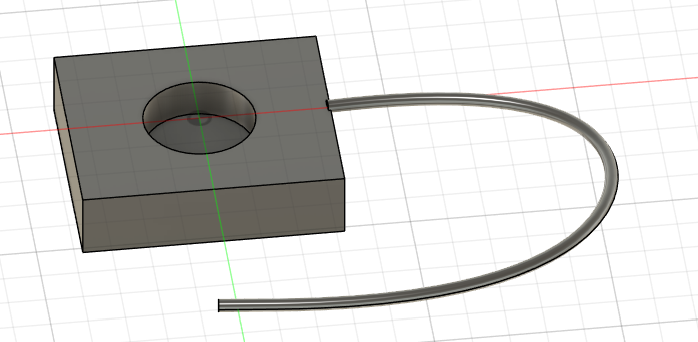
The 3D cable is now attached to the dock.
Step 6: USB-A Connector & Final Details
To finish the model, we need the USB plug.
We'll build it in two parts: first the plastic housing (a 4.5 x 12 mm rectangle)
and then the metallic tip. By extruding these separately, we get a much more realistic result.
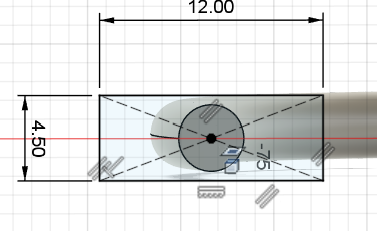
Sketching the USB-A plastic body.
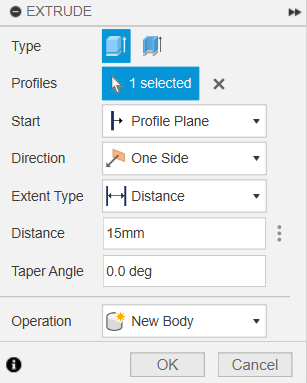
15mm extrusion for the main connector.
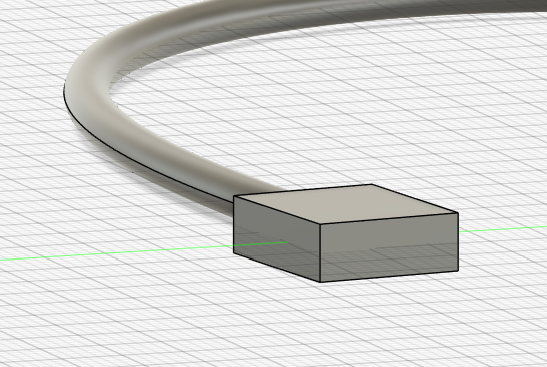
View of the plastic part of the USB.
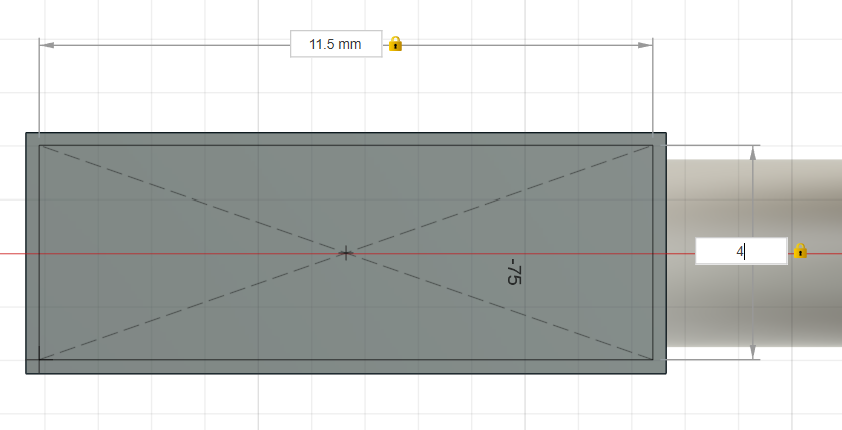
Drawing the metallic connection part.
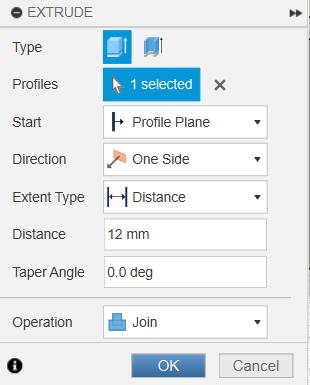
12mm extrusion for the USB port plug.
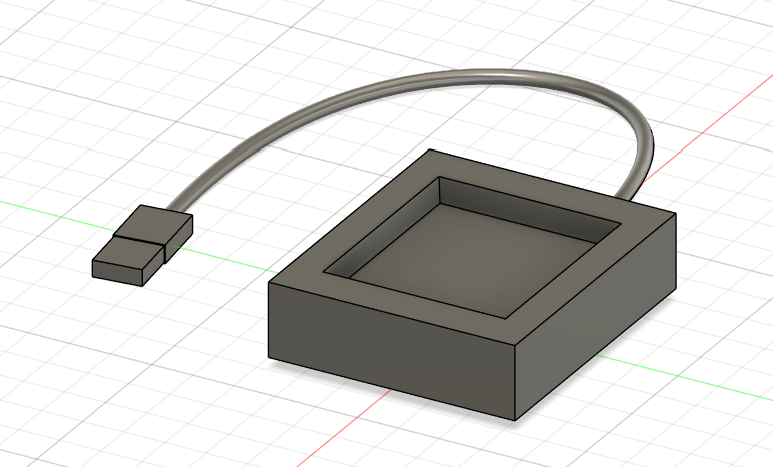
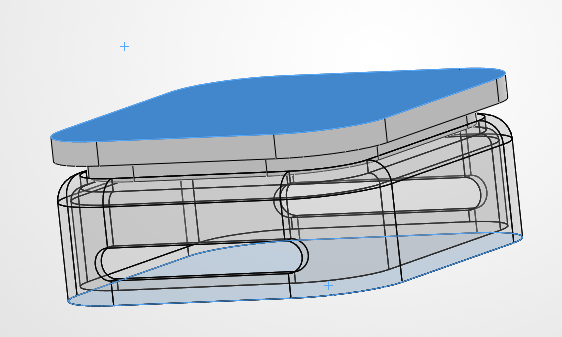
Complete Charging System.
Interactive 3D Preview
You can interact with the final 3D model below.